Get Updated Tamilnadu State Board Solutions for Class 10 Science Solutions Chapter 19 Origin and Evolution of Life Questions and Answer in PDF Format and download them free of cost. Samacheer Kalvi Class 10 Science Solutions Chapter 19 Origin and Evolution of Life provided are as per the latest exam pattern and syllabus. Access the topics of Chapter 19 Origin and Evolution of Life through the direct links available depending on the need. Clear all your queries on the Class 10 Science Subject by using the Samacheer Kalvi Board Solutions for Chapter 19 Origin and Evolution of Life existing.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 10th Science Solutions Chapter 19 Origin and Evolution of Life
If you are eager to know about the Tamilnadu State Board Solutions of Class 10 Science Solutions Chapter 19 Origin and Evolution of Life Questions and Answer you will find all of them here. You can identify the knowledge gap using these Tamilnadu State Board Class 10 Science Solutions PDF and plan accordingly. Don’t worry about the accuracy as they are given after extensive research by people having subject knowledge alongside from the latest Science Solutions Textbooks.
Samacheer Kalvi 10th Science Origin and Evolution of Life Textual Evaluation Solved
I. Choose the Correct Answer.
Samacheerkalvi.Guru Science Question 1.
Biogenetic law states that _____.
(a) Ontogeny and phylogeny go together.
(b) Ontogeny recapitulates phylogeny.
(c) Phylogeny recapitulates ontogeny.
(d) There is no relationship between phylogeny and ontogeny.
Answer:
(b) Ontogeny recapitulates phylogeny.
Samacheer Kalvi Guru Science Question 2.
The ‘use and disuse theory’ was proposed by _____.
(a) Charles Darwin
(b) Ernst Haeckel
(c) Jean Baptiste Lamarck
(d) Gregor Mendel.
Answer:
(c) Jean Baptiste Lamarck
Samacheerkalvi.Guru 10th Science Question 3.
Paleontologists deal with _____.
(a) Embryological evidences
(b) Fossil evidences
(c) Vestigial organ evidences
(d) All the above.
Answer:
(b) Fossil evidences
Origin And Evolution Of Life Class 10 Question 4.
The best way of direct dating fossils of recent origin is by _____.
(a) Radio – carbon method
(b) Uranium lead method
(c) Potassium – argon method
(d) Both (a) and (c).
Answer:
(a) Radio – carbon method
Samacheer Kalvi.Guru Science Question 5.
The term Ethnobotany was coined by _____.
(a) Khorana
(b) J.W. Harshberger
(c) Ronald Ross
(d) Hugo de Vries.
Answer:
(b) J.W. Harshberger
II. Fill in the blanks.
Question 1.
The characters developed by the animals during their life time, in response to the environmental changes are called _____.
Answer:
Acquired characters.
Question 2.
The degenerated and non-functional organs found in an organism are called _____.
Answer:
Vestigial organ.
Question 3.
The forelimbs of bat and human are examples of ______ organs.
Answer:
Homologous.
Question 4.
The theory of natural selection for evolution was proposed by _____.
Answer:
Charles Darwin.
III. State whether True or False. If false, write the correct statement.
Question 1.
‘The use and disuse theory of organs’ was postulated by Charles Darwin?
Answer:
False.
Correct statement: ‘The use and disuse theory of organs’ was postulated by Jean Baptiste Lamarck.
Question 2.
The homologous organs look similar and perform similar functions but they have different origin and developmental pattern?
Answer:
False.
Correct statement: The homologous organs look dissimilar and perform dissimilar functions, but they have the same origin and developmental pattern.
Question 3.
Birds have evolved from reptiles.
Answer:
True.
