You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 9th Maths Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 9th Maths Solutions Chapter 4 Geometry Ex 4.6
Question 1.
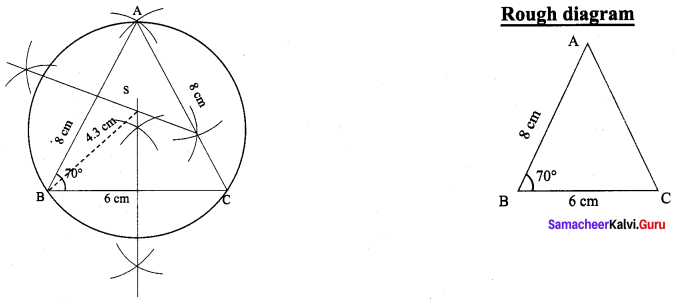
Draw a triangle ABC, where AB = 8 cm, BC = 6 cm and ∠B = 70° and locate its circumcentre and draw the circumcircle.
Solution:
∆ABC, where AB = 8 cm,
BC = 6 cm,
B = 70°
Construction:
(i) Draw the ∆ABC with the given measurements.
(ii) Construct the perpendicular bisector at any two sides (AB and BC) and let them meet at S which is the circumcircle.
(iii) S as centre and SA = SB = SC as radius, draw the circumcircle to pass through A, B, and C. Circum radius = 4.3 cm.
Question 2.
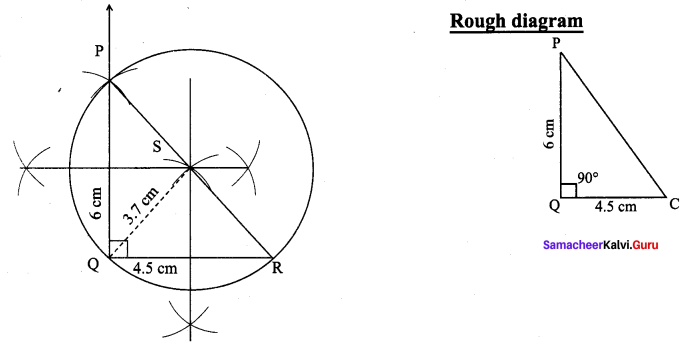
Construct the right triangle PQR whose perpendicular sides are 4.5 cm and 6 cm. Also locate its circumcentre and draw the circumcircle.
Solution:
Right triangle PQR whose perpendicular sides are 4.5 cm and 6 cm
Construction :
(i) Draw the right triangle PQR with the given measurements.
(ii) Construct the perpendicular bisector at any two sides (PQ and QR) and let them meet at S which is the circumcentre.
(iii) S as centre and SP = SQ = SR as radius, draw the circumcircle to pass through P, Q and R. Circumradius = 3.7 cm.
Question 3.
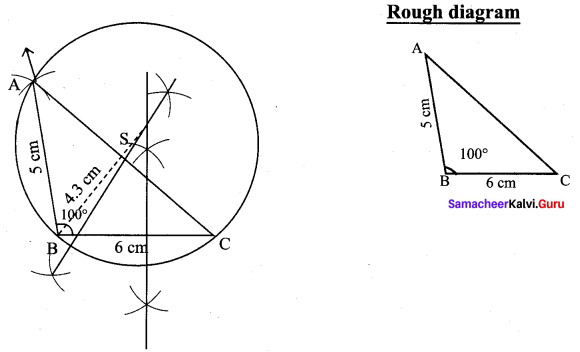
Construct ∆ABC with AB = 5 cm ∠B = 100° and BC = 6 cm. Also locate its circumcentre draw circumcircle.
Solution:
Construction :
(i) Draw the ∆ABC with the given measurements.
(ii) Construct the perpendicular bisector at any two sides (BC and AC) and let them meet at S which is the circumcentre.
(iii) S as centre and SA = SB = SC as radius, draw the circumcircle to pass through A, B, and C. Circumradius = 4.3 cm.
Question 4.
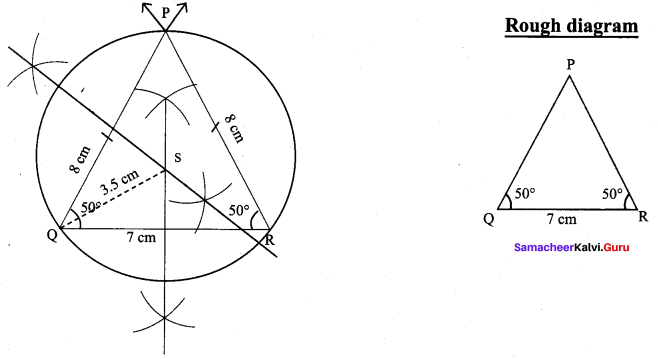
Construct an isosceles triangle PQR where PQ = PR and ∠Q = 50°, QR = 7cm. Also draw its circumcircle.
Solution:
Isosceles triangle PQR where PQ = PR and Q = 50°, QR = 7 cm.
Construction :
(i) Draw the ∆PQR with the given measurements.
(ii) Construct the perpendicular bisector at any two sides (PQ and QR) and let them meet at S which is the circumcentre.
(iii) S as centre and SP = SQ = SR as radius, draw the circumcircle to pass through P, Q, R. Circumradius = 3.5 cm.
Question 5.
Draw an equilateral triangle of sides 6.5 cm and locate its incentre. Also draw the incircle.
![]()
Solution:
Side = 6.5 cm
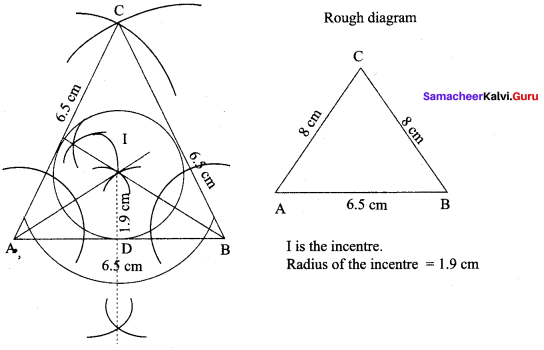
Construction :
Step 1 : Draw ∆ABC with AB = BC = CA = 6.5 cm
Step 2 : Construct angle bisectors of any two angles (A and B) and let them meet at I.I is the incentre of ∆ABC.
Step 3 : Draw perpendicular from I to any one of the side (AB) to meet AB at D.
Step 4 : With I as centre, ID as radius draw the circle. This circle touches all the sides of triangle internally.
Step 5 : Measure in radius. In radius = 1.9 cm.
Question 6.
Draw a right triangle whose hypotenuse is 10 cm and one of the legs is 8 cm. Locate its incentre and also draw the incircle.
Solution:
hypotenuse = 10 cm
One of the legs = 8 cm
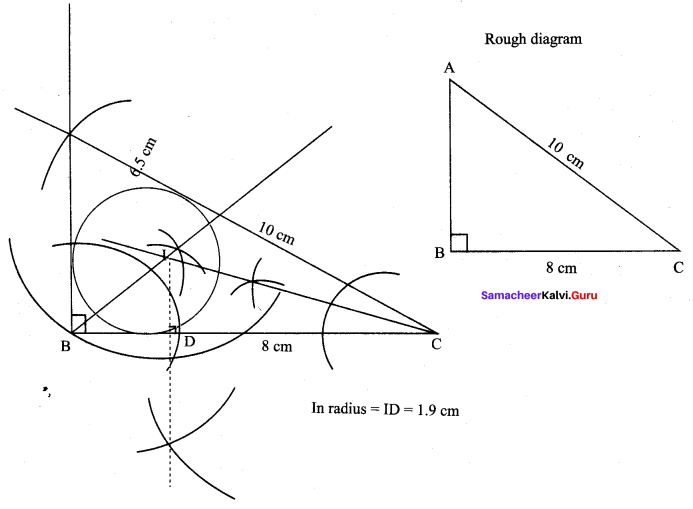
Step 1 : Draw AABC with BC = 8 cm. AC = 10 cm with right angle at B.
Step 2 : Construct angle bisectors of any two angles (B and C) and let them meet at 1.1 is the incentre.
Step 3 : Draw perpendicular from I to any side of the triangle to meet BC at D.
Step 4 : With I as centre, ID as radius draw the incircle, which touches all the three sides of the triangle internally. In radius = 1.9 cm.
Question 7.
Draw ∆ABC given AB = 9 cm, ∠CAB = 115° and ∆ABC = 40°. Locate its incentre and also draw the incircle. (Note: You can check from the above examples that the incentre of any triangle is always in its interior).
Solution:
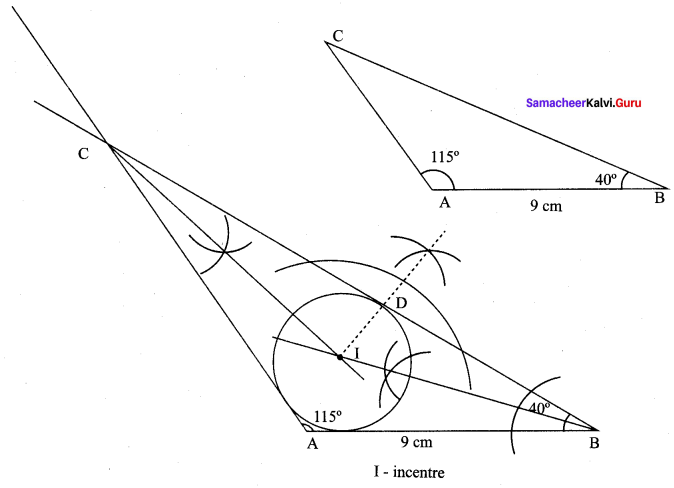
Construction :
Step 1 : Draw ∆ABC with AB = 9 cm. ∠A = 115°,∠B = 40°.
Step 2 : Construct angle bisectors of any two angles (B and C). Let them meet at I.I is the incentre of ∆ABC.
Step 3 : Draw perpendicular from I to any side (BC) to meet BC at D.
Step 4 : Draw incircle, with I as centre and ID a radius. Measures the in radius.
Question 8.
Construct ∆ABC in which AB = BC = 6 cm and B = 80° . Locate its incentre and draw the incircle.
Solution:
In ∆ABC, AB = BC = 6 cm, ∠B = 80°.
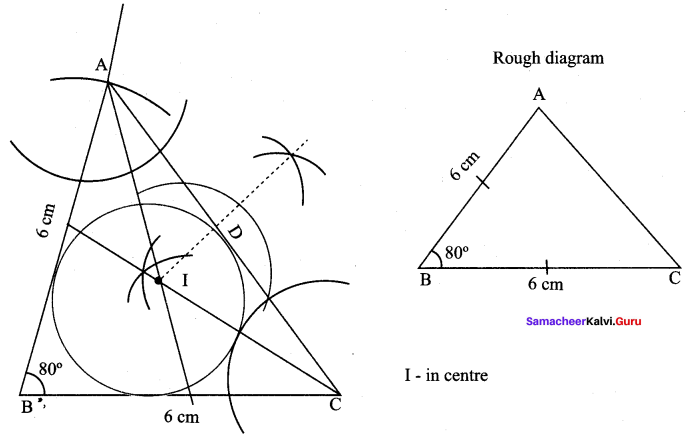
Construction :
Step 1 : Draw AABC with BC = 6 cm. AB = 6 cm, AB = 6 cm, and ∠B = 80°.
Step 2 : Construct the incentre I and ID is the in radius, as in the previous sums.
Step 3 : Draw incircle with I as centre and ID as radius. It touches all the three sides internally.
Step 4 : Measure in radius. In radius = 1.7