Students can Download Maths Chapter 2 Algebra Ex 2.2 Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 8th Maths Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 8th Maths Solutions Term 2 Chapter 2 Algebra Ex 2.2
Question 1.
Fill in the blanks:
Question (i)
The solution of the equation ax + b = 0 is ………
Answer:
– \(\frac{b}{a}\)
Solution:
ax + b = 0
ax = – b
∴ x = – \(\frac{b}{a}\)
![]()
Question (ii)
If a and b are positive integers then the solution of the equation ax = b has to be always ………
Answer:
positive
Hint:
Since a & b are positive integers,
The solution to the equation ax = b is x = – \(\frac{b}{a}\) is also positive.
Question (iii)
One-sixth of a number when subtracted from the number itself gives 25. The number is ……..
Answer:
30
Hint:
Let the number be x.
As per question, when one sixth of number is subtracted from itself it gives 25
x – \(\frac{x}{6}\) = 25
∴ \(\frac{6x-x}{6}\) = 25
∴ \(\frac{5x}{6}\) = 25
∴ x = \(\frac{25×6}{3}\) = 5 x 6 = 30
Question (iv)
If the angles of a triangle are in the ratio 2 : 3 : 4 then the difference between the greatest and the smallest angle is
Answer:
40°
Hint:
Given angles are in the ratio 2 : 3 : 4
Let the angles be 2x, 3x & 4x
Since sum of the angles of a triangle is 180°,
We get
2x + 3x + 4x = 180
∴ 9x = 180
∴ X = \(\frac{180}{9}\) = 20°
∴ The angles are 2x = 2 x 20 = 40°
3x = 3 x 20 = 60°
4x = 4 x 20 = 80°
∴ Difference between greatest & smallest angle is
80° – 40° = 40°
Question (v)
In an equation a + b = 23. The value of a is 14 then the value of b is ……..
Answer:
b = 9
Hint:
Given equation is a + b = 23
a = 14
14 + b = 23
b = 23 – 14 = 9
b = 9
![]()
Question 2.
Say True or False
Question (i)
“Sum of a number and two times that number is 48” can be written as y + 2y = 48
Answer:
True
Hint:
Let the number be ‘y’
Sum of number & two times that number is 48
Can be written as y + 2y = 48 – True
Question (ii)
5(3x + 2) = 3(5x – 7) is a linear equation in one variable.
Answer:
True
Hint:
5 (3x + 2) = 3 (5x – 7) is a linear equation in one variable – ‘x’ – True
Question (iii)
x = 25 is the solution of one third of a number is less than 10 the original number.
Answer:
False
Hint:
One third of number is 10 less than original number.
Let number be ‘x’ Therefore let us frame the equation
\(\frac{x}{3}\) = x – 10
∴ x = 3x – 30
3x – x = 30
2x = 30
x = 15 is the solution
![]()
Question 3.
One number is seven times another. If their difference is 18, find the numbers.
Solution:
Let the numbers be x & y
Given that one number is 7 times the other & that the difference is 18.
Let x = 7y
also, x – y = 18 (given)
Substituting for x in the above
We get 7y – y = 18
∴ 6y = 18
y = \(\frac{18}{6}\) = 3
x = 7y = 7 x 3 = 21
The number are 3 & 21
Question 4.
The sum of three consecutive odd numbers is 75. Which is the largest among them?
Solution:
Given sum of three consecutive odd numbers is 75
Odd numbers are 1, 3, 5,1,9, 11, 13,……..
∴ The difference between 2 consecutive odd numbers is always 2. or in other words, if one odd number is x, the next odd number would be x + 2 and the next number would be x + 2 + 2 = x + 4
i.e x + 4
Since sum of 3 consecutive odd nos is 75
∴ x + x + 2 + x + 4 = 75
3x + 6 = 75 ⇒ 3x = 75 – 6
3x = 69
x = \(\frac{69}{3}\) = 23
The odd numbers are 23, 23 + 2, 23 + 4
i.e 23, 25, 27
∴ Largest number is 27.
Question 5.
The length of a rectangle is \(\frac{1}{3}\)rd of its breadth. If its perimeter is 64 m, then find the length and breadth of the rectangle.
Solution:

Let length & breadth of rectangle be l and ‘6’ respectively
Given that length is \(\frac{1}{3}\) of breadth,
∴ l = \(\frac{1}{3}\) x b ⇒ l = \(\frac{b}{3}\) ⇒ b = 3l …..(1)
Also given that perimeter is 64 m
Perimeter = 2 x (l + b)
2 x l + 2 x b = 64
Substituting for vahie of b from (1), we get
2l + 2(3l) = 64
∴ 2l + 6l = 64
8l = 64
∴ l = \(\frac{64}{8}\) = 8 m
b = 3l = 3 x 8 = 24 m
length l = 8 m & breadth h = 24 m
![]()
Question 6.