IV. Match the following:
Question 1.
| Column A | Column B |
| 1. Atavism | (a) caudal vertebrae and vermiform appendix |
| 2. Vestigial organs | (b) a forelimb of a cat and a bat’s wing |
| 3. Analogous organs | (c) rudimentary tail and thick hair on the body |
| 4. Homologous organs | (d) a wing of a bat and a wing of an insect |
| 5. Wood park | (e) radiocarbon dating |
| 6. W.F. Libby | (f) Thiruvakkarai |
Answer:
- (c) rudimentary tail and thick hair on the body
- (a) caudal vertebrae and vermiform appendix
- (d) a wing of a bat and a wing of an insect
- (b) a forelimb of a cat and a bat’s wing
- (f) Thiruvakkarai
- (e) radiocarbon dating.
V. Answer in a word or Sentence
Question 1.
A human hand, a front leg of a cat, a front flipper of a whale and a bat’s wing look dissimilar and adapted for different functions. What is the name given to these organs?
Answer:
Homologous organs.
Question 2.
Which organism is considered to be the fossil bird?
Answer:
Fossil bird Archaeopteryx.
Question 3.
What is the study of fossils called?
Answer:
Palaeontology.
VI. Short Answers Questions
Question 1.
The degenerated wing of a kiwi is an acquired character. Why is it an acquired character?
Answer:
Kiwi does not have the need to fly that is why they do not have wings. The characters developed by the animals during their life in response to environmental changes. The vestigial wings are so small (invisible) under the bristly, hair-like two-branched feathers. So the degenerated wing of a kiwi is an acquired character.
Question 2.
What is the study of fossils called?
Answer:
Palaeontology is called as the study of fossils.
Question 3.
Define Ethnobotany and write its importance.
Answer:
Ethnobotany is the study of a region’s plants and their practical uses through the traditional knowledge of the local culture of people.
Importance of Ethnobotany:
- It provides traditional uses of the plant.
- It gives information about certain unknown and known useful plants.
- The ethnomedicinal data will serve as a useful source of information for the chemists, pharmacologists and practitioners of herbal medicine.
- Tribal communities utilize ethnomedicinal plant parts like bark, stem, roots, leaves, flowers, flower bud, fruits, seeds, oils, resins, dyes and gum for the treatment of diseases like diarrhoea, fever, headache, diabetes, jaundice, snakebites and leprosy, etc.
Question 4.
How can you determine the age of the fossils?
Answer:
The age of fossils is determined by radioactive elements present in it. They may be carbon, uranium, lead or potassium.
VII. Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
Natural selection is a driving force for evolution-How?
Answer:
Darwin published his observations under the name “origin of species”. It elaborates on the theory of natural selection for evolutionary transformation.
The principles of Darwinism tells that natural selection is a driving force for evolution.
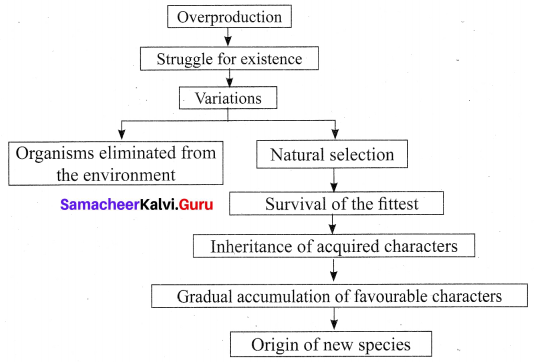
1. Overproduction: Living beings have the ability to reproduce and have the capacity to multiply in a geometrical manner.
2. Struggle for existence: Due to overproduction, a geometric ratio of increase in population occurs. The space to live and food available for the organisms remain the same. This creates a competition among the organisms, for food and space, leading to struggle.
- The competition may be among the individuals of the same species (Intraspecific struggle).
- Competition between the organisms of different species living together (Interspecific struggle).
- Natural conditions like extreme heat or cold drought and floods can affect the existence of organisms (Environmental struggle).
3. Variations: Small variations are important for evolution. According to Darwin, favourable variations are useful to the organisms and unfavourable variations are harmful or useless to the organisms.
