You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 6th Social Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 6th Social Science History Solutions Term 2 Chapter 1 Vedic Culture In North India and Megalithic Culture in South India
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Social Science Vedic Culture In North India and Megalithic Culture in South India Textual Evaluation
I. Choose the correct answer:
Vedic Culture Was Dash In Nature Question 1.
Aryans first settled in __________ region
(a) Punjab
(b) Middle Gangetic
(c) Kashmir
(d) Northeast
Answer:
(a) Punjab
Vedic Culture Was In Nature Answer Question 2.
Aryans came from ……………
(a) China
(b) North Asia
(c) Central Asia
(d) Europe
Answer:
(c) Central Asia
Vedic Culture Was In Nature Question 3.
Our National Motto “Sathyameva Jay ate” is taken from
(a) Brahmana
(c) Aranyaka
(b) Veda
(d) Upanishad
Answer:
(d) Upanishad
Vedic Culture In North India And Megalithic Culture In South India Book Back Answers Question 4.
What was the ratio of land revenue collected during Vedic Age ……………
(a) 1/3
(b) 1/6
(c) 1/8
(d) 1/9
Answer:
(b) 1/6
II. Match the statement with the Reason / Tick the appropriate answer:
6th Social Guide Term 1 Question 1.
Assertion : The vedic age is evidenced by good number of texts and adequate amount of material evidences.
Reason : Shrutis comprise the Vedas, the Brahmanas, the Aranyakas and the Upanishads.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Answer:
(d) A is false but R is true.
Vedic Culture In North India Question 2.
Statement I : Periplus mentions the steel imported into Rome from peninsular India was subjected to duty in the port of Alexandria.
Statement II : Evidence for iron smelting has come to light at Paiyampalli.
(a) Statement I is wrong
(b) Statement II is wrong
(c) Both the statements are correct
(d) Both the statements are wrong
Answer:
(c) Both the statements are correct
Vedic Culture Was What In Nature Question 3.
Which of the statement is not correct in the Vedic society
(a) A widow could re-marry.
(b) Child marriage was in practice.
(c) Father’s property was inherited by his son.
(d) Sati was unknown.
Answer:
(b) Child marriage was in practice.
6th Social Science Guide Question 4.
Which is the correct ascending order of the Rig Vedic society?
(a) Grama < Kula < Vis < Rashtra < Jana
(b) Kula < Grama < Vis < Jana < Rashtra
(c) Rashtra < Jana < Grama < Kula < Vis
(d) Jana < Grama < Kula < Vis < Rashtra
Answer:
(b) Kula < Grama < Vis < Jana < Rashtra
III. Fill in the blanks :
- Vedic culture was in nature.
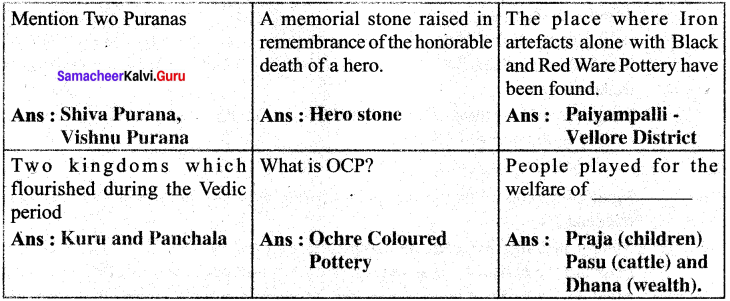
- was a tax collected from the people in Vedic period.
- system is an ancient learning method.
- Adhichanallur is in district.
Answer:
- kinship
- Bali
- Gurukula
- Thoothukudi
IV. True or False:
- The Roman artefacts found at various sites provide evidence of Indo – Roman trade relations.
- A Hero Stone is a memorial stone raised in remembrance of the honourable death of a hero.
- The army chief was called Gramani.
- The Black and Red were pottery became the characteristic of the Megalithic period.
- Evidence for iron smelting has come to light at Paiyampalii.
