Students can Download Accountancy Chapter 7 Subsidiary Books – II Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 11th Accountancy Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 11th Accountancy Solutions Chapter 7 Subsidiary Books – II
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Accountancy Subsidiary Books – II Text Book Back Questions and Answers
I. Multiple Choice Questions
Choose the Correct Answer
11th Accountancy Chapter 7 Book Back Answers Question 1.
Cash book is a ………………
(a) Subsidiary book
(b) Principal book
(c) Journal proper
(d) Both subsidiary book and principal book
Answer:
(d) Both subsidiary book and principal book
Subsidiary Books Questions And Answers Pdf Question 2.
The cash book records ………………
(a) All cash receipts
(b) All cash payments
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) All credit transactions
Answer:
(c) Both (a) and (b)
Samacheer Kalvi Guru 11th Accountancy Question 3.
When a firm maintains a simple cash book, it need not maintain ………………
(a) Sales account in the ledger
(b) Purchases account in the ledger
(c) Capital account in the ledger
(d) Cash account in the ledger
Answer:
(d) Cash account in the ledger
11th Accountancy Book Back Answers Question 4.
A cash book with discount, cash and bank column is called ………………
(a) Simple cash book
(b) Double column cash book
(c) Three column cash book
(d) Petty cash book
Answer:
(c) Three column cash book
11th Accountancy – Book Back Answers Question 5.
In Triple column cash book, the balance of bank overdraft brought forward will appear in ………………
(a) Cash column debit side
(b) Cash column credit side
(c) Bank column debit side
(d) Bank column credit side
Answer:
(d) Bank column credit side
Accounting 11 Chapter 7 Answer Key Question 6.
Which of the following is recorded as contra entry?
(a) Withdrew cash from bank for personal use
(b) Withdrew cash from bank for office use
(c) Direct payment by the customer in the bank account of the business
(d) When bank charges interest
Answer:
(b) Withdrew cash from bank for office use
Accounting Chapter 7 Answer Key Question 7.
If the debit and credit aspects of a transaction are recorded in the cash book, it is ………………
(a) Contra entry
(b) Compound entry
(c) Single entry
(d) Simple entry
Answer:
(a) Contra entry
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Accountancy Chapter 6 Question 8.
The balance in the petty cash book is ………………
(a) An expense
(b) A profit
(c) An asset
(d) A liability
Answer:
(c) An asset
11th Accountancy Book Answers Question 9.
Petty cash may be used to pay ………………
(a) The expenses relating to postage and conveyance
(b) Salary to the Manager
(c) Purchase of furniture and fixtures
(d) Purchase of raw materials
Answer:
(a) The expenses relating to postage and conveyance
Class 11 Accountancy Chapter 7 Solutions Question 10.
Small payments are recorded in a book called ………………
(a) Cash book
(b) Purchase book
(c) Bills payable book
(d) Petty cash book
Answer:
(d) Petty cash book
II. Very Short Answer Questions
Accountancy Class 11 Chapter 7 Solutions Question 1.
What is a cash book?
Answer:
The book in which only cash transactions are recorded in chronological order is known as the cash book. Cash receipts are recorded on the debit side and Cash payments are recorded on the credit side. It is like a subsidiary book and a principal book.
Accountancy Class 11 Subsidiary Books Solutions Question 2.
What are the different types of cash books?
Answer:
The main cash book may be of various types and the following are the three most common types.
- Simple or single column cash book (only cash column)
- Cashbook with cash and discount column (double column cash book)
- Cashbook with cash, discount, and bank columns (three column cash book)
Class 11 Accounts Subsidiary Books Solutions Question 3.
What is a simple cash book?
Answer:
- Single column cash book or simple cash book, like a ledger account, has only one amount column, i.e., cash column on each side.
- Only cash transactions are recorded in this book.
- All cash receipts and payments are recorded systematically in this book.
Chapter 7 Accountancy Class 11 Question 4.
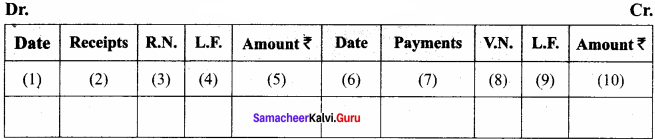
Give the format of ‘Single column cash book’.
Answer:
Simple Cash Book
Samacheer Kalvi Guru 11 Accountancy Question 5.
What is a double column cash book?
Answer:
- It is a cash book with cash and discount columns.
- As there are two columns, i.e., discount and cash columns, both on debit and credit sides, this cash book is known as ‘double column cash book’.
- The discount column represents the discount allowed on the debit side and the discount received on the credit side.
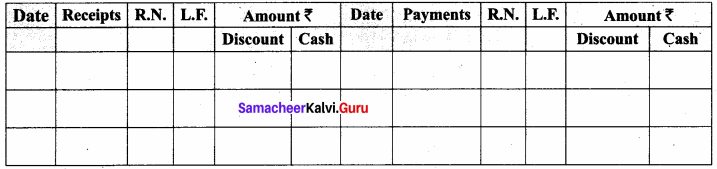
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Accountancy Book Question 6.
Give the format of ‘Double column cash book’.
Answer:
Cashbook with cash and discount columns
Samacheer Kalvi.Guru 11th Accountancy Question 7.
What is three column cash book?
Answer:
- A three-column cash book includes three amount columns on both sides, i.e., cash, bank, and discount.
- This cash book is prepared in the same way as simple and double column cash books are prepared.
- The transactions which increase the cash and bank balance are recorded on the debit side of the cash and bank columns respectively.
- Opening balance of cash and favorable bank balance appear as the first item on the debit side of the three-column cash book in case of existing business.
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Accountancy Chapter 4 Question 8.
