Students can Download Computer Science Chapter 9 Introduction to C++ Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 11th Computer Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 11th Computer Science Solutions Chapter 9 Introduction to C++
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Computer Science Introduction to C++ Text Book Back Questions and Answers
PART – 1
I. Choose The Correct Answer
11th Computer Science Chapter 9 Book Back Answers Question 1.
Who developed C++?
(a) Charles Babbage
(b) Bjame Stroustrup
(c) Bill Gates
(d) Sundar Pichi
Answer:
(b) Bjame Stroustrup
11th Computer Science Evaluate Yourself Answers Question 2.
What was the original name given to C++?
(a) CPP
(b) Advanced C
(c) C with Classes
(d) Class with C
Answer:
(c) C with Classes
Samacheer Kalvi Guru 11th Computer Science Question 3.
Who coined C++?
(a) Rick Mascitti
(b) Rick Bjame
(c) Bill Gates
(d) Dennis Ritchie
Answer:
(a) Rick Mascitti
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Computer Science Question 4.
The smallest individual unit in a program is:
(a) Program
(b) Algorithm
(c) Flowchart
(d) Tokens
Answer:
(d) Tokens
Computer Science Samacheer Kalvi Question 5.
Which of the following operator is extraction operator of C++?
(a) >>
(b) <<
(c) <>
(d) ^^
Answer:
(a) >>
Samacheer Kalvi.Guru 11th Computer Science Question 6.
Which of the following statements is not true?
(a) Keywords are the reserved words convey specific meaning to the C++ compiler.
(b) Reserved words or keywords can be used as an identifier name.
(c) An integer constant must have at least one digit without a decimal point.
(d) Exponent form of real constants consists of two parts
Answer:
(b) Reserved words or keywords can be used as an identifier name.
11th Samacheer Kalvi Computer Science Question 7.
Which of the following is a valid string literal?
(a) ‘A’
(b) ‘Welcome’
(c) 1232
(d) “1232”
Answer:
(d) “1232”
Samacheerkalvi.Guru Computer Science Question 8.
A program written in high level language is called as ……………….
(a) Object code
(b) Source code
(c) Executable code
(d) All the above
Answer:
(b) Source code
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Computer Science Book Back Answers Question 9.
Assume a = 5, b = 6; what will be result of a & b?
(a) 4
(b) 5
(c) 1
(d) 0
Answer:
(a) 4
Samacheer Kalvi Computer Science Book Question 10.
Which of the following is called compile time operators?
(a) size of
(b) pointer
(c) virtual
(d) this
Answer:
(a) size of
PART – 2
II. Answer to all the questions
Computer Science Chapter Question 1.
What is meant by a token? Name the token available in C++.
Answer:
The smallest individual unit in a program is known as a Token or a Lexical unit.
C++ has the following tokens:
- Keywords
- Identifiers (Variables)
- Literals (Constants)
- Operators
- Punctuators
Samacheer Kalvi Guru 11 Computer Science Question 2.
What are keywords? Can keywords be used as identifiers?
Answer:
Keywords are the reserved words which convey specific meaning to the C++ compiler. They are the essential elements to construct C++ programs. Most of the keywords are common to C, C++, and Java. Keywords are reserved and cannot be used as identifiers.
Question 3.
The following constants are of which type?
- 39
- 032
- OXCAFE
- 04.14
Answer:
- 39 – Decimal Constant
- 032 – Octal Constant
- 0XCAFE – Hexadecimal Constant
- 04.14 – Integer Constant.
(A fractional number that begins with 0, C++ has considered the number as an integer, not an Octal)
Question 4.
Write the following real constants into the exponent form:
- 23.197 00
- 7.214
- 0.00005
- 0.319
Answer:
- 23.197 = 0.23197 x 102 = 0.23197E2
- 00 7.214 = 0.7214 x 101 = 0.7214E1
- 0.00005 = 0.5 x 10-4 = 0.5E – 4
- 0.319 = 3.19 x 10-1 = 3.19E – 1
Question 5.
Assume n = 10; what will be result of n>>2;?
Answer:
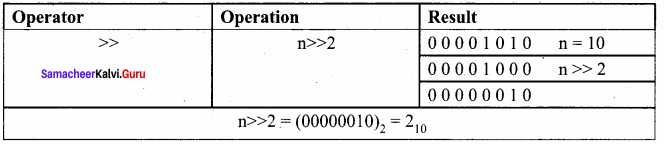
Question 6.
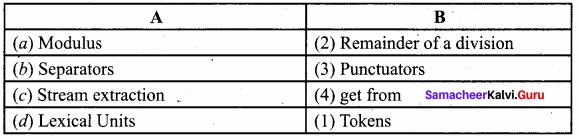
Match the following:
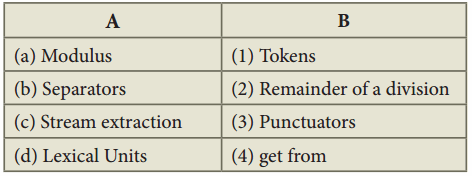
Answer:
PART – 3
III. Answer to all the questions
Question 1.
Describe the differences between keywords and identifiers?
Answer:
- Keywords are the reserved words which convey specific meaning to the C++ compiler.
Example: int / private / float / long - Identifiers are the user-defined names given to different parts of the C++ program viz. variables, functions, arrays, classes, etc. Example: sum, average, big, small
- Reserved words or keywords cannot be used as an identifier name.
Question 2.
Is C++ case sensitive? What is meant by the term “case sensitive”?
Answer:
C++ is a case-sensitive programming language so, all the keywords must be in lowercase. Case sensitive means that the uppercase and lowercase letters are considered differently.
Question 3.
Differentiate “=” and “==”.
Answer:
| = | = = |
| ‘=’ is an assignment operator | ‘= =’ is equal to the operator and it is a relational operator. |
| It is used to assign the value of a variable or expression | It is used for comparison of both left and right side operands. |
Question 4.
Assume a = 10, b = 15; What will be the value of a^b?
Answer:
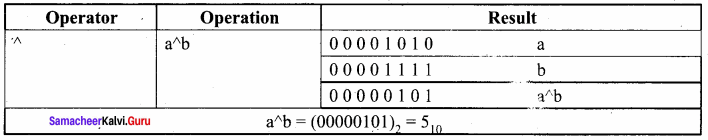
Question 5.
What is the difference between “Run time error” and “Syntax error”?
Answer:
- Syntax errors occur when grammatical rules of C++ are violated.
- A run time error occurs during the execution of a program. It occurs because of some illegal operation that takes place.
Question 6.
What are the differences between “Logical error” and “Syntax error”?
Answer:
Logical Error: Logical errors occur when there is an incorrect usage of variable/operator/order of execution etc. It is also called a Semantic Error.
Syntax Error: Syntax errors occur when grammatical rules of C++ are violated.
Question 7.
What is the use of a header file?
Answer:
- #include statement tells the compiler’s preprocessor to include the header file “iostream” in the program.
- The header file iostream should include in every C++ program to implement input/output functionalities.
- In simple words, iostream header file contains the definition of its member objects cin and cout. If we fail to include iostream in our program, an error message will occur on cin and cout; and we will not be able to get any input or send any output.
Question 8.
Why is the main function special?
Answer:
C++ program is a collection of functions. Every C++ program must have a main function. The main() function is the starting point where all C++ programs begin their execution. Therefore, the executable statements should be inside the main() function.
Question 9.
Write two advantages of using include compiler directive.
Answer:
- Usually, all C++ programs begin with include statements starting with a # (hash/pound). The symbol # is a directive for the preprocessor. That means these statements are processed before the compilation process begins.
- #include <iostream> statement tells the compiler’s preprocessor to include the header file “iostream” in the program.
Question 10.
Write the following in real constants.