Answer:
- True
- True
- False
- True
- True
V. Match the following
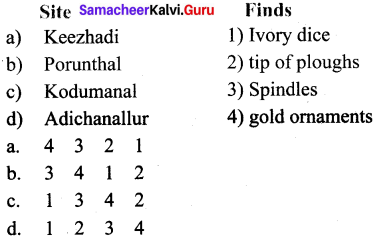
Answers:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
VI. Answer in one or two sentences:
Vedic Culture In North India And Megalithic Culture In South India Question 1.
Name the four Vedas.
Answer:
The four Vedas are Rig, Yajur, Sama and Atharva.
Question 2.
What were the animals domesticated by Vedic people?
Answer:
- Elephants
- Cow
- Goat
- Sheep
- Horse
Question 3.
What do you know about Megalith?
Answer:
The term ‘Megalith’ is derived from Greek. ‘Megas’ means great and ‘lithos’ means stone. Using big stone slabs built upon the places of burial is known as Megalith.
Question 4.
What are Dolmens?
Answer:
- Dolmens are Megalithic tombs.
- They are made of two or more upright stones with a single stone lying across the burial site.
Question 5.
What are Urns?
Answer:
Urns are large pottery jars used for burying the dead.
Question 6.
Name the coins used for business transactions in the Vedic period.
Answer:
- Nishka
- Satmana (gold)
- Krishnala (silver)
Question 7.
Name some Megalithic monuments found in Tamil Nadu.
Answer:
- Dolmens
- Menhir
Dolmens are Megalithic tombs. Megalithic Dolmens have been found in Veeraraghavapuram village, Kanchipuram district, Kummalamaruthupatti, Dindigulfc, district, and in Narasingampatti, Madurai district.
VII. Answer the following :
Question 1.
Write briefly about the archaeological site at Kodumanal.
Answer:
- Kodumanal is in Erode district.
- Kodumanal is identified with the Kodumanam of Pathitrupathu.
- More than 300 pottery inscriptions in Tamil Brahmi have been discovered.
- Spindles, whorls, piece of cloth, tools, weapons, ornaments and beads have been discovered.
- A Menhir was found at the burial site.
Question 2.
Write about the Vedic women in a paragraph.
Answer:
- In Rig Vedic society, women relatively enjoyed some freedom.
- The wife was respected as the mistress of the household.
- She could perform rituals in her house.
- In Rig Vedic period widows could remarry.
- But they were denied to inherit parental property.
- They played no role in public affairs.
- In the later Vedic period women’s position declined, demand to perform rituals and marriage rules became more rigid.
- Polygamy became common, and women were denied education
VIII. HOTS:
Question 1.
Difference between the Gurukula system of education and the Modern system of education.
Answer:
| S.No | Gurukula system of education | Modern system of education |
| 1. | Gurukula system is an ancient learning method. | Modern education system has evolved with time and has been influenced by the western system. |
| 2. | The shishyas resided with their guru and served them and simultaneously learnt and gained knowledge. | Educational centre like schools, colleges are there to give education. |
| 3. | No women could have formal education. | Men and women both have formal education. |
| 4. | The students received education through oral tradition meaning rote learning. | The education system has incorporated technologies like ebooks, video lectures, distance learning through video chat, demonstrations through 3-D imagery, etc. |
| 5. | The subjects of the study included the four Vedas, Ithihasas, Puranas, grammar, logic, ethics, astrology, maths and military science. | Modern education includes subjects of varied interests. Teaching methods are continuously upgraded as per advanced research and developments. |
|
6.
|
The students were also trained to lead a disciplined life. | The emphasis under modern education is on the theoretical part rather than the practical part. |
IX. Pride and Joy – Let us find out die fact
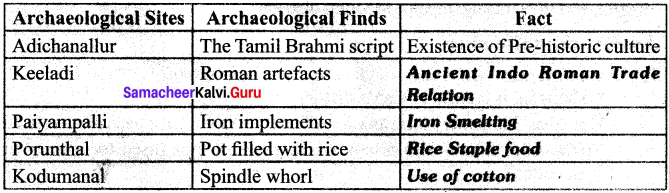
X. students Activity
Question 1.
Sentence making by using these new words.
(Shruti, Gramani, Rashtras, Iron Age, Semi-nomadic, Barter)
a. Shruti – Shruti works are considered to have been heard and transmitted by earthly sages.
b. Gramani – Gramani was the head of a village called Grama.
c. Rashtras – Rashtras were tribal kingdoms like Bharatas and Matsyas.
d. Iron Age – In India the Vedic period covers both the end of the Bronze Age and the start of the Iron Age.
e. Semi nomadic – Semi nomadic people lived usually in portable or temporary dwellings practicing seasonal migration.
f. Barter – Under barter system people exchanged services and goods for other services and goods in turn.
Question 2.
Word Search
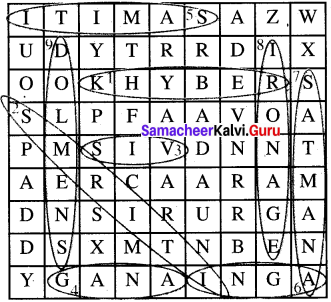
- A pass – KHYBER
- Text containing teachings on religion – SMRITI
- A group of villages – VIS
- A tribal assembly – GANA
- Assembly of people – SAMITI
- Fire – AGNI
- Gold coin – SATMANA
- Period of Vedic Age – IRON AGE
- Megalithic tomb – DOLMENS
XI. Life Skill
Question 1.
Collect information from Newspapers about archaeological finds with the help your teacher.
Answer:
(i) An archaeological site is a place where evidence of past activity is preserved.
(ii) Archaeological theory is used to interpret the archaeological record for a better understanding of human culture.
(iii) The archaeological record can consist of the earliest ancient findings as well as contemporary artefacts. For example ‘The Hindu’ dated August 10, 2017, published the information about Azhagankulam site. New finds link Azhagankulam site to Sangam Era. 12,000 artefacts unearthed so far; Archaeologists believe excavation could throw up more surprises. The excavation at Azhagankulam in the Vaigai River Valley show that the site could date back to the Sangam Age, quite like the archaeological site at Keezhadi in Sivaganga district.
(iv) Another example: Hindustan Times dated June 28, 2016. Archaeologists and Researchers have unearthed the crumbling remains of an ancient urban centre, equal in size and importance of that of Mohenjodaro. Keezhadi is a small village that lies past an unmanned railway crossing, several stretches of paddy fields and swaying palms in the Sivaganga district of Tamil Nadu, 12 kms from the city of Madurai.
XII. Answer Grid:
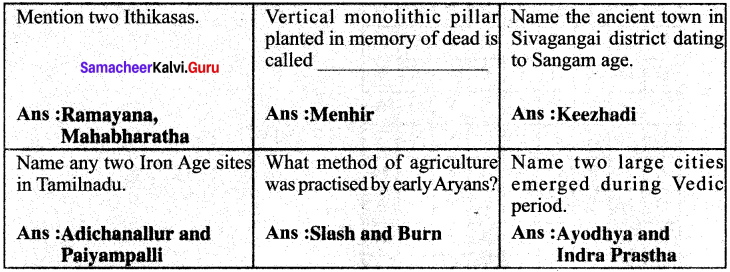
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Social Science Vedic Culture In North India and Megalithic Culture in South India Intext Questions
HOTS
Question 1.
State the differences between Indus and Vedic civilization.
Answer:
| S.No | Indus Civilization | Vedic Civilization |
| 1. | The sources of information are mainly archaeological. | Vedic Culture is mostly known from literary sources. |
| 2. | Harappans are said to have been the original inhabitants of India. | The Aryans are believed to have come from Central Asia. |
| 3. | The Harappan civilization was urban in nature. They had very good Town planning, drainage system. | Vedic culture was rural and pastoral. At best the Rig vedic Aryans lived in fortified places protected by mud walls; they cannot be regarded as towns in the Harappan sense. |
| 4. | Trade (both internal and external) crafts as well as industries were the main sources of economy. | Vedic economy was initially pastoral and later became based upon agriculture and cattle rearing. |
| 5. | Indus people did not know the use of iron. It was purly a copper, bronze culture. | In vedic culture, in its later phase is replete with references of iron. |
| 6. | The Indus valley people did not know about the animal horse. | The horse played a decisive role in the Aryan system of warfare. |
| 7. | Indus people were basically peace loving. | Aryans were warlike people and were conversant with all kinds of traditional arms and armour. |
Vedic Culture In North India and Megalithic Culture in South India Additional Questions
I. Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
The first phase of urbanisation in India came to an end with the decline of ______
(a) Indus civilization
(b) Vedic civilization
(c) Bronze civilization
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(a) Indus civilization
Question 2.
Sapta Sindhu was the land of ……………
(a) Five
(b) Seven
(c) Eight
(d) Ten
Answer:
(b) Seven
Question 3.
Sapta Sindhu means the land of ______
(a) Seven rivers
(b) Seven villages
(c) Seven Tribes
(d) Seven hills
Answer:
(a) Seven rivers
Question 4.
Paiyampalli is in …………… District.
(a) Erode
(b) Vellore
(c) Thoothukudi
(d) Dindigul
Answer:
(b) Vellore
Question 5.
In economic, political and military matters, the king was assisted by the ______
(a) Gramani
(b) Senani
(c) Purohit
(d) Vidhata
Answer:
(b) Senani
Question 6.
Non-Aryans were called ______
(a) Janas
(b) Dasyus
(c) Sabha
(d) Samitha
Answer:
(b) Dasyus
Question 7.
In the Later Vedic Period the role of women in society ______
(a) increased
(b) declined
(c) remained the same as before
(d) became equal with the role of man
Answer:
(b) declined
Question 8.
The staple crop of the Aryans was ______
(a) Rice
(b) Wheat
(c) Millets
(d) Barley
Answer:
(d) Barley
Question 9.
Paiympalli is located in ______ district.
(a) Vellore
(b) Madurai
(c) Sivaganga
(d) Dindigul
Answer:
(a) Vellore
II. Match the statement with the Reason. Tick the appropriate answer:
Question 1.
Assertion (A) : The Megalithic monuments bear witness to a highly advanced
state of civilisation with the knowledge of iron and community living.
Reason (R) : Megalithic Dolmens have been found in Veeraragavapuram village,
Kanchipuram District.
(a) Both A and R are true and R is correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is False.
(d) A is false and R is True.
Answer:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is correct explanation of A.
Question 2.
Statement I : The Aryans were semi-nomadic pastoralists.
Statement II : The Aryans practised slash and burn agriculture.
(a) Statement I is wrong.
(b) Statement II is wrong.
(c) Both the Statements are wrong,
(d) Both the statements are correct.
Answer:
(d) Both Statements are correct.
Question 3.
Which of the statement is not correct in the Vedic economy?
(a) Carpenters and Potters were there
(b) Two crops a year was raised
(c) The staple crop was wheat
(d) Barter system was prevalent
Answer:
(c) The staple crop was wheat
Question 4.
Which of the statement is correct in the Vedic culture?
(a) Bali was tax consisting of % of the agricultural produce or cattle for a person.
(b) Dasyus were Aryans Kshatriyas belonged to the warrior class Polygamy was unknown
(c) Kshatriyas belonged to the warrior class
(d) Polygamy was unknown
Answer:
(c) Kshatriyas belonged to the warrior class
III. Fill lit the blanks:
- Vedic Age gets its name from ______
- The Aryans moved eastward and settled in ______
- Smritis are not ______
- The basic unit of the Vedic Polity was ______
- Sabha means ______
- Samiti means ______
- The Vedic family was ______
- In the later Vedic period the rules of marriage became ______
- Pottery of the vedic period was ______
- In the Vedic period the mode of prayer was recitation of ______
- The ancient method of learning was ______
- Megalithic period in ancient Tamilakam synchronised with ______
Answer:
- Four Vedas
- Indo Gangetic Plain
- eternal
- Kula
- A Council of Elders
- Assembly of People
- patriarchal
- more rigid
- Painted Grey Ware Culture
- Vedic Hymns
- Gurukula System
- Pre sangam period
IV. State True or False
- Vedic Age is a period in History of India between 1500 BC (BCE) and – 600 BC (BCE).
- Ithihasas come under Shrutis.
- Smritis are constantly revised.
- Rajan was the head of a Village.
- The king performed various rituals to make his position strong.
- A rigid four fold vama system emerged under the Rig Vedic society.
- Women of Vedic society played a major role in Public Affairs.
- Idol worship was practised in the vedic period.
- Under Gurukula system the Shishyas resided with their Guru.
- The later Vedic culture in North India and the Iron Age in south India belong to the same period.
Answer:
- True
- False
- True
- False
- True
- False
- False
- False
- True
- True
V. Match the following:
Question 1.

Answer:
- 3
- 1
- 4
- 2
VI. Answer in one or two sentences:
Question 1.
What is slash and burn agriculture?
Answer:
Slash and bum agriculture is a farming method that involves clearing the land by cutting and burning all the trees and plants on it. Cultivation is done there for a short time.
Question 2.
What were the crops cultivated?
Answer:
- Wheat
- Rice
- Barley
Question 3.
Mention the archaeological sources of the Aryans.
Answer:
Material remains such as iron implements and pottery from the archaeological sites in Punjab, Uttar Pradesh and Rajasthan along the Indus and the Ganges form the archaeologic sources of the Aryans.
Question 4.
Classify the Vedic Age.
Answer:
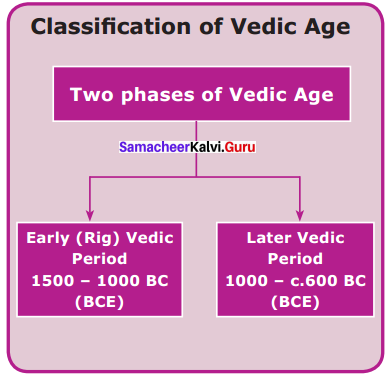
Question 5.
By whom were the powers of the Raj an limited?
Answer:
- The main responsibility of the Rajan was to protect his tribe.
- His powers were limited by tribal assemblies namely Vidhata, Sabha, Samiti and Gana.
Question 6.
When did hereditary kingship begin to emerge?
Answer:
- When the Aryans moved east ward- into Ganges-Yamuna-Doab regions, the early settlements were replaced by territorial kingdoms.
- Thus the hereditary kingship began to emerge.
Question 7.
How were Janapadas formed?
Answer:
In later Vedic period, many Janas or Tribes were amalgamated to form Janapadas or Rashtras.
Question 8.
Who formed Trevji in the early Vedic society?
- Within the early Vedic Society there were three divisions (Trevji) as given below:
- The general public were called Vis, the warrior class was called Kshatriyas and the Priestly class was named Brahmanas.
Question 9.
Mention the subject of the study under Gurukula system.
Answer:
The subjects of the study under Gurukula system included the four Vedas, Ithihasas, Puranas, grammar, logic, ethics, astrology, maths and military science.
Question 10.
Mention the four ashramas which emerged during the later vedic period.
Answer:
Towards the end of the later Vedic period, the concept of four stages in life (the four
ashramas) developed.
- Brahmacharya (Student Life)
- Grihastha (Married Life)
- Vanaprastha (Going to the forest to meditate)
- Sanyasa (Leading a life of an ascetic)
Question 11.
Define the term Menhir.
Answer:
In Breton Language ‘Men’ means “stone” and ‘hir’ means “long.” They are monolithic pillars planted vertically into the ground in memory of the dead.
Question 12.
Where are herostones found in Tamil Nadu?
Answer:
In Tamil Nadu hero stones are found at Maanur village near Palani, Dindigul district, Vellalankottai, Tuticorin district, and Pulimankombai, Dindigul district.
VII. Answer the following:
Question 1.
What about the Aryans and their home in India?
Answer:
(i) Aryans of the Rig Vedic Period were semi-nomadic. They were basically pastoral people with cattle as their main source of wealth.
(ii) In the Rig Vedic times, the Aryan homeland was Punjab, which was at that time called Sapta Sindhu, the land of seven rivers.
(iii) Around 1000 BC (BCE), Aryans in India moved eastward and settled in Indo- Gangetic Plain.
(iv) Use of iron axes and ploughs became widespread.
Question 2.
By whom was Rajan helped to protect his tribe?
Answer:
- The main responsibility of the Rajan was to protect his tribe.
- His powers were limited by tribal assemblies namely Vidhata, Sabha, Samiti and Gana.
- Of these Vidhata, (the tribal assembly) was the oldest.
- The king appointed a purohit (chief priest) to assist him.
- In economic, political and military matters, the king was assisted by the Senani (army chief).
- Gramani was the leader of the village.
Question 3.
How did trade become extensive under the Vedic age?
Answer:
- Under the Vedic age, use of iron plough and axe helped to put more areas of land under cultivation.
- Crops of wheat, rice and barley were cultivated.
- With the growth of agriculture, the idea of private possession of land came into existence.
- New crafts and arts developed leading to production of commodities for sale.
- Thus, trade became extensive.
- Barter system was prevalent.
- They used Nishka, Satmana (gold coins) and Krishnala (silver coins) for business transactions.
Question 4.
State the salient features of the Gurukula system of education.
Answer:
- The gurukula system is an ancient learning method.
- The word Gurukula is a combination of the Sanskrit Word Guru (teacher or master) and Kula (family or home).
- The shishyas resided with their guru and served them and simultaneously learnt L and gained knowledge.
- Only Dvijas could be Shishyas. No women could have formal education.
- The students received education through oral tradition meaning rote learning, and were required to memorise everything.
- The subjects of the study included the four Vedas, Ithihasas, Puranas, grammar, logic, ethics, astrology, maths and military science.
- The students were also trained to lead a disciplined life.
Question 5.
Write a note on Keezhadi in Sivaganga district. g ‘
Answer:
(i) The Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) excavated an ancient town dating to Sangam Age in Keezhadi village at Tirupathur taluk.
(ii) Excavations have produced evidence for brick buildings, and well laid – out drainage system.
(iii) Tamil – Brahmi inscription on pottery, beads of glass, camelian and quartz, pearl, gold ornaments and iron objects, shell bangles, ivory dice have been unearthed.
(iv) The Roman artefacts found at the site add to the evidence of ancient Indo -Roman trade relations.
(v) Periplus mentions the steel imported to Rome from Peninsular India was subj ected to duty in the port of Alexandria.
Question 6.
What are Menhirs ? Where are they find in Tamil Nadu?
Answer:
(i) Menhirs are monolithic pillars planted vertically into the ground in memory of the dead.
(ii) Menhir at Singaripalayam in Tirupur District and at Vembur in Theni District points to the existence of an ancient settlement along the banks of River Uppar.
(iii) Menhirs are found at Narasingampatti, Madurai district, Kumarikalpalayam and Kodumanal in Erode district.
VIII. Word search
Question 1.
Sentence making by using these new words.

- Shruti Literature – UPANISHADS
- An Archaeological site – RAJASTHAN
- A tribal kingdom – PURAS
- Three divisions of Early Vedic Society – TREYI
- Unknown to Rig vedic women – SATI
- Shyama – IRON
- Leading of life of an ascetic – SANYASA
- The Roman artefacts found here – KEEZHADI
- Used for making thread from cotton – WHORLS
- The Monolithic pillars planted vertically – MENHIR
IX. Answer Grid.