Students can Download Accountancy Chapter 13 Final Accounts of Sole Proprietors – II Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 11th Accountancy Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 11th Accountancy Solutions Chapter 13 Final Accounts of Sole Proprietors – II
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Accountancy Final Accounts of Sole Proprietors – II Text Book Back Questions and Answers
I. Multiple Choice Questions
Choose the Correct Answer
Question 1.
A prepayment of insurance premium will appear in ………………
(a) The trading account on the debit side
(b) The profit and loss account on the credit side
(c) The balance sheet on the assets side
(d) The balance sheet on the liabilities side
Answer:
(c) The balance sheet on the assets side
Question 2.
Net profit is ………………
(a) Debited to capital account
(b) Credited to capital account
(c) Debited to drawings account
(d) Credited to drawings account
Answer:
(b) Credited to capital account
![]()
Question 3.
Closing stock is valued at ………………
(a) Cost price
(b) Market price
(c) Cost price or market price whichever is higher
(d) Cost price or net realizable value whichever is lower
Answer:
(d) Cost price or net realizable value whichever is lower
Question 4.
Accrued interest on investment will be shown ………………
(a) On the credit side of profit and loss account
(b) On the assets side of the balance sheet
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c) Both (a) and (b)
Question 5.
If there is no existing provision for doubtful debts, the provision created for doubtful debts is ………………
(a) Debited to bad debts account
(b) Debited to sundry debtors account
(c) Credited to bad debts account
(d) Debited to profit and loss account
Answer:
(d) Debited to profit and loss account
II. Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What are adjusting entries?
Answer:
Adjustment entries are the journal entries made at the end of the accounting period to account for items which are omitted in the trial balance and to make adjustments for outstanding and prepaid expenses and revenues accrued and received in advance.
Question 2.
What is an outstanding expense?
Answer:
Expenses which have been incurred in the accounting period but not paid till the end of the accounting period are called outstanding expenses.
Question 3.
What is a prepaid expense?
Answer:
Prepaid expenses refer to any expense or portion of expense paid in the current accounting year but the benefit of services of which will be received in the next accounting period. They are also called unexpired expenses.
![]()
Question 4.
What are accrued incomes?
Answer:
Accrued income is an income or portion of income which has been earned during the current accounting year but not received till the end of that accounting year.
Question 5.
What is the provision for discounts on debtors?
Answer:
A cash discount is allowed by the suppliers to customers for prompt payment of the amount due either on or before the due date. A provision created on sundry debtors for allowing such discount is called a provision for discount on debtors.
III. Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What is the need for preparing final accounts?
Answer:
i) Provides information about gross profit or gross loss:
- It shows the gross profit or gross loss of the business for an accounting year.
- This helps the business persons to find out the gross profit ratio by expressing the gross profit as a percentage of sales.
- It helps to compare and analyze the ratios of the previous years. Thus, it provides data for comparison, analysis, and planning for a future period.
ii) Provides an opportunity to safeguard against possible losses:
- If the ratio of gross profit has decreased in comparison to the preceding years, effective measures can be taken to safeguard against future losses.
- For example, the sale price of goods may be increased or steps may be taken to analyze and control the direct expenses.
iii) Provides information about direct expenses and direct incomes:
- All the expenses incurred on the purchase of goods are direct expenses. They are recorded in the trading account.
- The trading account also shows sales revenue, which is a direct income. With the help of a trading account, the percentage of such expenses on sales revenue can be calculated and compared with similar ratios of the previous years. Thus, it enables the management to have control over the direct expenses.
Question 2.
What is meant by provision for doubtful debts? Why is it created?
Answer:
- Provision for bad and doubtful debts refers to the amount set aside as a charge against profit to meet any loss arising due to bad debt in the future.
- At the end of the accounting period, there may be certain debts that are doubtful, i.e., the amount to be received from debtors may or may not be received.
- The reason may be the incapacity to pay the amount of deficit.
- In general, based on past experience, the amount of doubtful debts is calculated on the basis of some percentage on debtors at the end of the accounting period after deducting further bad debts (if any).
- Since the amount of loss is impossible to ascertain until it is proved bad, doubtful debts are charged against profit and loss accounts in the form of provision.
- A provision for doubtful debts is created and is charged to the profit and loss account. When bad debts occur, it is transferred to provision for doubtful debts account and not to profit and loss account.
![]()
Question 3.
Explain how closing stock is treated in final accounts?
Answer:
The unsold goods in the business at the end of the accounting period are termed as closing stock. As per As-2 (Revised), the stock is valued at cost price or net realizable value, whichever is lower.
Presentation in final accounts:
- In the trading account: Shown on the credit side.
- In the balance sheet: Shown on the assets side under current assets.
Question 4.
Give the adjusting entries for interest on capital and interest on drawings.
Answer:
Adjusting Entry: Interest on Capital
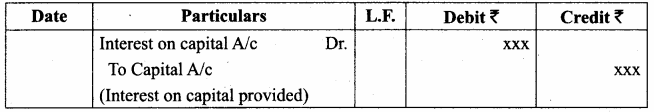
Adjusting Entry: Interest on Drawings
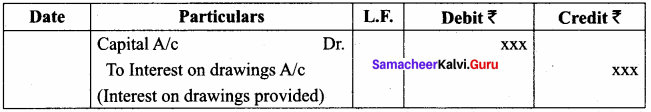
Question 5.
Explain the accounting treatment of bad debts, provision for doubtful debts, and provision for discount on debtors.
Answer:
- Bad Debts: When it is definitely known that the amount due from a customer (the debtor) to whom goods were sold on credit, cannot be realized at all, it is treated as bad debts.
- Provision for bad and doubtful debts refers to the amount set aside as a charge against profit to meet any loss arising due to bad debt in the future.
- A cash discount is allowed by the suppliers to customers for prompt payment of the amount due either on or before the due date.
IV. Exercises
Question 1.
Pass adjusting entries for the following:
(a) The closing stock was valued at ₹ 5,000
(b) Outstanding salaries ₹ 150
(c) Insurance prepaid ₹ 450
(d) ₹ 20,000 was received in advance for commission.
(e) Accrued interest on investments is ₹ 1,000.
Answer:
Adjusting Entries
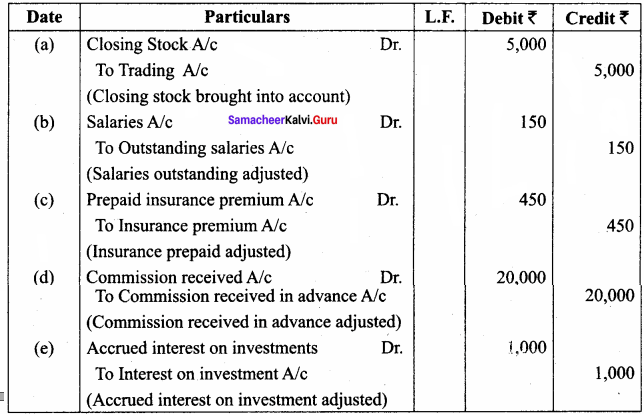
Question 2.
For the fol owing adjustments, pass adjusting entries:
(a) Outstanding wages ₹ 5,000.
(b) Depreciate machinery by ₹ 1,000.
(c) Interest on capital @ 5% (Capital: ₹ 20,000)
(d) Interest on drawings ₹ 50
(e) Write off bad debts ₹ 500
Answer:
Adjusting Entries
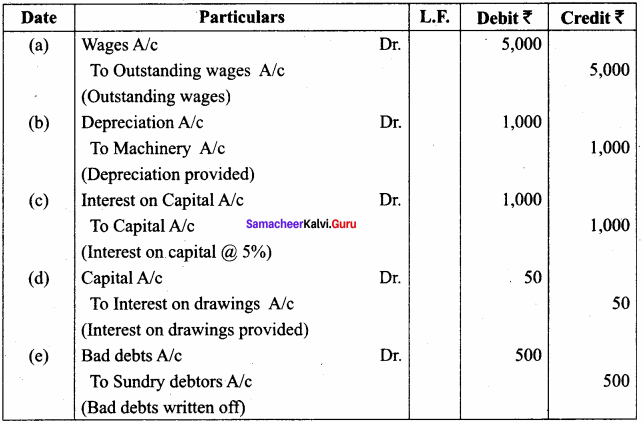
Question 3.
On preparing the final accounts of Suresh, the bad debt account has a balance of ₹ 800 and the sundry debtor account has a balance of ₹ 16,000 of which ₹ 1,200 is to be written off as further bad debts. Pass adjusting entry for bad debts. And also show how it would appear in the profit and loss account and balance sheet.
Answer:
Adjusting Entry

Profit and Loss Account
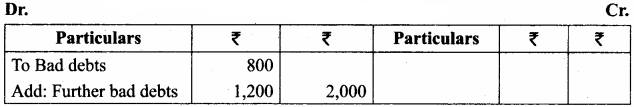
Balance Sheet

Question 4.
The trial balance on March 31, 2016, shows the following:
Sundry debtors ₹ 30,000; Bad debts ₹ 1,200
It is found that 3% of sundry debtors is doubtful of recovery and is to be provided for. Pass journal entry for the amount of provision and also show how it would appear in the profit and loss account and balance sheet.
Answer:

Profit and Loss Account for the year ended 31.03.2016
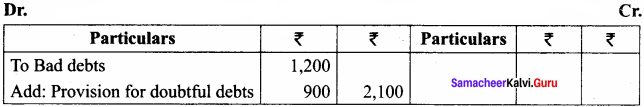
Balance Sheet as on 31.03.2016

Question 5.
The trial balance of a trader on 31st December 2016 shows debtors as ₹ 50,000.
Adjustments:
(a) Write off ₹ 1,000 as bad debts
(b) Provide 5% for doubtful debts
(c) Provide 2% for discount on debtors
Show how these items will appear in the profit and loss A/c and balance sheet of the trader.
Answer:
Profit and Loss Account for the year ended 31st December 2016
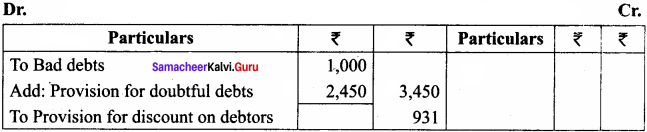
Balance Sheet as on 31st December, 2016

Question 6.
On 1st January 2016, the provision for doubtful debts account had a balance of ₹ 3,000. On December 31, 2016, sundry debtors amounted to ₹ 80,000. During the year, bad debts to be written off were ₹ 2,000. A provision for 5% was required for next year. Pass journal entries and show how these items would appear in the final accounts.
Answer:
Adjusting Entries
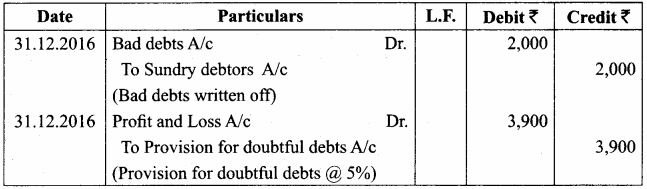
Profit and Loss Account for the year ended 31st December 2016
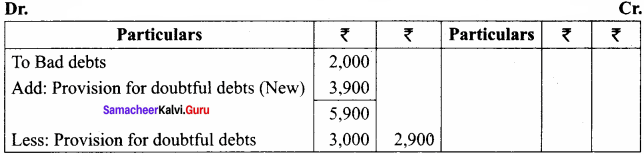
Balance Sheet as on 31.12.2016

Question 7.
The following are the extracts from the trial balance.
Sundry debtors ₹ 30,000; Bad debts ₹ 5,000 Additional information:
(a) Write off further bad debts ₹ 3,000.
(b) Create 10% provision for bad and doubtful debts.
You are required to pass necessary adjusting entries and show how these items will appear in the profit and loss account and balance sheet.
Answer:
Adjusting Entries
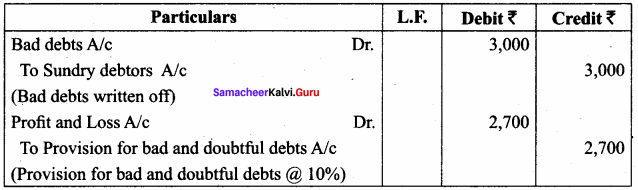
Profit and Loss Account
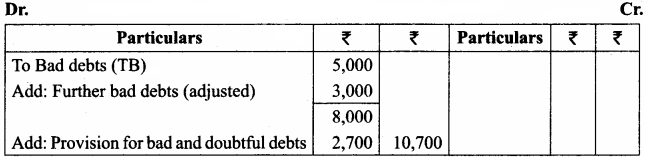
Balance Sheet

Question 8.
The following are the extracts from the trial balance.
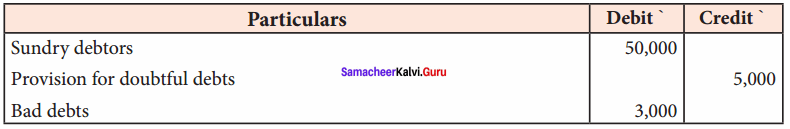
Additional information:
(a) Additional bad debts ₹ 3,000.
(b) Keep a provision for bad and doubtful debts @ 10% on sundry debtors.
You are required to pass necessary adjusting entries and show how these items will appear in the profit and loss account and balance sheet.
Answer:
Adjusting Entries
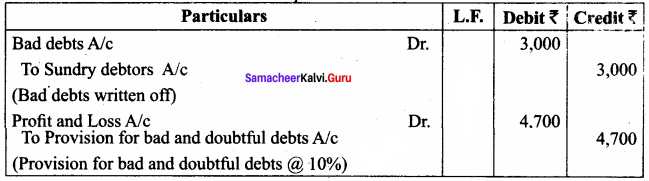
Profit and Loss Account
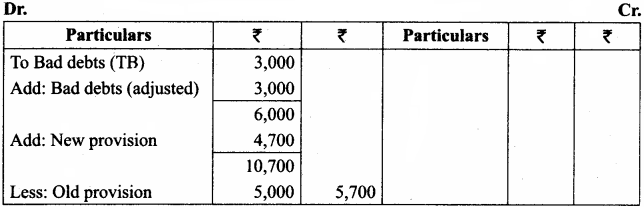
Balance Sheet

Question 9.
The accounts of Lakshmi traders showed the following balance on 31st March 2016.
Sundry debtors ₹ 60,000; Bad debts ₹ 2,000
Provision for doubtful debts ₹ 4,200
At the time of preparation of final accounts on 31st March, it was found that out of sundry debtors, ₹ 1,000 will be irrecoverable. It was decided to create a provision of 2% on debtors to meet any future possible bad debts.
Pass necessary journal entries and show how these items would appear in the final accounts.
Answer:
Adjusting Entries

Profit and Loss Account for the year ended 31.03.2016
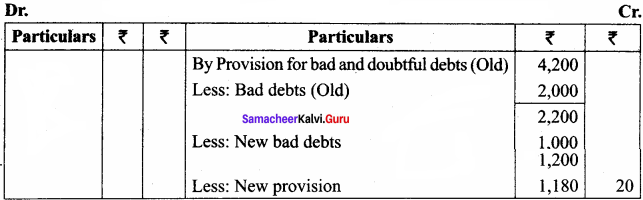
Balance Sheet as on 31.03.2016

Question 10.

The following are the extracts from the trial balance.
Additional information:
(a) Create a provision for doubtful debts @ 10% on sundry debtors.
(b) Create a provision for discount on debtors @ 5% on sundry debtors.
You are required to pass necessary adjusting entries and show how these items will appear in the final accounts.
Answer:
Adjusting Entries
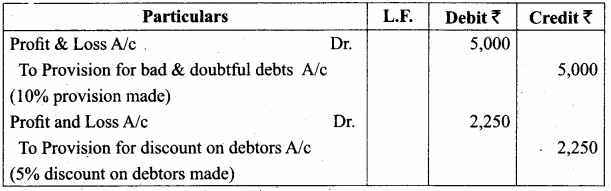
Profit and Loss Account
Balance Sheet

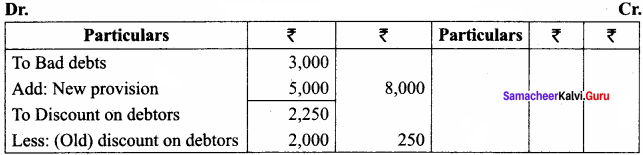
Question 11.
Following are the extracts from the trial balance.
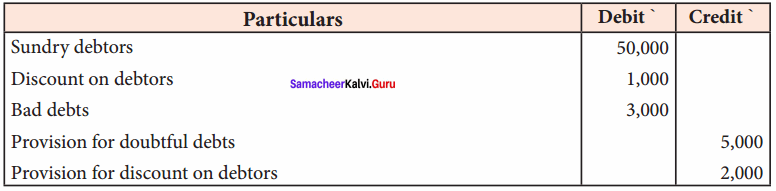
Additional information:
(a) Additional bad debts 1,000
(b) Create a provision for doubtful debts @ 5% on sundry debtors.
(c) Create a provision for discount on debtors @ 2% on sundry debtors.
You are required to pass necessary journal entries and show how these items will appear in the final accounts.
Answer:
Adjusting Entries
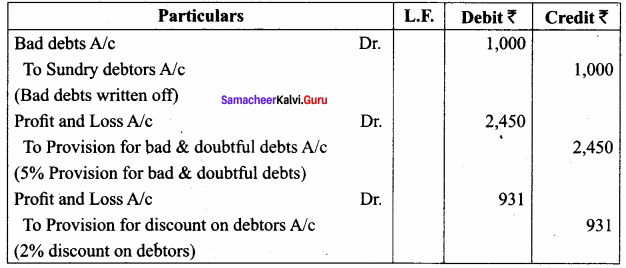
Profit and Loss Account
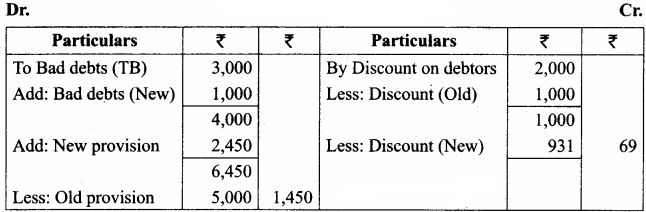
Balance Sheet
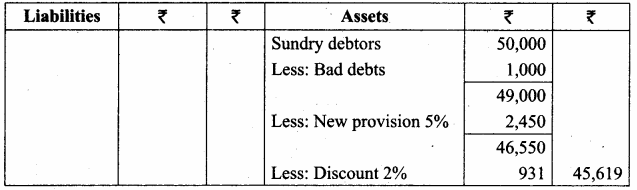
Question 12.
The following are the extracts from the trial balance.

Answer:
Profit and Loss Account
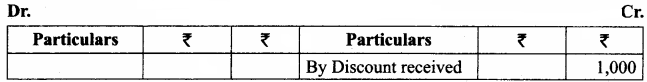
Balance Sheet

Question 13.
Prepare trading account of Archana for the year ending 31st December 2106 from the following information.
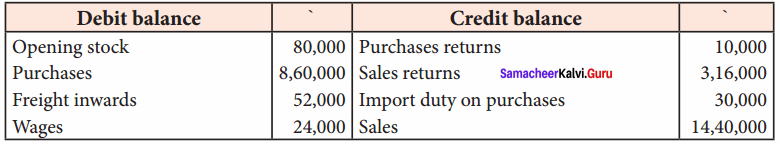
Adjustments:
(a) Closing stock ₹ 1,00,000
(b) Wages outstanding ₹ 12,000
(c) Freight inwards paid in advance ₹ 5,000
Answer:
Trading A/c of Archana for the year ended 31.12.2016
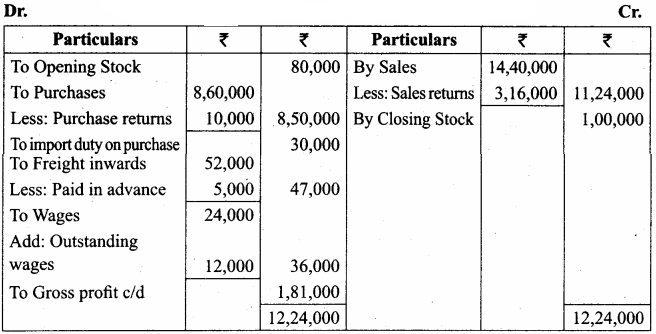
Question 14.
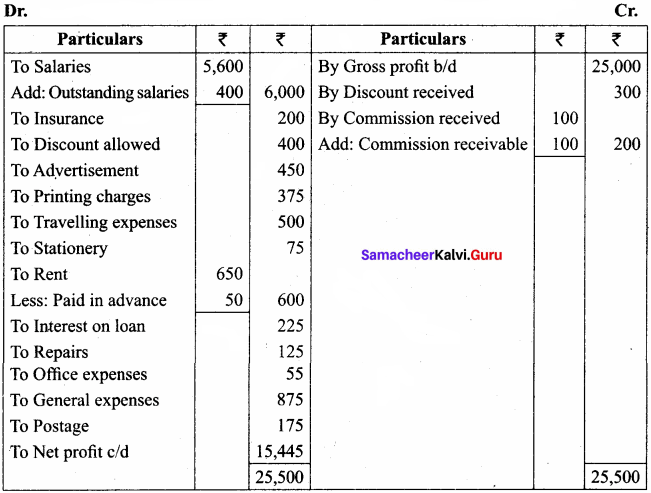
Prepare profit and loss account of Manoj for the year ending on 31st March 2016
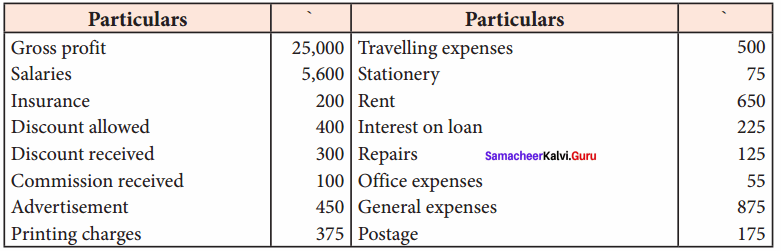
Adjustments:
(a) Salary outstanding ₹ 400
(b) Rent paid in advance ₹ 50
(c) Commission receivable ₹ 100
Answer:
Profit and Loss A/c of Manoj for the year ended 31.03.2016
Question 15.
From the trial balance of Sumathi and the adjustments prepare the trading and profit and loss account for the year ended 31st March, 2016, and a balance sheet as on that date.
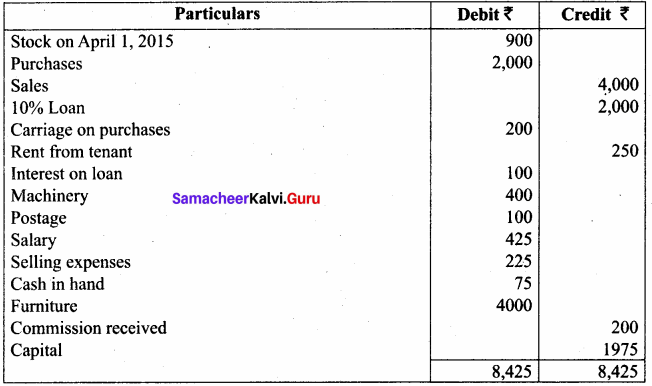
Adjustments
(a) Six months interest on the loan is outstanding.
(b) Two months rent is due from the tenant, the monthly rent being ₹ 25.
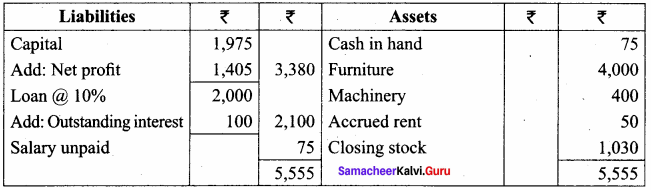
(c) Salary for the month of March 2016, ₹ 75 is unpaid.
(d) Stock in hand on March 31, 2016, was valued at ₹ 1,030.
Answer:
Trading and Profit & Loss A/c of Sumathi
for the year ended 31st March 2016
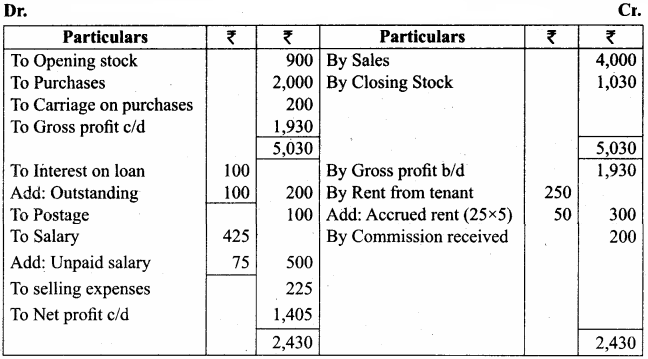
Balance Sheet of Sumathi as on 31.03.2016
Question 16.
The following trial balance was extracted from the books of Arun Traders as of 31st March 2018.
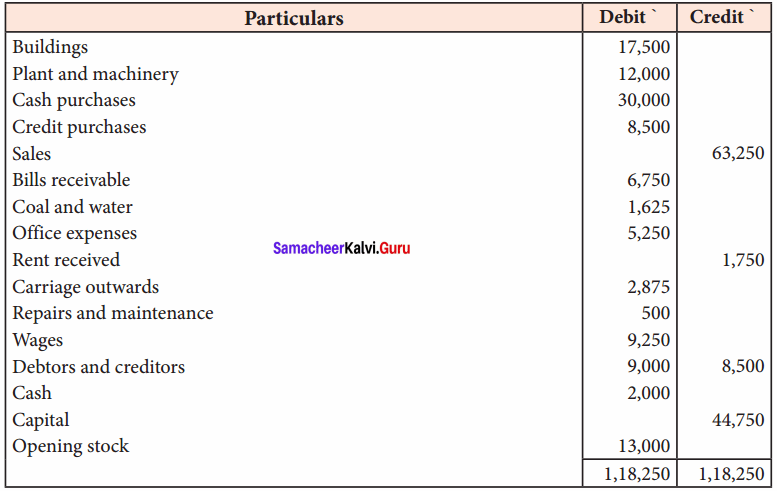
Answer:
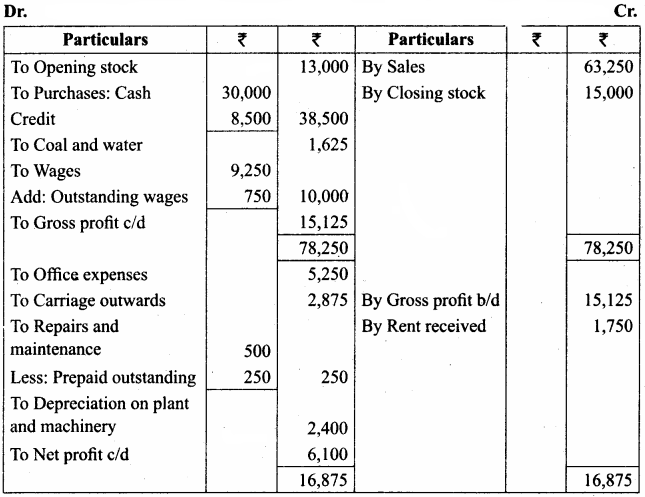
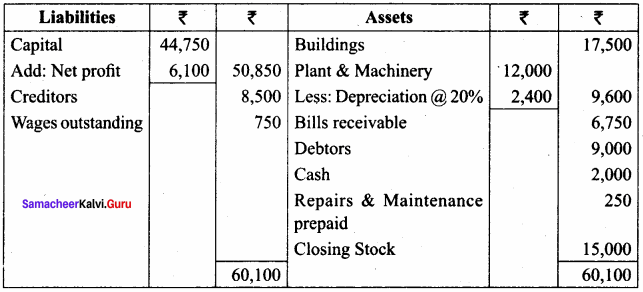
Prepare trading and profit and loss account for the year ending 31st March 2018 and balance sheet as of that date after considering the following:
(a) Depreciate Plant and machinery @ 20%
(b) Wages outstanding amounts to ₹ 750.
(c) Half of the repairs and maintenance paid is for the next year.
(d) Closing stock was valued at ₹ 15,000.
Answer:
Trading and Profit & Loss A/c of Arun Traders for the year ended 31.03.2018
Balance Sheet of Arun Traders as on 31.03.2018
Question 17.
The following is the trial balance of Babu as of 31st December 2016.
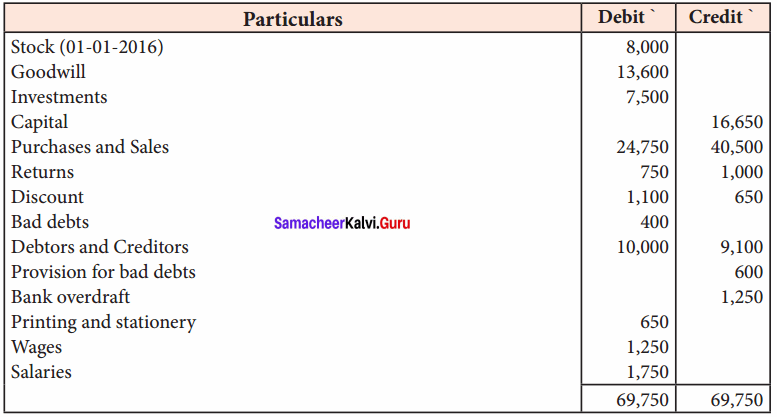
Prepare trading and profit and loss accounts for the year ended 31st December 2016 and a balance sheet as on that date after the following adjustments.
(a) Salaries outstanding ₹ 500
(b) Interest on investments receivable at 10%.
(c) Provision required for bad debts is 5%.
(d) Closing stock is valued at ₹ 9,900.
Answer:
Trading and Profit & Loss A/c for the year ended 31.12.2016
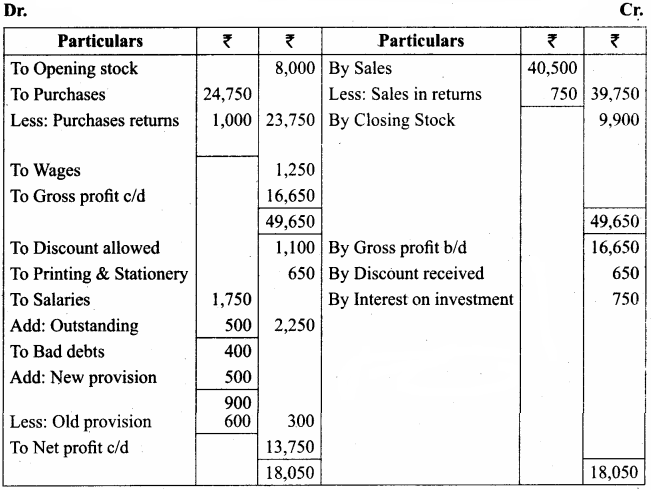
Balance Sheet as on 31.12.2016
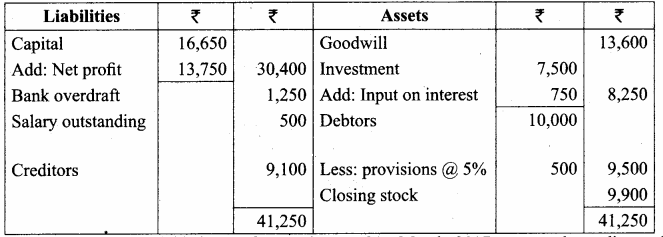
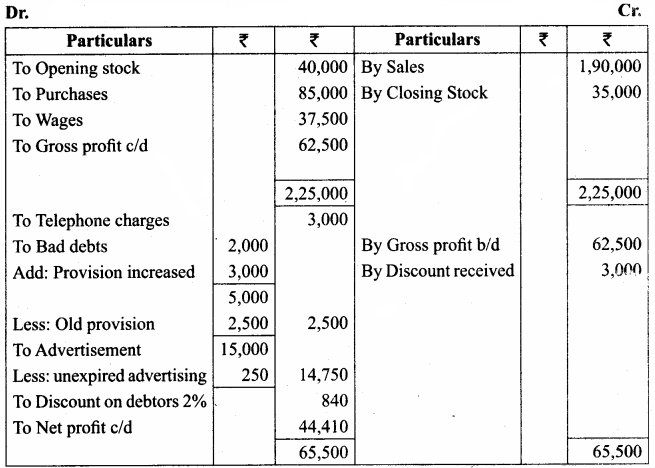
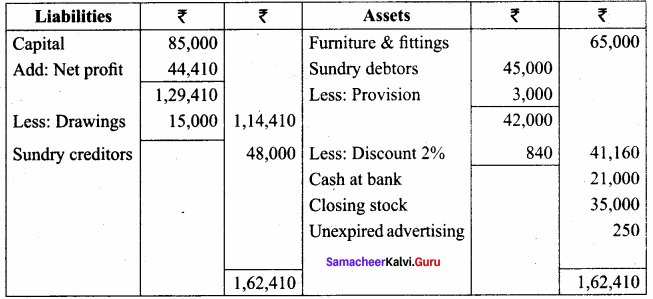
Question 18.
From the following trial balance of Ramesh as of 31st March 2017, prepare the trading and profit and loss account and the balance sheet as of that date.
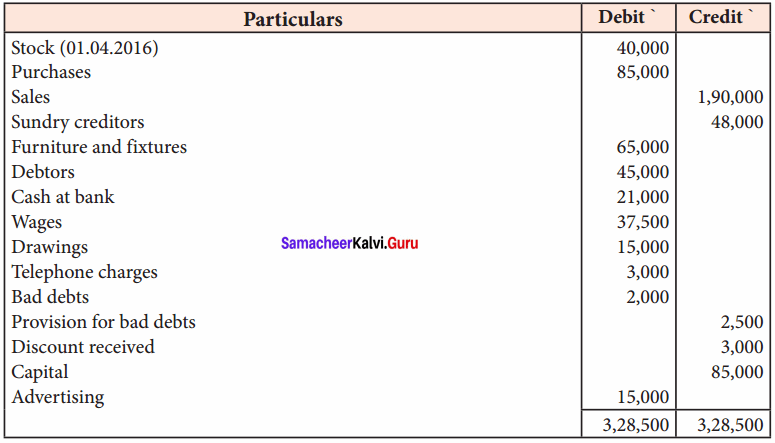
Answer:
Adjustments:
The closing stock was valued at ₹ 35,000
(b) Unexpired advertising ₹ 250
(c) Provision for bad and doubtful debts is to be increased to ₹ 3,000
(d) Provide 2% for discount on debtors.
Answer:
Trading and Profit & Loss A/c of Ramesh for the year ended 31.03.2017
Balance Sheet of Ramesh as on 31.03.2017
Question 19.
Following are the ledger balances of Devi as on 31st December, 2016.
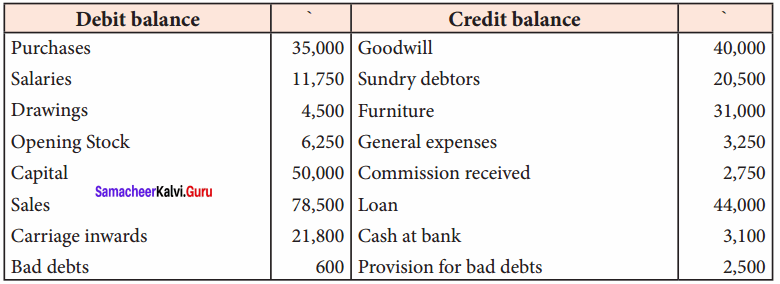
Prepare trading and profit and loss accounts for the year ended 31st December 2016 and balance sheet as on that date.
(a) Stock on 31st December, 2016 ₹ 5,800.
(b) Write off bad debts ₹ 500.
(c) Make a provision for bad debts @ 5%.
(d) Provide for discount on debtors @ 2%.
Answer:
Trading and Profit & Loss A/c of Devi for the year ended 31.12.2016
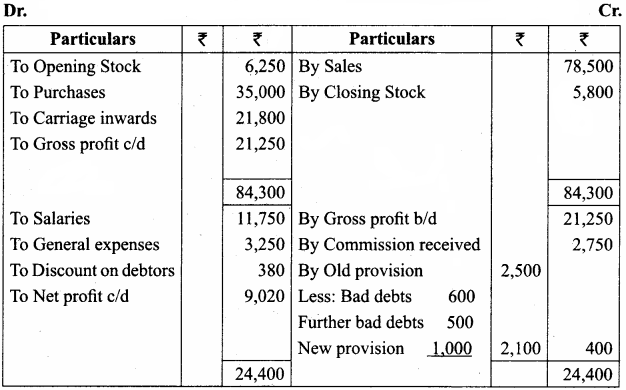
Balance Sheet of Devi as on 31.12.2016
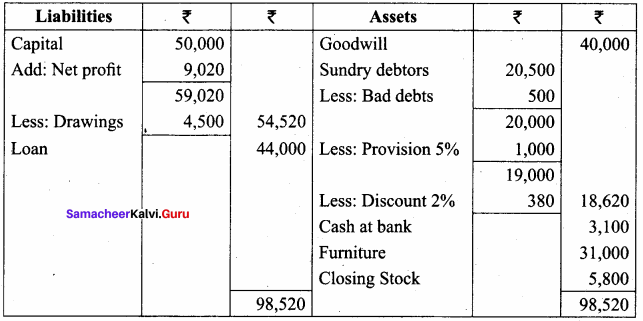
Question 20.
From the following trial balance of Mohan for the year ended 31st March 2017 and additional information, prepare trading and profit and loss account and balance sheet.
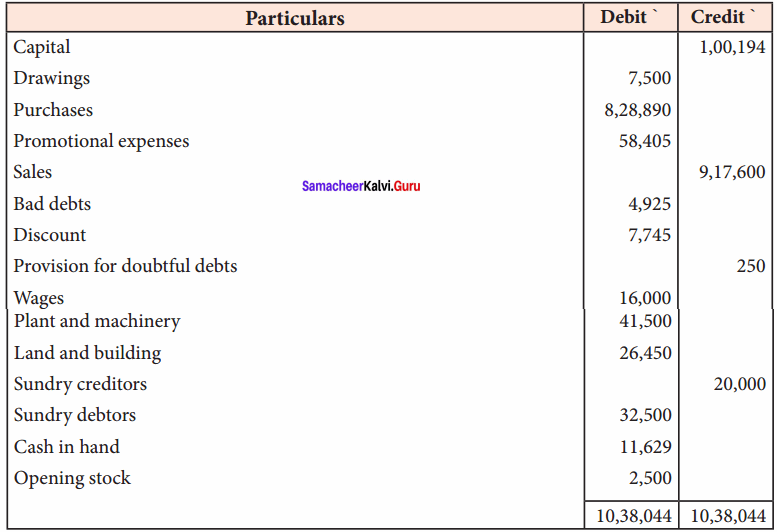
Additional information:
(a) Closing stock is valued at ₹ 15,500
(b) Write off ₹ 500 as bad debts and create a provision for bad debts @ 10% on debtors.
(c) Depreciation @ 10% required
Answer:
Trading and Profit and Loss A/c of Mohan for the year ended 31.03.2017
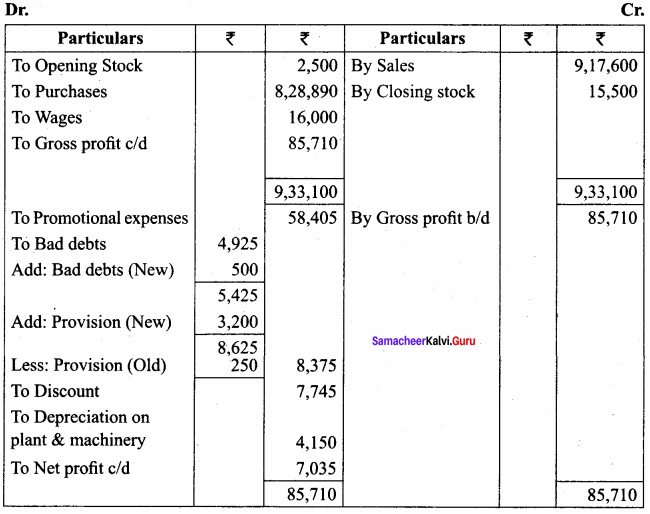
