You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 12th Maths Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Maths Solutions Chapter 3 Theory of Equations Ex 3.2
Question 1.
If k is real, discuss the nature of the roots of the polynomial equation 2x2 + kx + k = 0, in terms of k.
Solution:
The given quadratic equation is 2x2 + kx + k = 0
a = 2, b = k, c = k
∆ = b2 – 4ac = k2 – 4(2) k = k2 – 8k
(i) If the roots are equal
k2 – 8k = 0
⇒ k(k – 8) = 0
⇒ k = 0, k = 8
(ii) If the roots are real
k2 – 8k > 0
k(k – 8) > 0
k ∈ (-∞, 0) ∪ (8, ∞)
(iii) If this roots are imaginary
k2 – 8k < 0
⇒ k ∈ (0, 8)
Question 2.
Find a polynomial equation of minimum degree with rational coefficients, having 2 + √3 i as a root.
Solution:
Given roots is (2 + √3 i)
The other root is (2 – √3 i), since the imaginary roots with real co-efficient occur as conjugate pairs.
x2 – x(S.O.R) + P.O.R = 0
⇒ x2 – x(4) + (4 + 3) = 0
⇒ x2 – 4x + 7 = 0
Question 3.
Find a polynomial equation of minimum degree with rational coefficients, having 2i + 3 as a root.
Solution:
Given roots is (3 + 2i), the other root is (3 – 2i);
Since imaginary roots occur in with real co-efficient occurring conjugate pairs.
x2 – x(S.O.R) + P.O.R = 0
⇒ x2 – x(6) + (9 + 4) = 0
⇒ x2 – 6x + 13 = 0
![]()
Question 4.
Find a polynomial equation of minimum degree with rational coefficients, having √5 – √3 as a root.
Solution:
The given one roots of the polynomial equation are (√5 – √3)
The other roots are (√5 + √3), (-√5 + √3) and (-√5 – √3).
The quadratic factor with roots (√5 – √3) and (√5 + √3) is
= x2 – x(S.O.R) + P.O.R
= x2 – x(2√5) + (√5 – √3) (√5 + √3)
= x2 – 2√5 x + 2
The other quadratic factors with roots (-√5 + √3) (-√5 – √3) is
= x2 – x (S.O.R) + P.O.R
= x2 – x (-2√5 ) + (5 – 3)
= x2 + 2√5x + 2
To rationalize the co-efficients with minimum degree
(x2 – 2√5 x + 2) (x2 + 2√5 x + 2) = 0
⇒ (x2 + 2)2 – (2√5 x)2 = 0
⇒ x4 + 4 + 4x2 – 20x2 = 0
⇒ x4 – 16x2 + 4 = 0
Question 5.
Prove that a straight line and parabola cannot intersect at more than two points.
Solution:
Let the standard equation of parabola y2 = 4ax …..(1)
Equation of line be y = mx + c …(2)
Solving (1) & (2)
(mx + c)2 = 4ax
⇒ mx2 + 2mcx + c2 – 4ax = 0
⇒ mx2 + 2x(mc – 2a) + c2 = 0
This equation can not have more than two solutions and hence a line and parabola cannot intersect at more than two points.
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Maths Solutions Chapter 3 Theory of Equations Ex 3.2 Additional Problems
Question 1.
Find a polynomial equation of minimum degree with rational co-efficients having 1 – i as a root.
Solution:
Given root is 1 – i
The other root is 1 + i
Sum of the roots: 1 – i + 1 + i = 2
product of the roots: (1 – i) (1 + i) = (1)2 + (1)2 ⇒ 1 + 1 = 2
∴ The required polynomial equation of minimum degree with rational coefficients is
x2 – x (S.R.) + (P.R.) = 0
x2 – 2x + 2 = 0
Question 2.
Find a polynomial equation of minimum degree with rational co-efficients having \(\sqrt{3}+\sqrt{7}\) as a root.
Solution:
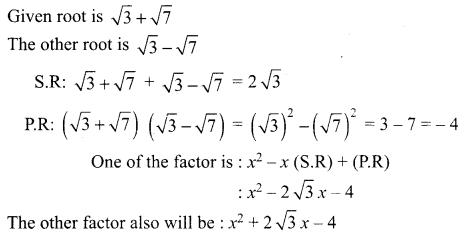
The required polynomial equation of minimum degree
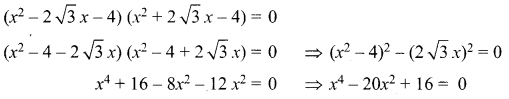
![]()
Question 3.
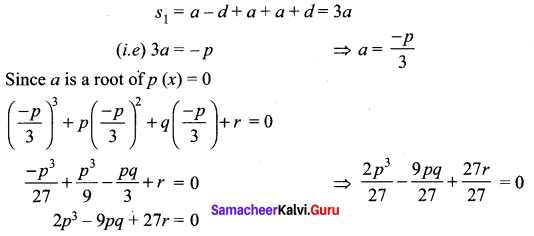
If the roots of the equation x3 + px2 + qx + r = 0 are in A.P then show that 2p3 – 9pq + 27 r = 0.
Solution:
Let the roots of the given equation is a – d, a, a + d
Question 4.
Solve 27x3 + 42x2 – 28x -8 = 0 given that its roots are in geometric progressive.
Solution:
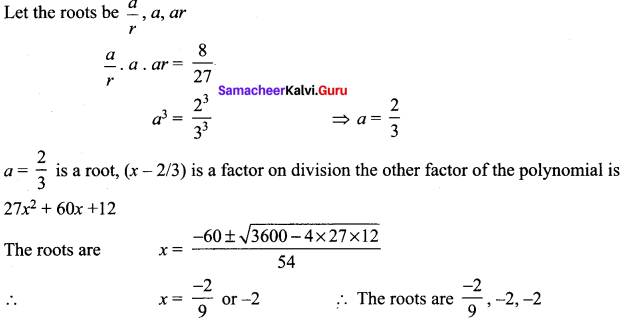
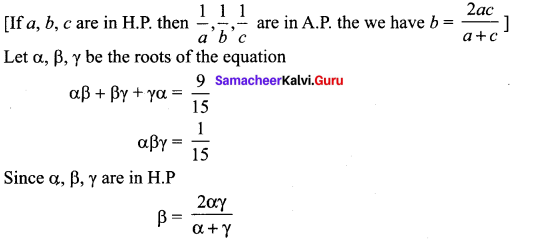
Question 5.
Solve the equation 15x3 – 23x2 + 9x – 1 = 0. Where roots are in H.P.
Solution: