Students can Download Accountancy Chapter 3 Books of Prime Entry Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 11th Accountancy Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 11th Accountancy Solutions Chapter 3 Books of Prime Entry
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Accountancy Books of Prime Entry Text Book Back Questions and Answers
I.11th Accountancy Chapter 3 Book Back Answers Multiple Choice Questions
Choose the Correct Answer
Books Of Prime Entry Questions And Answers Pdf Question 1.
Accounting equation signifies …………….
(a) Capital of a business is equal to assets
(b) Liabilities of a business are equal to assets
(c) Capital of a business is equal to liabilities
(d) Assets of a business are equal to the total of capital and liabilities
Answer:
(d) Assets of a business are equal to the total of capital and liabilities
11th Accountancy Chapter 3 Question 2.
‘Cash withdrawn by the proprietor from the business for his personal use’ causes …………….
(a) Decrease in assets and decrease in owner’s capital
(b) Increase in one asset and decrease in another asset
(c) Increase in one asset and increase in liabilities
(d) Increase in asset and decrease in capital
Answer:
(a) Decrease in assets and decrease in owner’s capital
11th Accountancy 3rd Chapter Solutions Question 3.
A firm has assets of ₹ 1,00,000 and the external liabilities of ₹ 60,000. Its capital would be …………….
(a) ₹ 1,60,000
(b) ₹ 60,000
(c) ₹ 1,00,000
(d) ₹ 40,000
Answer:
(d) ₹ 40,000
11th Accountancy 3rd Chapter Question 4.
The incorrect accounting equation is …………….
(a) Assets = Liabilities + Capital
(b) Assets – Capital + Liabilities
(c) Liabilities = Assets + Capital
(d) Capital = Assets – Liabilities
Answer:
(c) Liabilities = Assets + Capital
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Accountancy Chapter 3 Question 5.
Accounting equation is formed based on the accounting principle of …………….
(a) Dual aspect
(b) Consistency
(c) Going concern
(d) Accrual
Answer:
(a) Dual aspect
Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 3 Solutions Question 6.
Real account deals with …………….
(a) Individual persons
(b) Expenses and losses
(c) Assets
(d) Incomes and gains
Answer:
(c) Assets
11th Accounts Chapter 3 Question 7.
Which one of the following is representative personal account?
(a) Building A/c
(b) Outstanding salary A/c
(c) Mahesh A/c
(d) Balan & Co. A/c
Answer:
(b) Outstanding salary A/c
Accountancy Class 11 Chapter 3 Solutions Question 8.
Prepaid rent is a …………….
(a) Nominal A/c
(b) Personal A/c
(c) Real A/c
(d) Representative personal A/c
Answer:
(d) Representative personal A/c
Books Of Prime Entry Questions And Answers Question 9.
Withdrawal of cash from business by the proprietor should be credited to …………….
(a) Drawings A/c
(b) Cash A/c
(c) Capital A/c
(d) Purchases A/c
Answer:
(b) Cash A/c
Books Of Prime Entry Pdf Question 10.
In double entry system of book keeping, every business transaction affects …………….
(a) Minimum of two accounts
(b) Same account on two different dates
(c) Two sides of the same account
(d) Minimum three accounts
Answer:
(a) Minimum of two accounts
II. Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What are source documents?
Answer:
Source documents are authentic evidence of financial transactions.
These documents show the nature of the transaction, the date, the amount and the parties involved.
Source documents include cash receipt, invoice, debit note, credit note, pay-in-slip, salary bills, wage bills, cheque record slips, etc. They also serve as legal evidence in case of any legal dispute.
Question 2.
What is the accounting equation?
Answer:
The accounting equation is a mathematical expression which shows that the total of assets is equal to the total of liabilities and capital. This is based on the dual aspect concept of accounting. This means that the total claims of outsiders and the proprietor against a business enterprise will always be equal to the total assets of the business enterprise.
Question 3.
Write any one transaction which
(a) Decreases the assets and decreases the liabilities:
Answer:
E.g: Outstanding Rent paid by the company Rs. 30,000.
Here Outstanding Rent (Liability) is decreasing, Cash (Asset) is decreasing.
(b) Increases one asset and decreases another asset:
Answer:
E.g: Building purchased for Cash Rs. 50,000.
Here Building (Asset) is increasing and Cash (Asset) is decreasing.
Question 4.
What is meant by journalizing?
Answer:
The word journal has been derived from the French word ‘Jour’ which means day. So, journal means daily. Journalising is the beginning of the accounting process for financial transactions.
Question 5.
What is the real account?
Answer:
A real account is an account that retains and rolls forward its ending balance from period to period. The areas in the balance, sheet in which real accounts are found are assets, liabilities, and equity. Examples of real accounts are: Cash, Accounts receivable, Fixed Assets Accounts payable, Retained earnings.
Question 6.
How are personal accounts classified?
Answer:
Personal account: An account relating to persons is called a personal account. The personal account may be a natural, artificial, or representative personal account.
Question 7.
State the accounting rule for a nominal account.
Answer:
Debit all expenses and losses Credit all incomes and gains.
Question 8.
Give the golden rules of the double-entry accounting system.
Answer:
The consistency convention implies that

III. Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Write a brief note on the accounting equation approach of recording transactions.
Answer:
The relationship of assets with that of liabilities to outsiders and to owners in the equation form is known as the accounting equation.
Under the double-entry system of bookkeeping, every transaction has a two-fold effect, which causes the changes in assets and liabilities or capital in such a way that an accounting equation is completed and equated.
Capital + Liabilities = Assets
Capital can also be called owner’s equity and liabilities as outsider’s equity.
Question 2.
What is an Account? Classify the accounts with suitable examples.
Answer:
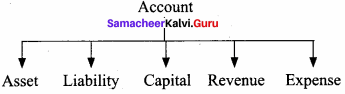
1. Asset account: Any physical thing or right owned that has a monetary value is called asset. The assets are grouped and shown separately; for example, Land and Buildings account, Plant and Machinery account.
2. Liability account: Financial obligations of the enterprise towards outsiders are shown under separate heads as liabilities; for example, creditors account, expenses outstanding account.
3. Capital account: Financial obligations of a business enterprise towards its owners are grouped under this category; for example, capital contributed by owner.
4. Revenue account: Accounts relating to revenues of an enterprise are grouped under this category, for example; revenues from the sale of goods, rent received.
5. Expense account: Expenses incurred and losses suffered for earning revenue are grouped under this category; for example, purchase of goods, salaries paid.
Question 3.
What are the three different types of personal accounts?
Answer:
- Natural person’s account: Natural person means human beings. Example: Vinoth account, Malini account.
- Artificial person’s account: Artificial person refers to persons other than human beings recognized by law as persons. They include business concerns, charitable institutions, etc. Example: BHEL account, Bank account.
- Representative personal accounts: These are the accounts which represent persons natural or artificial or a group of persons. Example: Outstanding salaries account, Prepaid rent account. When expenses are outstanding, it is payable to a person. Hence, it represents a person.
Question 4.
What is the accounting treatment for insurance premiums paid on the life of the proprietor?
Answer:
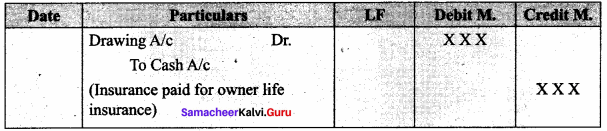
Question 5.
State the principles of the double-entry system of bookkeeping.
Answer:
Meaning:
A double-entry system of book keeping is a scientific and complete system of recording the financial transactions of an organization. The two aspects involved are denoted by Debit (Dr.) and Credit(Cr.).
The following are the principles of the double-entry system of book keeping:
- In every business transaction, there are two aspects.
- The two aspects involved are the benefit or value receiving aspect and the benefit or value giving aspect.
- These two aspects involve a minimum of two accounts; at least one debit and at least one credit.
- For every debit, there is a corresponding and equivalent credit. If one account is debited the other account must be credited.
Question 6.
Briefly explain about steps in journalizing.
Answer:
The following steps are followed in journalizing:
- Analyze the transactions and identify the accounts (based on aspects) which are involved in the transaction.
- Classify the above accounts under Personal account, Real account, or Nominal account
- Apply the rules of debit and credit for the above two accounts.
- Find which account is to be debited and which account is to be credited by the application of rules of the double-entry system.
- Record the date of the transaction in the date column.
- Enter the name of the account to be debited in the particulars column very close to the left-hand side of the particulars column followed by the abbreviation ‘Dr.’ at the end in the same line. Against this, the amount to be debited is entered in the debit amount column in the same line.
- Write the name of the account to be credited in the second line starting with the word ‘To’ prefixed a few spaces away from the margin in the particulars column. Against this, the amount to be credited is entered in the credit amount column in the same line.
- Write the narration within brackets in the next line in the particulars column.
Question 7.
What is the double-entry system? State its advantages.
Answer:
“Every business transaction has a two-fold effect and that it affects two accounts in opposite directions and if a complete record is to be made of each such transaction it is necessary to debit one account and credit another account. It is this recording of the two-fold effect of every transaction that has given rise to the term Double Entry” J.R. Batliboi.
Advantages of the double-entry system:
Following are the advantages of double entry system:
Accuracy
In this system, the two aspects of each transaction are recorded in the books of accounts. This helps in checking the accuracy of accounting.
Ascertainment of business results
Details regarding expenses, losses, incomes, gains, assets, liabilities, debtors, creditors, etc., are readily available. This helps to ascertain the net profit earned or loss incurred during an accounting period and also to know the financial position as on a particular date.
Comparative study
The business results of the current year can be compared with those of the previous years and also 4 with other business firms. It facilitates business planning for the future.
Common acceptance
The business records maintained under this system are accepted by financial institutions, government, and others because it is a systematic and scientific system.
IV. Exercises
Question 1.
Complete the accounting equation
(a) Assets = Capital + Liabilities
₹ 1,00,000 = ₹ 80,000 + 20,000
(b) Assets = Capital + Liabilities
₹ 2,00,000 = ₹ + ? 40,000
(c) Assets = Capital + Creditors
? = ₹ 1,60,000 + ₹ 80,000
Answer:
(a) Assets = Capital + Liabilities
₹ 1,00,000 = ₹ 80,000 + 20,000
(b) Assets = Capital + Liabilities
₹ 2,00,000 = ₹ 1,60,000 + ₹ 40,000
(c) Assets = Capital + Creditors
₹ 2,40,000 = ₹ 1,60,000 + ₹ 80,000
Question 2.
For the following transactions, show the effect on:
(a) Raj started business with cash – ₹ 40,000
(b) Opened bank account with a deposit of – ₹ 30,000
(c) Bought goods from Hari on credit for – ₹ 12,000
(d) Raj withdrew cash for personal use – ₹ 1,000
(e) Bought furniture by using a debit card for – ₹ 10,000
(f) Sold goods to Murugan and cash received – ₹ 6,000
(g) Money is withdrawn from bank for office use – ₹ 1,000
Answer:
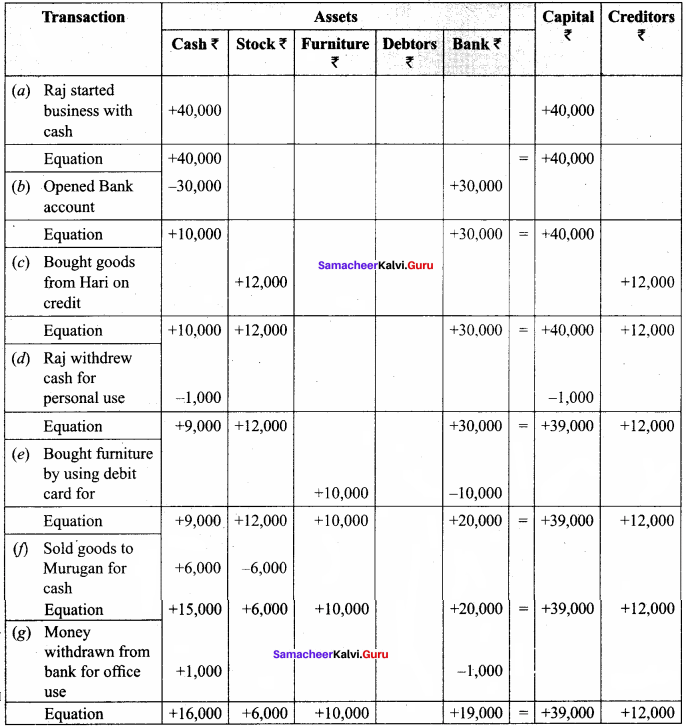
Question 3.
Prepare accounting equation for the following transactions. (5 Marks):
(a) Murugan commenced business with cash ₹ 80,000
(b) Purchased goods for cash ₹ 30,000
(c) Paid salaries by cash ₹ 5,000
(d) Bought goods from Kumar for ₹ 5,000 and deposited the money in CDM.
(e) Introduced additional capital of ₹ 10,000
Answer:
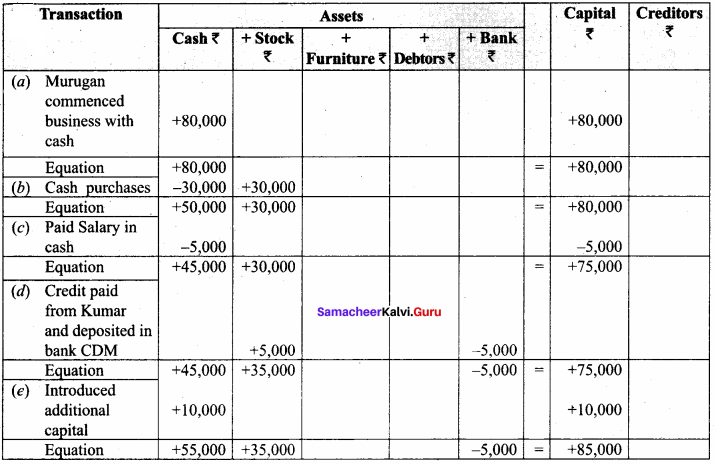
Question 4.
What will be the effect of the following on the accounting equation? (5 Marks)
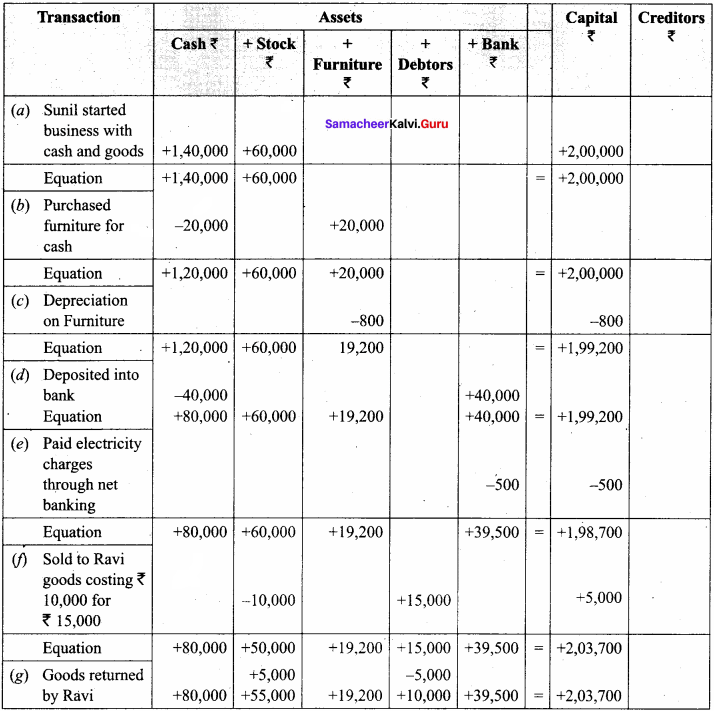
(a) Sunil started the business with ₹ 1,40,000 cash and goods worth ₹ 60,000
(b) Purchased furniture worth ₹ 20,000 in cash
(c) Depreciation on furniture ₹ 800
(d) Deposited into bank ₹ 40,000
(e) Paid electricity charges through net banking ₹ 500
(f) Sold goods to Ravi costing ₹ 10,000 for ₹ 15,000
(g) Goods returned by Ravi ₹ 5,000 (costing ₹ 4,000)
Answer:
Question 5.
Create an accounting equation on the basis of the following transactions: (5 Marks)
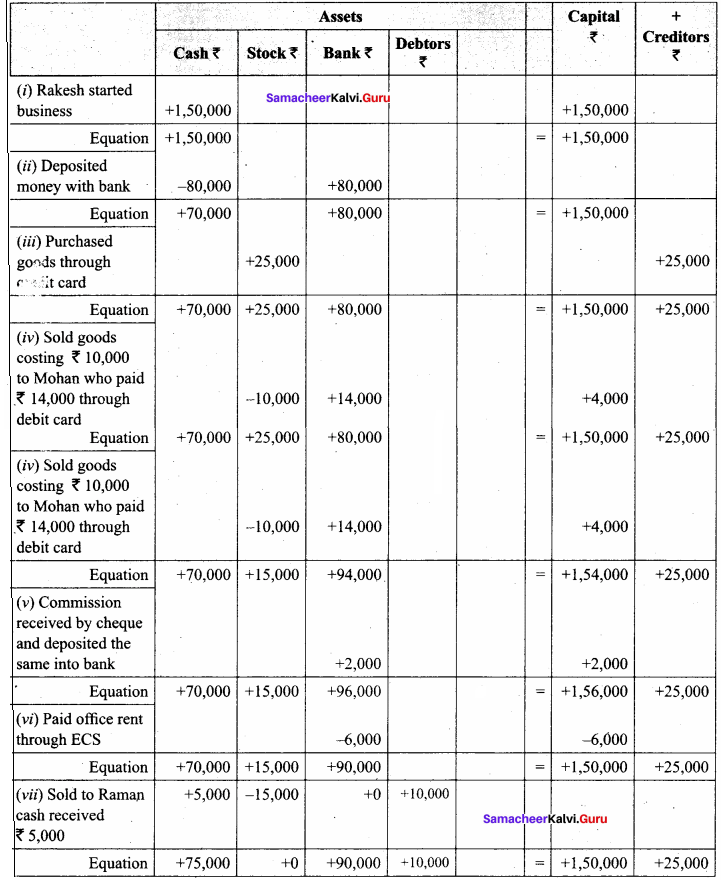
- Rakesh started the business with a capital of ₹ 1,50,000
- Deposited money with the bank ₹ 80,000
- Purchased goods from Mahesh and paid through credit card ₹ 25,000
- Sold goods (costing ₹ 10,000) to Mohan for ₹ 14,000 who pays through debit card
- Commission received by cheque and deposited the same in the bank ₹ 2,000
- Paid office rent through ECS ₹ 6,000
- Sold goods to Raman for ₹ 15,000 of which ₹ 5,000 was received at once
Answer:
Question 6.
Create an accounting equation on the basis of the following transactions: (5 Marks)
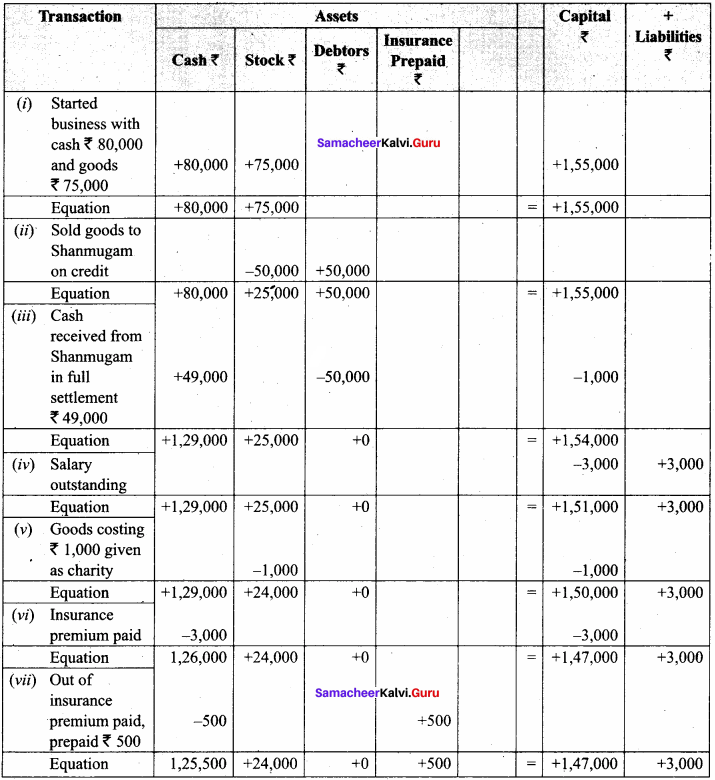
- Started business with cash ₹ 80,000 and goods ₹ 75,000
- Sold goods to Shanmugam on credit for ₹ 50,000
- Received cash from Shanmugam in full settlement ₹ 49,000
- Salary outstanding ₹ 3,000
- Goods costing ₹ 1,000 given as charity
- An insurance premium paid ₹ 3000
- Out of insurance premium paid, prepaid is ₹ 500
Answer:
Question 7.
Create an accounting equation on the basis of the following transactions:
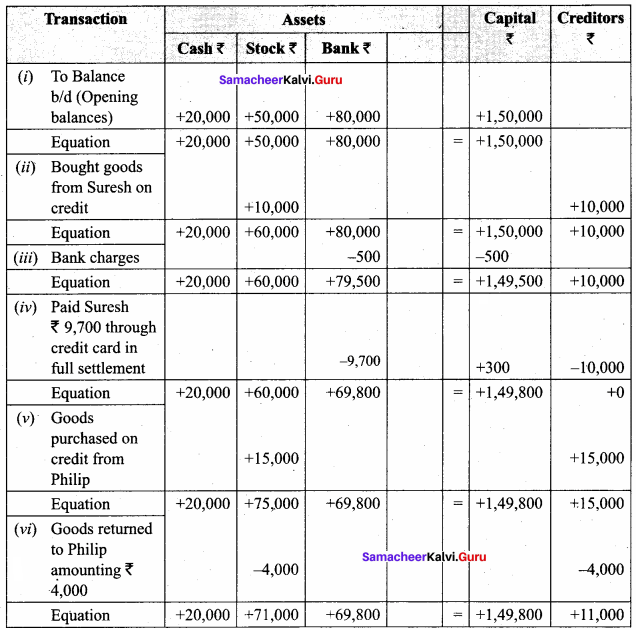
- Opening balance on 1st January, 2018: cash ₹ 20,000; stock ₹ 50,000 and bank ₹ 80,000
- Bought goods from Suresh ₹ 10,000 on credit
- Bank charges ₹ 500
- Paid Suresh ₹ 9,700 through credit card in full settlement.
- Goods purchased on credit from Philip for ₹ 15,000
- Goods returned to Philip amounting to ₹ 4,000
Answer:
Question 8.
Enter the following transactions in the journal of Manohar who is dealing in textiles:

Answer:
In the books of Manohar
Journal Entries
Question 9.
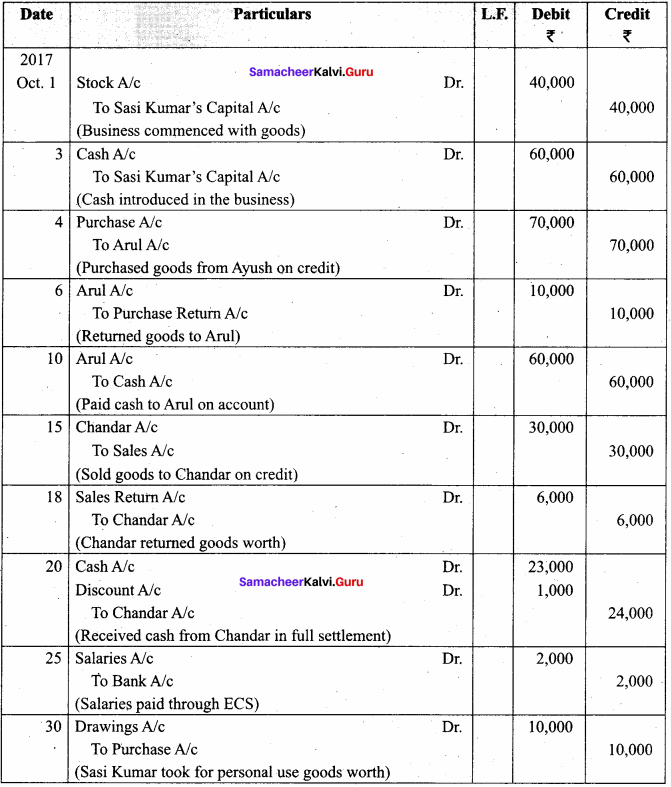
Pass journal entries in the books of Sasi Kumar who is dealing in automobiles.

Answer:
In the books of Sasi Kumar
Journal Entries
Question 10.
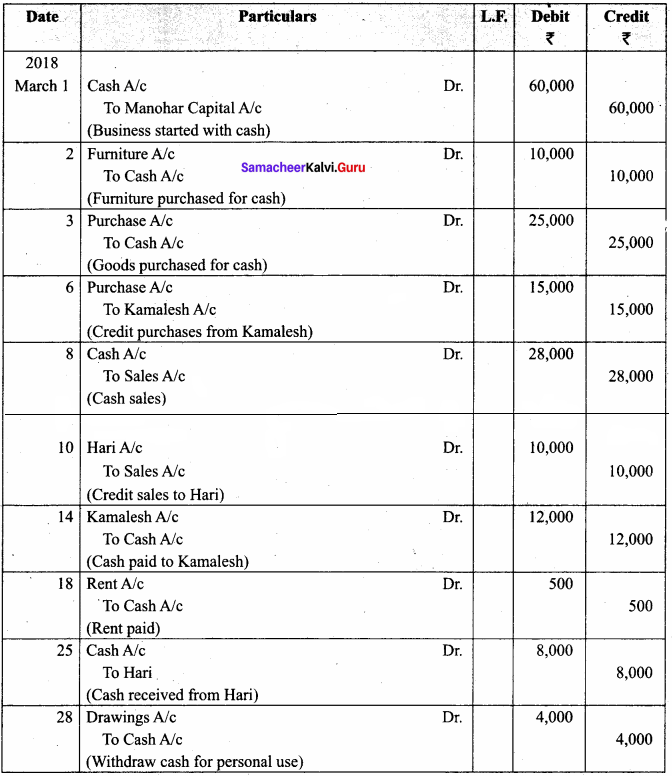
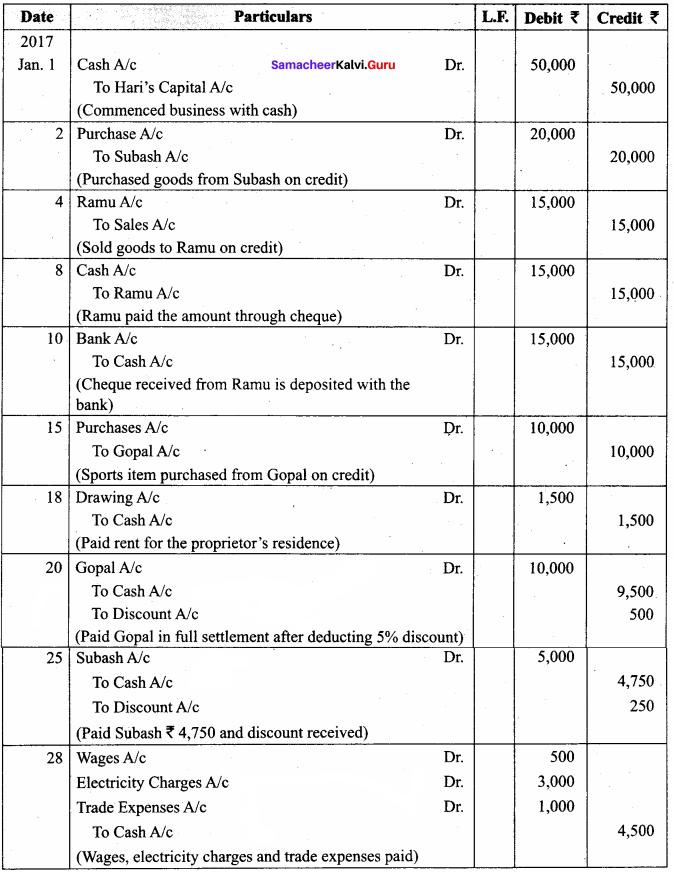
Pass Journal entries in the books of Hari who is a dealer in sports items
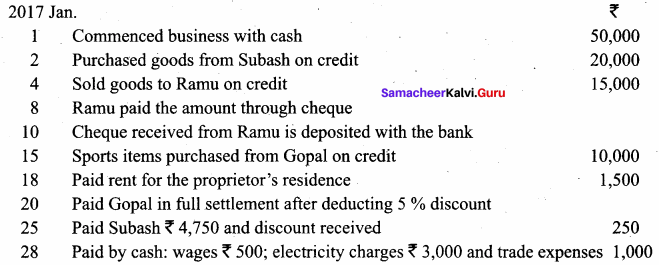
Answer:
In the Books of Hari
Journal Entries
Question 11.
Karthick opened a provisions store on 1st April, 2017. Journalise the following transactions in his books:
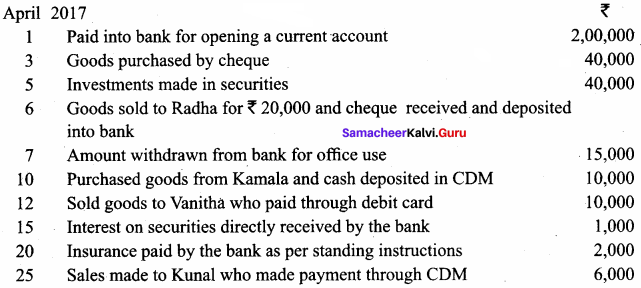
Answer:
In the Books of Karthick
Journal Entries
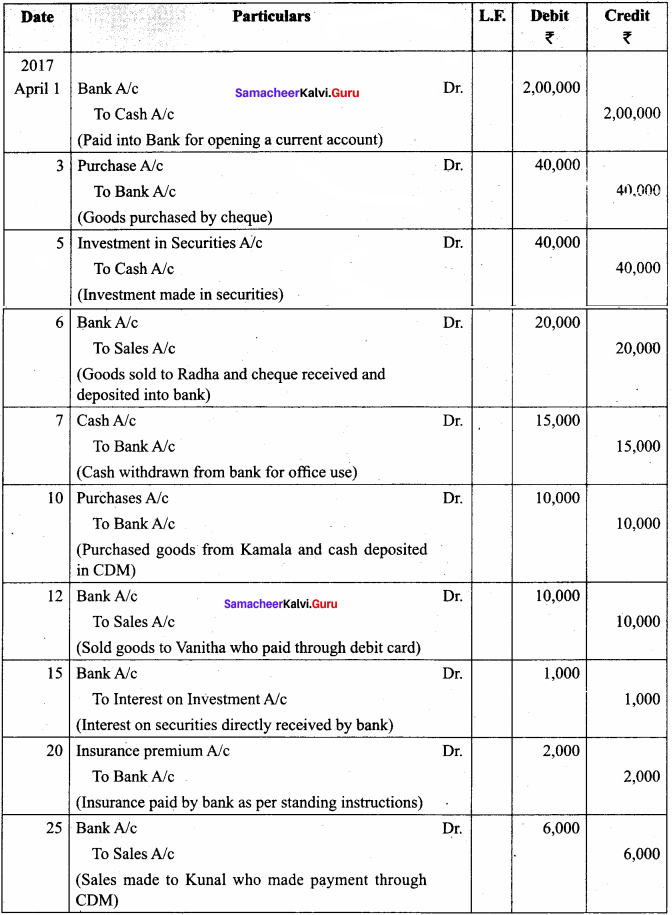
Question 12.
Journalise the following transactions in the books of Ramesh who is dealing in computers:
2018, March:
1 – Ramesh started the business with cash ₹ 3,00,000, Goods ₹ 80,000, and Furniture ₹ 27,000.
2 – Money deposited into bank ₹ 2,00,000
3 – Bought furniture from M/s Jayalakshmi Furniture for ₹ 28,000 on credit.
4 – Purchased goods from Asohan for ₹ 5,000 by paying through debit card.
5 – Purchased goods from Guna and paid through net banking for cash ₹ 10,000
6 – Purchased goods from Kannan and paid through credit card ₹ 20,000
7 – Purchased goods from Shyam on credit for ₹ 50,000
8 – Bill drawn by Shyam was accepted for ₹ 50,000
9 – Paid half the amount owed to M/s Jayalakshmi Furniture by cheque
10 – Shyam’s bill was paid
Answer:
In the Books of Ramesh
Journal Entries
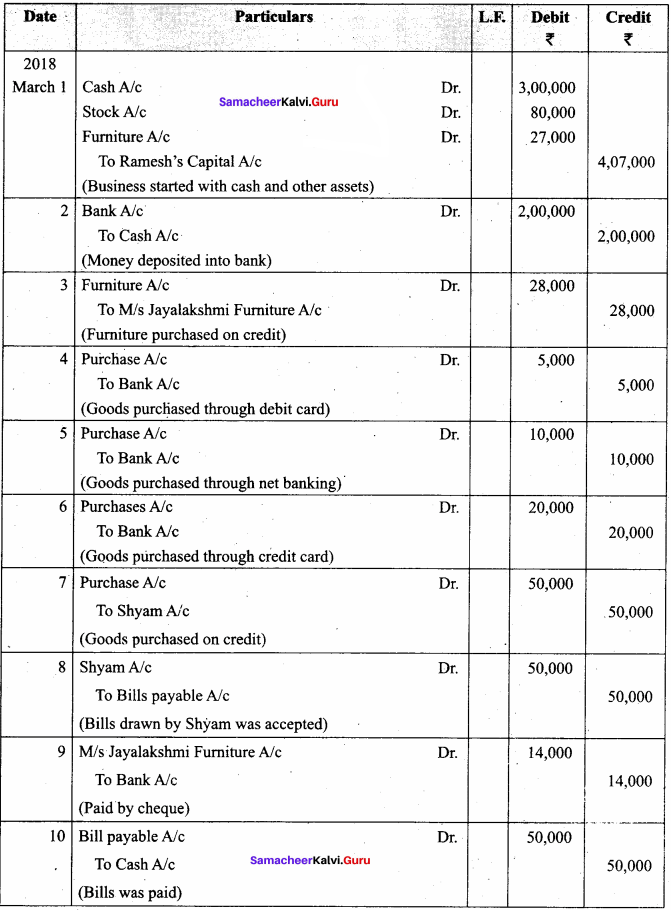
Question 13.
Journalise the following transactions in the books of Sundar who is a bookseller.

Answer:
In the Books of Mr.Sundar
Journal Entries
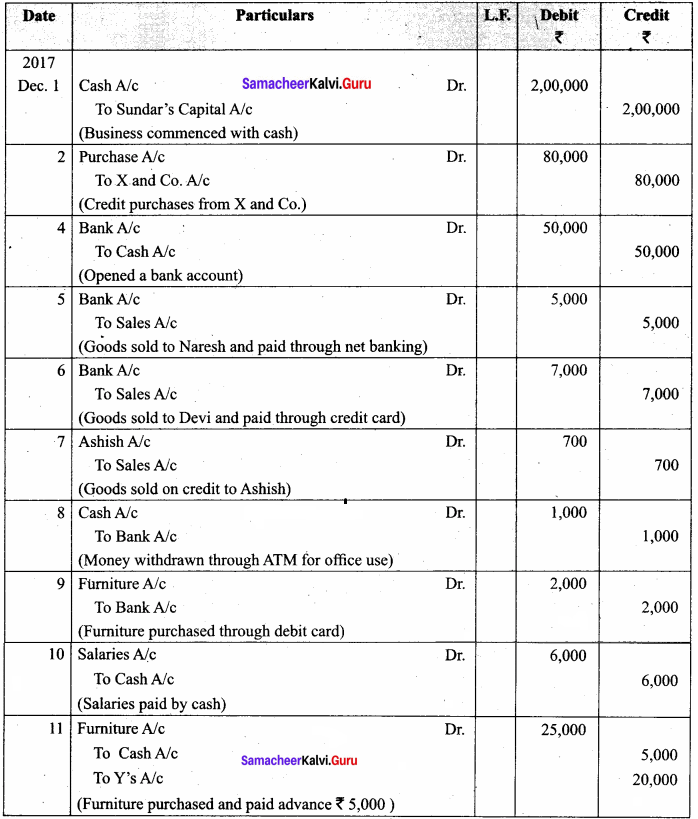
Question 14.
Raja has a hotel. The following transactions took place in his business. Journalize them.
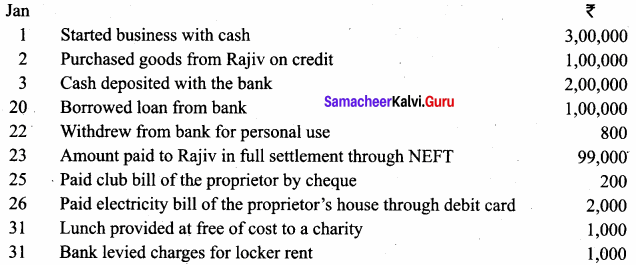
Answer:
In the Books of Raja
Journal Entries
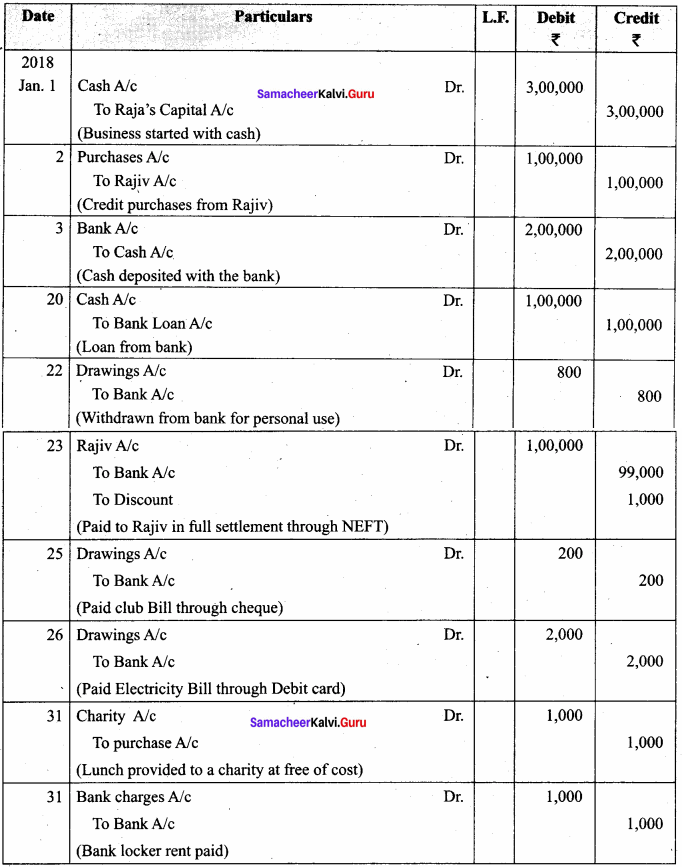
Question 15.
From the following transactions of Shyam, a stationery dealer, pass joumal entries for the month of August 2017.
August 2017 :
1 – Commenced business with cash ₹ 4,00,000, Goods ₹ 5,00,000
2 – Sold goods to A and money received through RTGS ₹ 2,50,000
3 – Goods sold to Z on credit for ₹ 20,000
5 – Bill drew on Z and accepted by him ₹ 20,000
8 – Bill received from Z is discounted with the bank for ₹ 19,000
10 – Goods sold to M on credit ₹ 12,000
12 – Goods distributed as free samples for ₹ 2,000
16 – Goods took for office use ₹ 5,000
17 – M became insolvent and only 0.80 paise per rupee is received in the final settlement
20 – Bill of Z discounted with the bank is dishonored
Answer:
In the Books of Shyam
Journal Entries
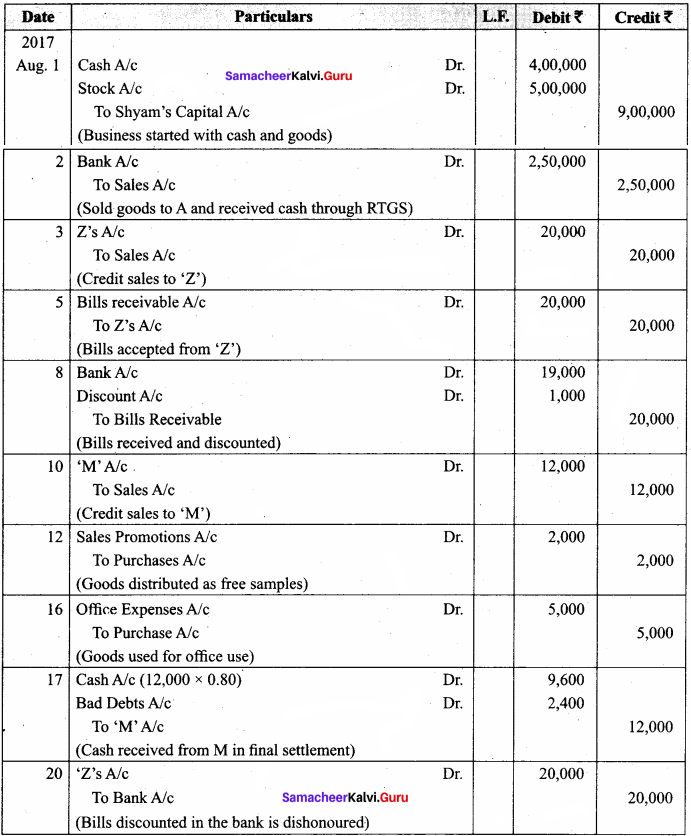
Question 16.
Mary is a cement dealer who has a business for more than 5 years. Pass journal entries in her books for the period of March 2018.

Answer:
In the Books of Mary
Journal Entries
Textbook Case Study
Pearl is a trader. She buys and sells electronic goods. She maintains double-entry bookkeeping. She purchases and sells goods both on cash and credit basis. If the purchased goods are not in good condition, she sends them back to her supplier. At the same time, she also accepts if her customers return the goods sold to them when the goods are not in good condition. She maintains a bank account for her business. She receives and pays the money through bank transactions.
Question 1.
Why does she maintain double entry book keeping?
Answer:
In this system, the two aspects of each transaction are recorded in the books of account. This helps in checking the accuracy in accounting.
Question 2.
Do all the business units engage in credit transactions?
Answer:
No, she purchases and sells goods both on a cash and credit basis.
Question 3.
Can you think of some business units that have only cash transactions?
Answer:
Yes, she has to spend money on expenses and capital also. Nominal accounts also maintained.
Question 4.
Is it necessary for Pearlite to maintain a separate bank account for business?
Answer:
Yes, she should maintain a bank account for her business.
Question 5.
What will happen if she uses her personal bank account for her business transactions?
Answer:
Because she maintains double-entry book-keeping, here the owner and the business are separated.
Question 6.
Identify the business documents involved in this case study.
Answer:
Debit note, credit note, Pay – in – slip, cash receipts, Invoice, cheques, and vouchers.
Question 7.
Can you think of some assets and liabilities for Pearlita’s business?
Answer:
The balance sheet of Pearlite
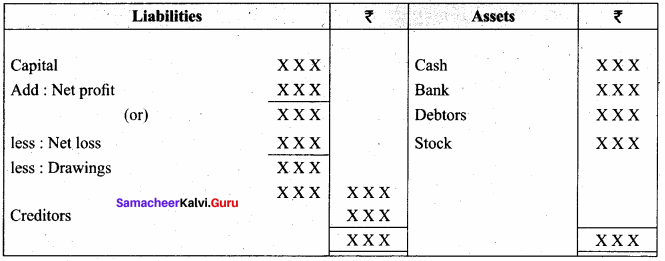
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Accountancy Books of Prime Entry Additional Questions and Answers
I. Multiple Choice Questions
Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
Journal is a book of ………
(a) Prime Entry
(b) Compound Entry
(c) Closing Entry
(d) Adjustment Entry
Answer:
(a) Prime Entry
Question 2.
A credit note is also called……………..
(a) Credit memo
(b) Debit note
(c) Vouchers
(d) Cash memo
Answer:
(a) Credit memo
Question 3.
Drawings account is …………..
(a) Personal A/c
(b) Real A/c
(c) Nominal A/c
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(c) Nominal A/c
Question 4.
Owner’s equity is otherwise called as …………….
(a) Capital
(b) Creditors
(c) Debitors
(d) Assets
Answer:
(a) Capital
Question 5.
Nominal Account relates to …………
(a) Drawings A/c
(b) Impersonal A/c
(c) Capital A/c
(d) Bank A/c
Answer:
(d) Bank A/c
Question 6.
The accounts relating to expenses, losses, revenues, and gains are called …………….
(a) Nominal accounts
(b) Real accounts
(c) Personal accounts
(d) Tangible Real accounts
Answer:
(a) Nominal accounts
Question 7.
Decrease in the number of creditors results in ……………
(a) Increase in cash
(b) Decrease in cash
(c) Increase in assets
(d) No change in assets
Answer:
(b) Decrease in cash
Question 8.
Outstanding salaries account is an example for accounts …………….
(a) Personal account
(b) Real account
(c) Nominal account
(d) Representative Personal account
Answer:
(d) Representative Personal account
Question 9.
Identify the personal accounts from the following
(a) Salary Payable Account
(b) Taxes Paid Account
(c) Investment Account
(d) Trademark Account
Answer:
(a) Salary Payable Account
Question 10.
Record of business transactions in the journal is known as ……………..
(a) Journal entry
(b) Ledger
(c) Book-keeping
(d) Accounting
Answer:
(a) Journal entry
II. Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What is an invoice?
Answer:
Invoice is used for credit purchases and credit of sales. The date, amount, and details of credit purchases and credit sales are given in the invoices. The invoice is generally prepared by the seller in three copies.
Question 2.
What is Pay – in – slip?
Answer:
When cash or cheques is deposited in a bank, a form is to be filled by a customer and submitted to the banker along with cash or cheque. This is called as Pay – in – slip or deposit slip.
Question 3.
What is a cheque?
Answer:
A cheque is a negotiable instrument. A checkbook is issued by a bank to its customers for withdrawing money for their own use or for making payment to others.
Question 4.
What is narration?
Answer:
A short description of each transaction which is written under each entry is called narration.
Question 5.
What is compound entry?
Answer:
A compound entry is an entry in which more than two accounts are involved. Either more than one account is debited or more than one account is credited or both.