A total of 90 currency notes, consisting only of X5 and ?10 denominations, amount to ₹ 500. Find the number of notes in each denomination.
Solution:
Let the number of ₹ 5 notes be ‘x’
And number of ₹ 10 notes be ly ’
Total numbers of notes is x + y = 90 (given)
The total value of the notes is 500 rupees.
Value of one ₹ 5 rupee note is 5
Value of x ₹ 5 rupee notes is 5 × x = 5x
Value ofy ₹ 10 rupee notes is 10 × y = 10y
∴ The total value is 5x + 10y which is 500
we have 2 equations:
x + y = 90
5x + 1oy = 500
Multiplying both sides of (1) by 5, we get
5 × x + 5 x y = 90 x 5
5x + 5y = 450
Subtracting (3) from (2), we get
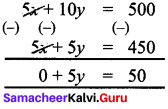
∴ y = \(\frac{50}{5}\) = 10
Substitute y = 10 in equation (1)
x + y = 90 ⇒ x + 10 = 90
⇒ x = 90 – 10 ⇒ x = 80
There are ₹ 5 denominations are 80 numbers and ₹ 10 denominations are 10 numbers
Question 7.
At present, Thenmozhi’s age is 5 years more than that of Murali’s age. Five years ago, the ratio of Thenmozhi’s age to Murali’s age was 3:2. Find their present ages.
Solution:
Let present ages ofThenmozhi & Murali be l’ & ‘m’
Given that at present
Thenmozhi’s age is 5 years more than Murali
∴ t = m + 5
5 years ago, Thenmozhi’s age would be t – 5
& Murali’s age would be m – 5
Ratio of their ages is given as 3 : 2
∴ \(\frac{t-5}{m-5}\) = \(\frac{3}{2}\) [∴ By cross multiplication]
![]()
2(t – 5) = 3(m – 5)
2 x t – 2 x 5 = 3 x m – 3 x 5 ⇒ 2t – 10 = 3m – 15
Substituting for t from (1)
2(m + 5) – 10 = 3m – 15
2m + 10 – 10 = 3m – 15
2m = 3m – 15
3m – 2m = 15
m = 15
t = m + 5 = 15 + 5 = 20
∴ Present ages of Thenmozhi & Murali are 20 & 15
Question 8.
A number consists of two digits whose sum is 9. If 27 is subtracted from the original number, its digits are interchanged. Find the original number.
Solution:
Let the units/digit of a number be ‘u’ & tens digit of the number be ‘t’
Given that sum of it’s digits is 9
∴ t + u = 9 ….(1)
If 27 is subtracted from original number, the digits are interchanged
The number is written as 10t + u
[Understand: Suppose a 2 digit number is 21,
it can be written as 2 x 10 + 1
∴ 32 = 3 x 10 + 2
45 = 4 x 10 + 5
tu = t x 10 + u = 10t + u]
Given that when 27 is subtracted, digits interchange
10t + u – 27 = 10u + t (number with interchanged digits)
∴ By transposition & bringing like variables together
10t – t + 10u =27
∴ 9t – 9u = 27
Dividing by ‘9’ throughout, we get
\(\frac{9t}{9}\) – \(\frac{9u}{9}\) = \(\frac{27}{9}\) ⇒ t – u = 3 ….(2)
Solving (1) & (2)

t = \(\frac{12}{2}\) = 6
∴ u = 3
t = 6 substitute in (1)
t + u = 9
⇒ 6 + u = 9
⇒ u = 9 – 6 = 3
Hence the number is 63.
![]()
Question 9.
The denominator of a fraction exceeds its numerator by 8. If the numerator is increased by 17 and the denominator is decreased by 1, we get \(\frac{3}{2}\). Find the original fraction.
Solution:
Let the numerator & denominator be ‘n’ & ‘d’
Given that denominator exceeds numerator by 8
∴ d = n + 8
If numerator increased by 17 & denominator decreased by 1,
it becomes (n + 17) & (d – 1), fraction is \(\frac{3}{2}\).
i.e = \(\frac{n+17}{d-1}\) = \(\frac{3}{2}\) by cross multiplying, we get
\(\frac{n+17}{d-1}\) = \(\frac{3}{2}\)
2(n + 17) = 3(d – 1)
2n + 2 x 17 = 3d – 3
![]()
∴ 34 + 3 = 3d – 2n
∴ 3d – 2n = 37
Substituting eqn. (1) in (2), we get,
3 x (n + 8) – 2n = 37
3n + 3 x 8 – 2n = 37
![]()
∴ n = 37 – 24 = 13
d = n + 8 = 13 + 8 = 21
The fraction is \(\frac{n}{d}\) = \(\frac{13}{21}\)
Question 10.
If a train runs at 60 km/hr it reaches its destination late by 15 minutes. But, if it runs at 85 kmph it is late by only 4 minutes. Find the distance to be covered by the train.
Solution:
Let the distance to be covered by train be ‘d’
Using the formula, time take (t) = \(\frac{Distance}{Speed}\)
Case 1:
If speed = 60 km/h
The time taken is 15 minutes more than usual (t + \(\frac{15}{60}\))
Let usual time taken be ‘t’ hrs.
Caution:
Since speed is given in km/hr, we should take care to maintain all units such as time should be in hour and distance should be in km.
Given that in case 1, it takes 15 min. more
15 m = \(\frac{15}{60}\) hr = \(\frac{1}{4}\) hr.
∴ Substituting in formula
\(\frac{Distance}{Speed}\) = time
∴ \(\frac{d}{60}\) = t + \(\frac{1}{4}\)
Since usually it takes ‘t’ hr, but when running at 60 km/h, it takes 15 min (\(\frac{1}{4}\)) extra.
Multiplying by 60 on both sides
d = 60 x t + 60 x \(\frac{1}{4}\) = 60t + 15 …..(1)
Case 2:
Speed is given as 85 km/h
Time taken is only 4 min (\(\frac{4}{60}\) hr) more than usual time
time taken = (t + \(\frac{1}{15}\)) hr. (\(\frac{4}{60}\) = \(\frac{1}{15}\))
Using the formula,
\(\frac{Distance}{Speed}\) = time
∴ \(\frac{d}{85}\) = t + \(\frac{1}{15}\)
Multiplying by 85 on both sides
\(\frac{d}{85}\) x 85 = 85 x t + 85 x \(\frac{1}{15}\)
∴ d = 85 t + \(\frac{17}{3}\)
From (1) & (2), we will solve for ‘t’
Equating & eliminating ‘d we get
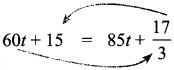
By transposing, we get
15 – \(\frac{17}{3}\) = 85t – 60t
\(\frac{45-17}{3}\) = 25t
∴ 25t = \(\frac{28}{3}\)
∴ t = \(\frac{28}{3×25}\) = \(\frac{28}{75}\) hr (\(\frac{28}{75}\) x 60 = 22.4 min)
Substituting this value of ‘t’ in eqn. (1), we get
d = 60t+ 15 = 60 x \(\frac{28}{75}\) + 15 = \(\frac{1680}{75}\) + 15 = 22.4 + 15
= 37.4 km
Objective Type Questions
Question 11.
Sum of a number and its half is 30 then the number is ……..
(a) 15
(b) 20
(c) 25
(d) 40
Answer:
(b) 20
Hint:
Let number be V
half of number is \(\frac{x}{2}\)
Sum of number and it’s half is given by
x + \(\frac{x}{2}\) = 30 [Multiplying by 2 on both sides]
2x + x = 30 x 2
3x = 60
x = \(\frac{60}{3}\) = 20
![]()
Question 12.
The exterior angle of a triangle is 120° and one of its interior opposite angle 58°, then the other opposite interior angle is ………
(a) 62°
(b) 72°
(c) 78°
(d) 68°
Answer:
(a) 62°
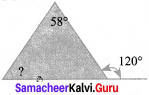
Hint:
As per property of ∆, exterior angle is equals to sum of interior opposite angles Let the other interior angle to be found be ‘x’
∴ x + 58 = 120°
∴ x = 120 – 58 = 62°
Question 13.
What sum of money will earn ₹ 500 as simple interest in 1 year at 5% per annum?
(a) 50000
(b) 30000
(c) 10000
(d) 5000
Answer:
(c) 10000
Hint:
Let sum of money be ‘P’
Time period (n) is given as 1 yr.
Rate of simple interest (r) is given as 5% p.a
∴ As per formula for simple interest.
S.I = \(\frac{Pxrxn}{100}\) = \(\frac{px5x1}{100}\)
P x 5 x 1 = 500 x 100
∴ P = \(\frac{500×100}{5}\) = 100 x 100 = 10,000
Question 14.
The product of LCM and HCF of two numbers is 24. If one of the number is 6, then the other number is ………
(a) 6
(b) 2
(c) 4
(d) 8
Answer:
(c) 4
Hint:
Product of LCM & HCF of 2 numbers is always product of the numbers. [this is property]
Product of LCM & HCF is given as 24.
∴ Product of the 2 nos. is 24
Given one number is 6.
Let other number be ‘x’
∴ 6 × x = 24
∴ x = \(\frac{24}{6}\) = 4