4. Survival of the fittest or Natural selection: During the struggle for existence, the organisms which can overcome the challenging situation, survive and adapt to the surrounding environment. Organisms, which are unable to face the challenges, are unfit to survive and disappear. The process of selection of organisms with favourable variation is called Natural selection.
5. Origin of species: According to Darwin, new species originates by the gradual accumulation of favourable variations for a number of generations.
Question 2.
How do you differentiate homologous organs from analogous organs?
Answer:
| Homologous organs | Analogous organs |
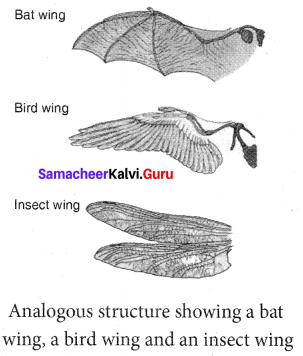
| 1. The homologous organs have been inherited from common ancestors, with similar developmental pattern in embryos. | 1. Analogous structures are shown in a batwing, a bird wing and an insect wing. |
| 2. The forelimbs of a human hand, a front leg of a cat, the flipper of a whale and a bat’s, wing look dissimilar and adapted for different functions. | 2. The analogous organs look similar but perform similar functions. |
| 3. Their mode of development and the basic structure of bone are similar. | 3. They have a different origin. Wings of insect are membranous extensions whereas wings of a bat is a bony structure. But performing the same function of flying. |
Question 3.
How does fossilization occur in plants?
Answer:
A plant fossil is any preserved part of a plant that has died long back. Fossils may be a prehistoric impression that may be hundred to millions of years old. Majority of the plant fossils are disarticulated parts of plants, it is rare to find plants to be preserved as whole.
VIII. Higher Order Thinking Skills (HOTS) Questions
Question 1.
Arun was playing in the garden. Suddenly he saw a dragonfly sitting on a plant. He observed the wings of it. He thought it looked similar to a wing of a crow. Is he correct? Give a reason for your answer.
Answer:
No. He is not correct. Both crow and dragonfly have the same function of flying with wings. But it’s the origin (basic structure) is different. Dragonfly wing is the membranous extension. But the wing of the crow is the modification of forelimb.
Question 2.
Imprints of fossils tell us about evolution- How?
Answer:
Fossil records show that evolution has taken a gradual process from simple to complex organisms. The study of fossils helps us to understand the link of evolution. The origin of modem birds is supported by the evidence of palaeontology.
Question 3.
Octopus, cockroach and frog all have eyes. Can we group these animals together to establish a common evolutionary origin? Justify your answer.
Answer:
Convergent evolution is the process, by which the independently evolved features, may similar to each other, but can arise through different developmental pathways. So the octopus, cockroach and frog all have eyes. The independently evolved eye may similar in each other, but can arise through different developmental pathways.
Samacheer Kalvi 10th Science Origin and Evolution of Life Additional Questions Solved
I. Fill in the blanks.
Question 1.
The history of life has two aspects namely ______ and ______.
Answer:
Origin of life; The evolution of life.
Question 2.
The theory which postulates that life originates from pre – existing life is ______.
Answer:
Biogenesis.
Question 3.
_____ is the gradual change occurring in living organisms over a period of time.
Answer:
Evolution.
Question 4.
Sexual reproduction, which involves meiosis helps in the recombination of ______ during gametic fusion.
Answer:
Genes.
Question 5.
The major concept in astrobiology is the ______.
Answer:
Habitable zone.
Question 6.
The organisms, which live in extreme environmental conditions on Earth are called ______.
Answer:
Extremophiles.
Question 7.
Fossil records show that evolution has taken a gradual process from simple to _______ organisms.
Answer:
Complex.
II. Match the following:
Question 1.
| 1. Big Bang theory | (a) study of regions and practical use of plants |
| 2. Petrifaction | (b) organisms buried and cause depression |
| 3. Archaeopteryx | (c) other names for astrobiology |
| 4. Ethnobotany | (d) preserve hard and soft parts |
| 5. Mould | (e) origin of the universe |
| 6. Exobiology | (f) fossil bird |
Answer:
- (e) origin of the universe
- (d) preserve hard and soft parts
- (f) fossil bird
- (a) study of regions and practical use of plants
- (b) organisms buried and cause depression
- (c) other names for astrobiology.
Question 2.
| 1. Oparin and Haldane | (a) use and disuse theory |
| 2. Ernest Haeckel | (b) Mutation theory |
| 3. Leonardo da Vinci | (c) Father of Indian palaeobotany |
| 4. Jean Baptiste Lamarck | (d) Life from the chemical reaction |
| 5. Darwin | (e) Father of palaeontology |
| 6. De Vries | (f) Radioactive carbon |
| 7. Birbal Sahni | (g) Ethnobotany |
| 8. W.F. Libby | (h) Origin of species |
| 9. J.W. Harshberger | (i) Biogenetic law |
Answer:
- (d) Life from a chemical reaction
- (i) Biogenetic law
- (e) Father of palaeontology
- (a) use and disuse theory
- (h) Origin of species
- (b) Mutation theory
- (c) Father of Indian palaeobotany
- (f ) Radioactive carbon
- (g) Ethnobotany.
III. Choose the correct answer.
Question 1.
The theory of idea embodies that life on Earth is a divine creation ______.
(a) chemical reaction
(b) special creation
(c) spontaneous generation
(d) Biogenesis.
Answer:
(b) special creation
Question 2.
Palaeontology deals with the study of ______.
(a) analogous organs
(b) fossils
(c) gradual change
(d) homologous organ.
Answer:
(c) gradual change
Question 3.
The other name for continuous variation is ______.
(a) germinal variation
(b) somatic variation
(c) discontinuous variation
(d) fluctuating variation.
Answer:
(d) fluctuating variation.
Question 4.
It is a branch of palaeontology that deals with the recovery and identification of plant remain of geological past ______.
(a) palaeobotany
(b) Embryology
(c) mutation
(d) palaeontology.
Answer:
(a) palaeobotany
Question 5.
Book ‘Philosophic Zoologique’ published in the year 1809 was written by:
(a) Darwin
(b) Lamarck
(c) Wallace
(d) Mendel
Answer:
(b) Lamarck
IV. Answer the following shortly.
Question 1.
What is Abiogenesis?
Answer:
Abiogenesis or spontaneous generation theory states that life originated spontaneously from lifeless matter. It was believed that fishes originated from mud, frogs from moist soil and insects from decaying matter.
Question 2.
What is the cosmic origin?
Answer:
Cosmic origin of extraterrestrial theories states that life came from outer space. The unit of life called spores (panspermia) were transferred to different planets including Earth.
Question 3.
What is the chemical evolution of life?
Answer:
Chemical evolution of life theory states that life arose by a series of sequential chemical reactions. The first form of life could have come from pre – existing non – living inorganic molecules, which gave rise to the formation of diverse organic molecules, which are transformed into a colloid system to produce life.
Question 4.
Name the evidence of evolution What do they support?
Answer:
- Evidence from morphology and Anatomy.
- Evidence from embryology.
- Evidence from palaeontology.
Evolution is best understood by observing the relationship between the existing organisms and the similarities of the extinct organisms. This evidence supports the concept that all organisms have evolved from common ancestors.
Question 5.
Explain the evidence of evolution from Embryology.
Answer:
The embryos from fish to mammals are similar in their early stages of development. The study of comparative embryology of different animals supports the concept of evolution. The differentiation of their special characters appears in the later stages of development. Ontogeny recapitulates phylogeny. The stages of development of the individual animal repeat the evolutionary history of the entire race of the animal.
