You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 11th Maths Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 11th Maths Solutions Chapter 3 Trigonometry Ex 3.9
Question 1.
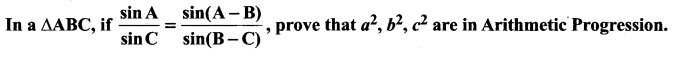
Solution:
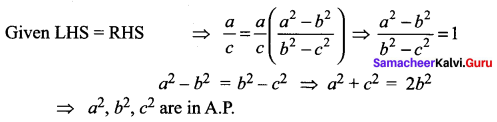
Question 2.
The angles of a triangle ABC, are in Arithmetic Progression and if b : c = \(\sqrt{3}: \sqrt{2}\), find ∠A.
Solution:
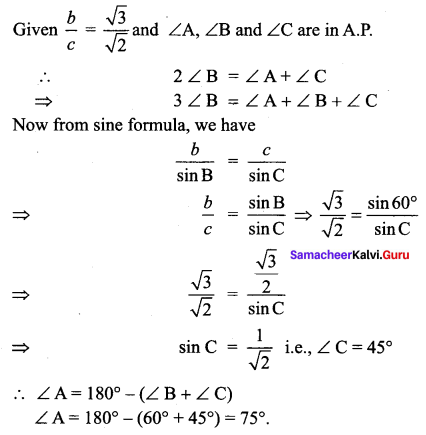
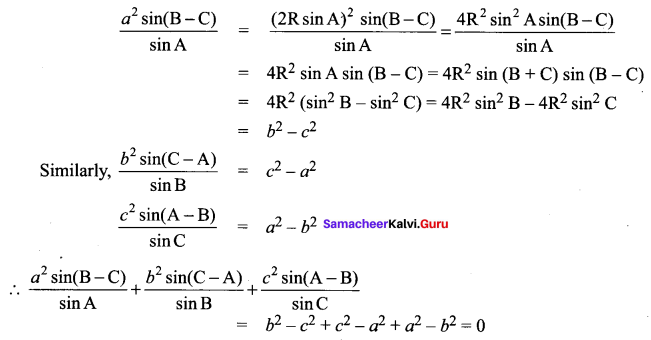
Question 3.
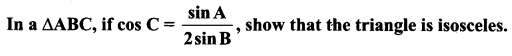
Solution:
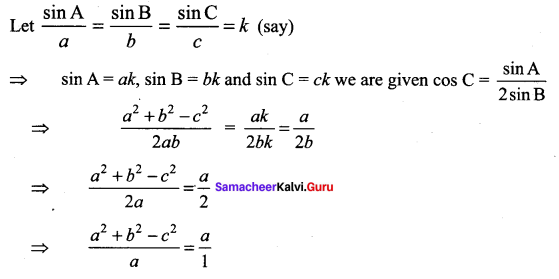
⇒ a2 + b2 – c2 = a2 ⇒ b2 – c2 = a2 – a2
⇒ b2 – c2 = 0 ⇒ b = c
∴ ∆ ABC is isosceles
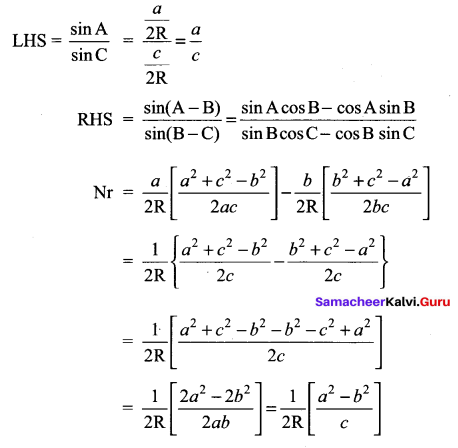
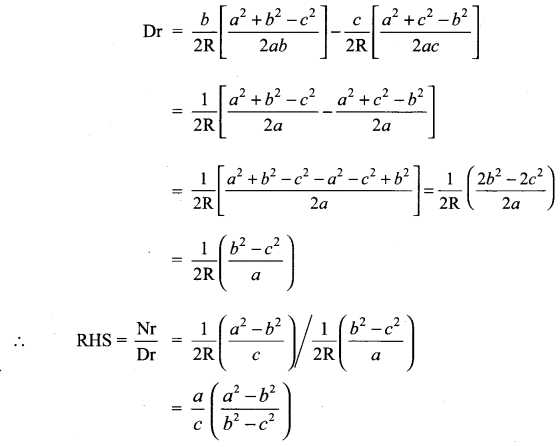
Question 4.
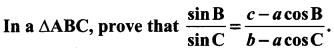
Solution:
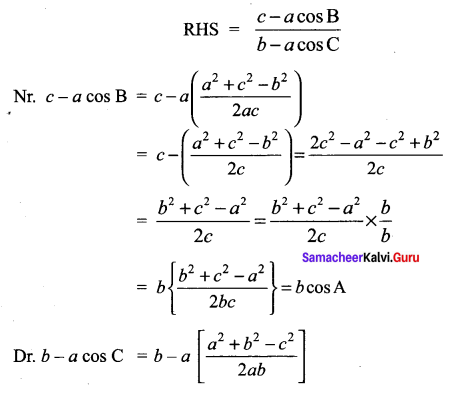
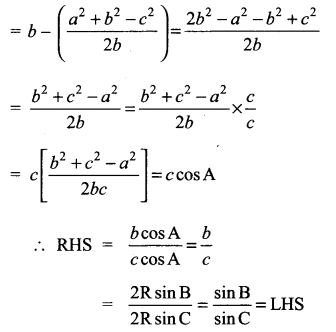
![]()
Question 5.
In a ∆ABC, prove that a cos A + b cos B + c cos C = 2a sin B sin C.
Solution:
LHS = a cos A+ 6 cos B + c cos C
Using sine formula, we get k sin A cos A + k sin B cos B + k sin C cos C k
= \(\frac{k}{2}\) [2 sin A cos A + 2 sin B cos B + 2 sin C cos C]
= \(\frac{k}{2}\) [sin 2A + sin 2B + sin 2C]
= \(\frac{k}{2}\) [2 sin (A + B) . cos (A – B) + 2 sin C . cos C]
= \(\frac{k}{2}\) [2 sin (A – B) . cos (A – B) + 2 sin C . cos C]
= \(\frac{k}{2}\) [2 sin C . cos (A – B) + 2 sin C . cos C]
= k sin C [cos(A – B) + cos C]
![]()
= k sin C [cos (A – B) – cos (A + B)]
= k sin C . 2 sin A sin B
= 2k sin A . sin B sin C
= 2a sin B sin C = RHS
Question 6.
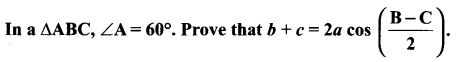
Solution:
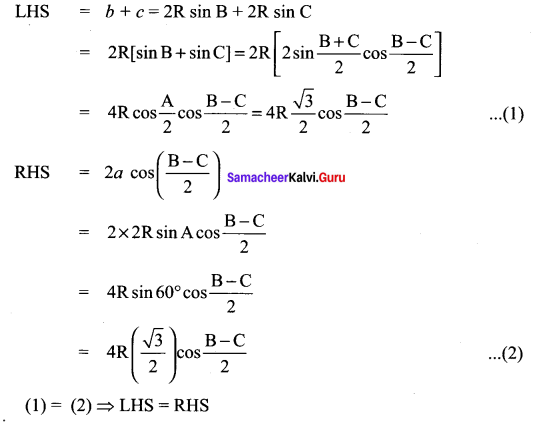
Question 7.
In a ∆ ABC, prove the following.
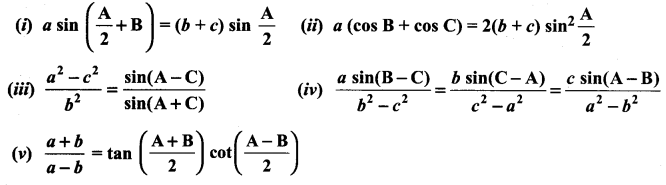
Solution:
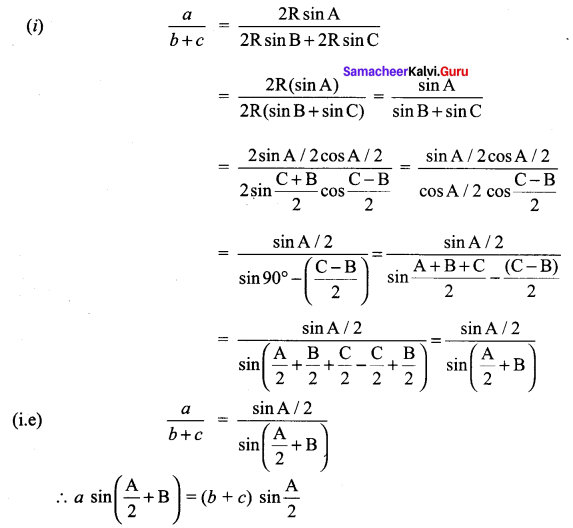
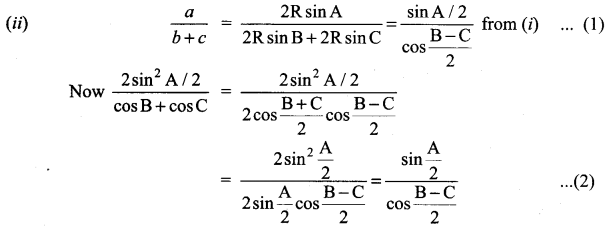
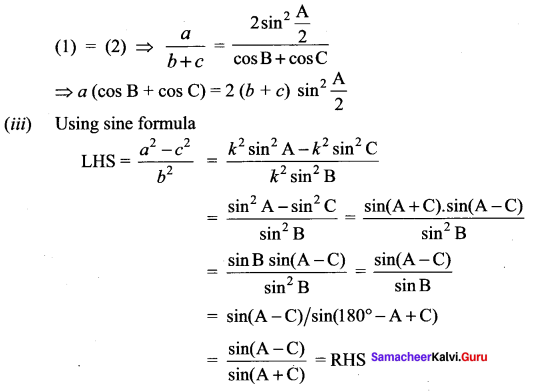

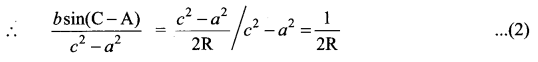
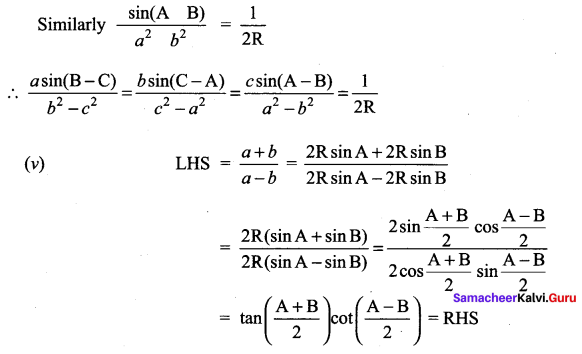
Question 8.
In a ∆ABC, prove that (a2 – b2 + c2) tan B = (a2 + b2 – c2)tan C
Solution:
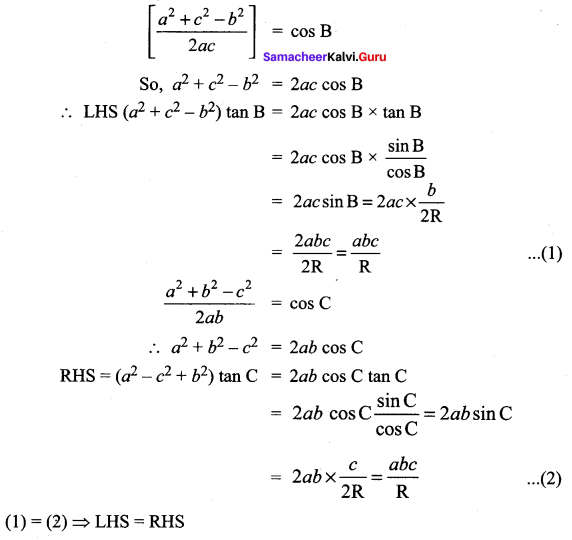
Question 9.
An Engineer has to develop a triangular shaped park with a perimeter 120 m in a village. The park to be developed must be of maximum area. Find out the dimensions of the park.
Solution:
Given, the perimeter of triangular shaped park = 120 m
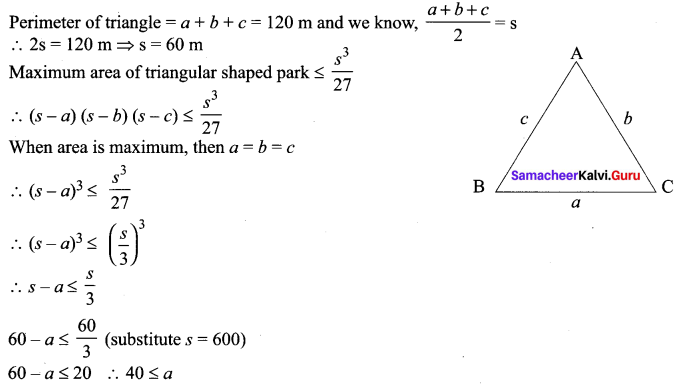
All sides of a triangular part would be 40 m.
i.e., a = 40 m,
b = 40 m,
c = 40 m.
![]()
Question 10.
A rope of length 12 m is given. Find the largest area of the triangle formed by this rope and find the dimensions of the triangle so formed.
Solution:
The largest triangle will be an equilateral triangle
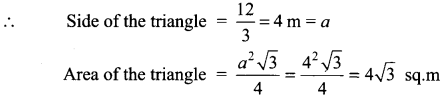
Question 11.
Derive Projection formula from
(i) Law of sines,
(ii) Law of cosines.
Solution:
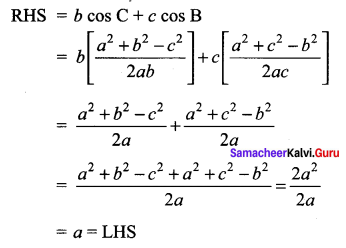
(i) To Prove a = b cos c + c cos B
Using sine formula
RHS = b cos C + c cos B
= 2R sin B cos C + 2R sin C cos B
= 2R [sin B cos C + cos B sin C]
= 2R sin (B + C) = 2R [sin π – A)
= 2R sin A = a = LHS
(ii) To prove a = b cos c + c cos B
Using cosine formula
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Maths Solutions Chapter 3 Trigonometry Ex 3.9 Additional Questions
Question 1.
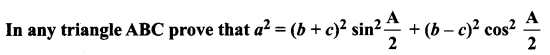
Solution:
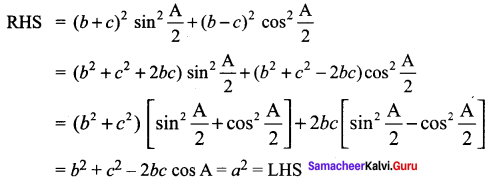
Question 2.
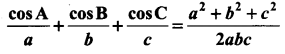
Solution:
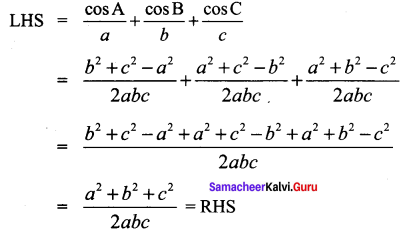
Question 3.
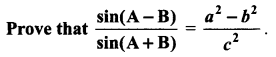
Solution:
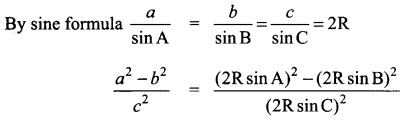
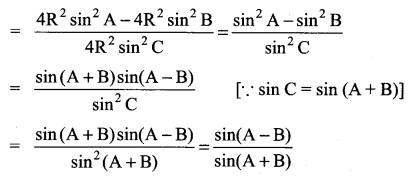
![]()
Question 4.
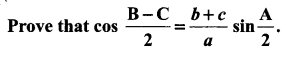
Solution:
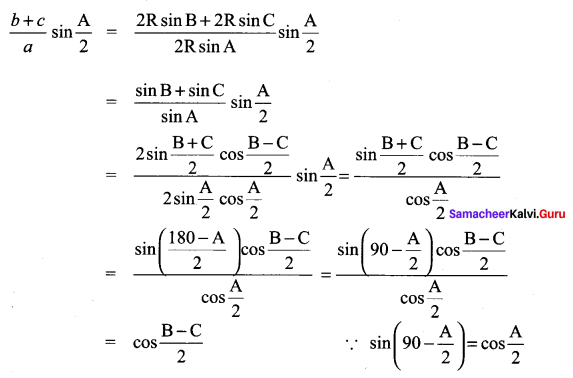
Question 5.
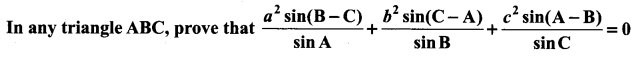
Solution: