Students can Download Computer Science Chapter 4 Theoretical Concepts of Operating System Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 11th Computer Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 11th Computer Science Solutions Chapter 4 Theoretical Concepts of Operating System
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Computer Science Theoretical Concepts of Operating System Text Book Back Questions and Answers
PART – 1
I. Choose The Correct Answer
11th Computer Science Chapter 4 Book Back Answers Question 1.
Operating system is a ……………….
(a) Application Software
(b) Hardware
(c) System Software
(d) Component
Answer:
(c) System Software
Theoretical Concepts Of Operating System Question 2.
Identify the usage of Operating Systems ……………….
(a) Easy interaction between the human and computer
(b) Controlling input & output Devices
(c) Managing use of main memory
(d) All the above
Answer:
(d) All the above
Samacheer Kalvi Guru 11th Computer Science Question 3.
Which of the following is not a function of an Operating System?
(a) Process Management
(b) Memory Management
(c) Security management
(d) Compiler Environment
Answer:
(d) Compiler Environment
Computer Science Chapter 4 Question 4.
Which of the following OS is a Commercially licensed Operating system?
(a) Windows
(b) UBUNTU
(c) FEDORA
(d) REDHAT
Answer:
(a) Windows
Samacheer Kalvi.Guru 11th Computer Science Question 5.
Which of the following Operating systems support Mobile Devices?
(a) Windows 7
(b) Linux
(c) BOSS
(d) iOS
Answer:
(d) iOS
Computer Chapter 4 Question 6.
File Management manages ……………….
(a) Files
(b) Folders
(c) Directory systems
(d) All the Above
Answer:
(d) All the Above
Chapter 4 Computer Question 7.
Interactive Operating System provides ……………….
(a) Graphics User Interface (GUI)
(b) Data Distribution
(c) Security Management
(d) Real Time Processing
Answer:
(a) Graphics User Interface (GUI)
Class 11 Computer Science Chapter 4 Question 8.
Android is a ……………….
(a) Mobile Operating system
(b) open Source
(c) Developed by Google
(d) All the above
Answer:
(d) All the above
Classification Of Operating System Pdf Question 9.
Which of the following refers to Android operating system’s version?
(a) JELLY BEAN
(b) UBUNTU
(c) OS/2
(d) MITTIKA
Answer:
(a) JELLY BEAN
PART – 2
II. Short Answers
Samacheer Kalvi Guru 11 Computer Science Question 1.
What are the advantages of memory management in an Operating System?
Answer:
- Keeping track of which portion of memory are currently being used and who is using them.
- Determining which and data to move in and out of memory.
- Allocation and de-allocation of memory blocks as needed by the program in main memory.
Question 2.
What is the multi-user Operating system?
Answer:
A Multi-user Operating system is a computer operating system (OS) that allows multiple users on different computers or terminals to access a single system with one OS on it.
Question 3.
What is a GUI?
Answer:
The GUI is a window based system with a pointing device to direct I/O, choose from menus, make selections, and a keyboard to enter text.
Question 4.
List out different distributions of the Linux operating systems.
Answer:
Different server distributions in Linux OS:
- Ubuntu
- Linux Mint
- Debian
- Fedora
- RedHat
Question 5.
What is the security management features available in Operating System?
Answer:
The Operating System provides three levels of securities to the user end. They are:
- File access level
- System-level
- Network-level
Question 6.
What is multiprocessing?
Answer:
Multiprocessing is one of the features of an operating system. It has two or more processors for a single running process. Each processor works on different parts of the same task or two or more different tasks.
Question 7.
What are the different Operating Systems used in computers?
Answer:
- Single User Operating Systems
- Multi-user Operating Systems
- Distributed Operating Systems
PART – 3
III. Explain in Brief
Question 1.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of Timesharing features?
Answer:
Advantages and disadvantages of Time Sharing Option (TSO)
Advantages:
- Each task and each user get their time.
- Systems have to give time to these application individual tasks and other applications also so that all system behaves correctly.
- Reduces the CPU ideal time
Disadvantages:
- Problem in Reliability
- It consumes many resources so it need special operating systems.
- Need High specification hardware
Question 2.
Explain and List examples of the mobile operating systems.
Answer:
Mobile, devices such as phones, tablets, and MP3 players are different from desktop and laptop computers and hence they need special Operating Systems.
Examples of mobile Operating Systems are Apple iOS and Google Android.
Operating systems for mobile devices generally are not as fully featured as those made for desktop and laptop computers and they are not able to run all software.
Question 3.
What are the differences between Windows and Linux Operating systems?
Answer:
Windows:
- Microsoft Windows is a proprietary OS which is commercial.
- Windows can be modified only by the company that owns it.
- Difficult to customize.
- Vulnerable to virus and malware attacks.
Linux:
- Linux is open source, i.e., free licensed.
- Linux can be modified by anyone.
- Easy to customize.
- More secure.
Question 4.
Explain the process management algorithms in Operating System.
Answer:
The following process management algorithms are mainly used to allocate the job to the processor.
- FIFO – This algorithm is based on queuing technique.
- SJF – This algorithm works based on the size of the job being executed by the CPU.
- Round Robin – The Round Robin (RR) scheduling algorithm is designed especially for time-sharing systems.
- Based on Priority – The given job (process) is assigned based on a Priority.
PART – 4
IV. Explain in Detail
Question 1.
Explain the concept of a Distributed Operating System.
Answer:
Distributed Operating System takes care of the data and applications that are stored and processed on multiple physical locations across the world over the digital network (internet/intranet).
The Distributed Operating System is used to access shared data and files that reside in any machine around the world. The user can handle the data from different locations. The users can access it as if it is available on their own computer.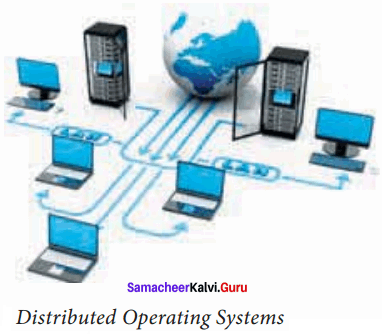
The advantages of distributed Operating System are as follows:
- A user at one location can make use of all the resources available at another location over the network.
- Many computer resources can be added easily in the network.
- Improves the interaction with the customers and clients.
- Reduces the load on the host computer.
Question 2.
Explain the main purpose of an operating system.
Answer:
The operating system has become essential to enable the users to design applications without the knowledge of the computer’s internal structure of hardware.
The operating system manages all the software and hardware. Most of the time there are many different computer programmes running at the same time, they all need to access the computers, CPU, memory, and storage. The need for an operating system is basically – an interface between the user and the hardware.
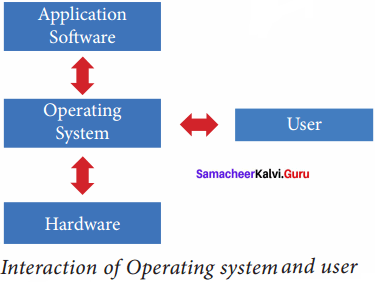
Operating System works as a translator, while it translates the user request into machine language(Binary language), processes it, and then sends it back to Operating System. Operating System converts processed information into the user-readable form.
Uses of Operating Systems:
- to ensure that a computer can be used to extract what the user wants it do.
- Easy interaction between the users and computers.
- Starting computer operation automatically when power is turned on (Booting).
- Controlling Input and Output Devices
- Manage the utilisation of main memory.
- Providing security to user programs.
Question 3.
Explain the advantages and disadvantages of open-source operating systems.
Answer:
Advantages of Open Source Software:
- It is generally free and you do not have to pay for using it.
- Created by skillful and talented people.
- Highly reliable.
- Help you become more flexible.
- Open-source software provides a great platform for innovations and creativity.
Disadvantages of Open Source Software:
- Vulnerable to malicious users.
- Most interfaces are not so user-friendly and easy to use.
- Don’t come with extensive support.
- Open-source software is hard to learn. It is not straightforward to use.
- Many of the latest hardware that is being produced is incompatible.
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Computer Science Theoretical Concepts of Operating System Additional Questions and Answers
PART – 1
I. Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
________ is a set of instructions that perform specific tasks.
a) hardware
b) freeware
c) software
d) None of these
Answer:
c) software
Question 2.
A computer consists of a collection of processes, they are classified as ………………. categories.
(a) 7
(b) 3
(c) 8
(d) 2
Answer:
(d) 2
Question 3.
Software, is classified into__________ types.
a) three
b) two
c) four
d) many
Answer:
b) two
Question 4.
The operating system provides ………………. levels of securities to the user end.
(a) three
(b) five
(c) seven
(d) ten
Answer:
(a) three
Question 5.
_________ is a set of programs to perform specific task.
a) application software
b) system software
c) both A and B
d) None of these
Answer:
a) application software
Question 6.
………………. is a family of multitasking.
(a) LINUX
(b) Microsoft Windows
(c) UNIX
(d) iOS
Answer:
(a) LINUX
Question 7.
_________ is an application software to create text document.
a) MS-Word
b) VLC player
c) MS-Excel
d) All the above
Answer:
a) MS-Word
Question 8.
The LINUX operating system was originated in ……………….
(a) 1996
(b) 1998
(c) 2000
(d) 1991
Answer:
(d) 1991
Question 9.
_________is a type of computer program that is designed to run the computer’s hardware and application programs,
a) application software
b) system software
c) both A and B
d) None of these
Answer:
b) system software
Question 10.
Which one of the following is an application software to play audio and video files?
(a) Audio Player
(b) Media Player
(c) VLC Player
(d) All of these
Answer:
(c) VLC Player
Question 11.
A(n)_________is system software which serves as an interface between and a computer.
a) Operating System
b) Language professor
c) VLC player
d) MS-Word
Answer:
a) Operating System
Question 12.
Which one of the following is a set of instructions that perform specific tasks?
(a) Hardware
(b) Software
(c) Processor
(d) I/O devices
Answer:
(b) Software
Question 13.
The function of an Operating System includes
a) file management and memory management
b) process management
c) device management
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 14.
The process of starting computer operation automatically when the power is turned on is called ……………….
(a) Booting
(b) Compiling
(c) executing
(d) Storing
Answer:
(a) Booting
Question 15.
When a computer is switched on, _________ is loaded into the memory automatically.
a) Operating System
b) Language
c) Application program
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Operating System
Question 16.
Identify the single user and single-task OS?
(a) MS – DOS
(b) UNIX
(c) LINUX
(d) iOS
Answer:
(a) MS – DOS
Question 17.
The popular Operating System used in personal computers and laptops is _________
a) Windows
b) UNIX
c) Linux
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 18.
To build a cheap computer, ………………. os is used.
(a) Windows
(b) Raspbion OS
(c) iOS
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) Raspbion OS
Question 19.
Operating System manage _________
a) Software
b) Hardware
c) Both A and B
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Both A and B
Question 20.
A ………………. is the unit of work or program in a computer.
(a) Process
(b) Code
(c) Concept
(d) Log file
Answer:
(a) Process
Question 21.
_________ works as translator
a) user and hardware
b) user and freeware
c) programmer and hardware
d) operating system
Answer:
d) operating system
Question 22.
System-level security is provided by ………………. in a multi-user environment.
(a) Permission
(b) execute
(c) Password
(d) Security code
Answer:
(c) Password
Question 23.
_________converts processed information into user readable form.
a) Operating System
b) Language Processor
c) Application program
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Operating System
Question 24
………………. os is used to access shared data that resides in any machine around the world.
(a) Time sharing
(b) fixed
(c) MS – Dos
(d) distributed
Answer:
(d) distributed
Question 25.
An operating system that allows only a single user to perform a task at a time is called as a _________ OS.
a) Single User
b) Single Task
c) Either A or B
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Single User
Question 26.
Unix was developed by?
(a) Ken Thompson
(b) Dennis Ritchie
(c) Both a & b
(d) Ricki Mascitti
Answer:
(c) Both a & b
Question 27.
_________is an example for a single user and single task Operating System.
a) Unix
b) MS-DOS
c) Both A and B
d) None of these
Answer:
b) MS-DOS
Question 28.
Google has developed ………………. for wristwatches.
(a) Android wear
(b) Android wrist
(c) Android wristwatches
(d) Android watches
Answer:
(a) Android wear
Question 29.
_________allows the same data and applications to be accessed by multiple users at the same time.
a) Multi-user
b) Multitask
c) Single user
d) MS-DOS
Answer:
a) Multi-user
PART – 2
II. Short Answers
Question 1.
What is software?
Answer:
Software is a set of instructions that perform specific tasks. It interacts basically with the hardware to generate the desired output.
Question 2.
What are the different types of Operating systems?
Answer:
Single user and single-task operating system, Multi-user operating system, Multi-Processing Operating system, Time sharing Operating system.
Question 3.
What is application software?
Answer:
Application software is a set of programs to perform specific tasks. For example, MS-word is an application software to create text document.
Question 4.
What is meant by Distributed Operating system?
Answer:
The data and applications are stored and processed in multiple locations around the world over the digital network.
Question 5.
List any 4 application software.
Answer:
- MS-Word.
- VLC player.
- MS-Excel.
- MS-Access.
Question 6.
What is an Interactive Operating system?
Answer:
This is the operating system that provides a GUI through which the user can navigate and interact.
Question 7.
Which serves as an interface between a user and a computer?
Answer:
An Operating System (OS) is system software which serves as an interface between a user and a computer.
Question 8.
What is Memory Management?
Answer:
It is the main functionality of an operating system which handles or manages primary memory and moves processes back and forth between main memory and disk during execution.
Question 9.
What are the popular operating systems used in personal computers and laptops?
Answer:
The popular Operating Systems used in personal computers and laptops are Windows, UNIX, and Linux.
Question 10.
What is Linux?
Answer:
Linux is a family of open-source operating systems.
Question 11.
What are the prominent operating Systems?
Answer:
Prominent OS is as follows:
- UNIX.
- Microsoft Windows.
- Linux.
- iOS.
- Android.
Question 12.
What are the types of software?
Answer:
Application software and System software
Question 13.
Write a note on ReactOS.
Answer:
ReactOS is a Windows-alternative open-source operating system, which is being developed on the principles of Windows – without using any of Microsoft’s code.
Question 14.
What is Round Robin Scheduling?
Answer:
This algorithm is designed especially for time-sharing systems.
Question 15.
Which OS is used to build a cheap computer?
Answer:
Build a cheap computer with raspbion OS and a Raspberry Pi.
Question 16.
Name an OS which is Multitasking and Multi-user operating system.
Answer:
UNIX.
PART – 3
III. Explain in Brief
Question 1.
Write a note on GUI.
Answer:
Modern operating systems use a Graphical User Interface(GUI). A GUI lets you use your mouse to click icons, buttons, menus, and everything is clearly displayed on the screen using a combination of graphics and text elements.
Each Operating System’s GUI has a different look and feel. Modern Operating Systems are designed to be easy to use and most of the basic principles are the same.
Question 2.
Why the operating system is needed?
Answer:
Need for the operating system:
Operating System has become essential to enable the users to design applications without the knowledge of the computer’s internal structure of hardware. Operating System manages all the Software and Hardware. Most of the time there are many different computer programmes running at the same time, they all need to access the Computers, CPU, Memory, and Storage. The need for an Operating System is basically – an interface between the user and hardware.
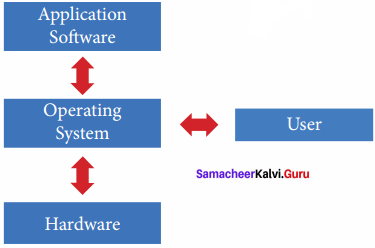
Operating System works as a translator, while it translates the user request into machine language(Binary language), processes it, and then sends it back to Operating System. Operating System converts processed information into the user-readable form.
Question 3.
Write a note on OS for mobile devices.
Answer:
Operating systems for mobile devices:
Mobile devices such as phones, tablets, and MP3 players are different from desktop and laptop computers and hence they need special Operating Systems. Examples of mobile Operating Systems are Apple iOS and Google Android. The iOS running on an iPad is Operating systems for mobile devices generally are not as fully featured as those made for desktop and laptop computers and they are not able to run all software.
Question 4.
Who developed the LINUX? Where it was developed?
Answer:
UNIX is a family of multitasking, multi-user operating systems that derive originally from AT&T Bell Labs, where the development began in the 1970s by Ken Thompson and Dennis Ritchie.
Question 5.
What is software? Explain its types in detail.
Answer:
Software is a set of instructions that perform specific tasks. It interacts basically with the hardware to generate the desired output.
Types of Software:
Software is classified into two types:
- Application Software
- System Software
Application Software:
Application software is a set of programs to perform a specific task. For example, MS-word is an application software to create text documents and VLC player is familiar application software to play audio, video files, and many more.
System Software:
The system software is a type of computer program that is designed to run the computer’s hardware and application programs. For example Operating System and Language Processor.
Question 6.
Explain the Operating systems for mobile devices?
Answer:
Mobile devices such as phones, tablets and MP3 players are different from desktop and laptop computers and hence they need special Operating Systems. Examples of mobile Operating Systems are Apple iOS and Google Android.
Operating systems for mobile devices generally are not as fully featured as those made for desktop and laptop computers and they are not able to run all software.
Question 7.
Write a note on Raspbion os?
Answer:
Raspbion os is a platform that is designed to teach how to build a computer, working principle of every part of a circuit board, write code apps or games. The platform is available in pre-designed kits.
Question 8.
Explain the memory management activities done by os?
Answer:
- Keeping track of which portion of memory are currently being used and who is using them.
- Determining which processes and data to move in and out of memory.
- Allocation and deallocation of memory blocks as needed by the program in main memory. (Garbage collection).
Question 9.
Explain iOS – iPhone OS.
Answer:
iOS (formerly iPhone OS) is a mobile Operating System created and developed by Apple Inc., exclusively for its hardware.
It is the Operating System that presently powers many of the company’s mobile devices, including the iPhone, iPad, and iPod Touch.
Question 10.
How are the processes classified on process management?
Answer:
A computer consists of a collection of the process they are classified into two categories:
- Operating system process which is executed by system code.
- User processes are executed by user code.
Question 11.
Explain memory management.
Answer:
Memory Management:
Memory Management is the process of controlling and coordinating a computer’s main memory and assigning memory blocks (space) to various running programs to optimize overall computer performance.
Memory management involves the allocation of specific memory blocks to individual programs based on user demands. At the application level, memory management ensures the availability of adequate memory for each running program at all times.
Question 12.
Write a note a Fault Tolerance?
Answer:
- The operating systems should be robust.
- When there is a fault, the operating system should not crash, instead, the os has fault tolerance capabilities and retain the existing state of the system.
Question 13.
What are the responsibilities of the Operating System irt connection with process management?
Answer:
The Operating System is responsible for the following activities associated with the process management:
Scheduling processes and threads on the CPUs.
- Creating and deleting both user and system processes.
- Suspending and resuming processes.
- Providing mechanisms for process synchronization.
- Providing mechanisms for process communication.
Question 14.
Give an example of the Time-Sharing concept?
Answer:
Let us assume that there are three processes called P1, P2, P3, and the time allocated for each process 30,40, 50 minutes. If the process P1 completes within 20 minutes then the processor takes the next Process P1 for the execution. If the process P2 could not complete within 40 minutes, then the current process P2 will be paused and switch over to the next process P3.
Question 15.
Explain Time Sharing with an example.
Answer:
This is one of the features of Operating Systems. It allows the execution of multiple tasks or processes concurrently. For each task a fixed time is allocated. This division of time is called Time-sharing. The processor switches rapidly between various processes after a time is elapses or the process is completed.
For example assume that there are three processes called P1, P2, P3 and time allocated for each process 30, 40, 50 minutes respectively. If the process PI completes within 20 minutes then the processor takes the next process P2 for the execution. If the process P2 could not complete within 40 minutes, then the current process P2 will be paused and switch over to the next process P3.
Question 16.
List any 6 Android Mobile Open Source OS.
Answer:
- Honeycomb
- Jelly Bean
- Kitkat
- Lollipop
- Marshmallow
- Nougat
PART – 4
IV. Explain in Detail
Question 1.
Write six uses of the operating system.
Answer:
The main use of the Operating System is
- to ensure that a computer can be used to extract what the user wants it to do.
- Easy interaction between the users and computers.
- Starting computer operation automatically when power is turned on (Booting).
- Controlling Input and Output Devices
- Manage the utilization of main memory.
- Providing security to user programs.
Question 2.
Draw the diagram for the key features of the operating system.
Answer:
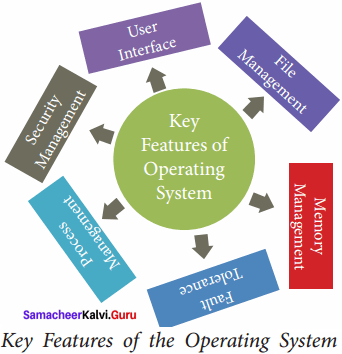
Question 3.
Explain the various types of operating systems.
Answer:
Operating systems are classified into the following types depending on their processing capabilities.
Single User Operating Systems:
An operating system allows only a single user to perform a task at a time. It is called a Single user and single Task operating system. For a user, a task is a function such as printing a document, writing a file to disk, editing a file or downloading a file, etc. MS-DOS is an example for a single user and single task Operating System.
Multi-user Operating Systems:
It is used in computers and laptops that allow the same data and applications to be accessed by multiple users at the same time. The users can also communicate with each other. Windows, Linux and UNIX are examples of multi-user Operating systems.
Question 4.
Explain Memory Management?
Answer:
Memory Management:
Memory Management is the process of controlling and coordinating a computer’s main memory and assigning memory blocks (space) to various running programs to optimize overall computer performance. Memory management involves the allocation of specific memory blocks to individual programs based on user demands. At the application level, memory management ensures the availability of adequate memory for each running program at all times.
The objective of the Memory Management process is to improve both the utilization of the CPU and the speed of the computer’s response to its users via main memory. For these reasons, the computers must keep several programs in the main memory that associates with many different Memory Management schemes.
The Operating System is responsible for the following activities in connection with memory management:
- Keeping track of which portion of memory are currently being used and who is using them.
- Determining which processes (or parts of processes) and data to move in and out of memory.
- Allocation and deallocation of memory blocks as needed by the program in main memory. (Garbage Collection)
Question 5.
Explain the various algorithms of process management.
Answer:
The following algorithms are mainly used to allocate the job (process) to the processor.
- FIFO
- SJF
- Round Robin
- Based on Priority
FIFO (First In First Out) Scheduling:
This algorithm is based on queuing technique. Assume that a student is standing in a queue to get grade sheet from his/her teacher. The other student who stands first in the queue gets his/ her grade sheet first and leaves from the queue. Followed by the next student in the queue gets it collected and so on. This is the basic logic of the FIFO algorithm.
Technically, the process that enters the queue first is executed first by the CPU, followed by the next and so on. The processes are executed in the order of the queue.
SJF (Shortest Job First)Scheduling:
This algorithm works based on the size of the job being executed by the CPU.
Consider two jobs A and B.
- A = 6 kilobytes,
- B = 9-kilobytes.
First, the job “A” will be assigned and then job “B” gets its turn.
Round Robin Scheduling:
The Round Robin (RR) scheduling algorithm is designed especially for time-sharing systems. Jobs (processes) are assigned and processor time in a circular method. For example take three jobs A, B, C. First the job A is assigned to CPU then job B and job C, and then again A, B, and C, and so on.
Based On Priority:
The given job (process) is assigned based on a Priority. The job which has higher priority is more important than other jobs. Take two jobs A and B. Let the priority of A be 5 and priority B be 7.
Job B is assigned to the processor before job A.