Balance Sheet of Mohan as on 31.03.2017
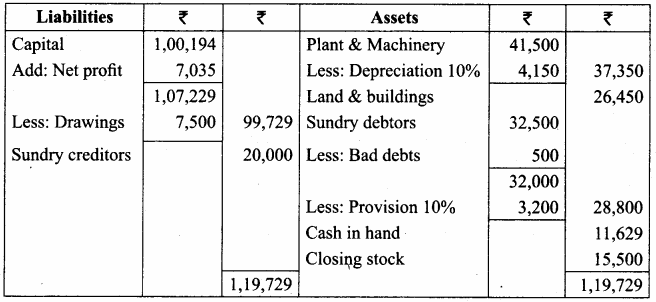
Question 21.
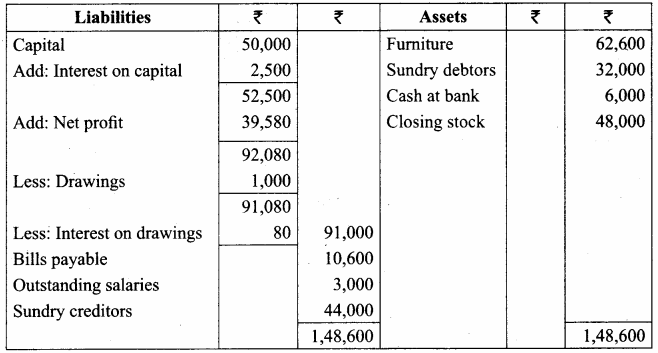
From the following trial balance of Subramaniam, prepare his trading and profit and loss account and balance sheet as of 31st December 2016.
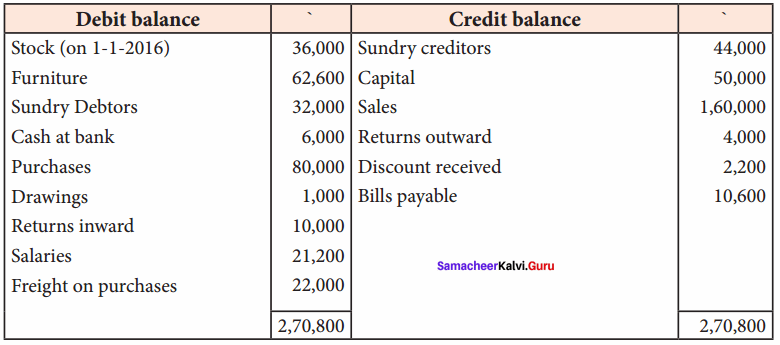
Take into account the following adjustments:
(a) Charge interest on drawings at 8%.
(b) Outstanding salaries ₹ 3,000
(c) Closing stock was valued at ₹ 48,000
(d) Provide for 5% interest on capital.
Answer:
Trading and Profit & Loss A/c of Subramaniam for the year ended 31.12.2016
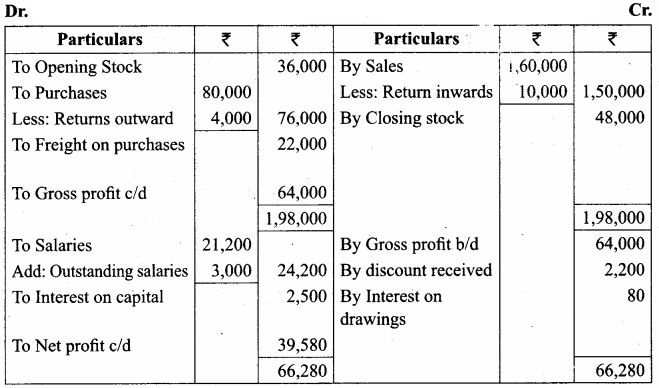
Balance Sheet of Subramaniam as on 31.12.2016
Question 22.
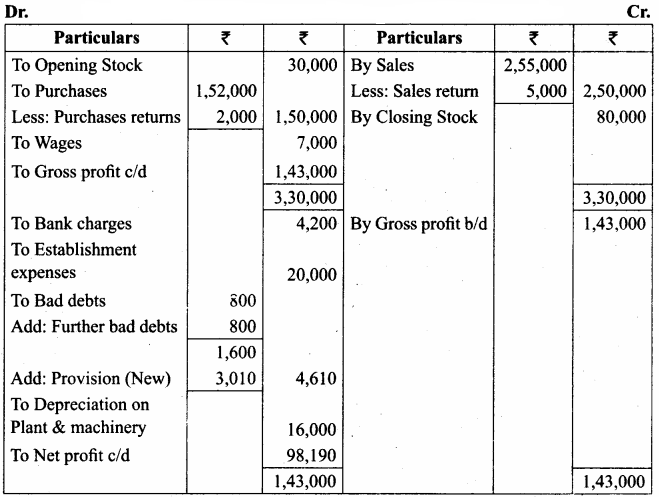
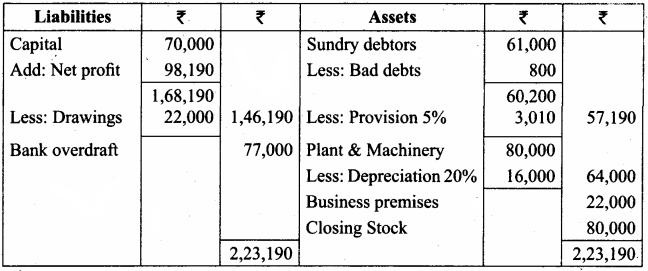
Prepare trading and profit and loss account and balance sheet from the following trial balance of Madan as of 31st March 2018.
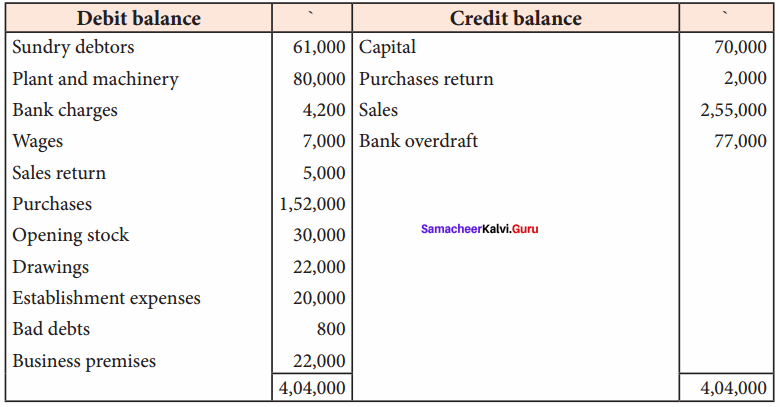
Adjustments:
(a) The closing stock was ₹ 80,000
(b) Provide depreciation on plant and machinery @ 20%
(c) Write off ₹ 800 as further bad debts
(d) Provide the doubtful debts @ 5% on sundry debtors
Answer:
Trading and Profit & Loss A/c for the year ended 31.03.2018
Balance Sheet as on 31.03.2018
Question 23.
From the following information prepare trading and profit and loss account and balance sheet of Kumar for the year ending 31st December 2017.
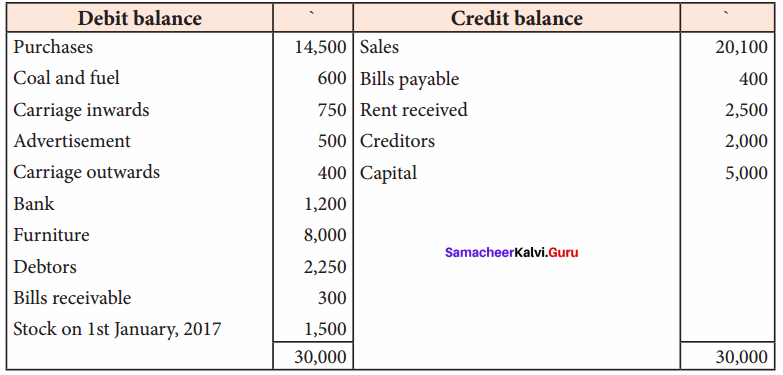
Adjustments:
(a) The closing stock on 31st December 2017 was valued at ₹ 3,900.
(b) Carriage inwards prepaid ₹ 250
(c) Rent received in advance ₹ 100
(d) Manager is entitled to receive commission @ 5% of net profit after providing such commission.
Answer:
Trading and Profit & Loss Account of Kumar for the year ended 31.12.2017
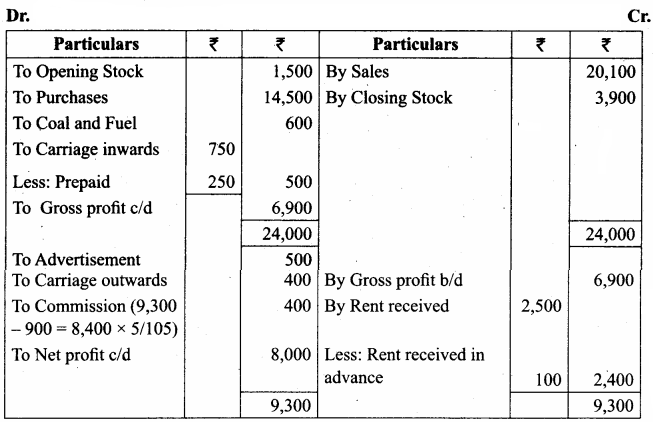
Balance Sheet of Kumar as on 31.12.2017
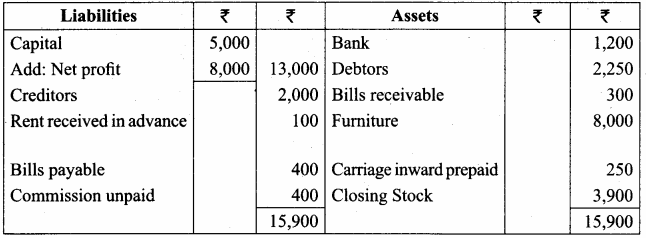
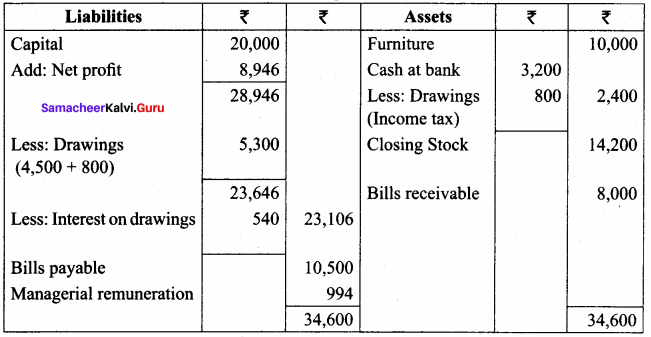
Question 24.
From the following information, prepare a trading and profit and loss account and balance sheet in the books of Sangeetha for the year ending 31st March 2018.
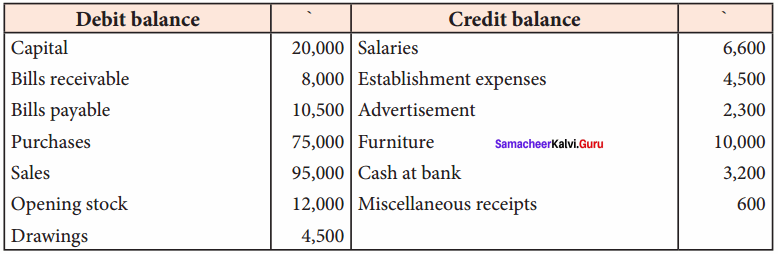
Adjustments:
(a) Stock on 31st March, 2018 ₹ 14,200
(b) Income tax of Sangeetha paid ₹ 800
(c) Charge interest on drawings @ 12% p.a.
(d) Provide managerial remuneration @ 10% of net profit before charging such commission.
Answer:
Trading and Profit & Loss Account of Sangeetha for the year ended 31.03.2018
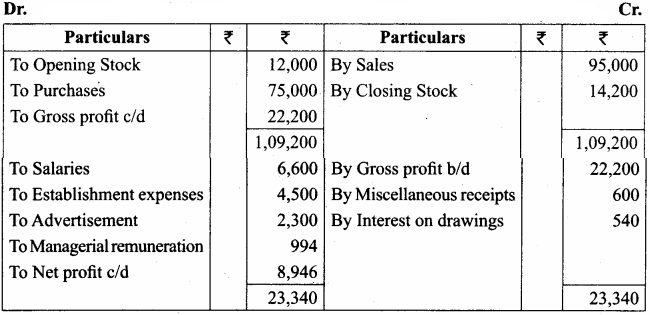
Balance Sheet of Sangeetha as on 31.03.2018
Textbook Case Study Solved
Question 1.
James is a trader who sells washing machines on credit. But, he does not remember the due date to collect the money from his debtors. Some of his customers do not pay on time. His cash inflow is becoming worse. As a result, he could not pay his telephone bill and rent at the end of the accounting period. Hence, he showed only the amount paid as an expense. He has many washing machines unsold at the year-end. He is worried about the performance of his business. So, he is planning to appoint a manager to take care of his business. The new manager insists James apply the accounting principle of prudence and matching and also allow cash discount.
Now, discuss the following points:
Question 1.
Why does James sell on credit?
Answer:
James sells goods on credit to increase the sales volume and reduce the stock.
![]()
Question 2.
Are there any ways to encourage his debtors to make the payment on time?
Answer:
Yes, there are many ways to encourage his debtors to make the payment on time by way of cash discount and trade discount.
Question 3.
What might happen if the debtors do not pay?
Answer:
If the debtors do not pay, the bad debts will be increased in the business.
Question 4.
In what ways prudence and matching principles can be applied for the business of James?
Answer:
The Prudence principle can be applied for the business here closing stock was valued on cost price or market price whichever is lower under the prudence principle. The matching principle can be applied here for revenue and expense.
Question 5.
What will be the impact on the income statement and the balance sheet, if the outstanding expenses are not adjusted?
Answer:
Outstanding expenses to be added with the concerned expenditure in the income Statement and the outstanding expenses will be recorded in the liabilities side.
![]()
Question 6.
On what basis the unsold washing machines should be valued?
Answer:
The unsold washing machine should be valued at cost price or market price, whichever is lower under prudence principle. Managerial commission can be given to motivate the new manager to retain him in the business of James.
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Accountancy Final Accounts of Sole Proprietors – II Additional Questions and Answers
I. Multiple Choice Questions (Other important questions)
Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
Net loss is __________.
a) Debited to capital account
b) Credited to capital account
c) Debited to drawings account
d) Credited to drawings account
Answer:
a) Debited to capital account
Question 2.
An outstanding expense account is a ………………. account.
(a) Nominal
(b) Real
(c) Representative personal
(d) Personal
Answer:
(c) Representative personal
![]()
Question 3.
Expenses which have been incurred in the accounting period but not paid till the end of the accounting period are called __________.
a) Outstanding expenses
b) Prepaid expenses
c) Accrued income
d) Income received in advance
Answer:
a) Outstanding expenses
Question 4.
Income tax paid by the business for the proprietor is treated as ……………….
(a) Expense
(b) Profit and Loss A/c
(c) Drawings
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c) Drawings
Question 5.
Commission on net profit after charging such commission:
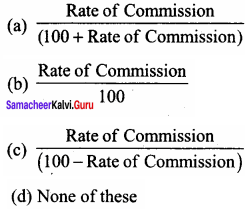
Answer:

Question 6.
__________ represents the number of goods withdrawn by the proprietor front the business for his personal use.
a) Drawings
b) Purchases
c) Sales
d) Capital
Answer:
a) Drawings
Question 7.
The decrease in book value of fixed assets due to usage or passage of time is called __________.
a) Bad debts
b) Depreciation
c) Closing stock
d) Capital
Answer:
b) Depreciation
Question 8.
Debts Which cannot be recovered or irrecoverable debts are called __________.
a) Bad debts
b) Depreciation
c) Closing stock
d) Capita
Answer:
a) Bad debts
Question 9.
Prepaid insurance is __________.
a) an asset
b) a liability
c) an income
d) an expense
Answer:
a) an asset
Question 10.
Wages outstanding is __________.
a) an asset
b) a liability
c) an income
d) an expense
Answer:
b) a liability