What is a cash discount?
Answer:
A cash discount is allowed to the parties making a prompt payment within the stipulated period of time or early payment. It is discount allowed (loss) for the creditor and discount received (gain) for the debtor who makes payment. The discount is allowed when payment is received or made and hence, the entry for discount is also passed with the entry of payment. The earlier the payment, the more may be the discount. Cash discount motivates the debtor to make the payment at an earlier date to avail discount facility.
11th Accountancy Book Back Answer Question 9.
What is a trade discount?
Answer:
- Trade discount is a deduction given by the supplier to the buyer on the list price or catalogue price of the goods.
- It is given as a trade practice or when goods are purchased in large quantities.
- It is shown as a deduction in the invoice.
- Trade discount is not recorded in the books of accounts.
- Only the net amount is recorded.
Example:
Suppose the sale of goods for ₹ 10,000 was made and 10% was allowed as trade discount, the entry regarding sales will be made for ₹ 9,000 (10,000 – 10 percent of 10,000). In the same way, the purchaser of goods will also record purchases as 19,000).
Subsidiary Books Questions And Answers Question 10.
What is a petty cash book?
Answer:
Business entities have to pay various small expenses like taxi fare, bus fare, postage, carriage, stationery, refreshment and other sundry items. These are small payments and repetitive in nature. If all these small payments are recorded in the main cash book, it will be loaded with lot of entries. Hence, all petty payments of the business may be recorded in a separate book, which is called a petty cash book, and the person who maintains the petty cash book is called the petty cashier.
III. Short Answer Questions
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Accountancy Book Solutions Question 1.
Explain the meaning of the imprest system of petty cash books.
Answer:
- Under this system, a fixed amount necessary or sufficient to meet petty payments determined on the basis of past experience is paid to the petty cashier on the first day of the period. (It may be a week or fortnight or month).
- The amount given to the petty cashier in advance is known as “Imprest Money”.
- The word imprest means payment in advance.
- The petty cashier makes payments from this amount and records them in the petty cash book.
- At the end of a particular period, the petty cashier submits the petty cash book to the head cashier.
- The head cashier scrutinies the petty payments and gives an amount equal to the amount spent by the petty cashier so that the total amount with the petty cashier is now equal to the amount he had received in the beginning as advance.
- Under the system, the total cash with the petty cashier never exceeds the imprest at any time during the period.
- This method thus provides effective control over petty payments.
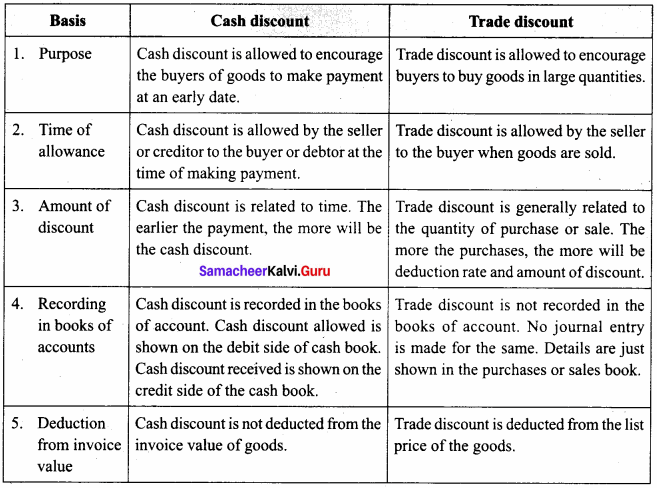
Subsidiary Books 11th Question 2.
Bring out the differences between cash discounts and trade discounts.
Answer:
Following are the difference between cash discount and trade discount:
11 Accountancy Book Answers Question 3.
Write the advantages of maintaining a petty cash book.
Answer:
Following are the advantages of maintaining a petty cash book:
- There can be better control over petty payments.
- There is a saving of time for the main cashier.
- Cashbook is not loaded with many petty payments.
- Posting entries from the main cash book and petty cash book is comparatively easy.
Subsidiary Book Questions And Answers Question 4.
Write a brief note on the accounting treatment of discounts in the cash book.
Answer:
In the discount columns, cash discount, i.e., cash discount allowed and cash discount received is recorded. The net amount received is entered in the Amount column on the debit side and the net amount paid is entered in the Amount column on the credit side. For the seller who allows cash discount, it is a loss and hence it is debited and shown on the debit side of the cash book. For the person making payment, the discount received is again because less payment is made and it is credited and shown on the credit side of the cash book.
Question 5.
Briefly explain contra entry with examples.
Answer:
1. When the two accounts involved in a transaction are cash account and bank account, then both the aspects are entered in the cash book itself. As both the debit and credit aspects of a transaction are recorded in the cash book, such entries are called contra entries.
Example:
- When cash is paid into a bank, it is recorded in the bank column on the debit side and in the cash column on the credit side of the cash book.
- When cash is drawn from the bank for office use, it is entered in the cash column on the debit side and in the bank column on the credit side of the cash book.
2. To denote that there are contra entries, the alphabet ‘C is written in the L.F. column on both sides.
3. Contra means that a particular entry is posted on the other side (contra) of the same book because the Cash account and Bank account are there in the cash book only and there are no separate ledger accounts needed for this purpose,
4. The alphabet ‘C’ indicates that no further posting is required and the relevant account is posted on the opposite side.
IV. Exercises
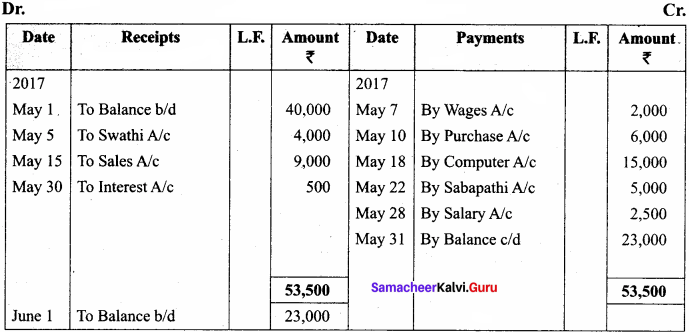
Question 1.
Enter the following transactions in a single column cash book of Seshadri for May 2017.

Answer:
In the books of Seshadri
Single column cash book
Question 2.
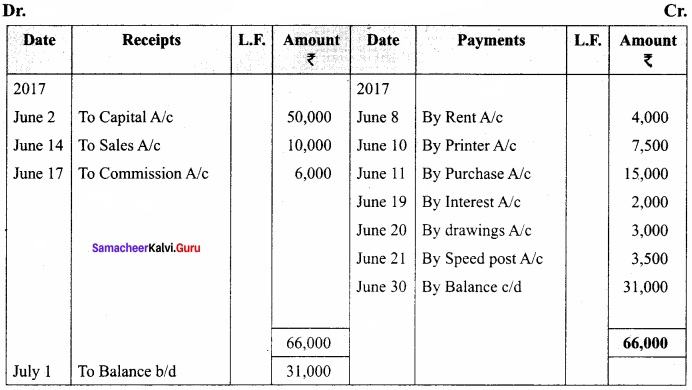
Enter the following transactions in a single column cash book of Pandeeswari for the month ofJune, 2017

Answer:
In the books of Pandeeswari
Single column cash book
Question 3.
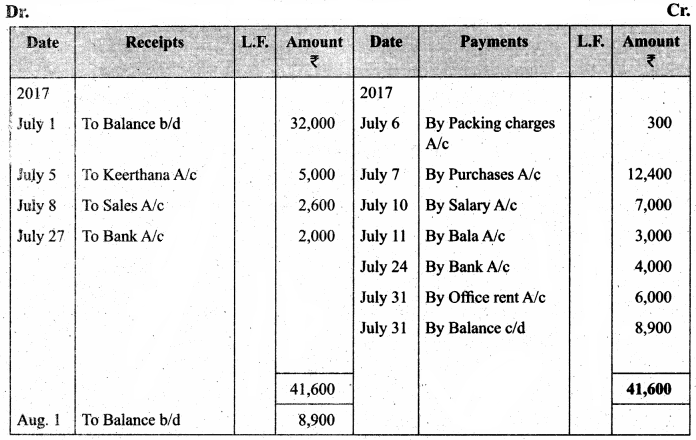
Enter the following transactions in a single column cash book of Ramalingam for the month of July 2017.

Answer:
In the books of Ramalingam
Single column cash book
Question 4.
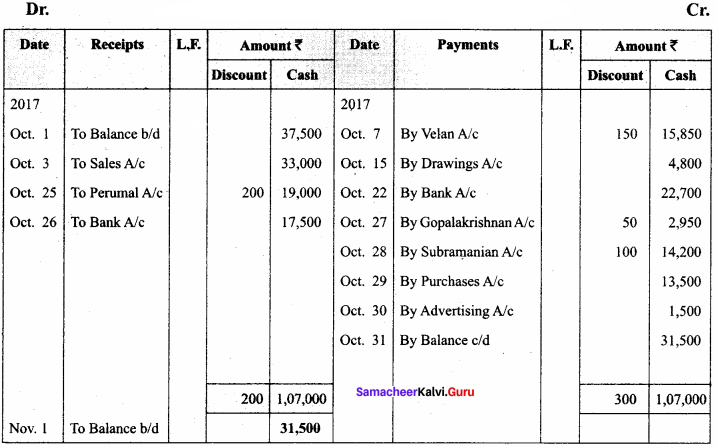
Enter the following transaction in Ahamad’s cash book with discount and cash columns.

Answer:
In the books of Ahamad’s
Cashbook with discount and cash columns
Question 5.
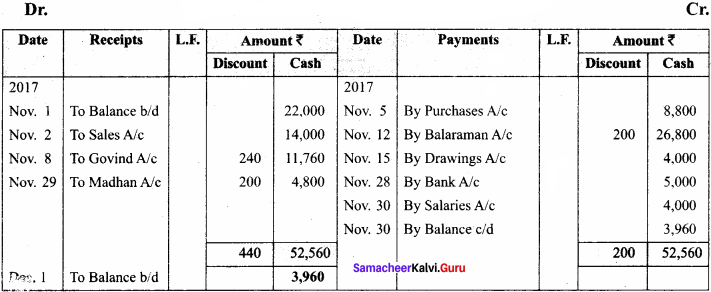
Enter the following transaction in Chandran’s cash book with the cash and discount column.

Answer:
In the books of chandran
Cash book with cash and discount columns
Question 6.
Enter the following transactions in cash book with discount and cash column of Anand

Answer:
In the books of Anand
Cashbook with cash and discount and cash columns
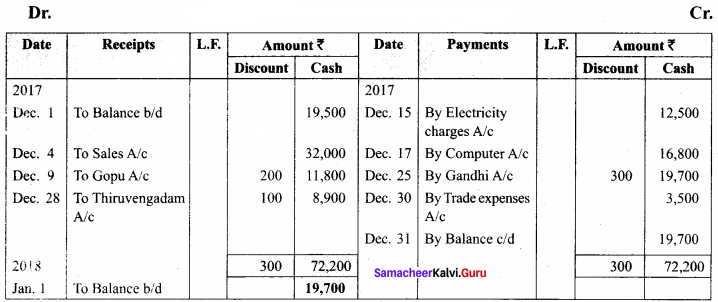
Question 7.
Write out a cash book with discount, cash, and bank columns in the books of Mahendran.

Answer:
In the books of Mahendran
There – column cash book
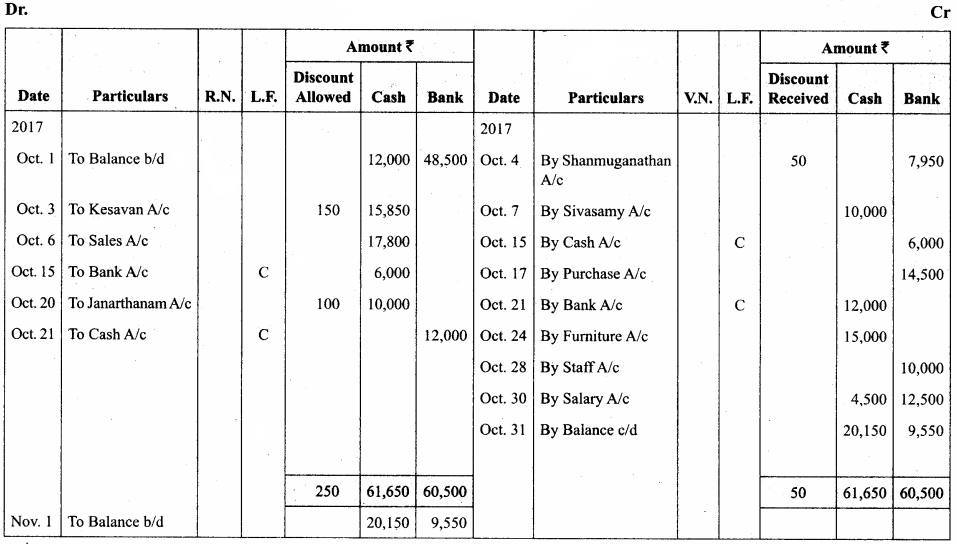
Question 8.
Enter the following transactions in the three column cash book of Kalyana Sundaram

Answer:
In the books of Kalyana Sundaram
There – column cash book
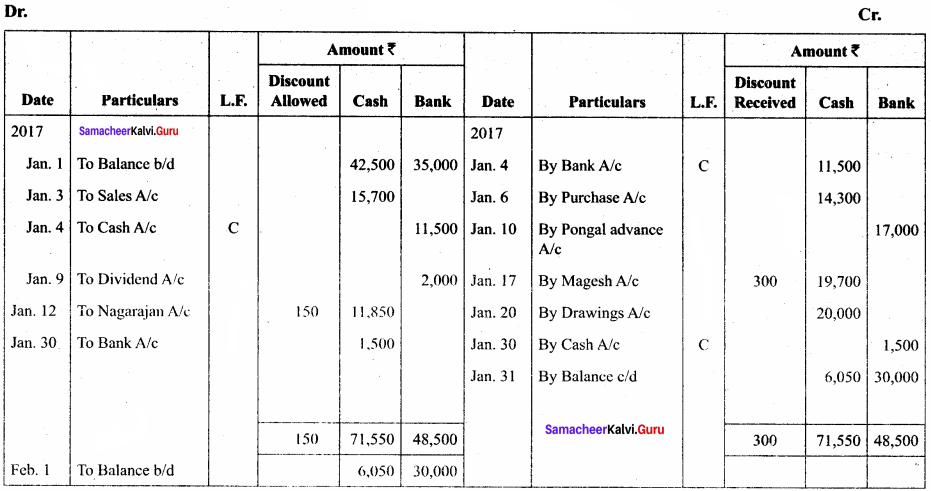
Question 9.
Enter the following transactions of Fathima in the cash book with cash, bank, and discount columns for the month of May 2017.

Answer:
In the books of Fathima
Three – column cash book with cash, bank, and discount
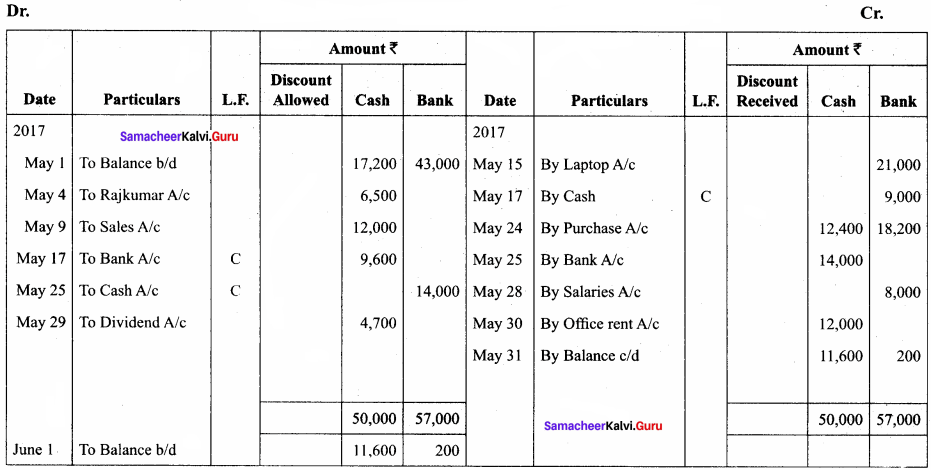
Question 10.
Enter the following transactions in the three-column cash book of Chozhan.

Answer:
In the books of Fathima
Three – column cash book with cash, bank, and discount
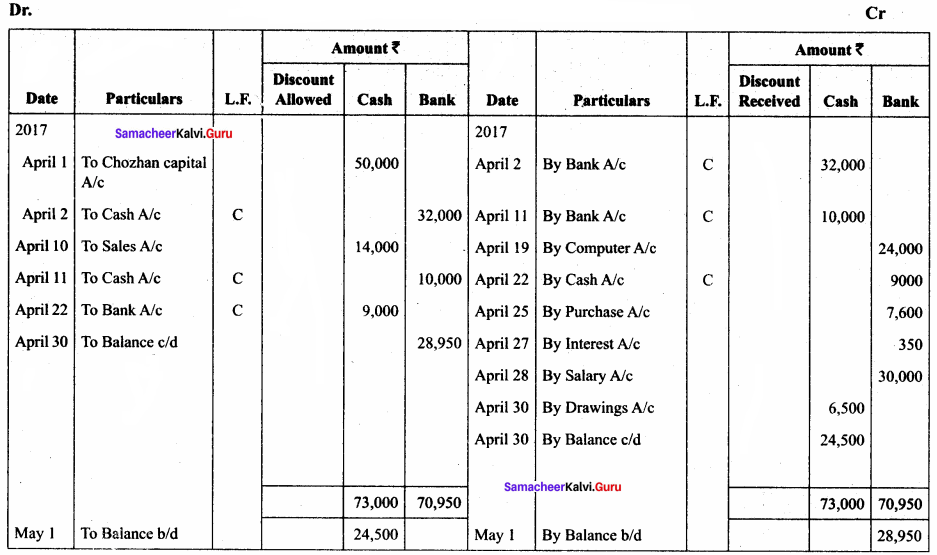
Question 11.
Enter the following transactions in a cash book with cash, bank, and discount columns of Sundari.

Answer:
In the books of Sundari
Three – column cash book
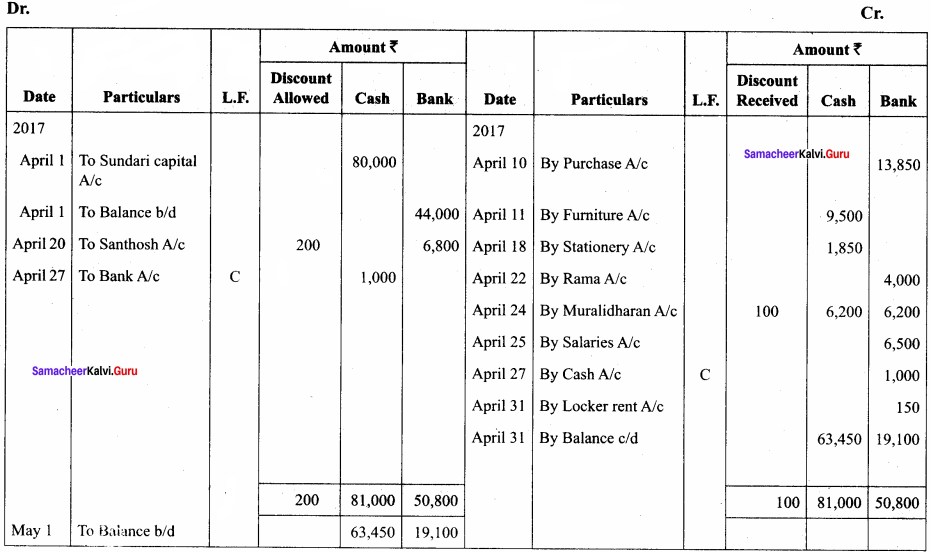
Question 12.
Record the following transactions in the three-column cash book of Rajeswari for the month of June 2017.

Answer:
In the books of Rajeswari
Three – column cash book
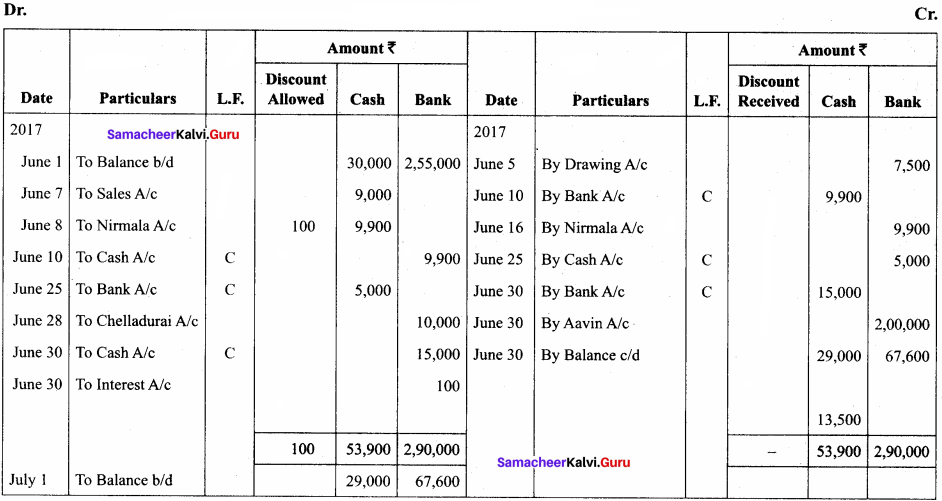
Question 13.
Record the following transactions in three column cash book of Ramachandran.

Answer:
In the books of Ramachandran
Three – column cash book
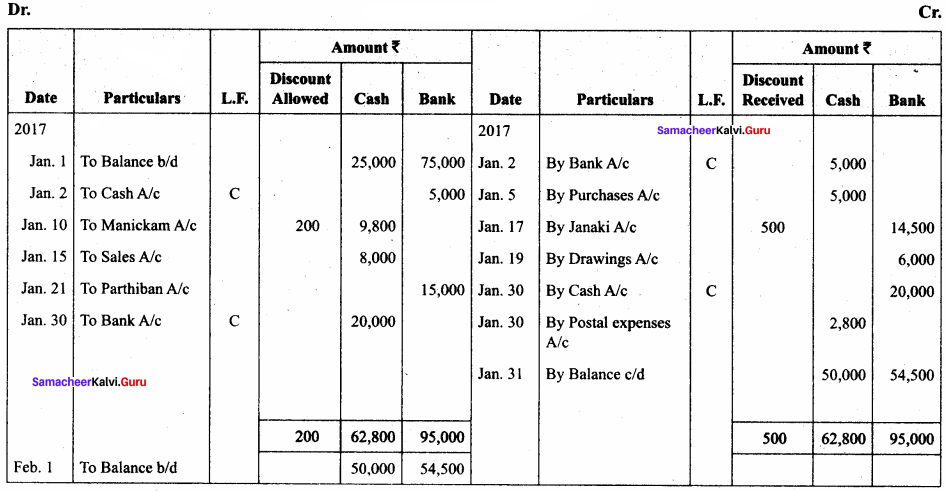
Question 14.
Record the following transactions in the three-column cash book of John Pandian.
In the books of John Pandian
Three – column cash book

Answer:
In the books of John Pandian
Three – column cash book
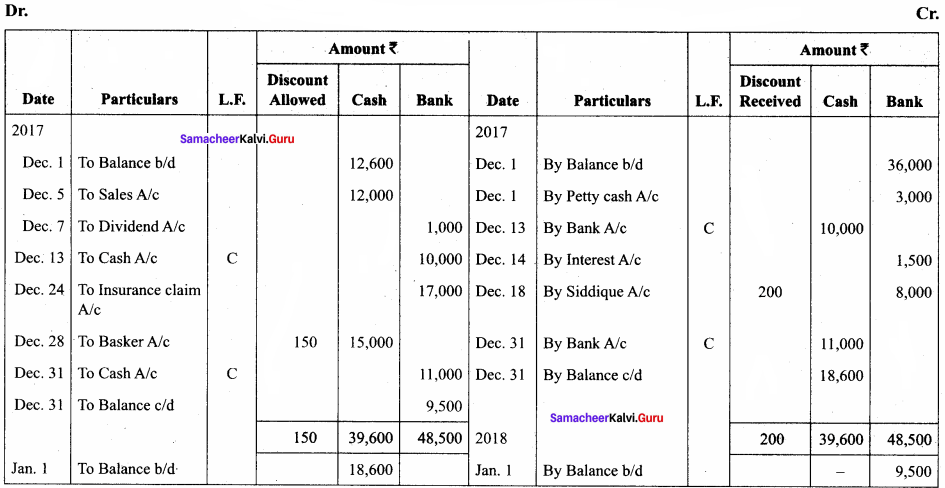
Question 15.
Prepare a triple column cash book of Rahim from the following transactions:

In the hooks of Rahim
Three – column cash book
Answer:
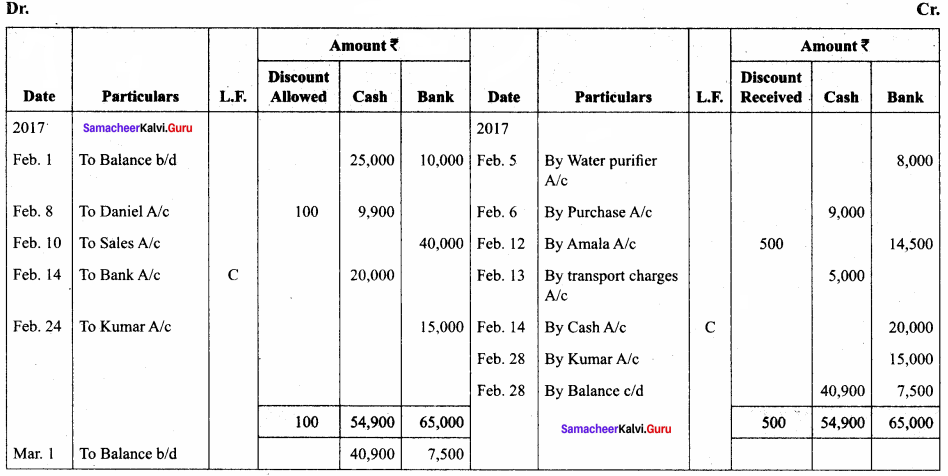
Question 16.
Prepare analytical petty cash book from the following particulars under imprest system:

Answer:
Analytical Petty Cash Book (in ₹)
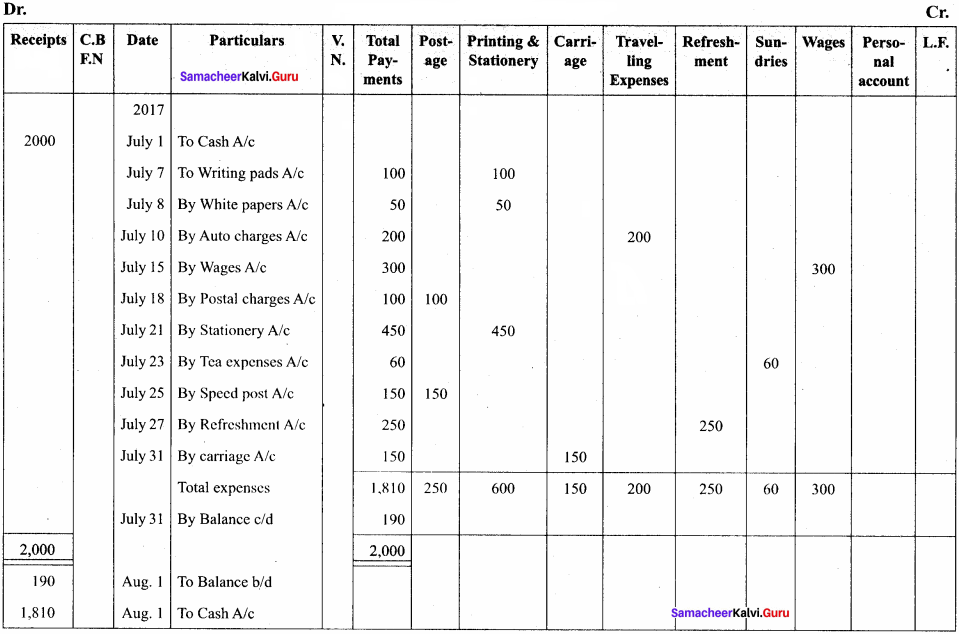
Question 17.
From the following information prepare an analytical petty cash book under imprest system:

Answer:
Analytical Petty Cash Book (in ₹)
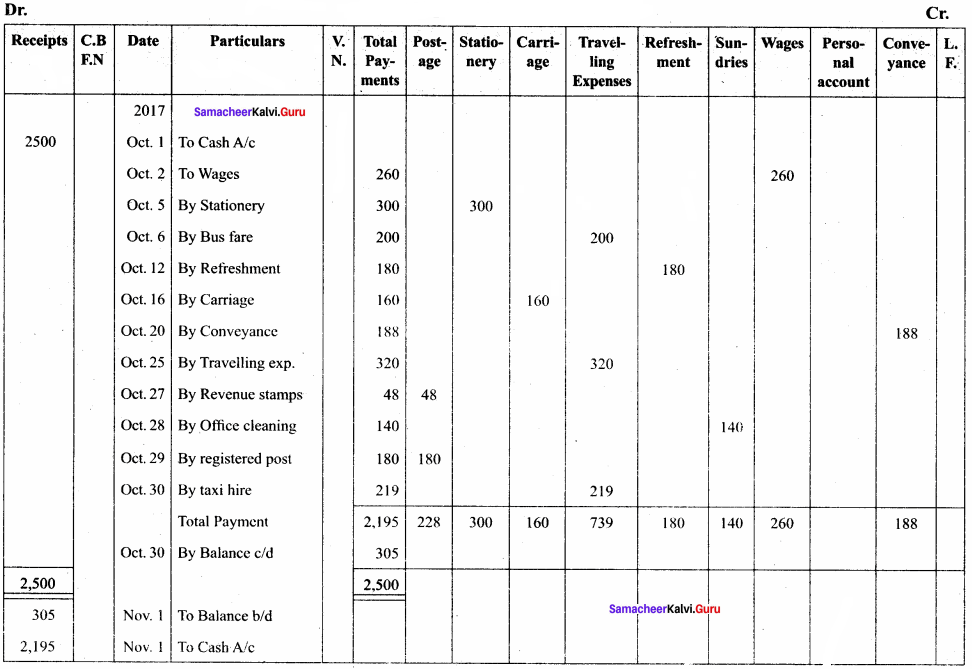
Question 18.
Record the following transactions in an analytical petty cash book and balance the same. On 1st November 2017, the petty cashier started with imprest cash of ₹ 2,000.

Answer:
Analytical Petty Cash Book (in ₹)
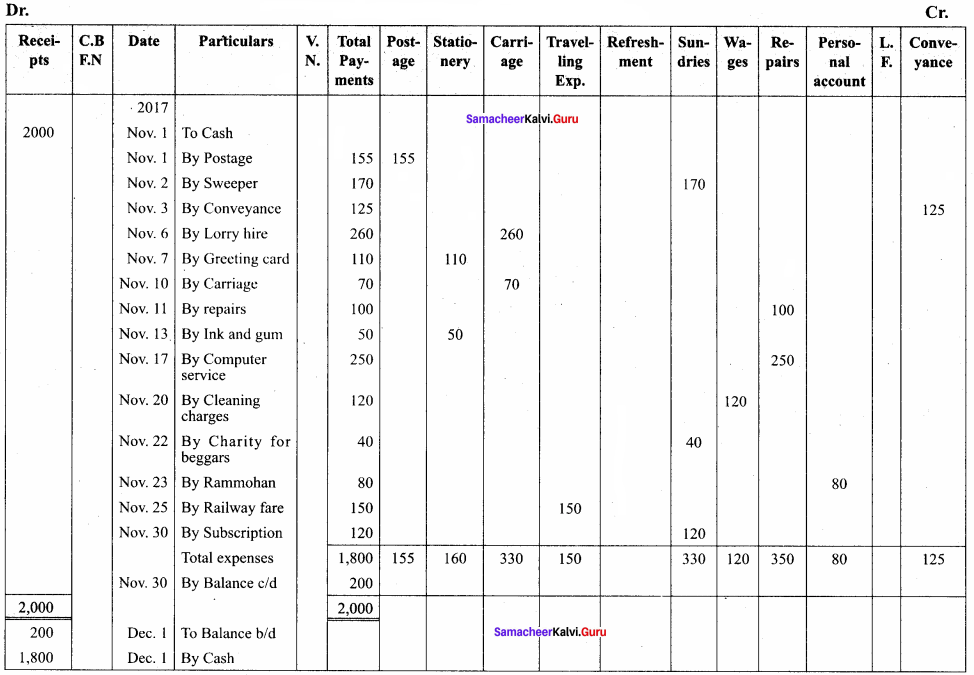
Question 19.
Enter the following transactions in Iyyappan’s petty cash book with analytical columns under the imprest system.

Answer:
Analytical Petty Cash Book (in ₹)
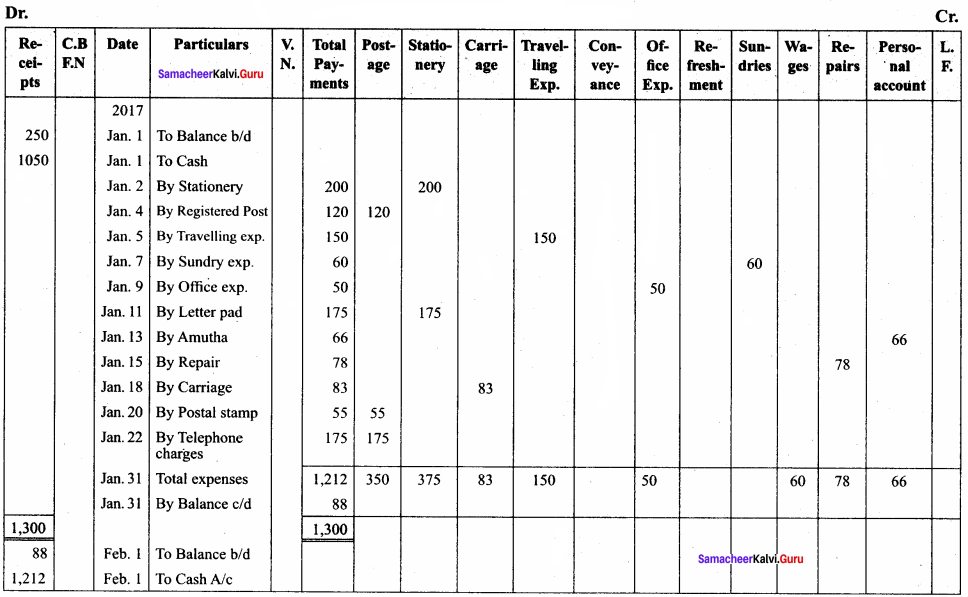
Textbook Case Study Solved
Vetri is a sole trader selling food products. He maintains a simple cash book. He sells and purchases goods both on cash and credit. He maintains the cash book by himself. He allows discounts and receives discounts. He has his personal bank account. He also has so many petty expenses. Now, he wants to establish his business. But he wants to maintain the cash book all by himself.
Now, discuss the following points:
Question 1.
What could be the reason that Vetri maintains the cash book by himself?
Answer:
He is a sole trader, he need not show the accounts to anybody else, he wants to know about profit or loss for himself only. So he maintains cash book only.
Question 2.
Is it convenient for him to record all the cash transactions in the simple cash book?
Answer:
No, it is not convenient for him to record all the cash transactions in the simple cash book.
Question 3.
Will his personal bank account serve the purpose of his business transactions?
Answer:
No, his personal bank account will not serve the purpose of his business transactions.
Question 4.
Suggest him some better ways of maintaining the cash transactions.
Answer:
Suggestions:
He may maintain a triple column cash book because he can know all cash transactions are the same account.
Instead of a personal bank account, he can open a business bank account (i.e.) current account.
Question 5.
When his business becomes large, what other books will he be maintaining?
Answer:
He will be maintaining the following other books:
- Triple column cash book.
- Petty cash book (Analytical).
- Purchases book for credit purchases
- Sales book for credit sales.
- Purchases return the book.
- Sales returns book.
- Business book account (i.e. current account to be maintained).
- Proper journal for other assets maintaining:
- All cash transactions recorded in the cash book.
- All petty expenses are to record in the analytical petty cash book.
- All credit transactions to recorded in special-purpose books (i.e. purchases book, sales book, purchases return book and sales returns book, and proper journal.
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Accountancy Subsidiary Books – II Additional Questions and Answers
I. Multiple Choice Questions
Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
Cash Book is a type of ________ but treated as a ________ of accounts.
a) Subsidiary book, Principal book
b) Principal book, subsidiary book
c) Subsidiary book, subsidiary book
d) Principal book, principal book
Answer:
a) Subsidiary book, Principal book
Question 2.
Cash payments are recorded on the ……………. of the cash book.
(a) debit side
(b) credit side
(c) contra
(d) journal
Answer:
(b) credit side
Question 3.
While balancing three column cash book, the discount columns are:
a) Totalled but not adjusted
b) Totalled and also adjusted
c) Totalled but not balanced
d) Balanced but not totaled
Answer:
c) Totalled but not balanced
Question 4.
……………. serves the purpose of a journal and a ledger.
(a) cash book
(b) purchase book
(c) sales book
(d) petty cash book
Answer:
(a) cash book
Question 5.
Double entry in cash book is completed when:
a) Salaries are paid by cheque
b) Withdrawal of money from the bank for personal use
c) Deposited cash into the bank
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Deposited cash into the bank
Question 6.
R.N. expands for …………….
(a) Receipts number
(b) Roll number
(c) Route number
(d) Rank number
Answer:
(a) Receipts number
Question 7.
Cash sales are entered in the ________.
a) Purchases book
b) Sales book
c) Cashbook
d) Petty cash book
Answer:
c) Cashbook
Question 8.
V.N. expands for …………….
(a) Value number
(b) Voucher number
(c) Vendor number
(d) Volume number
Answer:
(b) Voucher number
Question 9.
Subsidiary books are maintained in ________
a) Big business concerns
b) Small business concerns
c) Banks
d) None of the above
Answer:
a) Big business concerns
Question 10.
The word ……………. means payment in advance.
(a) imprest
(b) loan
(c) money
(d) petty cash
Answer:
(a) imprest
Question 11.
A cash book with discount and cash column is called ________.
a) Simple cash book
b) Double column cash book
c) Three column cash book
d) Petty cash book
Answer:
b) Double column cash book
Question 12.
When goods are purchased for cash, the entry will be recorded in the ________.
a) Cashbook
b) purchases book
c) Sales book
d) journal
Answer:
a) Cashbook
Question 13.
The balance of cash book indicates ________.
a) Net income
b) cash in hand
c) Debtors
d) creditors
Answer:
b) cash in hand
Question 14.
In triple column cash book, cash was withdrawn from bank for office use Will appear in ________.
a) Debit side of the cash book only
b) both sides of the cash book,
c) Credit side of the cash book only.
d) Journal proper
Answer:
b) both sides of the cash book,
Question 15.
If a cheque sent for collection is dishonoured, the debit is given to ________.
a) suppliers A/c
b) bank A/c
c) customers A/c
d) A and B
Answer:
c) customers A/c