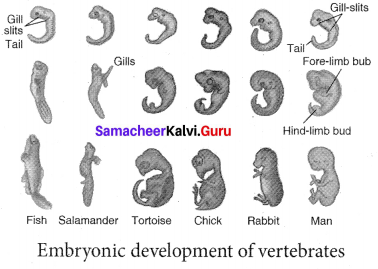
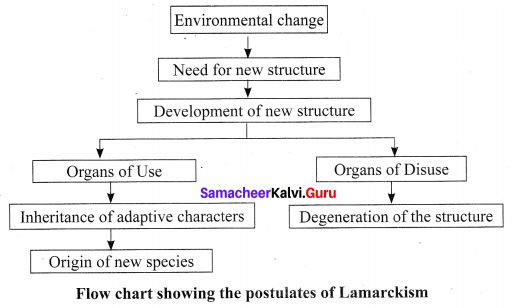
Question 6.
Represent a flow chart showing the postulates of Lamarckism?
Answer:
The postulates of Lamarckism:
Question 7.
Explain the evidence of evolution from palaeontology.
Answer:
Palaeontology deals with the study of fossils. The study of fossils helps us to understand the line of evolution of many invertebrates and vertebrates. Fossil records show that evolution has taken a gradual process from simple to complex organisms.
The origin of modem birds is supported by the evidence from palaeontology. Archaeopteryx is the oldest known fossil bird. It is considered to be a connecting link between reptiles and birds. It had wings with feathers, like a bird. It had a long tail, clawed digits and conical teeth like a reptile.
Question 8.
What is evolution?
Answer:
Formation of new species due to changes in specific characters over several generations as a response to natural selection is called evolution. Evolution is the gradual change occurring in living organisms over a period of time.
Question 9.
Represent a flow chart showing the postulates of Darwinism?
Answer:
The postulates of Darwinism:
Question 10.
Explain the types of variation?
Answer:
Variations are the differences found among individuals of the same species and the offspring of the same parent. New species originate by the gradual accumulation of variations. Evolution would not be possible without variation.
Somatic variation and germinal variation are the two types of variations:
- Somatic variation: The variation which affects the body (somatic) cells of the organisms are called somatic variation, which is not heritable. They occur due to environmental factors.
- Geminal variation: The variations, which are produced in germ cells and inherited are called germinal variation. They are classified into two types.
- Continuous variation: Small variations which occur among individuals of a population, and occur by gradual accumulation is called continuous variation. They are also called fluctuating variation, e.g. skin colour, height and weight and colour of the eye, etc.
- Discontinuous variation: These changes are sudden, which occur in an organism, due to mutations. These large variations are not useful for evolution, e.g. short – legged Ancon sheep and six or more digits (fingers) in human, etc.
Question 11.
Explain the importance of fossils?
Answer:
Importance of fossils:
- They throw light on phylogeny and evolution of plants.
- Fossil plants give a historical approach to the plant kingdom.
- Fossils are useful in the classification of plants.
- Fossil plants can be used in the field of descriptive and comparative anatomy.
Question 12.
What are Extremophiles?
Answer:
The organisms which live in extreme environmental conditions on Earth are called extremophiles within our own solar system, there are many areas that are different from the Earth. We may find the presence of life similar to extremophile bacteria.
Question 13.
What is Astrobiology or Exobiology? What does it deal?
Answer:
Astrobiology or exobiology is the science which looks for the presence of extraterrestrial in the universe.
Astrobiology deals with the origin, evolution and distribution of life in the universe and to investigate the possibility of living in another world.
The major concept in astrobiology is the habitable zone. Astrobiology explains that any planets can support the existence of life if it fulfils two criteria:
- It must have the right mass to retain an atmosphere.
- It must have an orbit at the right distance from Sun, that it allows liquid water to exist. The distance needs to be neither too hot nor too cold and is often called the Goldilocks zone for life.
V. Answer the following in detail.
Question 1.
Explain in detail with diagrams, the evidence of evolution, through morphology and anatomy.
Answer:
The comparative study of morphology and anatomy of organisms have evolved from a common ancestor.
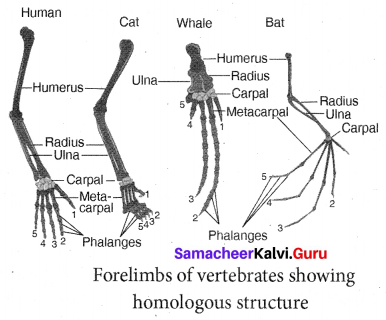
(i) Homologous organs: The homologous organs are those which have inherited from common ancestors with similar developmental pattern in embryos. The forelimbs of mammals are homologous structures. A human hand, a front leg of a cat, flipper of a whale and a bat’s wing look dissimilar and adapted for different functions. Their mode of development and the basic structure of bone are similar.
(ii) Analogous organs: The analogous organs look similar and perform similar functions but they have different origin and developmental pattern. The function of the wings of a bat, the wings of a bird and wings of an insect are similar, but their basic structures are different.
(iii) Vestigial organs: The degenerated and non¬functional organs of animals are called vestigial organs. The same organs are found to be well- developed and functional, in some of the related forms. Some of the vestigial organs in man are a vermiform appendix, nictitating membrane, caudal vertebra and coccyx, etc.
(iv) Atavism: The reappearance of ancestral characters in some individuals is called atavism, e.g. Presence of rudimentary tail in newborn babies, the presence of thick hair on the human body.
Question 2.
(a) Name the popular names of Lamarckism.
(b) Explain the principles of Lamarckism.
Answer:
(a) Lamarckism is the hypothesis that an organism can pass on characteristics, that it has acquired through use or disuse, during it’s lifetime to the offspring. Lamarck’s theory of evolution was published in ‘Philosophic Zoologique’ in the year 1809. Lamarckism is popularly known as ‘Theory of inheritance of Acquired Characters” or “Use and Disuse theory”
(b) (i) internal vital force: Due to the inherent ability of the living organisms or their component parts tend to increase in ‘ size continuously.
(ii) Environment and new needs: A change in the environment brings about changes in the need of the organisms. In response to the changing environment, the organisms develop certain adaptive characters. The adaptations may be in the form of development of new parts of the body.
(iii) Use and disuse theory: Lamarck’s use and disuse theory state that, if an organ is used constantly, the organ develops well and gets strengthened. When an organ is not used for a long time, it gradually degenerates. The ancestors of Giraffe were provided with a short neck and short forelimbs. Due to a shortage of grass, they are forced to feed on leaves from trees. The continuous stretching of their neck and forelimbs resulted in the development of long neck and long forelimbs, which is an example fcc constant use of an organ. The degenerated wing of Kiwi is an example for organ of disuse.
(iv) Theory of Inheritance of acquired characters: Animals respond to the changes when there is a change in the environment. The develop adaptive structures. The characters, developed during their lifetime, in response to the environmental changes are called acquired characters. The acquired characters are transmitted to the offspring by the process of inheritance.
VI. Higher-Order Thinking skills [HOTS] Questions
Question 1.
- What is the reason for the long neck of a giraffe.
- Name the theory based on the shown figure.
Answer:
- Due to a shortage of grass, they were forced to feed on leaves from trees. The continuous stretching of their neck and forelimb as resulted in the development of a long neck and long forelimbs.
- Theory of inheritance of acquired characters.
Question 2.
What are living fossils?
Answer:
Living fossils are living organisms that are similar in appearance to their fossilized distant ancestors and usually have no extinct close features, eg. Ginko Biloba.
Question 3.
What is Mars 2020 Astrobiology?
Answer:
NASA is developing the Mars 2020, Astrobiology to investigate an astrobiological relevant ancient environment on Mars, its surface geological processes and the possibility of past life on Mars and preservation of biosignatures within accessible geological materials.
Hope you liked the article on Tamilnadu State Board Solutions of Class 10 Science Solutions Chapter 19 Origin and Evolution of Life Questions and Answer and share it among your friends to make them aware. Keep in touch to avail latest information regarding different state board solutions instantly.