- 15.223
- 211.05
- 0.00025
Answer:
- 15.223 = 0.15223E2
- 211.05 = 0.21105E3
- 0.00025 = 0.25E – 3
PART – 4
IV. Answer all the questions
Question 1.
Write about Binary operators used in C++.
Answer:
Binary Operators Require two operands.
- The arithmetic operators addition(+), subtraction(-), multiplication(*), division(/) and Modulus(%) are binary operators which requires two operands.
- All six relational operators are binary operators.
- The logical operators &&(AND) and // (OR) are binary operators.
Question 2.
What are the types of Errors?
Answer:
| Type of Error | Description |
| Syntax Error | Syntax errors occur when grammatical rules of C++ are violated. |
| Semantic Error | Semantic Error occurs when there is the wrong use of variable/operator/order of execution etc. It is also called a Logical Error. |
| Run – time error | A run time error occurs during the execution of a program. It occurs because of some illegal operation that takes place. |
Question 3.
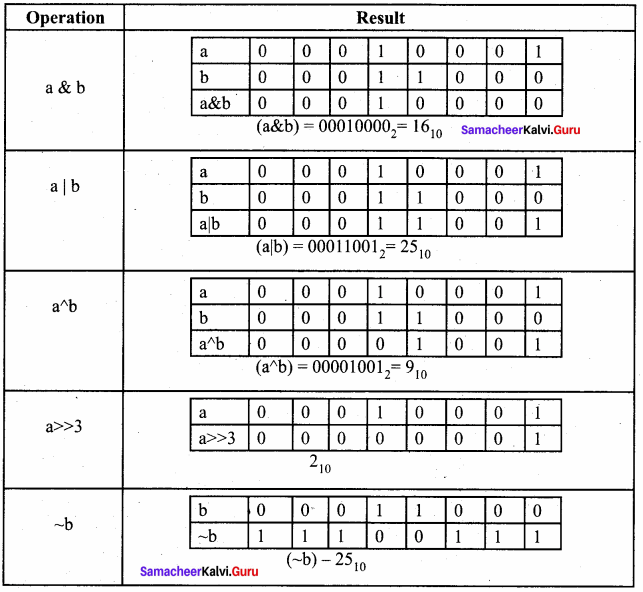
Assume a = 15, b = 20; What will be the result of the following operations?
(a) a&b
(b) a|b
(c) a^b
(d) a>>3
(e) (~b)
Answer:
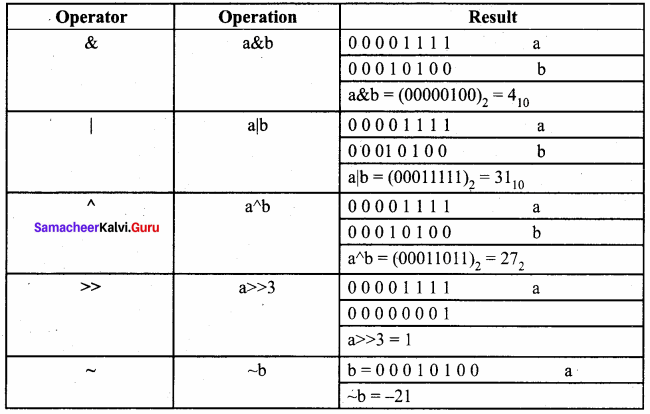
PART – 1
I. Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
How many categories of data types available in C++?
(a) 5
(b) 4
(c) 3
(d) 2
Answer:
(c) 3
Question 2.
Which of the following data types is not a fundamental type?
(a) signed
(b) int
(c) float
(d) char
Answer:
(a) signed
Question 3.
What will be the result of the following statement?
char ch= ‘B’;
cout<< (int) ch;
(a) B
(b) b
(c) 65
(d) 66
Answer:
(d) 66
Question 4.
Which of the character is used as a suffix to indicate a floating-point value?
(a) F
(b) C
(c) L
(d) D
Answer:
(a) F
Question 5.
How many bytes of memory allocates for the following variable declaration if you are using Dev C++? short int x;
(a) 2
(b) 4
(c) 6
(d) 8
Answer:
(a) 2
Question 6.
What is the output of the following snippet?
char ch =‘A’;
ch = ch + 1;
(a) B
(b) A1
(c) F
(d) 1A
Answer:
(a) B
Question 7.
Which of the following is not a data type modifier?
(a) signed
(b) int
(c) long
(d) short
Answer:
(b) int
Question 8.
Which of the following operator returns the size of the data type?
(a) sizeof()
(b) int ()
(c) long ()
(d) double ()
Answer:
(a) sizeof()
Question 9.
Which operator is used to access reference of a variable?
(a) $
(b) #
(c) &
(d) !
Answer:
(c) &
Question 10.
This can be used as alternate to endl command:
(a) \t
(b) \b
(a) \0
(d) \n
Answer:
(d) \n
PART – 2
II. Answer to all the questions
Question 1.
Write a short note const keyword with an example.
Answer:
const is the keyword used to declare a constant, const keyword modifies/restricts the accessibility of a variable. So, it is known as Access modifier.
Question 2.
What is the use of setw( ) format manipulator?
Answer:
setw manipulator sets the width of the field assigned for the output. The field width determines the minimum number of characters to be written in output.
Syntax:
setw(number of characters)
Question 3.
Why is char often treated as integer data type?
Answer:
Character data type accepts and returns all valid ASCII characters. Character data type is often said to be an integer type, since all the characters are represented in memory by their associated ASCII Codes. If a variable is declared as char, C++ allows storing either a character or an integer value.
Question 4.
What is a reference variable? What is its use?
Answer:
Reference variable in C++ is alias for existing variable. They store nothing but the address of the variable used at the time of its declaration. It is important to assign the reference variable at the time of declaration, else it will show an error.
Question 5.
Consider the following C++ statement. Are they equivalent?
char ch = 67;
charch = ‘C’;
Answer:
Both the statements are equivalent as they declare ‘ch’ to be char and initialize it with the value of 67. Since this is the ASCII code for ‘C’, the character constant also can be used to initialize ‘ch’ to 67.
Question 6.
What is the difference between 56L and 56?
Answer:
56L – The suffix L forces the constant to be represented as long, which occupies 4 bytes.
56 – This will be represented as int type constant which occupies 2 bytes as per Turbo C++.
Question 7.
Determine which of the following are valid constant? And specify their type.
- 0 0.5
- ‘Name’
- ‘\t’
- 27,822
Answer:
- 0.5 – is a valid constant. It is a decimal.
- ‘Name’ – Invalid constant as single quote is not allowed.
- ‘\t’ – Escape sequence (or) non – graphical character (horizontal tab).
- 27,822 – Invalid constant. Comma is not allowed.
Question 8.
Suppose x and y are two double type variable that you want add as integer and assign to an integer variable. Construct a C++ statement for the doing so.
Answer:
double x = 10.5, y = 4.5; int a;
a = int (x) + int (y);
Question 9.
What will be the result of following if num=6 initially.
(a) cout << num;
(b) cout << (num==5);
Answer:
(a) 6 (b) False
Question 10.
Which of the following two statements are valid? Why? Also w rite their result, int a; a = 3,014; a=(3,014);
Answer:
It is invalid as comma is not allowed in an integer constant. It is valid. Comma in bracket is allowed.
PART – 3
III. Answer to all the questions
Question 1.
What are arithmetic operators in C++? Differentiate unary and binary arithmetic operators. Give example for each of them.
Answer:
Arithmetic operators : perform simple arithmetic operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, division etc.
Unary Operators : Require only one operand . Example: +, -, *, /, %, >, <, <=, AND, OR
Binary Operators:
- Require two operands
- Example: ++ (Plus, Plus) Increment operator, – – (Minus, Minus) Decrement operator, NOT, ~,
Question 2.
