Students can Download Accountancy Chapter 12 Final Accounts of Sole Proprietors – I Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 11th Accountancy Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 11th Accountancy Solutions Chapter 12 Final Accounts of Sole Proprietors – I
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Accountancy Final Accounts of Sole Proprietors – I Text Book Back Questions and Answers
I. Multiple Choice Questions
Choose the Correct Answer
Question 1.
Closing stock is an item of ……………..
(a) Fixed asset
(b) Current asset
(c) Fictitious asset
(d) Intangible asset
Answer:
(b) Current asset
Question 2.
Balance sheet is ……………..
(a) An account
(b) A statement
(c) Neither a statement nor an account
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(b) A statement
Question 3.
Net profit of the business increases the ……………..
(a) Drawings
(b) Receivables
(c) Debts
(d) Capital
Answer:
(d) Capital
![]()
Question 4.
Carriage inwards will be shown ……………..
(a) In the trading account
(b) In the profit and loss account
(c) On the liabilities side
(d) On the assets side
Answer:
(a) In the trading account
Question 5.
Bank overdraft should be shown ……………..
(a) In the trading account
(b) Profit and loss account
(c) On the liabilities side
(d) On the assets side
Answer:
(c) On the liabilities side
Question 6.
Balance sheet shows the …………….. of the business.
(a) Profitability
(b) Financial position
(c) Sales
(d) Purchases
Answer:
(b) Financial position
Question 7.
Drawings appearing in the trial balance is ……………..
(a) Added to the purchases
(b) Subtracted from the purchases
(c) Added to the capital
(d) Subtracted from the capital
Answer:
(d) Subtracted from the capital
Question 8.
Salaries appearing ill the trial balance is shown on the ……………..
(a) Debit side of trading account
(b) Debit side of profit and loss account
(c) Liabilities side of the balance sheet
(d) Assets side of the balance sheet
Answer:
(b) Debit side of profit and loss account
![]()
Question 9.
Current assets does not include ……………..
(a) Cash
(b) Stock
(c) Furniture
(d) Prepaid expenses
Answer:
(c) Furniture
Question 10.
Goodwill is classified as ……………..
(a) A current asset
(b) A liquid asset
(c) A tangible asset
(d) An intangible asset
Answer:
(d) An intangible asset
II. Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Write a note on the trading account.
Answer:
- Trading refers to buying and selling of goods with the intention of making a profit.
- A trading account is a nominal account which shows the result of buying and selling goods for an accounting period.
- It is prepared to find out the difference between the revenue from sales and the cost of goods sold.
Question 2.
What are wasting assets?
Answer:
These are the assets which get exhausted gradually in the process of excavation. Examples: mines and quarry.
Question 3.
What are fixed assets?
Answer:
- Fixed assets are those assets which are acquired or constructed for continued use in the business and last for many years such as land and building, plant and machinery, motor vehicles, furniture, etc.
- It is classified into a. Tangible Assets and b. Intangible Assets.
![]()
Question 4.
What is meant by purchase returns?
Answer:
Goods purchased which are returned to suppliers are termed as purchases return or return outward.
Question 5.
Name any two direct expenses and indirect expenses.
Answer:
- Direct Expenses: Carriage inwards, Wages, Import Duty, and Royalty
- Indirect Expenses: Office Expenses, Selling Expenses, Administrative Expenses
Question 6.
Mention any two differences between trial balance and balance sheet.
Answer:
| S.No. | Basis | Trial Balance | Balance Sheet |
| 1. | Nature | Trial balance is a list of ledger balances on a particular date. | The balance sheet is a statement showing the position of assets and liabilities on a particular date. |
| 2. | Purpose | Trial balance is prepared to check the arithmetical accuracy of the accounting entries made. | The balance sheet is prepared to ascertain the financial position of a business. |
Question 7.
What are the objectives of preparing a trading account?
Answer:
- The trading account provides information about gross profit and gross loss.
- It provides an opportunity to safeguard against possible losses.
- It provides information about direct expenses and direct incomes.
Question 8.
What is the need for preparing a profit and loss account?
Answer:
- Ascertainment of net profit or net loss
- Comparison of profit
- Control on expenses
- Helpful in the preparation of the balance sheet.
III. Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What are final accounts? What are its constituents?
Answer:
- The business entities are interested in knowing periodically the results of business operations carried on and the financial soundness of the business.
- In other words, they want to know the profitability and the financial position of the business.
- These can be ascertained by preparing the final accounts or financial statements.
- The final accounts are usually prepared at the end of the accounting period on the basis of balances of ledger accounts shown by the trial balance.
The final accounts or financial statements include the following:
- Income Statement or Trading and Profit and Loss Account and
- Position Statement or Balance Sheet.
The purposes of preparing the financial statements are:
- To ascertain the financial performance of an enterprise and
- To ascertain the financial position of an enterprise.
- The income statement and balance sheet are prepared for these purposes respectively.
- An income statement gives the manner in which the profit or loss for an accounting period is arrived at.
- Hence, at the close of the accounting period, all nominal accounts (i.e. expenses, losses, revenues, gains, purchases, purchases returns, sales, and sales returns) are to be closed by transferring to the income statement or trading and profit and loss account.
![]()
Question 2.
What is meant by closing entries? Why are they passed?
Answer:
Balances of all the nominal accounts are required to be closed on the last day of the accounting year to facilitate the preparation of trading and profit and loss accounts. It is done by passing necessary closing entries in the journal properly. Purchases have debit balance and purchases returns have credit balance. At the end of the accounting year, the balance in the purchases returns account is closed by transferring to the purchase account.
Question 3.
What is meant by gross profit and net profit?
Answer:
- If the amount of sales exceeds the cost of goods sold, the difference is gross profit.
Sales – Cost of goods sold = Gross profit. - If the total of the credit side of the profit and loss account exceeds the debit side, the difference is termed as net profit.
Question 4.
“Balance sheet is not an account” – Explain.
Answer:
- A balance sheet is a part of the final accounts. However, the balance sheet is a statement and not an account. It has no debt or credit sides and as such the words ‘To’ and ‘By’ are not used before the names of the accounts shown therein.
- A balance sheet is a summary of the personal and real accounts, which have balances. Personal and real accounts having debit balances are shown on the right-hand side known as the assets side, whereas personal and real accounts having credit balances are shown on the left-hand side known as the liabilities side.
- The totals of the two sides of the balance sheet must be equal. If the totals are not equal, it indicates the existence of the error. It must satisfy the accounting equation, i.e., Assets = Capital + Liabilities, following the dual aspect concept.
- The balance sheet is prepared on a particular date and not for a fixed period. It discloses the financial position of a business on a particular date. It gives the balances only for the date on which it is prepared.
- It shows the financial position of the business according to the going concern concept.
Question 5.
What are the advantages of preparing a balance sheet?
Answer:
The balance sheet discloses the financial position of a business on a particular date, it gives the balances only for the date on which it is prepared. It shows the financial position of the business according to the going concern concept.
![]()
Question 6.
What is meant by grouping and marshaling assets and liabilities?
Answer:
- The assets and liabilities shown in the balance sheet are grouped and presented in a particular order.
- The term ‘grouping’ means showing the items of similar nature under a common heading.
- For example, the amount due from various customers will be shown under the head ‘Sundry debtors/ Similarly, under the head ‘Current assets’, the balance of cash, bank, debtors, stock, and other current assets will be shown.
- ‘Marshalling’ is the arrangement of various assets and liabilities in proper order.
- Marshaling can be made in one of the following two ways:
a) In the order of liquidity:
- According to this method, an asset which is most easily convertible into cash, i.e., cash in hand is shown first and then will follow those assets which are comparatively less easily convertible, So that the least liquid asset i.e., goodwill is shown last.
- In the same way, the liabilities which are to be paid at the earliest will be shown first. In other words, current liabilities are shown first, then fixed or long-term liabilities, and finally the proprietor’s capital.
b) In the order of permanence:
- This method is exactly the reverse of the first method.
- An asset which is more permanent, i.e., goodwill is shown first followed by assets which are less permanent. Similarly, those liabilities which are to be paid last will be shown first.
- In other words, the proprietor’s capital is shown first, then fixed or long-term liabilities, and lastly the current liabilities. Joint-stock companies are required under the Companies Act to prepare their balance sheet in the order of permanence.
IV. Exercises
Question 1.
Prepare trading account in the books of Sivashankar from the following figures:
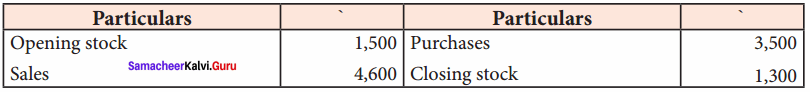
Answer:
Trading account of Sivashankar
Question 2.
Prepare trading account in the books of Mr. Sanj ay for the year ended 31st December 2017:
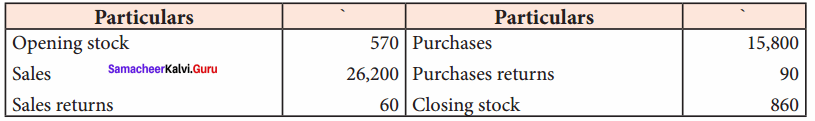
Answer:
Trading account of Mr. Sanjay for the year ended 31st December 2017
Question 3.
Prepare trading account in the books of Mr. Sanj ay for the year ended 31st December 2017:
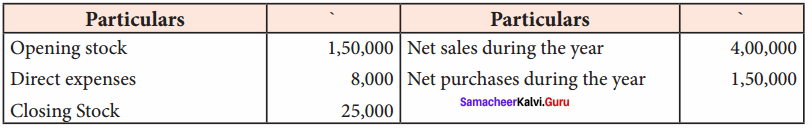
Answer:
Trading account of Saravanan for the year ended 31st December, 2017
Question 4.
From the following details for the year ended 31st March 2018, prepare a trading account
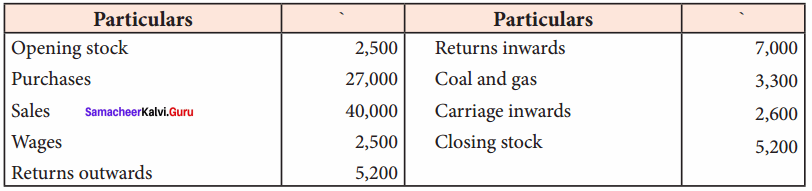
Answer:
Trading account for the year ended 31st March 2018
Question 5.
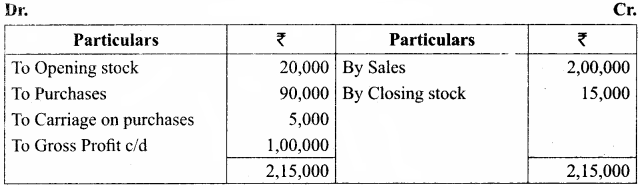
Ascertain gross profit or gross loss from the following:
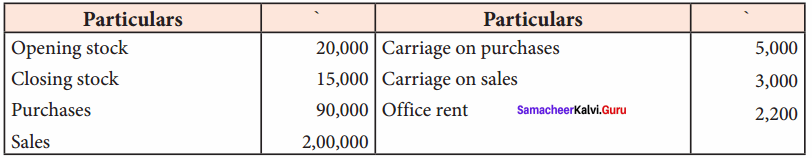
Answer:
Profit and Loss Account
Question 6.
From the following balances taken from the books of Victor, prepare a trading account for the year ended December 31, 2017:
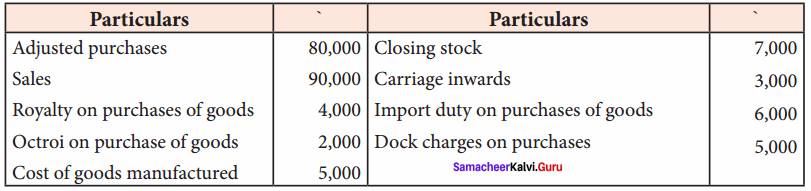
Answer:
Trading Account of Victor for the year ended 31st December, 2017
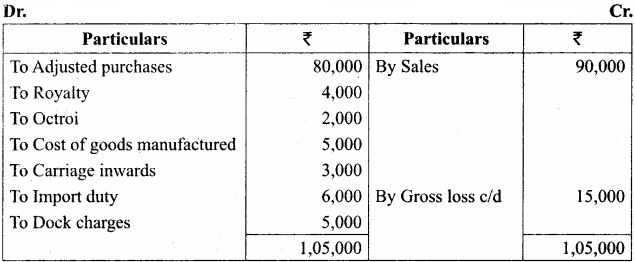
Hint: Closing stock will not appear in the trading account because adjusted purchases have been given.
Question 7.
Compute the cost of goods sold from the following information:
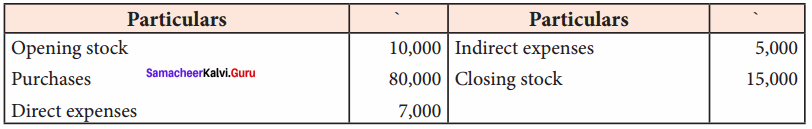
Answer:
Cost of goods sold = Opening stock + Net purchases + Direct expenses – Closing stock
= 10,000 + 80,000 + 7,000 – 15,000
= ₹ 82,000
Note: Indirect expenses do not form part of the cost of goods sold.
Question 8.
Find out the number of sales from the following information:
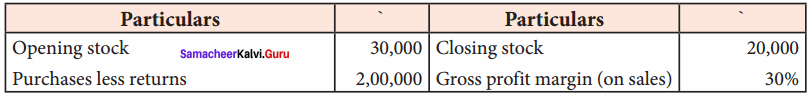
Answer:
Cost of goods sold = Opening stock + Net purchases + Direct expenses – Closing stock
= 30,000 + 2,00,000 + 0 – 20,000
= ₹ 2,10,000

Therefore, percentage of gross profit on cost of goods sold is
\(\frac { 30 }{ 70 }\) x 100 = 42.85% (42.857142 ……….)
Gross profit = 42.85% on 2,10,000 i.e., \(\frac { 42.85 }{ 100 }\) x 2,10,000 = ₹ 90,000
Sales = Cost of goods sold + Gross Profit
= 2,10,000 + 90,000 (Fractions to be rounded)
= ₹ 3,00,000
Question 9.
Prepare profit and loss account in the books of Kirubavathi for the year ended 31st December 2016 from the following information:
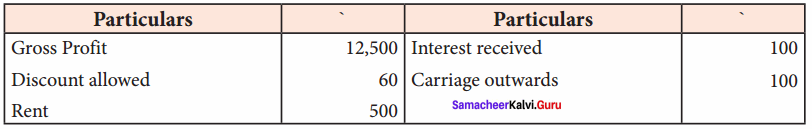
Answer:
Profit and loss account of Kirubavathi for the year ended 31st Dec 2016
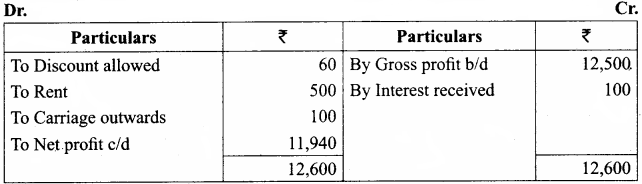
Question 10.
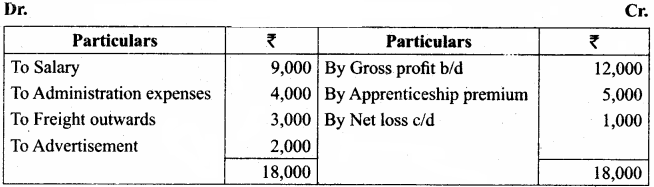
Ascertain net profit or net loss from the following:
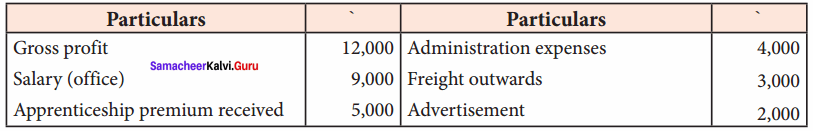
Answer:
Profit and loss account
Question 11.
From the following details, prepare a profit and loss account.
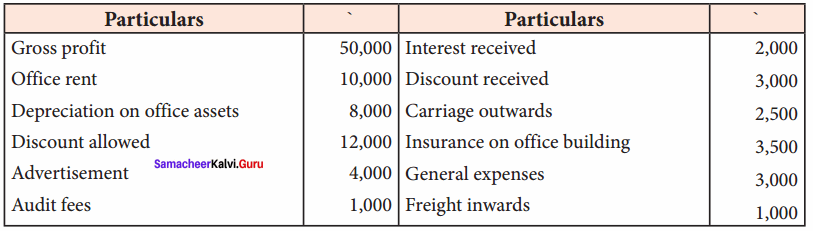
Answer:
Profit and loss account
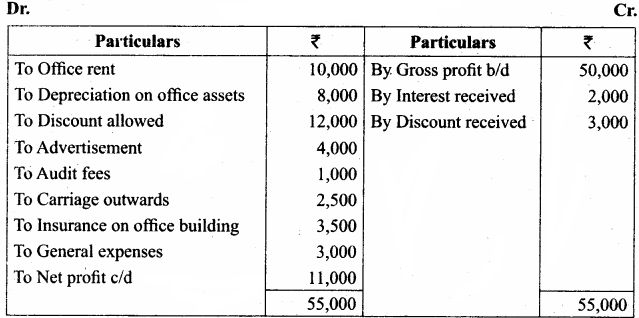
(Hint: Freight inwards will not appear in profit and loss account as it is a direct expense)
Question 12.
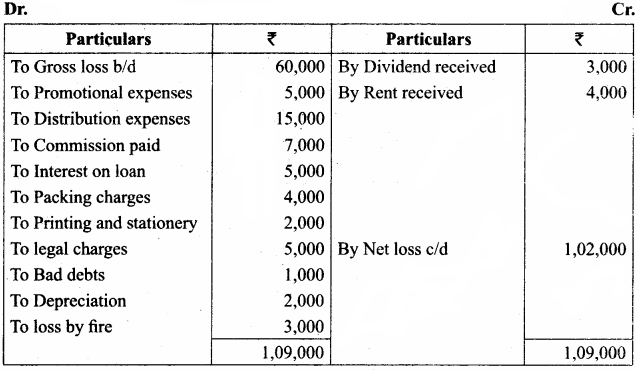
From the following information, prepare profit and loss accounts for the year ending 31st December 2016.
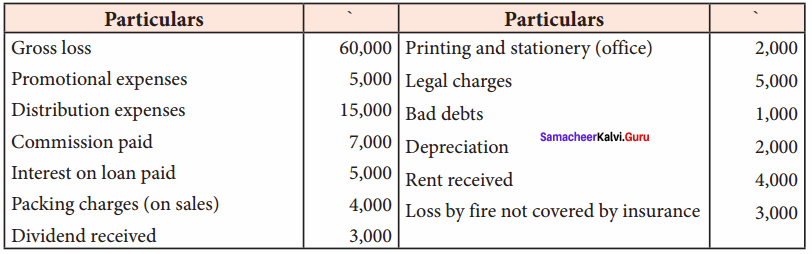
Answer:
Profit and loss account for the year ended 31st December 2016
Question 13.
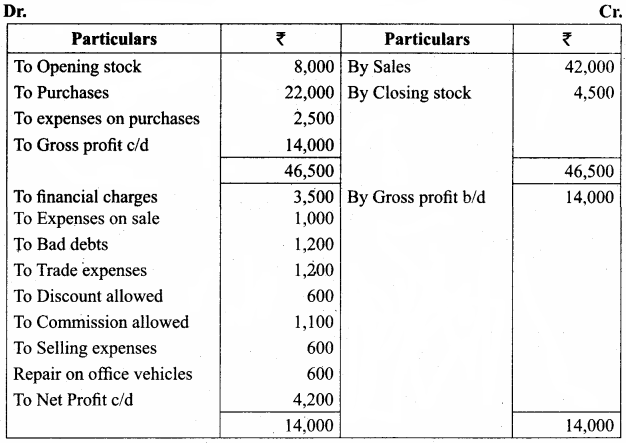
From the following balances obtained from the books of Mr. Ganesh, prepare trading and profit and loss account:
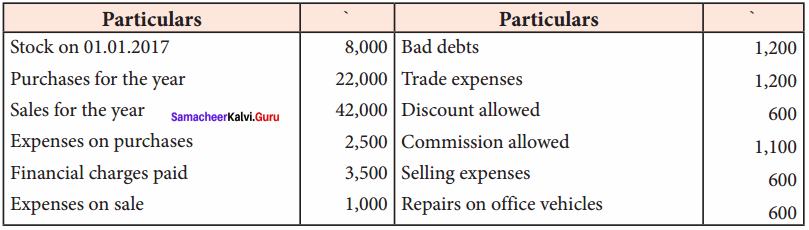
Answer:
Trading and Profit & loss account of Mr. Ganesh
Question 14.
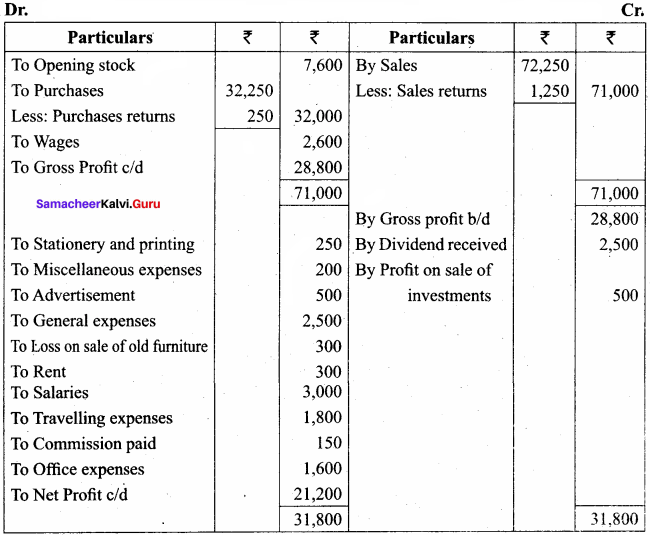
From the following balances extracted from the books of a trader, ascertain gross profit and net profit for the year ended March 31, 2017:
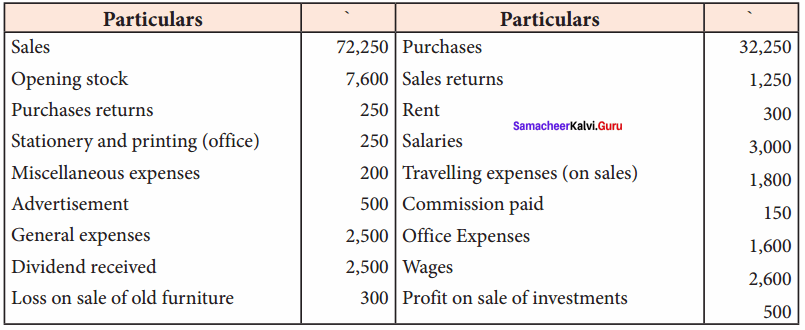
Answer:
Trading and Profit & Loss account for the year ended 31st March 2017
Question 15.
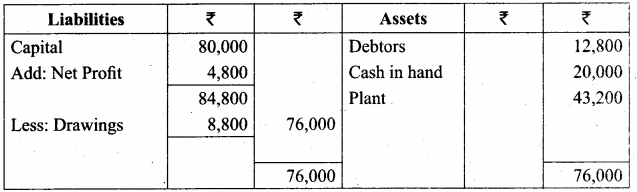
From the following particulars, prepare a balance sheet in the books of Bragathish as of 31st December 2017:
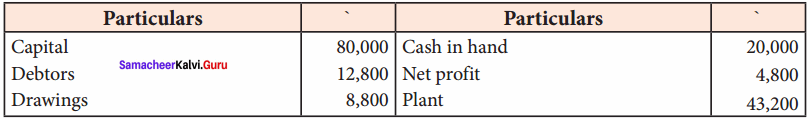
Answer:
Balance Sheet of Bragathish as of 31st December 2017
Question 16.
Prepare trading and profit and loss account in the books of Ramasundari for the year ended 31st December, 2017 and balance sheet as of that date from the following information:
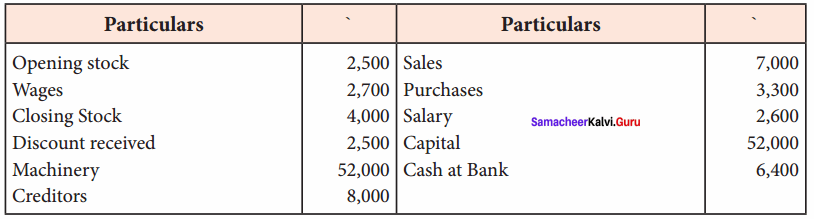
Answer:
Trading and Profit & Loss a/c of Ramasundari for the year ended 31 Dec 2017 Cr.
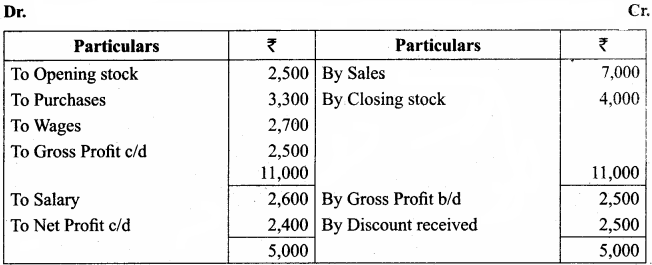
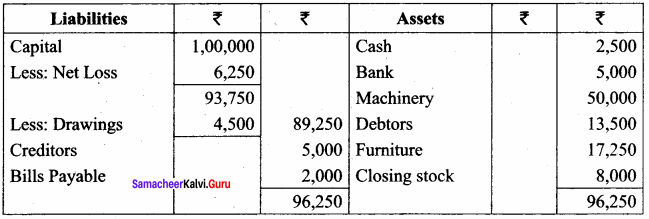
Balance Sheet of Ramasundari as of 31st March 2018
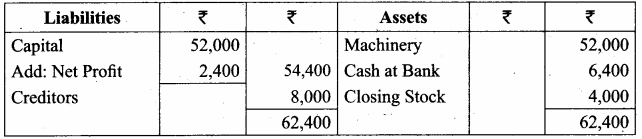
Question 17.
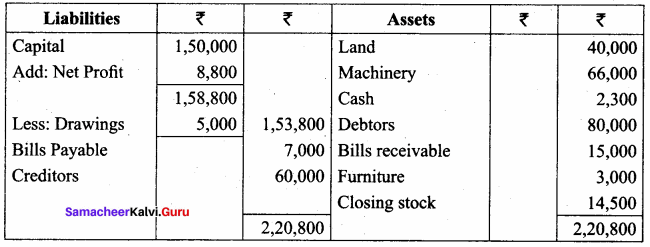
From the Trial balance, given by Saif, prepare final accounts for the year ended 31st March 2018 in his books:
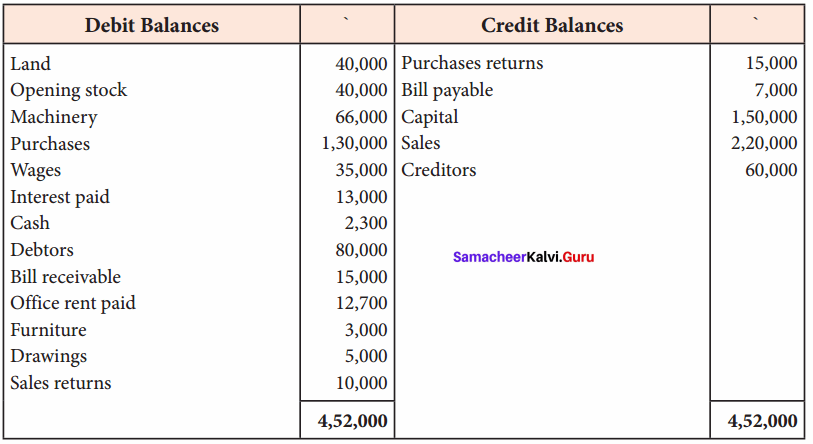
Answer:
Trading and Profit & Loss a/c of Saif for the year ended 31 March 2018
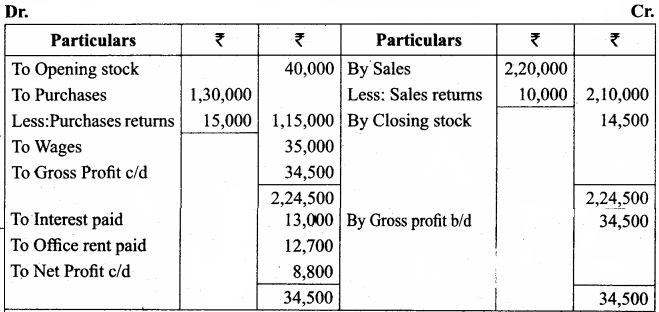
Balance Sheet of Saif as of 31st March 2018
Question 18.
Prepare trading and profit and loss account and balance sheet in the books of Deri, a trader, from the following balances as of March 31, 2018.
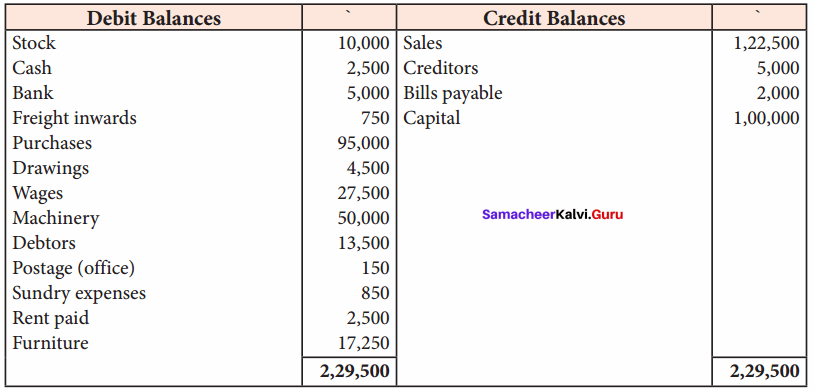
Answer:
Trading and Profit & Loss a/c of Deri for the year ended 31st March 2018
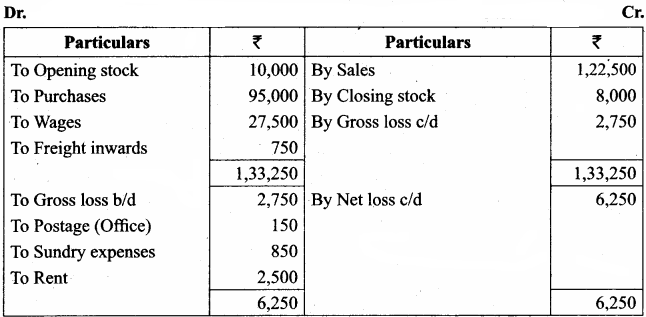
Balance Sheet of Deri as of 31st March 2018
Textbook Case Study Solved
Question 1.
Mr. Abhinav started a small shop selling dairy products. He wanted to maintain proper books of accounts. But, he had very little knowledge of accounting. He maintained only three books – purchases, sales, and cash book by himself. He bought some dairy products and a refrigerator to store the milk products for which the payment was made by cheque but recorded the same in the purchases book. He also spent for the transportation charges and paid some money to the person who unloaded the stock. He recorded the same in the cash book.
He made both cash and credit sale for the next few weeks. He entered the entire sales in the sales book. In the middle of the month, he was in need of some money for his personal use. So he took some money but did not record in the books.
Now, discuss the following points:
Question 1.
Do you think Mr. Abhinav needs an accountant? Why do you think so?
Answer:
Yes, Mr. Abhinav needs an accountant because he records all cash and credit transactions.
Question 2.
Does he maintain enough books of accounts?
Answer:
Yes, he maintains enough books of accounts.
![]()
Question 3.
What other books do you think that he needs to maintain?
Answer:
He needs to maintain a petty cashbook.
Question 4.
What will be the impact on the profit, if he records the purchase of the refrigerator in the purchases book?
Answer:
The purchase book will be overcast because this transaction will be recorded in the proper journal.
Question 5.
Is it important to record the money taken for personal use? Will it affect the final accounts?
Answer:
Yes, then only the actual profit or loss can be found out in the business.
Question 6.
Identify some of the accounting principles relevant to this situation.
Answer:
Some of the accounting principles relevant to this situation are matching principles, business entity concept, money measurement concept, dual output concept, periodicity concept, and going concern concept.
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Accountancy Final Accounts of Sole Proprietors – I Additional Questions and Answers
I. Multiple Choice Questions
Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
Carriage outwards will be shown ________.
a) In the trading account
b) In the profit and loss account
c) On the liabilities side
d) On the assets side
Answer:
b) In the profit and loss account
Question 2.
The first part of the income statement is ………………..
(a) Final account
(b) Trading account
(c) Profit and Loss account
(d) Balance Sheet
Answer:
(b) Trading account
![]()
Question 3.
___________ account enables the trader to find out gross profit or loss.
a) Trading Account
b) Profit and loss Account
c) Balance sheet
d) Trial balance
Answer:
a) Trading Account
Question 4.
Trading account is a ……………….. account.
(a) Personal
(b) Nominal
(c) Real
(d) Representative personal
Answer:
(b) Nominal
Question 5.
Fixed assets does not include ________.
a) Plant
b) Stock
c) Furniture
d) Computer
Answer:
c) Furniture
Question 6.
……………….. account is the second part of the income statement.
(a) Trading
(b) Profit and Loss
(c) Balance sheet
(d) Final
Answer:
(b) Profit and Loss
Question 7.
All incomes are ________ in the profit and loss account.
a) Debited
b) Credited
c) Assets
d) Liabilities
Answer:
b) Credited
![]()
Question 8.
Balances of all the personal and real account are shown in ………………..
(a) Trading account
(b) Profit and loss account
(c) Income statement
(d) Balance sheet
Answer:
(d) Balance sheet
Question 9.
Wages is an example of ________.
a) Capital expenses
b) Indirect expenses
c) Direct expenses
d) Revenue expenses
Answer:
c) Direct expenses
Question 10.
……………….. is a summary of the personal and real accounts.
(a) Balance sheet
(b) Final account
(c) Trading account
(d) Profit and loss account
Answer:
(a) Balance sheet
Question 11.
________ refers to buying and selling of goods with the intention of making a profit.
a) Trading
b) Trial balance
c) Profit and loss account
d) Balance sheet
Answer:
a) Trading
Question 12.
Marshaling can be made in one of the ……………….. ways.
(a) three
(b) two
(c) four
(d) five
Answer:
(b) two
Question 13.
________ is the arrangement of various assets and liabilities in proper order.
a) Marshalling
b) Grouping
c) Recording
d) Packing
Answer:
a) Marshalling
Question 14.
……………….. liabilities are not shown in the balance sheet.
(a) Contingent
(b) Current
(c) Liquid
(d) Fixed
Answer:
(a) Contingent