You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 11th Maths Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 11th Maths Solutions Chapter 12 Introduction to Probability Theory Ex 12.1
Question 1.
An experiment has the four possible mutually exclusive and exhaustive outcomes A, B, C and D. Check whether the following assignments of probability are permissible.
(i) P(A) = 0.15, P(B) = 0.30, P(C) = 0.43, P(D) = 0.12
(ii) P(A) = 0.22, P(B) = 0.38, P(C) = 0.16, P(D) = 0.34
(iii) P(A) = \(\frac{2}{5}\), P(B) = \(\frac{3}{5}\), P(C) = \(-\frac{1}{5}\), P(D) = \(\frac{1}{5}\)
Solution:
When A, B, C, D are the possible exclusive and exhaustive events the P(A) + P(B) + P(C) + P(D) = 1.
(i) P(A) = 0.15, P(B) = 0.30, P(C) = 0.43, P(D) = 0.12
Now P(A) + P(B) + P(C) + P(D) = 0.15 + 0.30 + 0.43 + 0.12 = 1
0.15 + 0.30 + 0.43 + 0.12 = 1
∴ The assignment of probability is permissible
(ii) P(A) = 0.22, P(B) = 0.38, P(C) = 0.16, P(D) = 0.34
Now P(A) + P(B) + P(C) + P(D) = 1
0.22 + 0.38 + 0.16 + 0.34 = 1.10 = ≠1
∴ The assignment of probability is not permissible.
(iii) P(A) = \(\frac{2}{5}\), P(B) = \(\frac{3}{5}\), P(C) = \(-\frac{1}{5}\), P(D) = \(\frac{1}{5}\)
P(C) = \(-\frac{1}{5}\) which is not possible
(i.e.) for any event A, (0 ≤ P(A) ≤ 1)
∴ The assignment of probability is not permissible.
![]()
Question 2.
If two coins are tossed simultaneously, then find the probability of getting
(i) one head and one tail
(ii) at most two tails
Solution:
When two coins are tossed the sample space will be
S = {(H, H), (H, T), (T, H), (T, T)}
n(S) = 4
(i) probability of getting 1 head and one tail = \(\frac{2}{4}=\frac{1}{2}\)
(ii) Probability of getting atmost two tails = \(\frac{4}{4}\) = 1
Question 3.
Five mangoes and 4 apples are in a box. If two fruits are chosen at random, find the probability that (i) one is a mango and the other is an apple (ii) both are of the same variety.
Solution:
(i) Mangoes (M) = 5
Apples (A) = 4 Total = 5 + 4=9
P(mango) = P(M) = 5/9
P(A) = 4/9.
When two Suits are chosen at random
P(one mango and one Apple) = P(MA or AM)
= P(M)P (A) × 2!
= \(\frac{5}{9} \times \frac{4}{8} \times 2 !=\frac{5}{9}\)
(PCM) = \(\frac{5}{9}\) (Sell from 5 mangoes and set 1 from a fruit)
P(A) = \(\frac{4}{8}\) (Sel 1 from 4 apples and set 1 from the remaining 8 fruits)
(ii) P(MMorAA)
= P(M) P(M) + P(A) P(A)
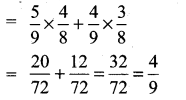
Question 4.
What is the chance that (i) non-leap year (ii) leap year should have fifty three Sundays?
Solution:
(i) Non leap year
No of days =365
= \(\frac{365}{7}\) weeks = 52 weeks + 1 day
In 52 week we have 52 Sundays. So we have to find the probability of getting the remaining one day as Sunday. The remaining 1 day can be Sunday, Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday, Friday, Saturday
(i.e.,) n(S) = 7
In the n (Sunday) = A {Saturday to Sunday or Sunday to Monday}
(i.e.,) n(A) = 1
So, P(A) = 1.
∴ Probability of getting 53 Sundays \(\frac{n(\mathrm{A})}{n(\mathrm{S})}=\frac{1}{7}\)
(ii) Leap Year:
In 52 weeks we have 52 Sundays. We have to find the probability of getting one Sunday form the remaining 2 days the remaining 2 days can be a combination of the following S = {Saturday to Sunday, Sunday to Monday, Monday, to Tuesday, Tuesday to wednes¬day, Wednesday to Thursday, Thursday to Friday, Friday and Saturday}.
(i.e) n(s) =7
In this = A {Saturday to Sunday, Sunday to Monday}
(i.e) n(A) = 2
So, P(A) = \(\frac{2}{7}\)
![]()
Question 5.
Eight coins are tossed once, find the probability of getting
(i) exactly two tails
(ii)at least two tails
(iii) at most two tails
Solution:
When a coin is tossed 8 times or 8 coins are tossed one time n(s) = 28 = 256
(i) Let A be the event of getting exactly 2 tails.
Here n(A) = 8C2 = \(\frac{8 \times 7}{2 \times 1}\) = 28
P(A) = \(\frac{n(\mathrm{A})}{n(\mathrm{S})}=\frac{28}{256}=\frac{7}{64}\)
(ii) Let B be the event of getting at least two facts.
n(B) = 8C2 + 8C3 + ……….. + 8C8
= n( S) – (8C0 + 8C1) = 256 – (1 + 8) = 247
P(B) = \(\frac{n(\mathrm{B})}{n(\mathrm{S})}=\frac{247}{256}\)
(iii) Let C be the event of getting atmost two facts.
n(C) = 8C0 + 8C1 + 8C0
= 1 + 8 + \(\frac{8 \times 7}{2 \times 1}\) = 1 + 8 + 28 = 37
P(C) = \(\frac{n(\mathrm{C})}{n(\mathrm{S})}=\frac{37}{256}\)
![]()
Question 6.
An integer is chosen at random from the first 100 positive integers. What is the probability that the integer chosen is a prime or multiple of 8?
Solution:
S= {1, 2, 3, …………. 100}
n(S) = 100
Let A be the event of choosing a prime number
∴ A = {2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37, 41, 43, 47, 53, 59, 61, 67, 71, 73, 79, 83, 89}
n(A) = 25 So P(A) = \(\frac{25}{100}\)
Let B be the event of getting a number multiple of 8
B = {8, 16, 24, 32, 40, 48, 56, 64, 72, 80, 88, 96}
n(B)= 12 So P(B) = \(\frac{12}{100}\)
also A ∩ B = ϕ
⇒ A and B are mutually exclusive
∴ P(A ∪ B) = P(A) + P(B) = \(\frac{25}{100}+\frac{12}{100}=\frac{37}{100}\)
Question 7.
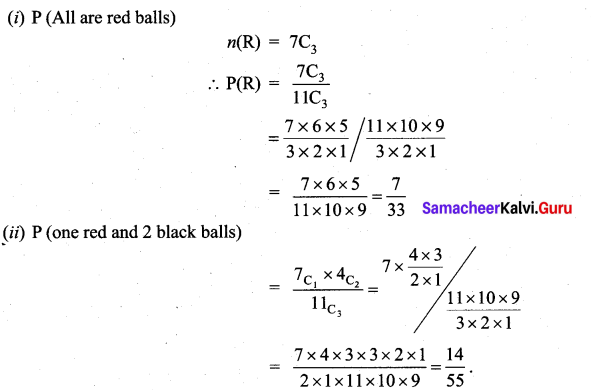
A bag contains 7 red and 4 black balls, 3 balls are drawn at random.
Find the probability that (i) all are red (ii) one red and 2 black.
Solution:
No. of Red balls = n(R) = 7
No. of Black balls = n(B) = 4
Total = 7 + 4 = 11 ⇒ n(S) = 11
Three balls are drawn at random
Question 8.
A single card is drawn from a pack of 52 cards. What is the probability that
(i) the card is an ace or a king
(ii) the card will be 6 or smaller
(iii) the card is either a queen or 9?
Solution:
Total No. of cards = 52 = n(S)
No. of ace cards = n(A) = 4
No. of king card = n(k) = 4
(i) P(A or K) = P(A) + P(K)
(∵ A and K are mutually exclusive).
= \(\frac{n(\mathrm{A})}{n(\mathrm{S})}+\frac{n(\mathrm{K})}{n(\mathrm{S})}=\frac{4}{52}+\frac{4}{52}\)
= \(\frac{8}{52}=\frac{2}{13}\)
(ii) Let B be the event of getting a number be 6 or smaller
So the numbers can be 6, 5, 4, 3, 2
There are 4 types of cards
So n(B) = 4 × 5 = 20
and So, p(B) = \(\frac{n(\mathrm{B})}{n(\mathrm{S})}=\frac{20}{52}=\frac{5}{13}\)
(iii) Let C be the event of getting a queen ⇒ so n(c) = 4
and Let D be the event of getting a number 9 ⇒ n(D) = 4
Now C ∩ D = ϕ
(i.e.,) C and D are mutually exclusive.
∴ P(C ∪ D) = P(C) + P(D) = \(\frac{4}{52}+\frac{4}{52}=\frac{8}{52}\)
= \(\frac{2}{13}\)
Question 9.
A cricket club has 16 members, of whom only 5 can bowl. What is the probability that in a team of 11 members at least 3 bowlers are selected?
Solution:
No. of players = 16
We need to select 11 players which can be done in 16 C11 ways
(i. e) n(S) = 16C11 ways
= 4368
Out of the selection of 11 members there should be a least 3 bowler So we can have 3 or 4 or 5 bowlers and S the remaining will be 8 or 7 or 6 players. So the selection can be done as follows.

Let A be the event of selecting atleast 3 bowlers out of a selection of 11 players.
So n(A) = (5C3 × 11C8) + (5C4 × 11C7) + (5C5) (11C6)
∴ 5C3 = 10, 5C4 = 5, 5C5 = 1
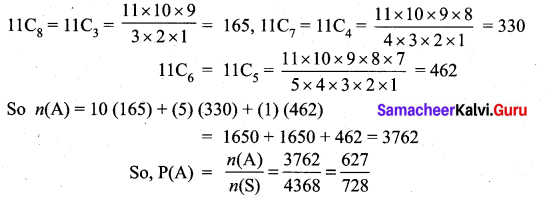
![]()
Question 10.
(i) The odds that the event A occurs is 5 to 7, find P(A)
(ii) Suppose P(B) = \(\frac{2}{5}\). Express the odds that the event B occurs.
Solution:
If the probability of an event is P then the odds is favour of its occurrence are P to (1 – P) and the odds against its occurrence are (1 – P) to P.
Here we are given the odds that The event A occurs = 5 to 7
So, the odds that the event B occurs is 2 to 3.
∴ P(A) = \(\frac{5}{5+7}=\frac{5}{12}\)
(ii) We are given P(B) = \(\frac{2}{5}\)
(i.e.,) P(B) = \(\frac{2}{2+3}\)
So, the odds that the event B occurs is 2 to 3.
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Maths Solutions Chapter 12 Introduction to Probability Theory Ex 12.1 Additional Problems
Question 1.
An experiment has the four possible mutually exclusive outcomes A, B, C and D. Check whether the following assignments of probability are permissible.
P(A) = 0.32, P(B) = 0.28, P(C) = -0.06, P(D) = 0.46
Solution:
Probability of an event cannot be negative. Here P(C) = – 0.06.
∴ the above set of events are not possible.
P(A) = \(\frac{1}{3}\), P(B) = \(\frac{1}{6}\), P(C) = \(\frac{2}{9}\), P(D) = \(\frac{5}{18}\)
Question 2.
In a single throw of two dice, find the probability of obtaining
(i) sum of less than 5
(ii) a sum of greater than 10
(iii) a sum of 9 or 11.
Solution:
The sample space when throwing two dice once =
{(1, 1), (1, 2), …………. (1, 6)
(2, 1), ………… (2, 6)
:
:
(6, 1), ……….. (6, 6)}
n(S) = 62 = 36
(i) Let A be the event of getting a sum less than 5.
Then A = {(1, 1), (1, 2), (1, 3) (2, 1),(2, 2) (3, 1)}
n(A) = 6
∴ P(A) = \(\frac{n(\mathrm{A})}{n(\mathrm{S})}=\frac{6}{36}=\frac{1}{6}\)
(ii) Let B be the event of getting a sum greater than 10.
∴ The sum will be 11 or 12.
Now the numbers whose sum is 11.
= {(5, 6), (6, 5)}
The number whose sum is 12 = {(6, 6)}
n(B) = 2 + 1 = 3
∴ P(B) = \(\frac{3}{36}=\frac{1}{12}\)
(iii) Let C be the event of getting a sum 9 or 11.
Now C = {(3, 6), (4, 5)
(5, 4), (6, 3)
(5, 6), (6, 5)}
n(C) = 6
∴ P(C) = \(\frac{6}{36}=\frac{1}{6}\)
Question 3.
Three coins are tossed once. Find the probability of getting
(i) exactly two heads
(ii) at least two heads
(iii) atmost two heads.
Solution:
The sample space when three coin are tossed once is as follows:
S = {(H, H, H), (H, T, H), (T, H, H), (H, H, T), (T, T, H), (H, T, T) (T, H, T), (T, T, T)}
n(S) = 23 = 8
(i) Let A be the event of getting exactly two heads.
∴ A = {(H, T, H) (T, H, H) (H, H, T)}
n(A) = 3
∴ n( A) = \(\frac{3}{8}\)
(ii) Let B be the event of getting at least two heads.
B = {(H, T, H), (T, H, H), (H, H, T), (H, H, H)}
n(B) = 4
∴ P(B) = \(\frac{4}{8}=\frac{1}{2}\)
(iii) Let C be the event of getting atmost two heads.
C = {(T, T, T), (H, T, T), (T, H, T), (T, T, H) (H, H, T), (T, H, H), (H, T, H)}
n( C) = 7 ∴ P(C) = \(\frac{7}{8}\)
![]()
Question 4.
A bag contains 5 white and 7 black balls. 3 balls are drawn at random. Find the probability that
(i) all are white
(ii) one white and 2 black.
Solution:
Number of white balls = 5
Number of black balls = 7
Total number of balls = 12
Selecting 3 from 12 balls can be done in

(ii) Let B be the event of selecting one white and 2 black balls.
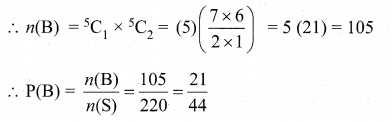
Question 5.
In a box containing 10 bulbs, 2 are defective. What is the probability that among 5 bulbs chosen at random, none is defective?
Solution:
Total number of bulbs = 10
Number of defective bulbs = 2
∴ Number of good bulbs = 10 – 2 = 8
Now selecting 5 from the 10 bulbs can be done in 10C5 ways.
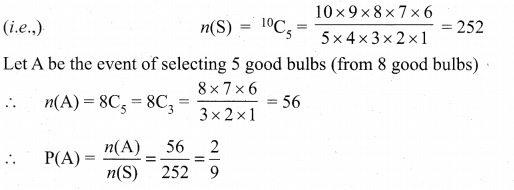
Question 6.
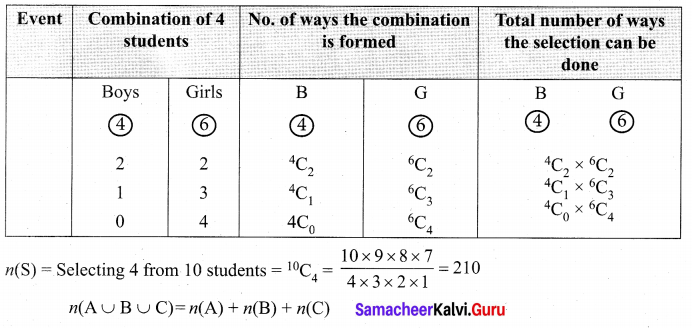
Out of 10 outstanding students in a school there are 6 girls and 4 boys. A team of 4 students is selected at random for a quiz programme. Find the probability that there are atleast two girls.
Solution:
Let A, B and C be the three possible events of selections. The number of combinations are shown below:
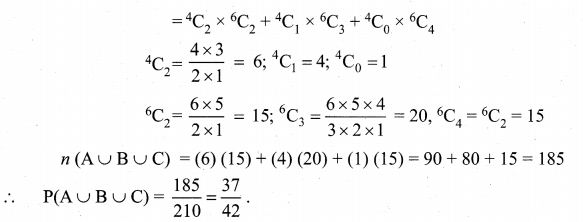
Question 7.
An integers is chosen at random from the first fifty positive integers. What is probability that the integer chosen is a prime or multiple of 4.
Solution:
S = {1, 2, 3, ……….. ,50} ∴ n(S) = 50
Let A be the event of getting prime number.
∴ A = {2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37, 41, 43, 47}
n(A) = 15, so P(A) = 15/50
Let B be the event of getting number multiple of 4
∴ B = {4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, 28, 32, 36, 40, 44, 48}
n(B) = 12, so P(B) = 12/50
Here A and B are mutually exclusive. (i.e.,) A ∩ B = ϕ
∴ P(A ∪ B) = P(A) + P(B) = 15/50 + 12/50 = 27/50.