Get Updated Tamilnadu State Board Solutions for Class 10 Science Solutions Chapter 13 Structural Organisation of Animals Questions and Answer in PDF Format and download them free of cost. Samacheer Kalvi Class 10 Science Solutions Chapter 13 Structural Organisation of Animals provided are as per the latest exam pattern and syllabus. Access the topics of Chapter 13 Structural Organisation of Animals through the direct links available depending on the need. Clear all your queries on the Class 10 Science Subject by using the Samacheer Kalvi Board Solutions for Chapter 13 Structural Organisation of Animals existing.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 10th Science Solutions Chapter 13 Structural Organisation of Animals
If you are eager to know about the Tamilnadu State Board Solutions of Class 10 Science Solutions Chapter 13 Structural Organisation of Animals Questions and Answer you will find all of them here. You can identify the knowledge gap using these Tamilnadu State Board Class 10 Science Solutions PDF and plan accordingly. Don’t worry about the accuracy as they are given after extensive research by people having subject knowledge alongside from the latest Science Solutions Textbooks.
Samacheer Kalvi 10th Science Structural Organisation of Animals Textual Evaluation Solved
I. Choose the correct answer.
Structural Organisation Of Animals Class 10 Question 1.
In leech, locomotion is performed by _____.
(a) Anterior sucker
(b) Posterior sucker
(c) Setae
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(d) None of the above.
10th Science Structural Organisation Of Animals Question 2.
The segments of leech are known as:
(a) Metameres (somites)
(b) Proglottids
(c) Strobila
(d) All the above
Answer:
(a) Metameres (somites)
You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 10th Science Book Back Answers Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Structural Organisation Of Animals Class 10 In Tamil Question 3.
Pharyngeal ganglion in leech is a part of _____.
(a) Excretory system
(b) Nervous system
(c) Reproductive system
(d) Respiratory system.
Answer:
(b) Nervous system
Samacheerkalvi.Guru Science Structural Organisation Of Animals Question 4.
The brain of leech lies above the:
(a) Mouth
(b) Buccal Cavity
(c) Pharynx
(d) Crop
Answer:
(c) Pharynx
Samacheer Kalvi Guru 10th Structural Organisation Of Animals Question 5.
The body of leech has _____.
(a) 23 segments
(b) 33 segments
(c) 38 segments
(d) 30 segments.
Answer:
(b) 33 segments
Samacheerkalvi.Guru 10th Science Structural Organisation Of Animals Question 6.
Mammals are ______ animals.
(a) Cold – blooded
(b) Warm – blooded
(c) Poikilothermic
(d) All the above.
Answer:
(b) Warm – blooded
Samacheer Kalvi.Guru 10th Structural Organisation Of Animals Question 7.
The animals which give birth to young ones are:
(a) Oviparous
(b) Viviparous
(c) Ovoviviparous
(d) All the above
Answer:
(b) Viviparous
II. Fill in the blanks.
Question 1.
The posterior sucker is formed by the fusion of the _______ segments.
Answer:
Last seven.
Question 2.
The existence of two sets of teeth in the life of an animal is called ______ dentition.
Answer:
Diphyodont.
Question 3.
The anterior end of leech has a lobe-like structure called _____.
Answer:
Sucker.
Question 4.
The blood-sucking habit of a leech is known as _____.
Answer:
Sanguivorous.
Question 5.
______ separate nitrogenous waste from the blood in the rabbit.
Answer:
Nephrons.
Question 6.
_____ spinal nerves are present in the rabbit.
Answer:
37 pairs of.
III. Identify whether the statements are true or false. Correct the false statement.
Question 1.
An anticoagulant present in the saliva of the leech is called heparin.
Answer:
False.
Correct Statement: The anticoagulant present in the saliva of the leech is called Hirudin.
Question 2.
The vas deferens serves to transport the ovum.
Answer:
False.
Correct Statement: The vas deferens serves to transport the sperm.
Question 3.
The rabbit has a third eyelid called tympanic membrane which is movable.
Answer:
False.
Correct Statement: The rabbit has a third eyelid called Nictitating membrane, which is movable.
Question 4.
Diastema is a gap between premolar and molar teeth in rabbit.
Answer:
True.
Question 5.
The cerebral hemispheres of the rabbit are connected by a band of nerve tissue called corpora quadrigemina.
Answer:
False.
Correct Statement: The cerebral hemisphere of the rabbit are connected by a band of nerve tissue called Corpus callosum.
IV. Match the Columns I, II and III correctly.
Question 1.
| Organs | Membranous Covering | Location |
| Brain | Pleura | abdominal cavity |
| Kidney | Capsule | Mediastinum |
| Heart | Meninges | enclosed in the thoracic cavity |
| Lungs | Pericardium | cranial cavity |
Answer:
| Organs | Membranous Covering | Location |
| Brain | Meninges | cranial cavity |
| Kidney | Capsule | abdominal cavity |
| Heart | Pericardium | enclosed in the thoracic cavity |
| Lungs | Pleura | mediastinum |
V. Answer in a sentence.
Question 1.
Give the common name of the Hirudinaria granulosa.
Answer:
Indian Cattle Leech.
Question 2.
How does leech respire?
Answer:
The leech respire through skin (diffusion).
Question 3.
Write the dental formula of the rabbit.
Answer:
Dental formula is \(\left(\mathrm{I} \frac{2}{1}, \mathrm{C} \frac{0}{0}, \mathrm{PM} \frac{3}{2}, \mathrm{M} \frac{3}{3}\right)\) in Rabbit, which is written as \(\frac{2033}{1023}\)
Question 4.
How many pairs of testes are present in leech?
Answer:
In leech, there are eleven pairs of testes. One pair in each segment from 12 to 22 segments.
Question 5.
How is diastema formed in rabbit?
Answer:
The diastema is formed in Rabbit, as a gap between the incisors and premolars,
Question 6.
What organs are attached to the two bronchi?
Answer:
Lung, Bronchioles and Alveoli are the Organs, attached to Bronchi.
Question 7.
Which organ acts as suction pump in leech?
Answer:
The muscular pharynx found below the buccal cavity acts as suction pump in leech. It is surrounded by large masses, unicellular glands called salivary glands.
Question 8.
What does CNS stand for?
Answer:
CNS stands for Central Nervous System.
Question 9.
Why are the teeth of a rabbit called heterodont?
Answer:
The teeth of Rabbit are of different types. So it is called heterodont.
Question 10.
How does leech suck blood from the host?
Answer:
In leech, blood is sucked by the muscular pharynx. The salivary secretion is poured in the wound. The saliva contains an active substance called hirudin which prevents the coagulation of the blood.
VI. Short Answer Questions.
Question 1.
Why are the rings of cartilages found in the trachea of a rabbit?
Answer:
Tracheal walls are supported by rings of cartilage, which help in the free passage of air.
Question 2.
List out the parasitic adaptations in leech.
Answer:
- The suckers are the primary organ of the blood sucking.
- The blood is sucked by muscular pharynx.
- Leeches attaches itself to the body of host by Anterior and Posterior ends of the body.
- The three jaws inside the mouth, causes a painless triradiate or Y shaped incision in the skin of the host.
- A protein called hirudin is produced in the salivary gland of leech to prevent blood coagulation. Thus, a continuous supply of the blood is maintained.
- Parapodia and setae are completely absent.
- Leeches also inject an anaesthetic substances that prevents the host from feeling their bite.
- In the crop, blood is stored which gives nourishment to the leech for several months. Due to this reason there is no eloborate secretion of the digestive juices and enzymes.
VII. Long Answer Questions.
Question 1.
How is the circulatory system designed in leech to compensate the heart structure?
Answer:
There are no true blood vessels in leeches. The blood vessels are replaced by canals called haemocoelic canals. These canals are filled with haemocoelic fluid. There are four longitudinal canals. One is dorsal lying above the alimentary canal, another is ventral lying below the alimentary canal. The remaining two are lateral lying on either side of the alimentary canal. These four canals are connected together at the posterior end. There is no heart, but the lateral channels serve as a heart by being contractile. They have values inside. The dorsal and ventral channels are non-contractile having no muscular walls.
Question 2.
How does locomotion take place in leech?
Answer:
Locomotion in leech takes place by:
- Looping or Crawling movement: This type of movement is brought about, by the contraction and relaxation of muscles. The two suckers, serve for attachment, during movement on a substratum.
- Swimming movement: Leeches swim very actively and perform undulating movements in the water.
Question 3.
Explain the male reproductive system of the rabbit with a labelled diagram.
Answer:
A pair of Testes, which are ovoid in shape, are enclosed by Scrotal Sac, in the abdominal cavity. Each testis consists of numerous fine tubules called Seminiferous tubules. This network of tubules leads into a coiled tubule called Epididymis, which lead into the sperm duct called vas deferens. The vas deferens join in the urethra, just below the Urinary Bladder. The Urethra runs backwards and passes into the penis.
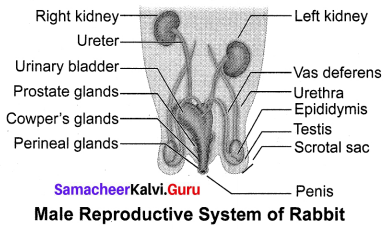
The Prostate gland, Cowper’s gland and Perineal gland are the three accessory glands, whose secretions are involved in reproduction.
VIII. Higher Order Thinking Skills (HOTS) Questions
Question 1.
Arjun is studying in tenth standard. He was down with fever and went to meet the doctor. As he went to the clinic he saw a patient undergoing treatment for severe leech bite. Being curious, Arjun asked the doctor why leech bite was not felt as soon as it attaches to the skin ? What would have been the reply given by the doctor?
Answer:
The leech makes a wound with the jaws by making a rasping movement. The blood is sucked by the muscular pharynx. The salivary secretion is poured in the wound. They inject an anaesthetic substances that prevents the host from feeling their bite. The saliva contains an active substances called hirudin which prevents the coagulation of the blood.
Question 2.
Shylesh has some pet animals at his home. He has few rabbits too, one day while feeding them he observed something different with the teeth. He asked his grandfather, why is it so? What would have been the explanation of his grandfather?
Answer:
The explanation of the grandfather would have been as follows: Teeth are hard bone – like structures, used to cut, tear and grind the food. There are incisors, canines, premolars and molars teeth are seen. Canines are absent. Something different from the teeth is the gap between incisors and premolar, which is called Diastema. It helps in mastication and chewing the food.
IX. Value-Based Questions.
Question 1.
Leeches do not have an secretion of digestive juices and enzymes -Why?
Answer:
The blood sucked by the leech is stored up in the crop. The blood gets haemolysed in the crop. Then the blood is passed drop by drop into the stomach where it is digested slowly by the peptolytic enzyme. The digested blood is absorbed slowly by the intestine.
Question 2.
How is the digestive system of rabbit suited for a herbivorous mode of feeding?
Answer:
The caecum is a thin – walled sac present at the Junction of the small intestine and large intestine. It contains bacteria, that helps in digestion of cellulose. So the digestive system of Rabbit is suited for a herbivorous mode of feeding.
Samacheer Kalvi 10th Science Structural Organisation of Animals Additional Questions Solved
I. Match the following.
Question 1.
| 1. Segmentation | (a) Hirudin |
| 2. Gregarious | (b) Vagina |
| 3. Blood clotting | (c) Metamerism |
| 4. Four chambered | (d) Move-in groups |
| 5. Oviducts | (e) Septum |
Answer:
1. (c) Metamerism
2. (d) Move-in groups
3. (a) Hirudin
4. (e) Septum
5. (b) Vagina.
II. Choose the correct pair.
Question 1.
The digestion of cellulose in rabbit takes place in:
(a) vemiform appendix
(b) colon
(c) caecum
(d) ileum
Answer:
(c) caecum
Question 2.
(a) Ureter and Dermis
(b) Clitella and Mouth
(c) Vagina and Egg case
(d) Sucker and Small intestine.
Answer:
(c) Vagina and Egg case
Question 3.
Total number of incisors teeth in rabbit is:
(a) 8
(b) 6
(c) 10
(d) 4
Answer:
(b) 6
Question 4.
(a) Mouth and Metamerism
(b) Ganglion and Colon
(c) Intestine and Integument
(d) Expiration and Inspiration.
Answer:
(d) Expiration and Inspiration
Question 5.
(a) Sweat glands and Sebaceous glands
(b) Triradiate and Thoracic
(c) Trachea and Tricuspid
(d) Seminiferous and Sansuivorous.
Answer:
(a) Sweat glands and Sebaceous glands
III. Fill in the Blanks.
Question 1.
In leech, the ______ tissue lies beneath longitudinal muscles and fills the entire colon around the gut.
Answer:
Botryoidal.
Question 2.
_____ teeth are absent in Rabbit.
Answer:
Canine.
Question 3.
Digestion in leech takes place in the stomach by the action of ______ enzyme.
Answer:
Proteolytic.
Question 4.
The anterior part of the windpipe is enlarged to form ______ or _____.
Answer:
Larynx or Voicebox.
Question 5.
The opening of the pulmonary artery and Aorta are guarded by three ________ valves.
Answer:
Semilunar.
Question 6.
The coelomic fluid contains _____.
Answer:
Haemoglobin.
Question 7.
The Jaws of Leeches are provided with _____.
Answer:
Papillae.
Question 8.
The pain of testes is enclosed by a sac called _____.
Answer:
Scrotal Sac.
Question 9.
Central Nervous System consists of _______ and _____.
Answer:
Brain, Spinal Chord.
Question 10.
Autonomous nervous system comprises _______ and _____.
Answer:
Sympathetic, Parasympathetic.
Question 11.
Each kidney is made up of several _____.
Answer:
Nephrons.
Question 12.
In Rabbits, as male and female sexes are separate, _____ is exhibited.
Answer:
Sexual dimorphism.
Question 13.
The other name for the voice box is _____ and the other name for the windpipe is _____.
Answer:
Larynx, Trachea.
Question 14.
The right and left ventricles are separated by _____.
Answer:
Inter Ventricular Septum
Question 15.
The external ear or ______ is situated at the top of the head in Rabbits.
Answer:
Pinnae.
IV. Choose the correct answer.
Question 1.
The largest portion of the Alimentary Canal in Leech is _____.
(a) Mouth
(b) Pharynx
(c) Oesophagus
(d) Crop.
Answer:
(d) Crop.
Question 2.
In Leech, the dense network of tiny blood vessels, containing Haemocoelic fluid is called _____.
(a) Artery
(b) Capillaries
(c) Vein
(d) Blood Vessel.
Answer:
(b) Capillaries
Question 3.
Body wall of Leech includes ______ layers.
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 5
(d) 4.
Answer:
(c) 5
Question 4.
In female Rabbits, these four or five structures are present on the ventral surface between the thorax and abdomen _____.
(a) Nipples or Trets
(b) Limbs
(c) Vibrissae
(d) Diaphragm.
Answer:
(a) Nipples or Trets
Question 5.
In male rabbits, this structure is found in the ventral side of Anus _____.
(a) Claws
(b) Sweat glands
(c) Penis
(d) Abdomen.
Answer:
(c) Penis
V. Read the following statements and correct them, if it is not true.
Question 1.
Dorsal surface of Leech is Orange Yellow or Red in colour.
Answer:
False.
Correct Statement: Dorsal surface of Leech is Olive green in colour.
Question 2.
The clitellum is formed on segments 9 to 11, which is meant to produce cocoon, during the breeding season.
Answer:
True.
Question 3.
The lower side of the thoracic cavity in Rabbit is the dome-shaped Sternum.
Answer:
False.
Correct Statement: The lower side of the thoracic cavity in Rabbit is the dome-shaped Diaphragm.
Question 4.
Mammary glands are the modified glands of the skin.
Answer:
True.
Question 5.
The supra pharyngeal ganglion lies below the Pharynx and is formed by the fusion of four pairs of Ganglia.
Answer:
False.
Correct Statement: The sub pharyngeal ganglion lies below the Pharynx and is formed by the fusion of four pairs of Ganglia.
VI. Find the Odd One Out.
Question 1.
Cuticle, Epidermis, Sphincters, Muscular layer.
Answer:
Sphincters.
Question 2.
Undigested food, Genital pore, Rectum, Anus.
Answer:
Genital pore.
Question 3.
Gregarious, Thorax, Abdomen, Pinnae.
Answer:
Gregarious.
Question 4.
Nephrons, Nitrogenous waste, Scrotal Sac, Urea.
Answer:
Scrotal Sac.
Question 5.
Teats or Nipples, Hairs, Claws, Nails
Answer:
Teats or Nipples.
V. Answer the following in a word or sentence.
Question 1.
Where is mouth located in Leech?
Answer:
The mouth is located in the middle of the Anterior Sucker.
Question 2.
List out the structures derived from the skin of rabbit.
Answer:
The structures derived from the skin of rabbit are hair, claws, nails and glands like sweat glands, sebaceous glands and mammary glands.
Question 3.
What is Epiglottis?
Answer:
Epiglottis is a flap, in the neck, which prevents the entry of food into the trachea through the glottis.
Question 4.
The excretory system of rabbit is called a urinogenital system?
Answer:
The Urinogenital system of rabbit comprises the urinary system and genital or reproductive system. So they are called urinogenital system.
Question 5.
Where are Annular and Segmental receptors located?
Answer:
Annular receptors are located in each annulus and Segmental receptors are located on the first annulus of each segment.
Question 6.
What are Vibrissae?
Answer:
In Rabbit, from each side of upper lip tactile hairs or Whiskers present, which are called Vibrissae.
Question 7.
What is the scientific name of rabbit?
Answer:
The scientific name of rabbit is Oryctolagus cuniculus.
Question 8.
Which glands regulate the body temperature of Rabbits?
Answer:
The Sweat glands and Sebaceous glands embedded in the skin regulate the body temperature of Rabbits.
VI. Answer Briefly.
Question 1.
Explain the Excretory System of Leech briefly.
Answer:
In Leech, excretion takes place by segmentally arranged paired tubules called Nephridia. There are 17 pairs of Nephridia, which open out by nephridiopores from 6th to 22nd segments.
Question 2.
Explain the types of coelom in leech.
Answer:
Leech contains special longitudinal canals called haemocoelic canals filled with a blood like fluid called haemocolic fluid. This type of coelom is called Haemocoel.
Question 3.
What are Receptors? Write a short note on Receptors.
Answer:
Sensory projections are called Receptors on the dorsal side, there are five pairs of eyes on the first five segments. Annular receptors are located in each Annulus and segmental receptors are located on the first annulus of each segment.
Question 4.
What is hermaphrodite?
Answer:
If the male and female reproductive organs are present in the same animals, ‘ then the organism is said to hermaphrodite.
Question 5.
Name three accessory glands, which involve in the male reproductive system of Rabbit.
Answer:
- Prostate gland
- Cowper’s gland
- Perineal gland.
Their secretion involved in Reproduction.
Question 6.
Name the following:
(a) Three membranes, which cover the Brain in Rabbit
(b) Division of brain
Answer:
(a) Three membranes, which cover the Brain in Rabbit
- Dura mater
- Inner Piameter
- Arachnoid membrane.
(b) Division of brain
- Forebrain (Prosencephalon)
- Midbrain (Mesencephalon)
- Hindbrain (Rhombencephalon).
Question 7.
Write a note on Medicinal value of Leech.
Answer:
- Leeches breaks up blood clots.
- Increases blood circulation
- Leeches are used to treat cardio vascular diseases.
- Saliva of leeches are used in the preparation of drugs that can treat hypertension.
Question 8.
With the Tabular Column, mention the Divisions of the body of Leech.
Answer:
| Region | Segments |
| Cephalic region | 1st – 5th |
| Pre-clitellar region | 6th, 7th and 8th |
| Clitellar region | 9th, 10th and 11th |
| Middle region | 12th – 22nd |
| Caudal region | 23rd – 26th |
| Posterior sucker | 27th – 33rd |
Question 9.
Explain the hermaphrodite structure of leech.
Answer:
Leech is hermaphrodite because it contain both male and female genital organ in same animal.
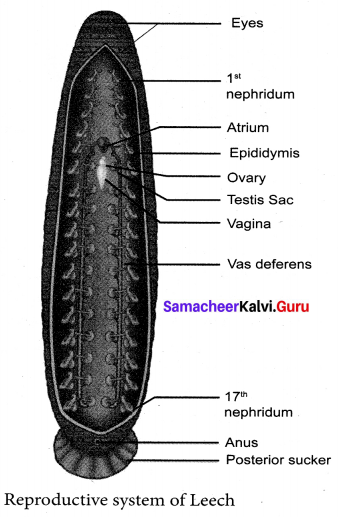
Male Reproductive system: It is formed of: (i) Testes, (ii) Vas efferens, (Hi) Epididymis, (iv) Ejaculatory ducts and atrium.
There are eleven pairs of testes, one pair in each segment from 12 to 22 segments. They are in the form of spherical sacs called testes sacs. From each testes arises a short duct called vas efferens, which join with the vas deferens. The vas deferens becomes convoluted to form the epididymis or sperm vesicle, to store spermatozoa.
The epididymis leads to a short duct called ejaculatory duct. The ejaculatory ducts on both sides join to form the genital atrium. The atrium consists of two regions, the coiled prostate glands and the penial sac consisting of penis that opens through the male genital pore.
Female Reproductive system : It consists of ovaries, oviducts and vagina. There is a single pair of ovary in the 11th segment on the ventral side. Each ovary is a coiled ribbon-shaped structure. The ova are budded off from the ovary. From each ovary runs a short oviduct. The oviducts of the two sides joins together, to form a common oviduct. The common oviduct opens into a pear-shaped vagina which lies mid-ventrally in the posterior part of the 11th segment.
VIII. Label the following diagrams.
Question 1.
Draw and label the female Reproductive System of Rabbit.
Answer:
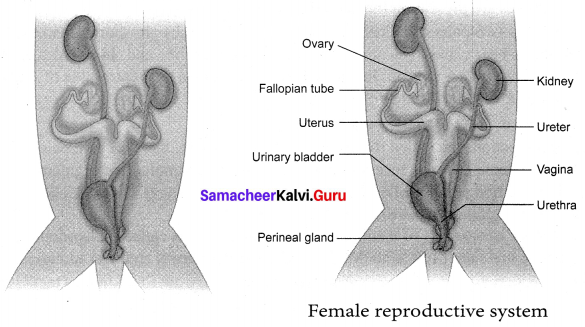
Question 2.
Draw and label the Digestive System of Leech.
Answer:
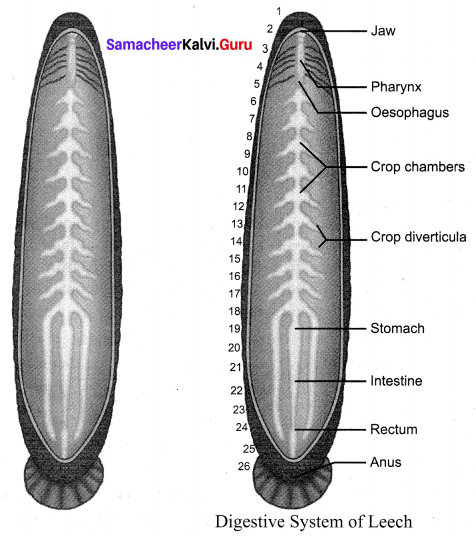
Question 3.
Draw and label the Brain of the rabbit.
Answer:
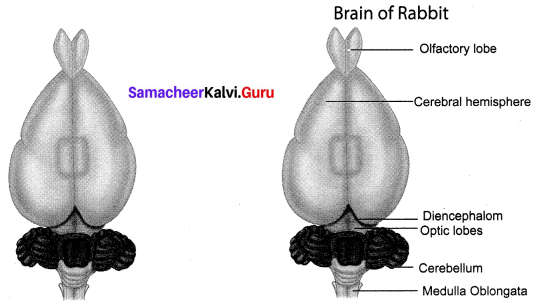
Question 4.
Draw and label the Lung of Rabbit.
Answer:
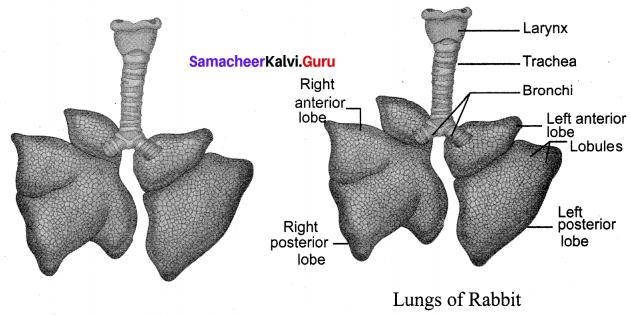
IX. Answer the following in Detail.
Question 1.
Explain the Digestive System of Rabbit with a neat labelled diagram.
Answer:
Teeth are hard, bone – like structures used to cut, tear and grind the food materials. The digestive system includes the Alimentary canal and the associated digestive glands. The alimentary canal consists of a mouth, buccal cavity, pharynx, oesophagus, stomach, small intestine and anus. The mouth is a transverse slit, bounded by upper and lower lips.
It leads to a buccal cavity muscular tongue is at the floor of the buccal cavity. Jaws bear teeth. Buccal cavity leads into Oesophagus. Oesophagus opens into the stomach followed by the small intestine. The thin-walled Sac, called Caecum, present at the Junction of the small intestine and large intestine, contains bacteria, which helps in digestion of cellulose.
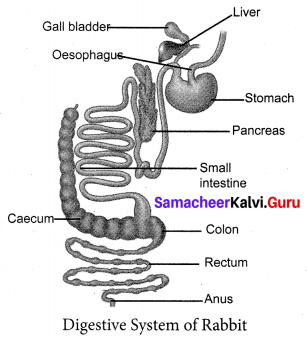
The digestive glands such as salivary glands, gastric glands, Liver, Pancreas and intestinal glands secrete digestive juices, which help in the digestion of food in the Alimentary canal. After digestion, from the small intestine, the undigested food and wastes enter into the large intestine, which has colon and rectum. The rectum opens outside by the Anus.
Question 2.
Explain the male and the female Reproductive system of Leech with a neat labelled diagram.
Answer:
Leech is hermaphrodite, both the male and female reproductive organs are present in the same.
Male Reproductive system: There are eleven pairs of testes, one pair in each segment from 12 to 22 segments. They are in the form of Spherical Sacs called testes sacs. From each testis arises a short duct called Vas efferents, which join with the Vas deferens.
The Vas deferens becomes convoluted to form the epididymis or sperm vesicle, to store spermatozoa. The epididymis leads to a short duct called the ejaculatory duct. The ejaculatory duct on both sides joins to form Genital Atrium. The Atrium consists of prostate glands and the Penial sac, with Penis, that opens through the genital pore.
Female Reproductive system: It consists of Ovaries, Oviducts and Vagina. Each ovary is coiled, ribbon-shaped, and the single pair of the ovary is in the 11th segment. The Ova are budded off from the ovary. From each ovary runs a short oviduct, and the oviducts of two sides join together, to form a common Oviduct, which opens into a pear-shaped Vagina. Vagina lies mid ventrally in the posterior part of 11th segment.
Internal fertilisation takes place. This is followed by cocoon formation. The cocoon or egg case is formed around 9th, 10th and 11th segments. Development directs, proceeds in a cocoon, which contain one to 24 embryos. The emerging young leech resembles the adult Leech.
Question 3.
Explain the Circulatory system of Rabbit with a neat labelled diagram of a Heart.
(i) Observe the external morphology of leech specimen in your biology laboratory.
(ii) Can you find leeches in your locality?
(iii) In which geographical areas are leeches found more predominantly in India?
Answer:
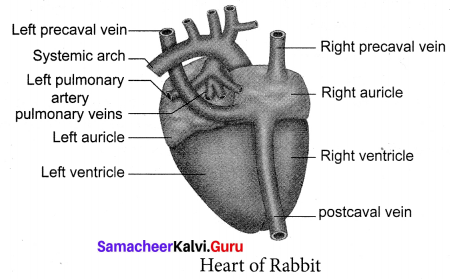
The Circulatory system consists of blood, blood vessels and Heart. The Heart is pear-shaped, lies in between the lungs, in the thoracic cavity. The heart is covered by a double-layered Pericardium. The Heart is four-chambered, with two Auricles and two ventricles. The right and the left ventricles are separated by inter auricular septum. The right and the left ventricles are separated by the interventricular septum. The right auricle opens into the right ventricle, by right Auriculoventricular aperture, guarded by a tricuspid valve. The left auricle opens into the left ventricle by left Auriculoventricular aperture, guarded by a bicuspid valve or Mitral valve. The opening of the Pulmonary Artery and Aorta are guarded by three semilunar valves.
The right Auricle receives deoxygenated blood through two Precaval (superior vena cava) and one postcaval (Inferior vena cava) veins from all parts of the body. The left auricle receives oxygenated blood from the pulmonary veins from the lungs.
From the right ventricle arises Pulmonary trunk, which carries the deoxygenated blood to the lungs and from the left ventricle arises the systemic arch (aorta) which supplies Oxygenated blood to all parts of the body.
(i) Observe the external morphology of Leech in the preserved bottle specimens in the Biology Laboratory.
(ii) No, Not in our areas. The Leeches are common in hilly areas
(iii) Most Leech species are found in shallow, slow-moving freshwater and moist soil on land.
IX. Higher Order Thinking Skills (HOTS) Questions
Question 1.
How were Leeches used in Ancient times?
Answer:
Leeches were used in medicines from Ancient times. Until the 19th century, Leeches were used to draw blood from patients.
Question 2.
How are Leeches used in modern times?
Answer:
In modem times, Leeches find medical use in the treatment of Joint diseases such as Epicondylitis and Osteoarthritis, Extremity vein diseases and Microsurgery. Hirudin is a valuable dmg for some blood clotting disorders. There are doctors who will use Leeches to treat muscle cramps.
Question 3.
What is the benefit of Rabbit?
Answer:
Rabbit meat is white meat of high quality, easily digestible with low fat, low cholesterol and high protein compared to most other meats. It is an excellent source of vitamins B3 and B12, minerals, and trace elements (Phosphorus, Potassium and Selenium) Rabbit meat is an excellent balance of fatty acids, Omega 3 than chicken or pork.
Hope you liked the article on Tamilnadu State Board Solutions of Class 10 Science Solutions Chapter 13 Structural Organisation of Animals Questions and Answer and share it among your friends to make them aware. Keep in touch to avail latest information regarding different state board solutions instantly.