Every chapter available in the Samacheer Kalvi Class 11th Bio Zoology Solutions subject is explained clearly in an easy way. Learn the depth concept by referring to the Samacheer Kalvi 11th Bio Zoology Solutions Chapter 3 Tissue Level of Organisation Questions and Answers. Have a look at every topic and get the complete knowledge on the Bio Zoology Solutions subject. You do not need to search for many materials for a better understanding of Bio Zoology Solutions. Just refer to Tamilnadu State Board Solutions pdf and have a grip on the total subject.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 11th Bio Zoology Solutions Chapter 3 Tissue Level of Organisation
I believe that the best book is like a best friend to know the complete world by sitting in one place. When you have the best book you have many options to get great knowledge. Selecting the best book will lead to reaching your goal. Students who are looking for the best book to learn Bio Zoology Solutions can use Samacheer Kalvi Class 11th Bio Zoology Solutions Chapter 3 Tissue Level of Organisation Questions and Answers. Immediately start your learning with Samacheer Kalvi Class 11th Bio Zoology Solutions Solutions Pdf.
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Bio Zoology Tissue Level of Organisation Text Book Back Questions and Answers
Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
The main function of the cuboidal epithelium is –
(a) Protection
(b) Secretion
(c) Absorption
(d) Both (b) and (c)
Answer:
(d) Both (b) and (c)
Question 2.
The ciliated epithelium lines the –
(a) Skin
(b) Digestive tract
(c) Gall bladder
(d) Trachea
Answer:
(d) Trachea
Question 3.
What type of fibres are found in connective tissue matrix?
(a) Collagen
(b) Areolar
(c) Cartilage
(d) Tubular
Answer:
(a) Collagen
Question 4.
Prevention of substances from leaking across the tissue is provided by –
(a) Tight junction
(b) Adhering junction
(c) Gap junction
(d) Elastic junction
Answer:
(a) Tight junction
Question 5.
Non-shivering thermogenesis in neonates produces heat through –
(a) White fat
(b) Brown fat
(c) Yellow fat
(d) Colourless fat
Answer:
(b) Brown fat
Question 6.
Some epithelia are pseudostratified. What does this mean?
Answer:
Pseudostratified epithelial cells are columnar but unequal in size. Although the epithelium is single-layered yet it appears to be multilayered due to the fact that nuclei lie at different levels in different cells.
Question 7.
Differentiate white adipose tissue from brown adipose tissue.
Answer:
Adipose tissue:
- Adipose tissue is the group of fat cells.
- It stores fats.
- It releases energy while fasting.
Brown Adipose Tissue:
- The adipose tissue which contains abundant mitochondria is called brown adipose tissue.
- It is used to warm the bloodstream to warm the body.
- It produces heat by non-shivering thermogenesis.
Question 8.
Why blood is considered a typical connective tissue?
Answer:
Blood is considered a typical connective tissue because it is the fluid connective tissue containing plasma, RBCs, WBCs, and platelets. It functions as the transport medium for the cardiovascular system carrying nutrients, nitrogenous wastes, and respiratory gases throughout the body.
Question 9.
Differentiate between elastic fibers and elastic connective tissue.
Answer:
Elastic fibers:
- It contains elastin and other proteins and glycoproteins.
- It attaches muscles and bones and one bone to another bone.
- It withstands tensile stress when pulling force is applied in one direction or in many directions.
Elastic connective tissue:
- It contains high proportion of elastic fibers.
- It is found in the walls of large arteries, ligaments associated with the vertebral column, and within the walls of the bronchial tubes.
- It allows recoil of tissues after stretching.
Question 10.
Name any four important functions of epithelial tissue and provide at least one example of a tissue that exemplifies each function.
Answer:
1. Secretion and absorption :
Cuboidal epithelium in kidney tubules, ducts. Columnar epithelium found in the digestive tract.
2. Filtration :
Squamous epithelium found in the glomerulus of the kidney.
3. Ciliated epithelium :
Found in the bronchi, uterine tubes propels the materials due to ciliary actions.
Question 11.
Write the classification of connective tissue and their functions.
Answer:
There are four main classes of connective tissues.
- Connective tissue proper
- Cartilage
- Bones
- Blood
The major functions of connective tissues are binding and support, protection, insulation and transportation of substances.
Question 12.
What is an epithelium? Enumerate the characteristic features of different epithelia.
Answer:
Epithelial tissue is sheet of cells that covers the body surface or lines the body cavity.
- Simple epithelium is single layered.
- Squamous epithelium is made of flattened cells with irregular boundaries.
- Columnar epithelium is made of column like cells with round to oval nuclei at the base.
- Ciliated epithelium has ciilia at the free end.
- Compound epithelium is made of multi-layered cells.
In-Text Questions Solved
Question 1.
Stratified epithelia are “built” for protection or to resist abrasion. What are the simple epithelia better at?
Answer:
The simple epithelia are better at absorption, secretion of mucus, enzymes and other substances.
Question 2.
What type of connective tissue is damaged when one get cut on his index finger accidently?
Answer:
The Areolar connective tissue is damaged when finger gets cut.
Question 3.
The stored lipids are in the form of adipose tissue. Are they coloured? Why?
Answer:
The white adipose tissue is called white fat. The adipose that has abundant mitochondria is called Brown fat.
Question 4.
You are looking at a slide of a tissue through the compound microscope and you see striped branching cells that connect with one another. What type of muscle are you viewing?
Answer:
I am viewing the skeletal muscle.
Question 5.
A player has sustained a severe injury during football practice and was told that he has a torn knee cartilage. Can he expect a quick uneventful recovery? Explain your response.
Answer:
The knee cartilage is an important connective tissue. Since the knee moves during locomotion, a quick, uneventful recovery cannot take place. Complete rest to the knee joint is necessary.
Question 6.
An overweight high school student, is overheard telling her friend that she is going to research how she can transform some of her white fat to brown fat. What is her rationale here (assuming it is possible)?
Answer:
The white fat stores nutrients while the brown fat warms the body. The student feels that she may bring down her weight by converting brown fat to white fat.
Textbook Activities Solved
Question 1.
Students are asked to identify the unlabelled slides of tissues and to classify them. Similar exercise can also be accomplished by projecting unlabelled histological images on a screen. They can identify the slides of different tissues through microscope.
Answer:
Do it yourself.
Question 2.
The preparation of smear of stratified squamous epithelia from the inner lining of cheek allows the students to make their own slides using biological stain. They will have the experience of examining their cheek cells.
Answer:
Do it yourself.
Entrance Examination Questions Solved
Question 1.
Transitional epithelium occurs in ………… (MHTCET 2008)
(a) Blood vessels
(b) Trachea
(c) Kidney
(d) Ureter/urinary bladder
Answer:
(d) Ureter/urinary bladder
Question 2.
The study of tissues is known as …………….. (MPPMT 2010)
(a) Physiology
(b) Ecology
(c) Histology
(d) Anatomy
Answer:
(c) Histology
Question 3.
Find out the wrong match :
(a) Eosinophils Allergic response
(b) Basophils Secrete histamine and serotonin
(c) Monocytes Secrete heparin
(d) Lymphocytes Immune response
Answer:
(c) Monocytes Secrete heparin
Question 4.
The outer covering of cartilage is called (WB 2010)
(a) Peritoneum
(b) Periosteum
(c) Endosteum
(d) Perichondrium
Answer:
(d) Perichondrium
Question 5.
Skin is …………… (CPMT2010)
(a) Cuboidal epithelium
(b) Stratified epithelium
(c) Columnar epithelium
(d) Pseudostratified epithelium
Answer:
(b) Stratified epithelium
Question 6.
Match the animals listed in the column – I to blood listed in the column – II. (KCET 2010)
|
Column -I |
Column – II |
|
(i) Plasma and cells are colourless |
(P) Man |
|
(ii) Plasma colourless and nucleated RBC |
(Q) Earth worm |
|
(ii) Plasma colourless and enucleated RBC |
(R) Cockroach |
|
(iv) Plasma red and nucleated colourless RBC |
(S) Frog |
|
(v) Plasma and RBS have haemoglobin |
– |
(a) (P – iii), (Q – iv), (R – i), (S – ii)
(b) (P – iv), (Q – v), (R – iii), (S – ii)
(c) (P – i), (Q – iv), (R – ii), (S – iii)
(d) (P – v), (Q – iii), (R – i), (S – iv)
Answer:
(a) (P – iii), (Q – iv), (R – i), (S – ii)
Question 7.
Matrix of bone and cartilage can be distinguished by the presence of –
(a) Lacunae
(b) Chromatophores
(c) Haversian canals
(d) Adipose cells
Answer:
(c) Haversian canals
Question 8.
Which type of tissue forms glands? (MPPMT- 2010)
(a) Epithelial
(b) Muscular
(c) Nervous
(d) Connective
Answer:
(a) Epithelial
Question 9.
Which of the following blood cells help in blood coagulation?
(a) RBCs
(b) Lymphocytes
(c) Thrombocytes
(d) Basophils
Answer:
(c) Thrombocytes
Question 10.
Fibroblasts macrophages and mast cells are present in –
(a) Cartilage tissue
(b) Areolar tissue
(c) Adipose tissue
(d) Glandular epithelium
Answer:
(b) Areolar tissue
Question 11.
Which type of epithelium is involved in a function to move particles or mucus in a specific direction? (HPPMT 2010)
(a) Squamous epithelium
(b) Cuboidal epithelium
(c) Columnar epithelium
(d) Ciliated epithelium
Answer:
(d) Ciliated epithelium
Question 12.
Which of these is not found in connective tissue? (MPPMT2010)
(a) Collagen fibres
(b) Basement membrane
(c) Hyaluronic acid
(d) Fluid
Answer:
(b) Basement membrane
Question 13.
Multi-lobed nucleus and granular cytoplasm are characteristics of which of the WBCs?
(a) Neutrophils
(b) Monocytes
(c) Lymphocytes
(d) Eosinophils
Answer:
(a) Neutrophils
Question 14.
Which one of the following plasma proteins are involved in the coagulation of blood? (2011)
(a) globulin
(b) Fibrinogen
(c) albumin
(d) Serum amylase
Answer:
(b) Fibrinogen
Question 15.
Which of the following is not a connective tissue? (CPMT – 2010)
(a) Blood
(b) bone
(c) Lymph
(d) Nerve
Answer:
(d) Nerve
Question 16.
The ciliated columnar epithelial cells in humans are known to occur in –
(a) Bile duct and esophagus
(b) Fallopian tubes and urethra
(c) Eustachian tube and stomach lining
(d) Bronchioles and fallopian tubes
Answer:
(d) Bronchioles and fallopian tubes
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Bio Zoology Tissue Level of Organisation Additional Questions & Answers
Multiple Choice Questions
Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
Groups of cells that are similar in structure and perform a common function are called –
(a) tissues
(b) organs
(c) cells
(d) organ systems
Answer:
(a) tissues
Question 2.
Which of the following have flattened cells?
(a) cuboidal epithelium
(b) columnar epithelium
(c) squamous epithelium
(d) ciliated epithelium
Answer:
(c) squamous epithelium
Question 3.
Microvilli and Goblet cells are the modifications of –
(a) cuboidal epithelium
(b) columnar epithelium
(c) squamous epithelium
(d) ciliated epithelium
Answer:
(b) Columnar epithelium
Question 4.
Which of the following is not exocrine gland?
(a) Sweat glands
(b) Sebaceous glands
(c) Mammary glands
(d) Thyroid gland
Answer:
(d) Thyroid gland
Question 5.
Pancreas is the example of glands –
(a) Merocrine
(b) Holocrine
(c) Apocrine
(d) Epithelial
Answer:
(a) Merocrine
Question 6.
Which is the site of production of blood cells?
(a) Cartilage
(b) Blood
(c) PLasma
(d) Bone marrow
Answer:
(d) Bone marrow
Question 7.
Biceps and Triceps are the examples of –
(a) Smooth muscle
(b) Cardiac muscle
(c) Striped muscle
(d) Involuntary muscle
Answer:
(c) Striped muscle
Question 8.
The walls of internal organs are made up of –
(a) Smooth muscle
(b) involuntary muscle
(c) Skeletal muscle
(d) Cardiac muscle
Answer:
(a) Smooth muscle
Question 9.
Bone cells are called as –
(a) Neurons
(b) Epithelial cells
(c) Osteoblasts
(d) Chondrocytes
Answer:
(c) Osteoblasts
Question 10.
Cartilage is the –
(a) Loose connective tissue
(b) Dense connective tissue
(c) Areolar connective tissue
(d) Specialized connective tissue
Answer:
(d) Specialized connective tissue
Question 11.
Salivary gland is –
(a) Unicellular, glandular cells
(b) Multicellular, glandular cells
(c) Unicellular, sensory cells
(d) Multicellular, sensory cells
Answer:
(c) Unicellular, sensory cells
Question 12.
lines gall bladder.
(a) ciliated epithelium
(b) columnar epithelium
(c) non – ciliated epithelium
(d) pseudo – stratified epithel lurn
Answer:
(c) non – ciliated epithelium
Question 13.
Dry epidermis of the skin is formed as –
(a) keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
(b) non – keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
(c) stratified cuboidal epithelium
(d) stratified columnar epithelium
Answer:
(a) keratinized stratified squamous epithelium
Question 14.
The walls of the Bronchial tubes have –
(a) Dense irregular connective tissues
(b) Reticular connective tissue
(c) elastic connective tissue
(d) Adipose tissue
Answer:
(c) elastic connective tissue
Question 15.
Bones have –
(a) Osteocytes
(b) Fibroblasts
(c) Adipocytes
(d) Myofibrils
Answer:
(c) Adipocytes
II. Answer the following Questions
Question 1.
Define tissues.
Answer:
Define tissues.
Answer:
Group of cells that are similar in structure and perform common or related functions are called tissues.
Question 2.
What is the study of tissues called?
Answer:
Histology.
Question 3.
Differentiate Simple epithelium and compound epithelium.
Answer:
Simple epithelium:
- It consists of a simple layer.
- It helps in protection, absorption, filtration, excretion, secretion, and sensory reception.
Compound epithelium:
- It is multilayered.
- It provides protection against chemical and mechanical stresses.
Question 4.
Explain the types of simple epithelium.
Answer:
Simple epithelium is a simple layered sheet of cells that covers the body surface or lines the body cavity.
Types:
1. Squamous epithelium:
It is made of flattened cells with irregular boundaries. It is found in glomeruli, air sacs of lungs, lining of heart, blood vessels.
2. Cuboidal epithelium:
It is made of cube-like cells. It is found in kidney tubules, ducts and glands. It is important for secretion and absorption.
3. Columnar epithelium :
It is made of column-like cells. It lines the digestive tract. It is important for secretion and absorption.
4. Ciliated epithelium :
It has cilia at the free end. It is found in bronchi, uterine tubes. It is helpful in propelling materials.
5. Glandular epithelium :
Cuboidal or columnar epithelium specialized for secretion is called the glandular epithelium. E.g., goblet cells and salivary gland.
Question 5.
Distinguish between exocrine glands and endocrine glands.
Answer:
Exocrine glands:
- These glands release their products through ducts.
- These secrete mucous, saliva, ear wax, oil, milk, digestive enzymes etc. e.g., salivary glands
Endocrine glands:
- These are ductless gland and their secretions are released directly into the blood.
- These secrete hormones, e.g., the Pituitary gland
Question 6.
Classify multicellular exocrine glands based on their structure.
Answer:
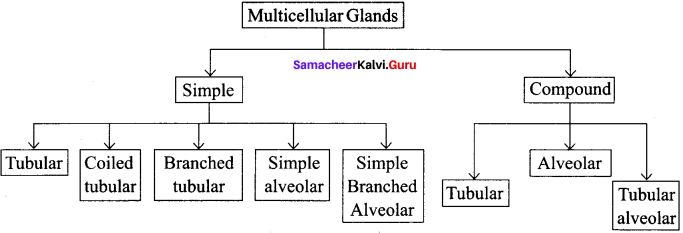
Question 7.
Classify exocrine glands based on mode of secretion.
Answer:
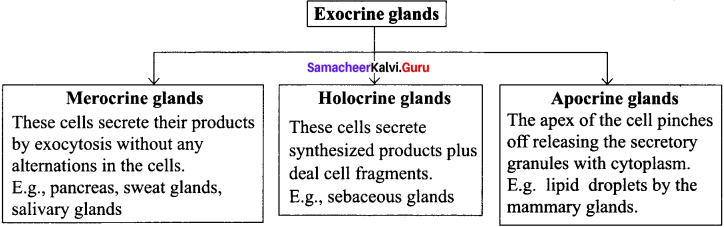
Question 8.
Explain compound epithelium.
Answer:
- The compound epithelium is made up of multilayered cells.
- These protect organs against chemical and mechanical stresses.
- These cover the dry surface of the skin, moist surface of the buccal cavity, pharynx, inner lining of ducts of salivary glands and pancreatic ducts.
Question 9.
Classify compound epithelium.
Answer:
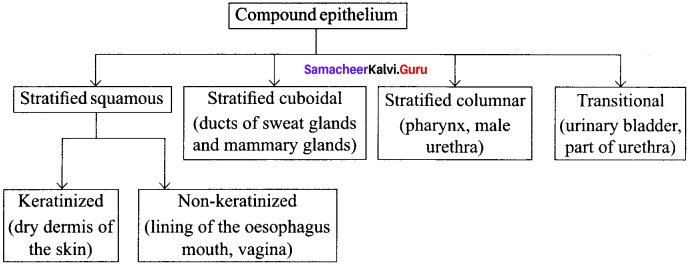
Question 10.
Explain the types of simple epithelium.
Answer:
Simple epithelium is a simple layered sheet of cells that covers the body surface or lines the body cavity.
Types:
1. Squamous epithelium:
It is made of flattened cells with irregular boundaries. It is found in glomeruli, air sacs of lungs, the lining of heart, blood vessels.
2. Cuboidal epithelium:
It is made of cube-like cells. It is found in kidney tubules, ducts, and glands. It is important for secretion and absorption.
3. Columnar epithelium:
It is made of column-like cells. It lines the digestive tract. It is important for secretion and absorption.
4. Ciliated epithelium:
It has cilia at the free end. It is found in bronchi, uterine tubes. It is helpful in propelling materials.
5. Glandular epithelium:
Cuboidal or columnar epithelium specialized for secretion is called the glandular epithelium. E.g., goblet cells and salivary gland.
Question 11.
Write a short note on connective tissue.
Answer:
Connective tissue develops from the mesoderm. Proper, cartilage, bones, and blood are the four main classes of connective tissues. Binding, support, protection, insulation, and transportation of substances are the major functions of connective tissue.
Question 12.
What are the types of proper connective tissues?
Answer:
Loose connective tissue and dense connective tissues.
Question 13.
Write a short note on loose connective tissues.
Answer:
In this tissue, the cells and fibers are loosely arranged in semifluid ground substances, e.g., fibroblasts, macrophages, fat cells and mast cells. Areolar connective tissue present beneath the skin acts as a support framework for epithelium. It acts as a reservoir of water and salts for the surrounding body tissues. Hence, these are called tissue fluids.
Adipose tissue is similar to areolar tissue in structure and function. It is located beneath the skin, surrounding the kidneys, eyeball, heart etc. Adipocytes store fat. It is called white fat. The adipose tissue which contains a lot of mitochondria is called brown fat or brown adipose tissue. Reticular connective tissue is filled with fibroblasts called reticular cells. These cells store fats and excess nutrients.
Question 14.
Distinguish between tendons and ligaments.
Answer:
Tendons:
Tendons attach skeletal muscles to bones
Ligaments:
Ligaments attach one bone to another.
Question 15.
Explain specialized connective tissues.
Answer:
Cartilage :
The intercellular material of cartilage is solid and pliable and resists compression. Cells of cartilage (chondrocytes) are enclosed in small cavities within the matrix secreted by them. Cartilage is present in the tip of the nose, outer ear joints, ear pinna, between adjacent bones of the vertebral column, limbs, and hands-on adults.
Bones :
Bones have a hard and non-pliable ground substance rich in calcium salts and collagen fibers. Bones support and protect softer tissues and organs. Osteoblasts are present in the spaces called lacunae.
Blood :
It is the fluid connective tissue. It contains RBCs, WBCs and platelets. It functions as a transport medium for nutrients, wastes and respiratory gases.
Question 16.
Explain the types of muscle.
Answer:
Each muscle is made of long, cylindrical fibres. They are composed of fine fibrils called myofibrils. Muscle fibres contract and relax. Skeletal muscle is attached to skeletal bones. It is striped or striated. It is a voluntary muscle. The smooth muscle fibres are fusiform and do not have striations. It is an involuntary muscle. Cardiac muscle tissue is present in the heart. It is striated and branched and involuntary.
Question 17.
Write a note on neural tissue.
Answer:
- Neurons are units of the neural system. The neuroglial cells protect and support the neurons.
- Neurons transmit sensations as electric impulses.
Hope all the information given regarding Class 11th Tamilnadu State Board Bio Zoology Solutions will help you to get good knowledge. For any queries, you can contact us and clear your doubts. Connect with us using the comment section. Also, we love your feedback and review. Get your Chapter Wise Samacheer Kalvi Class 11th Textbook Solutions for Bio Zoology Solutions Chapter 3 Tissue Level of Organisation Questions and Answers PDF start learning for the exam.