Evaluate x + = x + + + x; Let x = 5;
Answer:
x + = x + + + x (x = 5) x + = x + + + 5 (x becomes 6)
x + = 6 + 6
x + = 12
x = 6 + 12
x = 18
Question 3.
How relational operators and logical operators are related to one another?
Answer:
Relational operators are used to determine the relationship between its operands. When the relational operators are applied on two operands, the result will be a boolean value 1 or 0 which represents True or False respectively which represents logical operator.
Question 4.
Evaluate the following C++ expressions where x, y, z are integers and m, n are floating point numbers. The value of x = 5, y = 4 and m = 2.5;
Answer:
- n = x + y / x;
- z = m * x + y;
- z = (x++) * m + x;
Answer:
1. n = x + y / x;
= 5 + 4/5
= 5 + 0 (both x and y are int type. Therefore only integer part of quotient is considered)
=5
2. z = m * x + y;
= 2.5 * 5 + 4 (m is float type, so x value is promoted to float [implicit conversion])
= 12.5 + 4 ‘
= 16 (2 is int type. So ‘.2’, the fractional part is discarded)
3. z = (x++) * m + x;
= 5*2.5 + x
= 12.5 + 5
= 18 (z is int type, therefore the fractional part is removed, x is incremented after the addition)
Samacheer kalvi 11th Computer Science Introduction to C++ Additional Questions and Answers
PART – 1
I. Choose The Correct Answer
Question 1.
Who invented the C++ language?
a) Linus Torvalds
b) Rick Mascitti
c) Dennis Ritchie
d) None of these
Answer:
d) None of these
Question 2.
The smallest individual unit in a program is known as ……………..
(a) token
(b) lexical unit
(c) lexical element
(d) all the above
Answer:
(d) all the above
Question 3.
C++ language was developed during ……………..
a) 1989
b) 1979
c) 1969
d) 2009
Answer:
b) 1979
Question 4.
The exponent form of real constants consists of parts.
(a) 3
(b) 2
(c) 5
(d) 4
Answer:
(b) 2
Question 5.
C++is called a ……………. language.
a) Hybrid
b) Hierarchical
c) Homogeneous
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Hybrid
Question 6.
Match the following

(a) 1 – (i) 2 – (ii) 3 – (iii) 4 – (iv)
(b) 1 – (iv) 2 – (ii) 3 – (iii) 4 – (i)
(c) 1 – (i) 2 – (iii) 3 – (ii) 4 – (iv)
(d) 1 – (i) 2 – (ii) 3 – (iv) 4 – (iii)
Answer:
(b) 1 – (iv) 2 – (ii) 3 – (iii) 4 – (i)
Question 7.
Bjarne Stroustrup named his new language as……………
a) C with Classes
b) C with Objects
c) C with Structures
d) None of these
Answer:
a) C with Classes
Question 8.
Match the following

(a) 1 – (i) 2 – (ii) 3 – (iii) 4 – (iv)
(b) 1 – (ii) 2 – (iv) 3 – (i) 4 – (iii)
(c) 1 – (i) 2 – (iii) 3 – (ii) 4 – (iv)
(d) 1 – (i) 2 – (ii) 3 – (iv) 4 – (iii)
Answer:
(d) 1 – (i) 2 – (ii) 3 – (iv) 4 – (iii)
Question 9.
In the name C++,++is the ………….. language increment operator.
a) Ada
b) BCPL
c) Simula
d) C
Answer:
d) C
Question 10.
In programming language …………….. are referred as variables and the values are referred to as data.
(a) constant
(b) integer
(c) fields
(d) files
Answer:
(c) fields
Question 11.
Which year the name was changed to C++ by Rick Mascitti?
a) 1983
b) 1993
c) 2003
d) 1973
Answer:
a) 1983
Question 12.
Syntax for reference is ……………..
(a) =
(b) = <& reference>
(c) <&reference_variable>=
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c) <&reference_variable>=
Question 13.
…………. is the language of choice for multidevice, multi-platform app development.
a) Ada
b) BCPL
c) Simula
d) C++
Answer:
d) C++
Question 14.
…………….. is used to set the number of decimal places to be displayed.
(a) Set precision
(b) Garbage
(c) Constant
(d) All the above
Answer:
(a) Set precision
Question 15.
Match the following

(a) 1 – (iv) 2 – (iii) 3 – (ii) 4 – (i)
(b) 1 – (i) 2 – (ii) 3 – (iii) 4 – (iv)
(c) 1 – (iv) 2 – (i) 3 – (i) 4 – (iii)
(d) 1 – (iv) 2 – (iii) 3 – (i) 4 – (ii)
Answer:
(a) 1 – (iv) 2 – (iii) 3 – (ii) 4 – (i)
PART – 2
II. Short Answers
Question 1.
What are the languages influenced by C++?
Answer:
C# (C-Sharp), D, Java, and newer versions of C languages have been influenced by C++.
Question 2.
What is the use of Boolean literals?
Answer:
Boolean literals are used to represent one of the Boolean values (True or false). Internally true has value 1 and false has value 0.
Question 3.
Define Character set.
Answer:
The character set is a set of characters which are allowed to write a C++ program.
Question 4.
What are the types of bitwise operators?
Answer:
In C++, there are three kinds of bitwise operators, which are:
- Logical bitwise operators
- Bitwise shift operators
- One’s complement operators
Question 5.
Define Literals or Constants.
Answer:
Literals are data items whose values do not change during the execution of a program. Therefore Literals are called as Constants.
Question 6.
Expand IDE and GNU.
Answer:
IDE stands for Integrated Development Environment and GNU stands for General Public License.
Question 7.
What is the use of suffix L and U?
Answer:
The suffix L or I and L) or u added with any constant forces that to be represented as a long or unsigned constant respectively.
Question 8.
Write a C++ program to accept any character and display its next character.
Answer:
C++ Program to accept any character and display its next character

The output produced by the program will be
Enter a character: A
The Next character: B
Question 9.
Write C++ program to find the area of circle.
Answer:
C++Program to find the area of circle
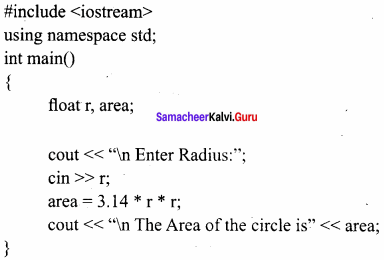
Output:
Enter Radius: 6.5
The Area of the circle is 132.665
Question 10.
What is Junk (or) Garbage values?
Answer:
If you declare a variable without any initial value, the memory space allocated to that variable will be occupied with some unknown value. These unknown values are called as “Junk” or “Garbage” values.
PART – 3
III. Explain in Brief
Question 1.
What are the uses of Set precision?
Answer:
setprecision () prints the values from left to right. For the above code, first, it will take 4 digits and then prints one digit from fractional portion. setprecision can also be used to set the number of decimal places to be displayed. In order to do this task, you will have to set an ios flag within self() manipulator. This may be used in two forms: fixed and (i) fixed (ii) scientific These two forms are used when the keywords fixed or scientific are appropriately used before the set precision manipulator.
Question 2.
Define – Expression?
Answer:
An expression is a combination of operators, constants, and variables arranged as per the rules of C++. It may also include function calls which return values.
Question 3.
What do you mean by lexical units or lexical elements? Explain.
Answer:
C++ program statements are constructed by many different small elements such as commands, variables, constants, and many more symbols called operators and punctuators. These individual elements are collectively called Lexical units or Lexical elements or Tokens.
C++ has the following tokens:
- Keywords
- Identifiers
- Literals
- Operators
- Punctuators
Question 4.
What is typecasting? Write its syntax?
Answer:
C++ allows explicit conversion of variables or expressions from one data type to another specific data type by the programmer. It is called “typecasting”.
Syntax:
(type – name) expression;
Where type – name is a valid C++ data type to which the conversion is to be performed.
Question 5.
What kind of constants is the following?
- 0X568
- – 27
- – 27
Answer:
- Hexadecimal
- Decimal
- Octal
Question 6.
What is a numeric constant? Mention its types.
Answer:
Numeric Constants: The numeric constants are numeric values, which are used as constants. Numeric constants are further classified as:
- Integer Constants (or) Fixed point constants.
- Real constants (or) Floating-point constants.
Question 7.
Convert the following real constants into exponent form:
- 12.0005
- 0.00000009
- 7.9283
Answer:
0 12.0005 = 0.120005 x 102 = 0.120005E2
0.00000009 = 0.9 x 10-7 = 0.9E-7
7.9283 = 0.79283 x 101 = 0.79283E1
Question 8.
If a = 15; what is the result of a<<3 and a >> 2?
If a = 15; equivalent binary value of a is 00001111
Answer:
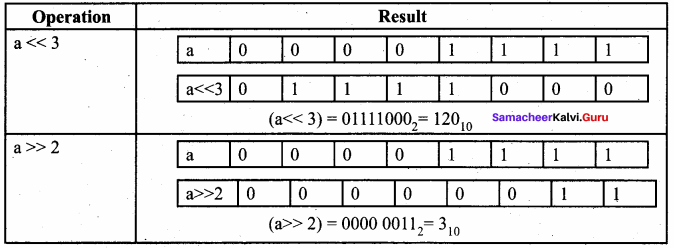
Question 9.
If b = 15 what is the result of ~b?
If b = 15; equivalent binary value of b is 00001111
Answer:
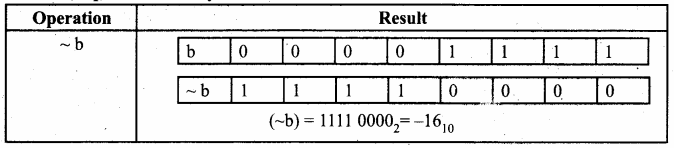
Question 10.
If a = 65, b = 15, what is the result of a|b?
Equivalent Binary values of 65 = 01000001; 15 = 00001111
Answer:
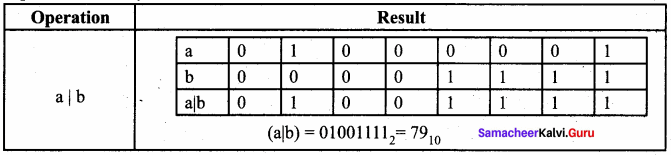
PART – 4
IV. Explain in Detail
Question 1.
Explain steps involved in creating and executing of C++ program.
Answer:
For creating and executing a C++ program, one must follow four important steps.
1. Creating Source code: Creating includes typing and editing the valid C++ code as per the rules followed by the C++ Compiler.
2. Saving source code with extension .cpp
After typing, the source code should be saved with the extension .cpp
3. Compilation:
This is an important step in constructing a program. In compilation, the compiler links the library files with the source code and verifies each and every line of code. If any mistake or error is found, it will inform you to make corrections. If there are no errors, it translates the source code into a machine-readable object file with an extension .obj
4. Execution
Execution is the final step of the construction of a C++ Program. In this stage, the object file becomes an executable file with extension .exe. Once the program becomes an executable file, the program has an independent existence. This means you can run your application without the help of any compiler or IDE.
Question 2.
Explain working with Dev C++.
Answer:
Dev C++ is an open-source, cross-platform (alpha version available for Linux), full-featured Integrated Development Environment (IDE) distributed with the GNU General Public License for programming in C and C++. It is written in Delphi. It can be downloaded from
http://www.bloodshed.net/dev/devcpp.html
After installation Dev C++ icon is available on the desktop. Double click to open IDE. Dev C++ IDE appears.
To create a source file, Select File → New → Source file or Press Ctrl + N.
On the screen that appears, type your C++ program, and save the file by clicking File → Save or Pressing Ctrl + S. It will add .cpp by default at the end of your source code file. No need to type .cpp along with your file name.
After save, Click Execute → Compile and Run or press F11 key.
After successful compilation, output will appear in output console, as follows
Question 3.
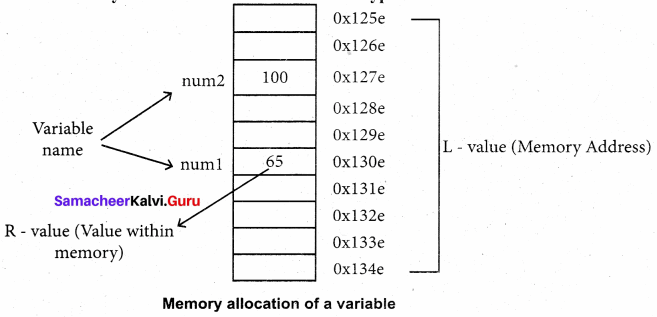
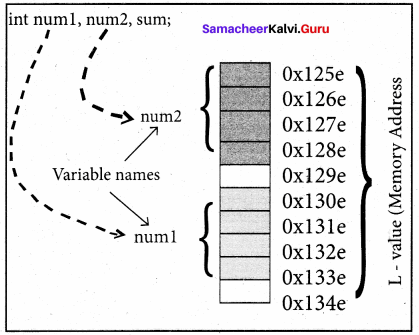
Draw memory allocation of a variable and int type variable.
Answer:
Question 4.
Write the C++ program to find the curved surface area of the cylinder.
C++ Program to find the Curved Surface Area of a cylinder (CSA) (CSA = 2 nr * h)
Answer:
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
float pi = 3.14, radius, height, CSA;
cout << “\n Curved Surface Area of a cylinder”;
cout << “\n Enter Radius (in cm):”; cin >> radius;
cout << “\n Enter Height (in cm):”; cin >> height;
CSA = (2*pi*radius)*height; system (“els”);
cout << “\n Radius:” << radius « “cm”;
cout << “\n Height:” << height« “cm”;
cout << “\n Curved Surface Area of a Cylinder is” << CSA «“sq. cm.”;
}
Output:
Curved Surface Area of a cylinder
Enter Radius (in cm) : 7
Enter Height (in cm) : 20
Radius : 7cm
Height : 20cm
The curved Surface Area of a Cylinder is 879.2 sq. cm.
Question 5.
Write the C++ program to calculate Net salary.
Program to Calculate Net Salary
Answer:
#include
#include using namespace std;
int main()
{
float basic, da, hra, gpf, tax, gross, np; char name[30];
cout << “\n Enter Basic Pay:”; cin >> basic;
cout<< “\n Enter D.A cin >> da;
cout << “\n Enter H.R.A:”; cin >> hra;
gross = basic+da+hra; // sum of basic, da nad hra
gpf = (basic+da) * 0.10; //10% of basic and da
tax = gross * 0.10; //10% of gross pay
np = gross – (gpf+tax); //netpay = earnings – deductions
cout << setw(25) << “Basic Pay:” << setw(10) << basic << endl;
cout << setw(25) << “Dearness Allowance:”<< setw(10) << da << endl;
cout << setw(25) << “House Rent Allowance:” << setw(10) << hra << endl;
cout << setw(25) << “Gross Pay:” << setw(10) << gross << endl;
cout << setw(25) << “G.P.F:” << setw(10) << gpf << endl;
cout << setw(25) << “Income Tax:” << setw(10) << tax << endl;
cout << setw(25) << “Net Pay:” << setw(10) << np << endl;
}
The output will be,
Enter Basic Pay: 12000
Enter D.A: 1250
Enter H.R.A : 1450
Basic Pay: 12000
Dearness Allowance: 1250
House Rent Allowance: 1450
Gross Pay: 14700
G.P.F : 1325
Income Tax: 1470
Net Pay: 11905
Question 6.
If a = 17, b = 24, what is the result of the following?
- a & b
- a|b
- a^b
- a>>3
- ~ b
Answer: