You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 8th Social Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 8th Social Science History Solutions Term 1 Chapter 2 From Trade to Territory
Samacheer Kalvi 8th Social Science From Trade to Territory Textbook Evaluation
I. Choose the correct answer
8th Social From Trade To Territory Question 1.
The ruler of Bengal in 1757 was ……………
(a) Shuja – ud – daulah
(b) Siraj – ud – daulah
(c) Mirkasim
(d) Tippu Sultan
Answer:
(b) Siraj – ud – daulah
Samacheer Kalvi 8th Social Solutions Question 2.
The Battle of Plassey was fought in ………………
(a) 1757
(b) 1764
(c) 1765
(d) 1775
Answer:
(a) 1757
From Trade To Territory Class 8 Questions And Answers Question 3.
Which among the following treaty was signed after Battle of Buxar?
(a) Treaty of Allahabad
(b) Treaty of Carnatic
(c) Treaty of Alinagar
(d) Treaty of Paris
Answer:
(a) Treaty of Allahabad]
Class 8 Social Science From Trade To Territory Question 4.
The Treaty of Pondichery brought the …………….. Carnatic war to an end .
(a) First
(b) Second
(c) Third
(d) None
Answer:
(b) Second
Samacheer Kalvi Guru 8th Social Science Question 5.
When did Hyder Ali crown on the throne of Mysore?
(a) 1756
(b) 1761
(c) 1763
(d) 1764
Answer:
(b) 1761
Samacheer Kalvi Guru 8th SocialQuestion 6.
Treaty of Mangalore was signed between ……………..
(a) The French and Tippu Sultan
(b) Hyder Ali and Zamorin of Calicut
(c) The British and Tippu Sultan
(d) Tippu Sultan andMarathas
Answer:
(c) The British and Tippu Sultan]
Samacheer Kalvi 8th Social Book Solutions Question 7.
Who was the British Governor General during Third Anglo – Mysore War?
(a) Robert Clive
(b) Warren Hastings
(c) Lord Cornwallis
(d) Lord Wellesley
Answer:
(c) Lord Cornwallis]
Class 8 History Chapter 2 Question 8.
Who signed the Treaty of Bassein with the British?
(a) Bajirao II
(b) DaulatraoScindia
(c) SambhajiBhonsle
(d) SayyajiraoGaekwad
Answer:
(a) Bajirao II
History Class 8 Question 9.
Who was the last Peshwa of Maratha empire?
(a) BalajiVishwanath
(b) BajiRao II
(c) BalajiBajiRao
(d) BajiRao
Answer:
(d) BajiRao
Samacheer Kalvi Guru 8th Social Guide Question 10.
Who was the first Indian state to join the subsidiary Alliance?
(a) Oudh
(b) Hyderabad
(c) Udaipur
(d) Gwalior
Answer:
(b) Hyderabad
II. Fill in the Blanks
- The Treaty of Alinagar was signed in ……………..
- The commander in Chief of Sirajuddaula was ……………….
- The main cause for the Second Carnatic war was ……………….
- ………………. adopted the policy of Doctrine of Lapse to extend the British Empire in India.
- Tippu Sultan was finally defeated at the hands of ……………….
- After the death of Tippu Sultan Mysore was handed over to ……………….
- In 1800, ………………… established a college at Fort William in Calcutta.
Answer:
- 1757
- Mir Jafar
- The issue of succession
- Lord Dalhousie
- Arthur Wellesely
- Krishna Raja Odayar
- Lord Wellesley]
III. Match the following
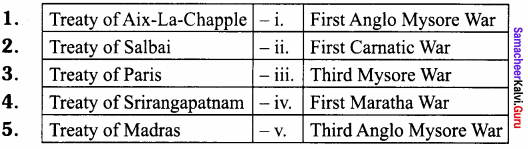
Answer:
- ii
- iv
- iii
- V
- i.
IV. State true or false
Chapter 2 History Class 8 Question 1.
After the death of Alivardi Khan, Siraj – ud – daula ascended the throne of Bengal.
Answer:
True
Samacheer Kalvi Guru 8 Social Science Question 2.
Hector Munro, led the British forces in the battle of Plassey.
Answer:
False
Correct statement:
Robert Clive, led the British forces in the battle of Plassey.
Samacheer Kalvi Guru 8th Social Science Book Back Answers Question 3.
The outbreak of the Austrian war of succession in Europe was led to Second Carnatic War in India.
Answer:
False
Correct statement:
The outbreak of the Austrian war of succession in Europe was led to First Carnatic War in India.
Class 8 Social Science History Chapter 2 Question 4.
Sir Elijalmpey was the first Chief Justice of the Supreme Court at Fort William in Bengal.
Answer:
True
Class 8 Social Science History Chapter 2 Question Answer Question 5.
The Police system was created by Lord Cornwallis.
Answer:
True
V. Which one of the following is correctly matched?
- Battle of Adayar – 1748
- Battle of Ambur – 1754
- Battle of Wandiwash – 1760
- Battle of Arcot – 1749
Answer:
3. Battle of Wandiwash – 1760
VI. Answer the following in one or two sentences
History Chapter 2 Class 8 Question Answer Question 1.
Write a short note on Black Hole Tragedy.
Answer:
There was a small dungeon room in the Fort William in Calcutta, where troops of the Nawab of Bengal Siraj – ud – daula, held 146 British Prisoners of war for one night. Next day morning, when the door was opened 123 of the prisoners found dead because of suffocation.
Class 8 Chapter 2 History Question 2.
What were the benefits derived by the English after the Battle of Plassey?
Answer:
After the Battle of Plassey in 1757, the company was granted undisputed right to have free trade in Bengal, Bihar and Orissa. It received the place of 24 parganas in Bengal.
Class 8 History Chapter 2 Solution Question 3.
Mention the causes for the Battle of Buxar.
Answer:
Mir Qasim the son in law of the Nawab of Bengal revolted as he was angry with the British for misusing the destakes (free duty passes).
Question 4.
What were the causes for the First Mysore War?
Causes:
- Haider Ali’s growing power and his friendly relations with the French became a matter of concern for the English East India Company.
- The Marathas, the Nizam and the English entered into a triple alliance against Haider Ali.
Question 5.
Bring out the results of the Third Maratha War.
- The Maratha confederacy was dissolved and Peshwaship was abolished.
- Most of the territory of Peshwa BajiRao II was annexed and became part of the Bombay Presidency
- The defeat of the Bhonsle and Holkar also resulted in the acquisition of the Maratha kingdoms of Nagpur and Indore by the British.
- The BajiRao II, the last Peshwa of Maratha was given an annual pension of 8 lakh rupees.
Question 6.
Name the states signed into Subsidiary Alliance.
Answer:
Hyderabad (1798). It was followed by Tanjore (1799), Auadh (1801), Peshwa (1802), Bhonsle (1803), Gwalior (1804), Indore (1817), Jaipur, Udaipur and Jodhpur (1818).
VII. Answer the following in detail
Question 1.
Write an essay on second Carnatic war.
Answer:
In the 18th century, three Carnatic wars were fought between various Indian rulers, British and French East Indian Company on either side.
Second Carnatic War:
1. The main cause of this war was the issue of succession in Carnatic and Hyderabad. Anwaruddin Khan and Chanda Sahib were the two claimants to the throne of Carnatic, whereas Nasir Jang and Muzaffar Jang were claimants to the throne of Hyderabad.
2. The French supported Chanda sahib and Muzaffar Jang, while the British supported the other claimants with the objective of keeping their interest and influence in the entire Deccan region.
Battle of Ambur (1749):
1. Finally Dupleix, Chanda Sahib and Muzaffar Jang formed a grand alliance and defeated and killed Anwar-ud-din Khan, the Nawab of Carnatic, in the Battle of Ambur.
2. Muhammad Ali, the son of Anwar – ud – din, fled to Trichinopoly.
3. Chanda Sahib became the Nawab of Carnatic and rewarded the French with the grant of 80 villages around Pondicherry.
4. In the Deccan, the French defeated and killed Nasir Jang and made Muzaffar Jang as the Nizam.
5. The new Nizam gave ample rewards to the French.
6. He appointed Dupleix as the governor of all the territories in south of the river Krishna. Muzaffar Jang was assassinated by his own people.
7. Salabat Jang, brother of Nasir Jang was raised to the throne by Bussy.
8. Salabat Jang granted the Northern Circars to the French.
9. Dupleix’s power was at its zenith by that time.
Battle of Arcot (1751):
1. In the meantime, Dupleix sent forces to besiege the fort of Trichy
2. Chanda Sahib also joined with the French in their efforts to besiege Trichy. Robert Clive’s proposal was accepted by the British governor, Saunders, and with only 200 English and 300 Indian soldiers, Clive was entrusted the task of capturing Arcot. His attack proved successful.
3. Robert Clive defeated the French at Ami and Kaveripak. With the assistance of Lawrence, Chanda Sahib was killed in Trichy. Muhammad Ali was made the Nawab of Arcot under British protection. The French Government recalled Dupleix to Paris.
Treaty of Pondicherry (1755):
1. Dupleix was succeeded by Godeheu who agreed the treaty of Pondicherry. According to it, both the powers agreed not to interfere in the internal affairs of the native states. They were to retain their old positions. New forts should not be built by either power. The treaty made the British stronger.
2. The second Carnatic war also proved inconclusive. The English proved their superiority on land by appointing Mohammad Ali as the Nawab of Carnatic. The French were still very powerful in Hyderabad. However, the predominant position of the French in the Deccan peninsula was definitely undermined in this war.
Question 2.
Give an account of the Fourth Anglo Mysore war.
Answer:
The Fourth Anglo – Mysore War:
Tipu Sultan did not forget the humiliating treaty of Srirangapatnam imposed upon him by Cornwallis in 1790.
Causes:
- Tipu sought alliance with foreign powers against the English and sent ambassadors to Arabia, Turkey, Afghanistan and the French.
- Tipu was in correspondence with Napoleon who invaded Egypt at that time.
- The French officers came to Srirangapatnam where they founded a Jacobin Club and planted the Tree of Liberty.
Course:
1. Wellesley declared war against Tipu in 1799. The war was short and decisive. As planned, the Bombay army under General Stuart invaded Mysore from the west.
2. The Madras army, which was led by the Governor – General’s brother, Arthur Wellesley, forced Tipu to retreat to his capital Srirangapatnam.
3. On 4th May 1799 Srirangapatnam was captured. Tipu fought bravely and was killed finally. Thus ended the fourth Mysore War and the whole of Mysore lay prostrate before the British.
Mysore after the War:
- The English occupied Kanara, Wynad. Coimbatore. Darapuram and Srirangapattinam.
- Krishna Raja Odayar of the former Hindu royal family was brought to the throne.
- Tipu’s family was sent to the fort of Vellore.
Question 3.
Describe the policy adopted by Lord Dalhousie to expand the British empire in India.
Answer:
Doctrine of Lapse:
1. Lord Dalhousie was one of the chief architects of the British Empire in India. He was an imperialist. He adopted a new policy known as Doctrine of Lapse to extend British Empire.
2. He made use of this precedent and declared in 1848 that if the native rulers adopted children without the prior permission of the Company, only the personal properties of the rulers would go to the adopted sons and the kingdoms would go to the British paramount power. This principle was called the Doctrine of Lapse.
3. It was bitterly opposed by the Indians and it was one of the root causes for the great revolt of 1857.
Question 4.
How did Lord Wellesley expand the British
Answer:
The Subsidiary Alliance:
- Lord Wellesley introduced the system of Subsidiary Alliance to bring the princely states under the control of the British.
- It was the most effective instrument for the expansion of the British territory and political influence in India.
- The princely state was called ‘the protected state’ and the British came to be referred as ‘the paramount power’.
- It was the duty of the British to safeguard the state from external aggression and to help its ruler in maintaining internal peace.
Main Features of Subsidiary Alliance:
- An Indian ruler entering into this alliance with the British had to dissolve his own armed forces and accept British Forces.
- A British Resident would stay in his capital.
- Towards the maintenance charges of the army, he should make annual payments or cede some territory permanently to the Company.
- All the non – English European officials should be turned out of his state.
- The native ruler should deal with foreign states only through the English Company.
- The British would undertake to defend the state from internal trouble as well as external attack.
VIII. HOTs
Question 1.
Explain the causes for the success of the English in India.
Answer:
1. Lack of unity among Indian Stats:
Even though there were powerful kings and who ruled Punjab, Mysore and Maratha region, they lacked unity and fought with each other for various reasons. They failed to perceive the danger arising from the East India Company.
2. Greater Naval Power:
The British came through the sea and established a strong naval power in the Indian Ocean before coming to the Indian main land. There was no strong naval power in India to challenge the Brititsh.
3. Development of textile:
By the beginning of the 19th century English made cotton textiles successfully ousted Indian goods from their traditional markets.
4. Scientific division of labour:
The production and growth of modem science in India was encouraged by the British with a view to further colonial interests.
5. Economic prospertiy:
The British had enough funds to pay its share holders that compelled them to finance the English wars in India.
IX. Mark the following on the River map of India
Question 1.
- Plassy
- Buxar
- Purandhar
- Arcot
- Wandiwash
Answer:
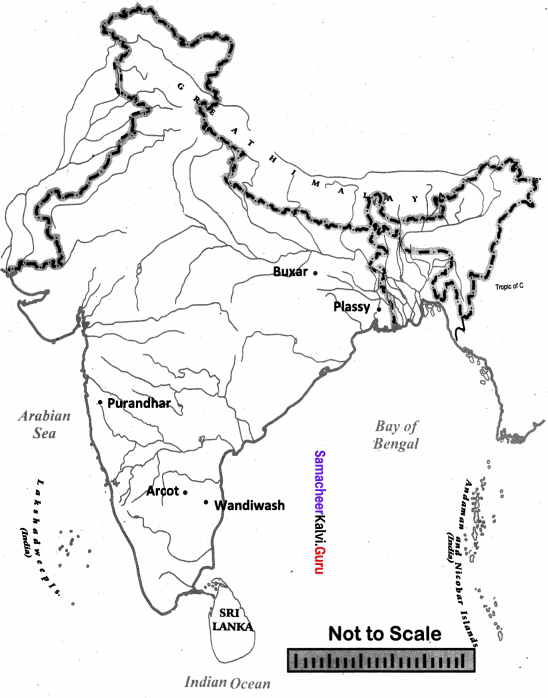
Samacheer Kalvi 8th Social Science History From Trade to Territory Additional Questions
I. Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
The rule of …………… in India became effective after the conquest of Bengal.
(a) Mughals
(b) East India Company
(c) Portuguese
(d) French
Answer:
(b) East India Company
Question 2.
Siraj – ud – daula captured the British factory at …………….
(a) Kasim bazar
(b) Delhi
(c) Alinagar
(d) Chandranagore
Answer:
(a) Kasim bazar]
Question 3.
Buxar was a small fortified town in the territory of ……………….
(a) West Bengal
(b) Karnataka
(c) Bihar
(d) Rajasthan
Answer:
(c) Bihar
Question 4.
In the battle of Adayar, the French army fought under captain ……………..
(a) Hector Munro
(b) Robert Clive
(c) Eyre Coote
(d) Paradise
Answer:
(d) Paradise
Question 5.
Under the terms of the Treaty of Aix – la – Chapelle, ……………. was returned back to the English.
(a) Madras
(b) Trichinopoly
(c) Hyderabad
(d) Calcutta
Answer:
(a) Madras
Question 6.
The out break of the seven years’ was in Europe led to the ……………. war in India.
(a) I Carnatic
(b) II Carnatic
(c) III Carnatic
(d) Wandiwash
Answer:
(c) III Carnatic
Question 7.
In the III Carnatic war, France captured Fort ……………
(a) Gwalior
(b) St. David
(c) William
(d) Vellore
Answer:
(b) St. David
Question 8.
The Battle of Wandiwash was fought by the English army under General …………….
(a) Forde
(b) Dupleix
(c) Hector Munro
(d) Eyre Coote
Answer:
(d) Eyre Coote
Question 9.
The Seven year’s war was concluded …………… by the treaty of.
(a) Paris
(b) Pondicherry
(c) Madras
(d) Mangalore
Answer:
(a) Paris
Question 10.
The state of Mysore rose to prominence uder the leadership of …………….
(a) Chanda sahib
(b) Salabat Jang
(c) Haider Ali
(d) MirJafar
Answer:
(c) Haider Ali
Question 11.
In 1781, the British General Sir Eyre Coote defeated Haider Ali at ………………
(a) Hyderabad
(b) Porto Novo
(c) Mysore
(d) Mangalore
Answer:
(b) Porto Novo
Question 12.
………….. Saved the British Dominion from the wrath of powerful enemies.
(a) Wellesley
(b) Cornwallis
(c) Warren Hastings
(d) Dalhousie
Answer:
(c) Warren Hastings
Question 13.
Tipu attacked in ……………. 1789.
(a) Madras
(b) Mangalore
(c) Mahe
(d) Travancore
Answer:
(d) Travancore
Question 14.
During the course of the third Anglo – Mysore war …………… took the command of the British Armyi
(a) Cornwallis
(b) Dalhousie
(c) Robert Clive
(d) Curzon
Answer:
(a) Cornwallis
Question 15.
The internal conflict among the ……………. was best utilised by the British.
(a) Nizams
(b) Marathas
(c) Nawabs
(d) Chauhans
Answer:
(b) Marathas
Question 16.
Colonel Upton concluded the treaty of ……………. in 1776.
(a) Mangalore
(b) Mysore
(c) Purandhar
(d) Pondicherry
Answer:
(c) Purandhar
Question 17.
The death of …………….. in 1800 gave the British an added advantage.
(a) Mahadaji Scindia
(b) Daulat Rao Scindia
(c) Madhav Rao
(d) Nana Phadnavis
Answer:
(d) Nana Phadnavis]
Question 18.
In the III Anglo Maratha war, Hastings was supported by a force under General ……………
(a) Thomas Hislop
(b) Mathews
(c) Medows
(d) Upton
Answer:
(a) Thomas Hislop]
Question 19.
……………… the Governor General of India in 1786, enforced the ruler against private trade.
(a) Warren Hastings
(b) Wellesley
(c) Cornwallis
(d) Robert Clive
Answer:
(c) Cornwallis
Question 20.
As per the Government of India Act of 1858, the maximum age for competitors of civil services examination was fixed at ……………
(a) 20
(b) 23
(c) 25
(d) 21
Answer:
(b) 23
II. Fill in the blanks
- ………………. of Portugal discovered a new sea route from Europe to India.
- ………………. ascended the throne of Bengal in 1756.
- British captured …………….. the French settlement in 1757.
- ………………. concluded two treaties with Siraj – Ud – daula and Shah Alam II.
- ………………. and ……………… were rival countries in Europe.
- The battle of ………………… was fought between the French forces and forces of Anwar – ud – din.
- ……………. was deputed from France to conduct the third Carnatic war.
- Robert Clive sent ………….. from Bengal to occupy the Norhem Circars.
- Haider Ali and his son …………. played a prominent role against the expansion of British empire in India.
- The Nizam, with the help of British troops led by General invaded Mysore in 1767.
- Tipu captutred Brigadier …………. the supreme commander of the forces in 1783.
- After the death of Narayan Rao, ……………. became the Peshwa.
- Raghunath Rao’s authority was challenged by a strong party at poona under ……………..
- ……………. made an attempt to form a coalition of Indian rulers to fight against the British.
- The Royal Commission on Public Service was Chaired by Lord ……………. in 1912.
- In 1918 ………….. and ……………. recommended that 33% of Indians should be recruited in Indian civil services.
- The …………….. was the second important pillar of the British administration in India.
- The highest rank in the army that an Indian could ever reach was that of a ……………..
- Circles or Thanas were headed by a …………….
- The heriditary village police became ……………
Answer:
- Vasco da Gama
- Siraj – Ud – daula
- Chandra nagore
- Robert Clive
- Britain and France
- San Thome (Madras)
- Count de Lally
- Colonel Forde
- Tipu Sultan
- Joseph Smith
- Mathews
- Raghunath Rao
- Nana Phadnavis
- Yashwant Rao Holkas
- Islington
- Montague, Chelmsford
- Army
- Subedar
- Daroga
- Chowkidars
III. Match the following
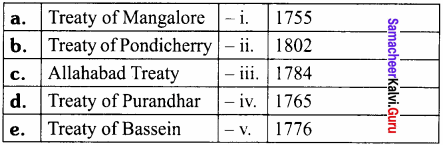
Answer:
- iii
- i
- iv
- v
- ii
IV. State true or false
Question 1.
Within a year after the Battle of Wandiwash the English army totally routed the French Army.
Answer:
True
Question 2.
In 1761, Tipu Sultan became the de facto ruler of Hyderabad.
Answer:
False
Correct statement:
In 1761, Tipu Sultan became the de facto ruler of Mysore.
Question 3.
Warren Hastings consolidated the British power in India. [Ans : True]
The Treaty of Salbai was signed between Cornwallis and Mahadaji Scindia.
Answer:
False
Correct statement:
The Treaty of Salbai was signed between Warren Hastings and Mahadaji Scindia.
Question 4.
The idea of competition for recruitment was introduced first by the Charter Act, 1833.
Answer:
True
V. Answer the following in one or two sentences.
Question 1.
What was the motive behind the discovery of sea routes to India?
Answer:
The main motive behind those discoveries was to maximize profit through trade and to establish political supremacy.
Question 2.
What were the causes of the Second Anglo Mysore war?
Answer:
1. The English did not fulfill the terms of the treaty of 1769, when Haider’s territories were attacked in 1771 by Marathas, Haider did not get help from the British.
2. British captured Mahe, a French settlement within Haider’s Jurisdiction. It led to the formation of an alliance by Haider with the Nizam and Marathas against the English in 1779.
Question 3.
Prepare flow chart to explain the period of the three Carnatic wars.
Answer:
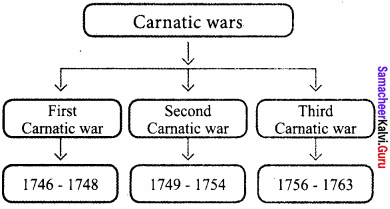
Question 4.
What were the results of the First Anglo Maratha War?
Answer:
- RaghunathRao was pensioned off and MadhavRao II was accepted as the Peshwa.
- Salsette was given to the British.
- The Treaty of Salbai established the British influence in Indian politics. It provided the British twenty years of peace with the Marathas.
Question 5.
Explain with a flow chart the period of the Anglo Mysore wars.
Answer:
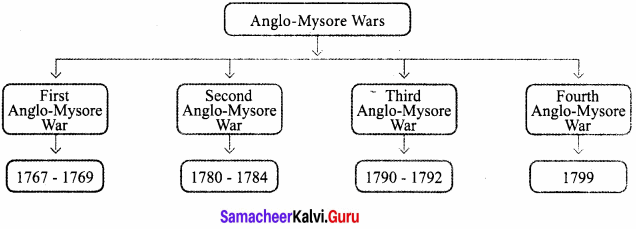
Question 6.
Prepare a flow chart mentioning the period in which the Anglo Maratha wars were fought.
Answer:
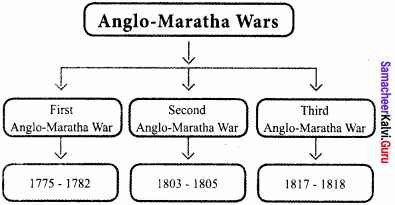
Question 7.
What did the Indian Civil Service Act of 1861 state?
Answer:
The Indian Civil Service Act of 1861 passed by the British Parliament exclusively reserved certain categories of high executive and judicial posts for the covenanted civil service which was later designated as the Indian Civil Service.
Question 8.
Name the three Indians who became successful in the I.C.S. examination in 1869.
Answer:
In 1869, three Indians – Surendra Nath Banerje, Ramesh Chandra Dutt and Bihari Lai Gupta became successful in the I.C.S. examination.
Question 9.
What did the Royal Commission of Public Service or the Lee Commission recommend in 1923?
Answer:
In 1923, a Royal Commission on Public Services was appointed with Lord Lee of Fareham as chairman. This commission recommended that recruitment to all-Indian services like the Indian Civil Service, the Indian Police Service and the Indian Forest Service should be made and controlled by the Secretary of State for India. The Lee Commission recommended the immediate establishment of a Public Service Commission.
Question 10.
Write a short note on the Act of 1935.
Answer:
The Act of 1935 also made provisions for the establishment of a Federal Public Service Commission at the Centre and the Provincial Public Service Commissions in the various provinces. Provision was also made for a Joint Public Service Commission in two or more Provinces. Although, the main aim of this measure was to serve the British interests, it became the base of the civil service system in independent India.
Question 11.
Name the provinces in which separates armies were organised during the British rule.
Answer:
During the early stage of British rule, three separate armies had been organised in three Presidencies of Bengal, Bombay and Madras.
Question 12.
Name the places where high courts were setup according to the Act of 1861.
Answer:
According to the Indian High Courts Act, 1861, three High Courts were set up in Calcutta, Bombay and Madras.
Question 13.
Brief the merits of the subsidiary Alliance for the British.
Answer:
Merits for the British:
- The British Company maintained a large army at the expense of the Indian rulers.
- All Frenchmen in the service of native rulers were dismissed, and the danger of French revival was completely eliminated.
- The British Company began to control the foreign policy of the Princely States,
- Wellesley’s diplomacy made the British the paramount power in India. He transformed the British Empire in India into the British empire of India.
Question 14.
What were the factors for the success of the British?
Answer:
Factors for the success of the British
- Greater naval power.
- Development of textile.
- Scientific division of labour.
- Economic prosperity and skilful diplomacy of the British.
- Feelings of insecurity among the Indian merchants.
- The inequality and ignorance of the Indian kings.
Question 15.
What was the impact of the policies of Subsidiary Alliance and Doctrine of Lapse in India?
Answer:
This policy led to a South Indian rebellion (1800 – 01), Vellore Rebellion (1806) and the Great Rebellion (1857).