You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 11th Maths Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 11th Maths Solutions Chapter 4 Combinatorics and Mathematical Induction Ex 4.1
Question 1.
(i) A person went to a restaurant for dinner. In the menu card, the person saw 10 Indian and 7 Chinese food items. In how many ways the person can select either an Indian or a Chinese food?
Solution:
Selecting an Indian food item from the given 10 can be done in 10 ways. Selecting a Chinese food item from the given 7 can be done in 7 ways.
∴ Selecting an Indian or a Chinese food can be done in 10 + 7 = 17 ways.
(ii) There are 3 types of toy car and 2 types of toy train available in a shop. Find the number of ways a baby can buy a toy car and a toy train?
Solution:
Given, Number of toy cars = 3
Number of toy trains = 2
∴ A baby buying a toy car from 3 can be done in 3 ways
∴ A baby buying a toy train from 2 can be done in 2 ways
∴ Buying a toy car and a toy train together can be done in 3 × 2 = 6 ways
(iii) How many of two-digit numbers can be formed using 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 without repetition of digits?
Solution:
The given digits are 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
A two digit number has unit place and 10’s place. We are given 5 digits (1, 2, 3, 4, 5). The unit place can be filled (using the 5 digits) in 5 ways. After filling the unit place since repetition is not allowed one number (filled in the unit place) should be excluded. So the 10’s place can be filled (using the remaining 4 digits) in 4 ways
∴ Unit place and 10’s place together can be filled in 5 × 4 = 20 ways. So the number of two digit numbers = 20
(iv) Three persons enter in to a conference hall in which there are 10 seats. In how many ways they can take their places?
Solution:
Given, Number of the persons = 3 and Number of seats = 10
The first person can take his place (from 10 seats) in 10 ways
The second person can take his place (from the remaining 9 seats) in 9 ways
The third person can take his place (from the remaining 8 seats) in 8 ways
∴ The three persons together can take their places in 10 × 9 × 8 = 720 ways
(v) In how many ways 5 persons can be seated in a row?
Solution:
5 persons can be arranged among themselves in 5! ways
(i.e) 5 × 4 × 3 × 2 × 1 = 120 ways
![]()
Question 2.
(i) A mobile phone has a passcode of 6 distinct digits. What is the maximum number of attempts one makes to retrieve the passcode?
Solution:
Number of digits = 10
∴ Number of attempts made = 10 × 9 × 8 × 7 × 6 × 5 = 151200 ways
(ii) Given four flags of different colours, how many different signals can be generated if each signal requires the use three flags, One below the other?
Solution:
Number of flags given = 4
Number of flag needed (to show a signal) = 3
The first flag can be chosen in 4 ways (from the 4 flags)
The second flag can be chosen (from the remaining 3 flags) in 3 ways
The third flag can be chosen (from the remaining 2 flags) in 2 ways
So the first, second and the third flags together can be chosen in (to generate a signal) 4 × 3 × 2 = 24 ways
(i.e) 24 signals can be generated
Question 3.
Four children are running a race.
(i) In how many ways can the first two places be filled?
Solution:
Number of children in the running race = 4
The first place can be filled in (from the 4 children) 4 ways
After filling in first place only 3 children are left out
So the second place can be filled in (from the remaining 3 children) 3 ways
So the first and the second places together can be filled in 4 × 3 = 12 ways
(ii) In how many different ways could they finish the race?
Solution:
The first and second places can be filled in 12 ways
The third place can be filled (from the remaining 2 children) in 2 ways and the fourth place can be filled in 1 way
So the race can be finished in 12 × 2 × 1 = 24 ways
Question 4.
Count the number of three-digit numbers which can be formed from the digits 2, 4, 6, 8? if.
(i) repetitions of digits is allowed
Solution:
Number of digit given = 4 (2,4, 6, 8)
So the unit place can be filled in 4 ways, 10’s place can be filled in 4 ways and 100’s place can be filled in 4 ways
∴ The unit place, 10’s place and 100’s place together can be filled (i.e) So the Number of 3 digit numbers = 4 × 4 × 4 = 64 ways
(ii) repetitions of digits is not allowed.
Solution:
The unit place can be filled (using the 4 digits) in 4 ways after filling the unit place since repetition of digits is not allowed that digit should be excluded.
So the 10’s place can be filled in (4 – 1) 3 ways and the 100’s place can be filled in (3 – 1) 2 ways
So the unit place, 10’s and 100’s places together can be filled in 4 × 3 × 2 = 24 ways
(i.e) The number of 3 digit numbers = 4 × 3 × 2 = 24 ways
Question 5.
How many three-digit numbers are there with 3 in the unit place?
(i) with repetition
Solution:
with repetition
The unit place is filled (by 3) in 1 way
The 10’s place can be filled in 10 ways
The 100’s place can be filled in 9 ways (excluding 0)
So the number of 3 digit numbers with 3 unit – place = 9 × 10 × 1 = 90
(ii) without repetition
Solution:
The digits are 0, 1,2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9
A three digit number has 3 digits l’s, 10’s and 100’s place.
The unit place is (filled by 3) filled in one way.
After filling the unit place since the digit ‘0’ is there, we have to fill the 100’s place. Now to fill the 100’s place we have 8 digits (excluding 0 and 3) So 100’s place can be filled in 8 ways.
Now to fill the 10’s place we have again 8 digits (excluding 3 and any one of the number) So 10’s place can be filled in 8 ways.
∴ Number of 3 digit numbers with ‘3’ in unit place = 8 × 8 × 1 = 64
Question 6.
How many numbers are there between 100 and 500 with the digits 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 if
(i) repetition of digits allowed
Solution:
repetition of digits allowed
The given digits are 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
We have to find numbers between 100 and 500. So the 100’s place can be filled (by the numbers 1, 2, 3, 4) in 4 ways.
The 10’s place can be filled in (using 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5) 6 ways
and the unit-place can be filled in (using 0,1, 2, 3, 4, 5) 6 ways
But the number 100 should be excluded
So the number of numbers between 100 and 500 = 4 × 6 × 6 = 144
(ii) the repetition of digits is not allowed
Solution:
The 100’s place can be filled (by using 1, 2, 3, 4) 10’s in 4 ways
The 10’s place can be filled in (6 – 1) 5 ways and the unit place can be filled in (5 – 1) 4 ways
So the number of 3 digit number 4 × 5 × 4 = 80
![]()
Question 7.
How many three-digit odd numbers can be formed by using the digits 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 if
(i) The repetition of digits is not allowed
Solution:
The repetition of digits is not allowed
The given digits are 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5. Here the odd number are 1, 3, 5.
So the unit place can be filled in 3 ways (using the 3 odd number)
After filling the unit place since 0 is a given digit be fill the 100’s place which can be
filled in
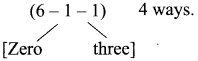
Then the 10’s place can be filled in (6 – 2) 4 ways.
So the number of 3 digit odd numbers = 3 × 4 × 4 = 48
(ii) The repetition of digits is allowed
Solution:
The unit place can be filled in 3 ways. We are given 6 digits.
So 10’s place can be filled in 6 ways and the 100’s place can be filled in (6 – 1) (excluding zero) 5 ways
So the Number of 3 digit numbers = 3 × 6 × 5 = 90
Question 8.
Count the numbers between 999 and 10000 subject to the condition that there are
(i) no restriction
Solution:
no restriction
We have to find 4 digit numbers
The 1000’s place can be filled in 9 ways (excluding zero) and the 100’s, 10’s and unit places respectively can be filled in 10, 10, 10 ways (including zero)
So the number of numbers between 999 and 10000 = 9 × 10 × 10 × 10 = 9000
(ii) no digit is repeated
Solution:
Since 0 is given as a digit we have to start filling 1000’s place.
Now 1000’s place can be filled in 9 ways (excluding 0)
Then the 100’s place can be filled in 9 ways (excluding one digit and including 0)
10’s place can be filled in (9 – 1) 8 ways and unit place can be filled in (8 – 1) 7 ways So the number of 4 digit numbers are 9 × 9 × 8 × 7 = 4536 ways
(iii) at least one of the digits is repeated
Solution:
Required number of numbers = 9000 – 4536 = 4464 numbers
Question 9.
How many three-digit numbers, which are divisible by 5, can be formed using the digits 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 if
(i) The repetition of digits are not allowed?
Solution:
The repetition of digits are not allowed.
The given digits are 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5. A number will be divisible by 5 if the digit in the unit place is 0 or 5
So the unit place can be filled by 0 or 5
(a) When the unit place is 0 it is filled in 1 way
And so 10’s place can be filled in 5 ways (by using 1, 2, 3, 4, 5) and 100’s place can be filled in (5 – 1) 4 ways
So the number of 3 digit numbers with unit place 0 = 1 × 5 × 4 = 20
(b) When the unit place is 5 it is filled in 1 way
Since 0 is given as a digit to fill 100’s place 0 should be excluded
So 100’s place can be filled in (excluding 0 and 5) 4 ways and 10’s place can be filled in (excluding 5 and one digit and including 0) 4 ways So the number of 3 digit numbers with unit place 5 = 1 × 4 × 4 = 16
∴ Number of 3 digit numbers ÷ by 5 = 20 + 16 = 36
(ii) The repetition of digits are allowed.
Solution:
The digits are
0 1 2 3 4 5
To get a number divisible by 5 we should have the unit place as 5 or 0 So the unit place (using 0 or 5) can be filled in 2 ways.
The 10’s place can be filled (Using 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5) in 6 ways and the 100’s place (Using 1, 2, 3, 4, 5) can be filled in 5 ways.
So the number of 3 digit numbers ÷ by 5 (with repetition) = 2 × 6 × 5 = 60
Question 10.
To travel from a place A to place B, there are two different bus routes B1, B2 two different train routes T1, T2 and one air route A1. From place B to place C there is one bus route say B1‘, two different train routes say T1‘, T2‘ and one air route A1‘. Find the number of routes of commuting from place A to place C via place B without using similar mode of transportation.
Solution:
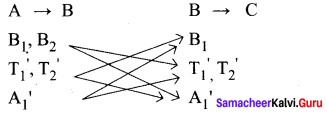
From the above diagram the number of routes from A to C
= (2 × 2 + 2 × 1) + [(2 × 1) + (2 × 1)] + [(1 × 1) + (1 × 2)]
= 4 + 2 + 2 + 2 + 1 + 2 = 13
![]()
Question 11.
How many numbers are there between 1 and 1000 (both inclusive) which are divisible neither by 2 nor by 5?
Solution:
From 1 to 1000, the numbers ÷ by 2 = 500
the number ÷ by 5 = 200
and the numbers ÷ by 10 = 100(5 × 2 = 10)
So number ÷ by 2 or 5 = 500 + 200 – 100 = 600
Total numbers from 1 to 1000 = 1000
So the number of numbers which are ÷ neither by 2 nor by 5 = 1000 – 600 = 400
Question 12.
How many strings can be formed using the letters of the word LOTUS if the word
(i) either starts with L or ends with S?
Solution:
either starts with L or ends with S?
To find the number of words starting with L
Number of letters in LOTUS = 5 when the first letter is L it can be filled in 1 way only. So the remaining 4 letters can be arranged in 4! =24 ways = n(A). When the last letter is S it can be filled in the 1 way and the remaining 4 letters can be arranged is 4! = 24 ways = n(B)
![]()
(1) (1) 3! = 6 = n(A ∩ B)
Now n(A ∪ B) = n(A) + n(B) – n(A ∩ B)
= 24 + 24 – 6 = 42
Now, neither words starts with L nor ends with S = 42
(ii) neither starts with L nor ends with S?
Solution:
Number of letters of the word LOTUS = 5.
They can be arranged in 5 ! = 120 ways
Number of words starting with L and ending with S = 42
So the number of words neither starts with L nor ends with S = 120 – 42 = 78
Question 13.
(i) Count the total number of ways of answering 6 objective type questions, each question having 4 choices.
Solution:
Count the total number of ways of answering 6 objective type questions, each question having 4 choices.
One question can be answered in 4 ways
Two questions can be answered in 4 × 4 = 42 ways
∴ Six questions can be answered in 46 ways
(ii) In how many ways 10 pigeons can be placed in 3 different pigeon holes ?
Solution:
First pigeons can be placed in pigeon hole in 3 ways (selecting 1 from 3 holes)
Second pigeons can be placed in pigeon hole in 3 ways Tenth pigeons can be placed in pigeon hole in 3 ways
So total number of ways in which all the number 10 place can be sent = 3 × 3 × 3 × 3 × 3 × 3 × 3 × 3 × 3 × 3 = 310 ways
(iii) Find the number of ways of distributing 12 distinct prizes to 10 students?
Solution:
To give the first prize we have to select, from the 10 students which can be done in 10 ways.
To give the second prize we have to select one from the 10 students which can be done is 10 ways.
To give the 12th prize we have to select one from 10 students which can be done in 10 ways.
So all the 12 prizes can be given in (10 × 10 × 10 …. 12 times) = 1012 ways.
![]()
Question 14.
Find the value of
(i) 6!
Solution:
6! = 6 × 5 × 4 × 3 × 2 × 1 = 720
(ii) 4! + 5!
Solution:
4! + 5! = (4 × 3 × 2 × 1) + (5 × 4 × 3 × 2 × 1)
= 24 + 120 = 144
(iii) 3! – 2!
Solution:
3! – 2! = (3 × 2 × 1) – (2 × 1)
= 6 – 2 = 4
(iv) 3! × 4!
Solution:
3! × 4! = (3 × 2 × 1) × (4 × 3 × 2 × 1) = 6 × 24 = 144
12!
(v) \(\frac{12 !}{9 ! \times 3 !}\)
Solution:
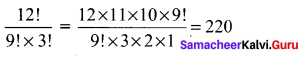
(vi) \(\frac{(n+3) !}{(n+1) !}\)
Solution:
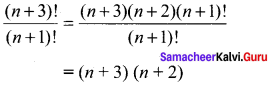
Question 15.
Evaluate \(\frac{n !}{r !(n-r) !}\) when
(i) n = 6,
r = 2
Solution:
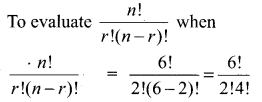
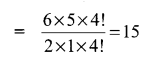
(ii) n = 10,
r = 3
Solution:
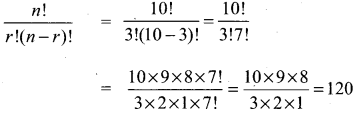
(iii) For any n with r = 2
Solution:
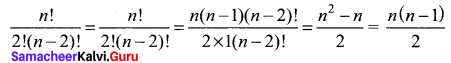
Question 16.
Find the value of n if
(i) (n + 1)! = 20(n – 1)!
Solution:

(ii) \(\frac{1}{8 !}+\frac{1}{9 !}=\frac{n}{10 !}\)
Solution:
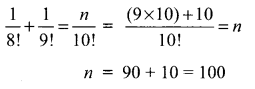
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Maths Solutions Chapter 4 Combinatorics and Mathematical Induction Ex 4.1 Additional Questions Solved
Question 1.
If the letter of the word ‘RACHIT’ are arranged in all possible ways as listed in dictionary, then what is the rank of the word ‘RACHIT’?
Solution:
The alphabetical order of RACHIT is A, C, H, I, R and T
Number of words beginning with A = 5!
Number of words beginning with C = 5!
Number of words beginning with H = 5!
Number of words beginning with 1 = 5!
and Number of words beginning with R (i.e) RACHIT = 1
∴ The rank of the word ’RACHIT’ in the dictionary = 5! + 5! + 5! + 5! + 1 = 4 × 5! + 1
= 4 × 5 . 4 . 3 . 2 . 1 + 1 = 4 × 120 + 1 = 480 + 1 = 481
Question 2.
Find the number of positive integers greater than 6000 and less than 7000 which are divisible by 5, provided that no digit is to be repeated.
Solution:
Any number divisible by 5, its unit place must have 0 or 5. We have to find 4-digit number greater than 6000 and less than 7000.
So, the unit place can be filled with 2 ways (0 or 5) since, repetition is not allowed.
∴ Tens place can be filled with 7 ways and hundreds place can be filled with 8 ways.
But the required number is greater than 6000 and less than 7000. So, thousand place can be filled with 1 digits (i.e) 6.
So, the total number of integers =1 × 8 × 7 × 2 = 112
Hence, the required number of integers = 112
Question 3.
Find the number of integers greater than 7000 that can be formed with the digits 3, 5, 7, 8 and 9 where no digits are repeated.
Solution:
Given that all the 5 digit numbers are greater than 7000.
So, the ways of forming 5-digit numbers = 5 × 4 × 3 × 2 × 1 = 120
Now, all the four digit number greater than 7000 can be formed as follows.
Thousand place can be filled with 3 ways
Hundred place can be filled with 4 ways
Tenths place can be filled with 3 ways
Units place can be filled with 2 ways
So, the total number of 4-digits numbers = 3 × 4 × 3 × 2 = 72
∴ Total number of integers = 120 + 72 = 192
Hence, the required number of integers = 192
![]()
Question 4.
How many words (with or without dictionary meaning) can be made from the letters of the word MONDAY, assuming that no letter is repeated, if

Solution:

(c) All letters are used but the first is a vowel = 2 × 5! = 2 × 120 = 240
Hence, the required matching is
(a) ↔ (iii), (b) ↔ (i), (c) ↔ (ii)
Question 5.
Five boys and 5 girls form a line. Find the number of ways of making the seating arrangement under the following condition.
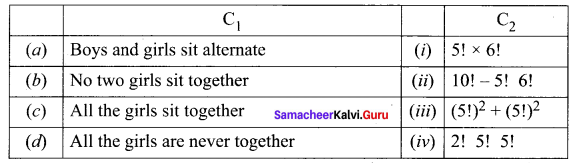
Solution:
(a) Total number of arrangement when boys and girls alternate : = (5!)2 + (5!)2
(b) No two girls sit together = 5! 6!
(c) All the girls sit together = 2! 5! 5!
(d) All the girls sit never together = 10! – 5! 6!
Hence, the required matching is (a) ↔ (iii), (b) ↔ (i), (c) ↔ (iv), (d) ↔ (ii)
Question 6.
How many automobile license plates can be made, if each plate contains two different letters followed by three different digits?
Solution:
We have 26 English alphabet and 10 digits (0 to 9)
Since, it is given that each plate contains 2 different letters followed by 3 different digits.
∴ Number of arrangement of 26 letter taken 2 at a time
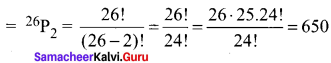
Three digit number can be formed out of 10 digit = 10P3
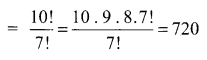
Total number of license plates = 650 × 720 = 468000
Hence, the required number of plates = 468000.