Are you searching for the Tamilnadu State Board Class 12th Bio Zoology Solutions Chapter 7 Human Health and Diseases Questions and Answers. Then, you are at the correct place. Verify all the Bio Zoology Solutions subject concepts and begin your practice for the exam. Every concept in Samacheer Kalvi 12th Bio Zoology Book Solutions Chapter 7 Human Health and Diseases solutions is explained in detail. Students can easily create an interest in Bio Zoology Solutions by referring to Samacheer Kalvi Class 12th Bio Zoology Solutions pdf.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Bio Zoology Solutions Chapter 7 Human Health and Diseases
Get updated Samacheer Kalvi Solutions pdf and download it for free. Don’t pay a single penny to get a free pdf of Tamilnadu State Board Solutions for Class 12th Bio Zoology Solutions Chapter 7 Human Health and Diseases Questions and Answers. The Samacheer Kalvi Class 12th Bio Zoology Solutions Pdf material is developed as per the latest exam pattern. Get access to all the topics available on Class 12th Samacheer Kalvi Bio Zoology Solutions.
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Bio Zoology Human Health and Diseases Text Book Back Questions and Answers
Question 1.
A 30 year old woman has bleedy diarrhoea for the past 14 hours, which one of the following organisms is likely to cause this illness?
(a) Streptococcus pyogens
(b) Clostridium difficile
(c) Shigella dysenteriae
(d) Salmonella enteritidis
Answer:
(c) Shigella dysenteriae
Question 2.
Exo-erythrocytic schizogony of Plasmodium takes place in __________
(a) RBC
(b) Leucocytes
(c) Stomach
(d) Liver
Answer:
(d) Liver
Question 3.
The sporozoites of Plasmodium vivax are formed from __________
(a) Gametocytes
(b) Sporoblasts
(c) Oocysts
(d) Spores
Answer:
(c) Oocysts
Question 4.
Amphetamines are stimulants of the CNS, whereas barbiturates are __________
(a) CNS stimulant
(b) both a and b
(c) hallucinogenic
(d) CNS depressants
Answer:
(d) CNS depressants
Question 5.
Choose the correctly match pair.
(a) Amphetamines – Stimulant
(b) LSD-Narcotic
(c) Heroin – Psychotropic
(d) Benzodiazepine – Pain killer
Answer:
(a) Amphetamines – Stimulant
Question 6.
The Athlete’s foot disease in human is caused by __________
(a) Bacteria
(b) Fungi
(c) Virus
(d) Protozoan
Answer:
(b) Fungi
Question 7.
Cirrhosis of liver is caused by chronic intake of __________
(a) Opium
(b) Alcohol
(c) Tobacco
(d) Cocaine
Answer:
(b) Alcohol
Question 8.
The sporozoite of the malarial parasite is present in __________
(a) saliva of infected female Anopheles mosquito.
(b) RBC of human suffering from malaria.
(c) Spleen of infected humans.
(d) Gut of female Anopheles mosquito
Answer:
(a) saliva of infected female Anopheles mosquito.
Question 9.
Where do the following events in the life cycle of Plasmodium takes place?
(a) Fertilization – __________
(b) Development of gametocytes – __________
(c) Release of sporozoites – __________
(d) Schizogony – __________
Answer:
(a) Fertilization – Gut of mosquito
(b) Development of gametocytes – Human RBC’s
(c) Release of sporozoites – From Mosquito to the human blood
(d) Schizogony – Human liver cells
Question 10.
Paratope is an __________
(a) Antibody binding site on variable regions
(b) Antibody binding site on heavy regions
(c) Antigen binding site on variable regions
(d) Antigen binding site on heavy regions
Answer:
(c) Antigen binding site on variable regions
Question 11.
Allergy involves __________
(a) IgE
(b) IgG
(c) IgA
(d) IgM
Answer:
(a) IgE
Question 12.
Spread of cancerous cells to distant sites is termed as __________
(a) Metastasis
(b) Oncogenes
(c) Proto-oncogenes
(d) Malignant neoplasm
Answer:
(a) Metastasis
Question 13.
AIDS virus has __________
(a) Single stranded RNA
(b) Double stranded RNA
(c) Single stranded DNA
(d) Double stranded DNA
Answer:
(a) Single stranded RNA
Question 14.
B cells that produce and release large amounts of antibody are called __________
(a) Memory cells
(b) Basophils
(c) Plasma cells
(d) killer cells
Answer:
(c) Plasma cells
Question 15.
Given below are some human organs.
Answer:
Identify one primary and one secondary lymphoid organ. Explain its role.
Liver, thymus, stomach, thyroid, tonsils Primary lymphoid organ – thymus Secondary lymphoid organ – tonsils Immunocompetency of T cells is achieved in Thymus Whereas tonsils help to fight viral and bacterial infections.
Question 16.
Name and explain the type of barriers which involve macrophages.
Answer:
Phagocytic barriers involves macrophages (monocytes, neutrophils) which phagocytose and . digest whole micro organisms.
Question 17.
What are interferons? Mention their role.
Answer:
Interferons are the antiviral proteins which induce antiviral state in the infected cells.
Question 18.
List out chemical alarm signals produced during inflammation.
Answer:
Serotonin, histamine and prostaglandins.
Question 19.
Explain the process of replication of retrovirus after it gains entry into the human body.
Answer:
After getting into the body of the person, the retrovirus enters into macrophages where RNA genome of the virus replicates to form viral DNA with the help of the enzyme reverse transcriptase. This viral DNA gets incorporated into the DNA of host cells and directs the infected cells to produce viral particles. The macrophages continue to produce virus and in this way acts like a HIV factory.
Question 20.
Explain the structure of immunoglobulin with suitable diagram.
Answer:
An antibody molecule is Y shaped structure that comprises of four polypeptide chains, two identical light chains (L) of molecular weight 25,000 Da (approximately 214 amino acids) and two identical heavy chains (H) of molecular weight 50,000 Da (approximately 450 amino acids). The polypeptide chains are linked together by di-sulphide (S-S) bonds. One light chain is attached to each heavy chain and two heavy chains are attached to each other to form a Y shaped structure. Hence, an antibody is represented by H2 L2 The heavy chains have a flexible hinge region at their approximate middles Antigen binding
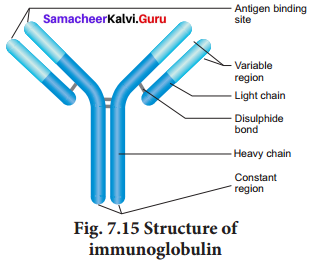
Each chain (L and H) has two terminal They are C – terminal (Carboxyl) and amino or N-terminal. Each chain (L and H) has two regions. They have variable (V) region at one end and a much larger constant (C) region at the other end. Antibodies responding to different antigens have very different (V) regions but their (C) regions are the same in all antibodies. In each arm of the monomer antibody, the (V) regions of the heavy and light chains combines to form an antigen – binding
site shaped to ‘fit’ a specific antigenic determinant. Consequently each antibody monomer has two such antigen – binding regions. The (C) regions that forms the stem of the antibody monomer determine the antibody class and serve common functions in all antibodies.
Question 21.
What are the cells involved innate immune system?
Answer:
Cells involved in innate immunity are monocytes (macrophages), neutrophils, helper T-cells, B-cells, dendritic cells.
Question 22.
What is vaccine? What are its types?
Answer:
A vaccine is a biological preparation that provides active acquired immunity to a particular disease and resembles a disease causing microorganism and is often made from weakened or attenuated or killed forms of the microbes, their toxins, or one of its surface proteins. The vaccines are classified as first, second and third generation vaccines.
Question 23.
A person is infected by HIV. How will you diagnose for AIDS?
Answer:
A simple blood test is available that can determine whether the person has been infected with HIV. The ELISA test (Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay) detects the presence of HIV antibodies. It is a preliminary test. Western blot test is more reliable and a confirmatory test. It detects the viral core proteins. If both tests detect the presence of the antibodies, the person is considered to be HIV positive.
Question 24.
Autoimmunity is a misdirected immune response. Justify.
Answer:
Autoimmune diseases : Autoimmunity is due to an abnormal immune response in which the immune system fails to properly distinguish between self and non-self and attacks its own body. Our body produces antibodies (auto antibodies) and cytotoxic T cells that destroy our own tissues. If a disease-state results, it is referred to as auto-immune disease. Thus, autoimmunity is a misdirected immune response.
Question 25.
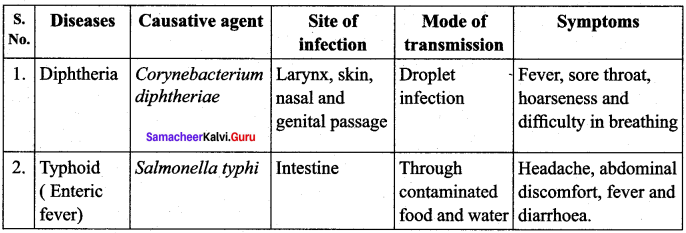
List the causative agent, mode of transmission and symptoms for Diphtheria and Typhoid
Answer:
Question 26.
A patient was hospitalized with fever and chills. Merozoites were observed in her blood. What is your diagnosis?
Answer:
Appearance of merozoites in a patients blood may be an indication of malarial parasite – plasmodium.
Question 27.
- Write the scientific name of the filarial worm that causes filariasis.
- Write the symptoms of filariasis.
- How is this disease transmitted?
Answer:
- Scientific name of the filarial worm – Wuchereria bancrofti
- Symptoms of filariasis – Inflammation of lymph nodes, obstruction of lymph vessels causes elephantiasis of limbs, genital etc.
- Mode of disease transmission : Vector transmission (female Culex mosquito)
Question 28.
List the common withdrawal symptoms of drugs and alcohol abuse.
Answer:
The withdrawal symptoms may range from mild tremors or convulsions, severe agitation and fits, depressed mood, anxiety, nervousness, restlessness, irritability, insomnia, dryness of throat, etc, depending on the type of drug abuse.
Question 29.
Why do you think it is not possible to produce vaccine against ‘common cold’?
Answer:
Vaccines target specific pathogens and elicit immunity. In case of common cold, more than 200 strains of viruses are responsible for causing the disease. Hence it is practically difficult to develop vaccine against it.
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Bio Zoology Human Health and Diseases Additional Questions and Answers
1 – Mark Questions
Question 1.
Pick out the disease which is caused by virus.
(a) Candidiasis
(b) Ascariasis
(c) Poliomyelitis
(d) Dysentery
Answer:
(c) Poliomyelitis
Question 2.
__________ test is done to confirm typhoid.
(a) ELISA
(b) Western blot
(c) Widal test
(d) Southern blot
Answer:
(c) Widal test
Question 3.
Match the following. Disease

Answer:
(a) a – iv, b – iii, c – i, d- ii
Question 4.
Identify the mismatched pair.
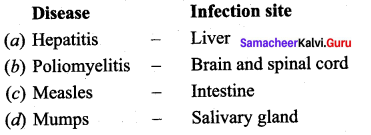
Answer:
(c) Measles – Intestine
Question 5.
Identify the wrong statement regarding polio disease.
(a) Polio is caused by a RNA virus.
(b) One of the infection site of polio is intestine.
(c) Culex mosquito acts as a vector for polio.
(d) Paralysis and respiratory failure are the symptoms
Answer:
(c) Culex mosquito acts as a vector for polio.
Question 6.
Yellow fever is a __________ type of disease.
(a) Neurotropic
(b) Viscerotropic
(c) Pneumotropic
(d) Dermotropic
Answer:
(b) Viscerotropic
Question 7.
Which one of the following pairs is wrong.
(a) Amoebiasis – Home fly
(b) African sleeping sickness – Tsetse flies
(c) Kala-azar – Sandfly
(d) Malaria – female Anopheles mosquito
Answer:
(d) Malaria – female Anopheles mosquito
Question 8.
__________ is the malignant form of malaria.
Answer:
P. falciparum
Question 9.
Schizogony of plasmodium parasite in human liver cells returns in __________
(a) sporozoites
(b) merozoites
(c) trophozoites
(d) schizont
Answer:
(b) merozoites
Question 10.
Incubation period of malaria is about __________
Answer:
12 days
Question 11.

Answer:
(a) a – iii, b – i, c – iv, d – ii
Question 12.
Assertion (A): Plasmodium vivax is a digenic parasite
Reason (R): The primary host of P. vivax is man.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true. (R) explains (A)
(b) (A) is true (R) is false
(c) Both (A) and (R) are false
(d) (A) is false (R) is true
Answer:
(b) (A) is true (R) is false
Question 13.
Assertion (A): Dermatomycosis is a cutaneous infection.
Reason (R): Fungus belongs to the order Trichophyton
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true. (R) explains (A)
(b) (A) is true (R) is false
(c) Both (A) and (R) are false.
(d) (A) is false (R) is true
Answer:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true. (R) explains (A)
Question 14.
Assertion (A): Spleen is a primary lymphoid organ
Reason (R): Primary lymphoid organs trap antigen and destroy them.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true. (R) explains (A)
(b) (A) is true (R) is false
(c) Both (A) and (R) are false.
(d) (A) is false (R) is true
Answer:
(c) Both (A) and (R) are false.
Question 15.
Assertion (A): Paratope is the antigen-binding site.
Reason (R): It is a part of antibody
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true. (R) explains (A)
(b) (A) is true (R) is false
(c) Both (A) and (R) are false.
(d) (A) is false (R) is true
Answer:
(b) (A) is true (R) is false
Question 16.
Assertion (A): HIV is a DNA virus.
Reason (R): HIV belongs to genus Lentivirus
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true. (R) explains (A)
(b) (A) is true (R) is false
(c) Both (A) and (R) are false.
(d) (A) is false (R) is true
Answer:
(d) (A) is false (R) is true
Question 17.
Secretion of HCL in stomach is an example for __________
(a) Anatomical barriers
(b) Phagocytic barriers
(c) Physiological barriers
(d) Inflammatory barriers
Answer:
(c) Physiological barriers
Question 18.
Identify the incorrect statement.
(a) Antibody Mediated Immunity was elicited by T cells.
(b) It is a character of vertebrates only
(c) Immunoglobulins act against pathogens and kill them.
(d) It is also called humoral immunity
Answer:
(a) Antibody Mediated Immunity was elicited by T cells.
Question 19.
Production process of blood cells in bone marrow is called __________
Answer:
haematopoiesis
Question 20.
Which of the following is not a feature of passive immunity?
(a) It is transient and less effective
(b) Immunological memory is present
(c) Immunity develops immunity
(d) Antibodies are obtained from out side
Answer:
(b) Immunological memory is present
Question 21.
__________ is a primary lymphoid organ of birds.
Answer:
Bursa of Fabricius
Question 22.
Match the following.
(a) Peyer’s patches (i) trachea
(b) BALT (ii) intestine
(c) Adenoid (iii) heart
(d) Thymus (iv) roof of the mouth
Answer:
a – ii b – i c – iv d – iii
Question 23.
Which is not a granulocyte?
(a) Lymphocytes
(b) Neutrophils
(c) Basophils
(d) Eosinophils
Answer:
(a) Lymphocytes
Question 24.
The L and H chains of immunoglobulin are joined by
(a) Hydrogen bonds
(b) disulphide bonds
(c) phosphodiester bonds
(d) ionic bond
Answer:
(b) disulphide bonds
Question 25.
__________ type of Immunoglobulin is involved in allergic reactions.
Answer:
IgE
Question 26.
Identify the wrong statement.
(a) Vaccine provide passive acquired immunity
(b) It is made from attenuated or killed microbes.
(c) Vaccines teach our body how to defend from microbes.
(d) MMR is a fist generation vaccine.
Answer:
(a) Vaccine provide passive acquired immunity
Question 27
__________ developed first vaccine for small pox.
Answer:
Edward Jenner
Question 28.
The enzyme attached to RNA of HIV is __________
(a) RNA polymerase
(b) reverse transcriptase
(c) primase
(d) endonuclease
Answer:
(b) reverse transcriptase
Question 29.
Infection of Ascariasis occur due to __________
(a) Sand fly
(b) contaminated food
(c) mosquito bite
(d) stagnant water
Answer:
(b) contaminated food
Question 30.
Which of the following statement(s) is true regarding cancer cells?
(a) Neoplasm or tumor cells show uncontrolled growth
(b) They are metastatic
(c) They lack contact inhibition
(d) They may be benign or malignant.
(a) (a) only
(b) (b) and (c)
(c) (d) only
(d) All the above
Answer:
(d) All the above
Question 31.
Study dealing with body’s defence mechanism against disease is called __________
(a) Pathology
(b) Immunology
(c) Microbiology
(d) Dermatology
Answer:
(b) Immunology
Question 32.
AIDS is characterized by sharp reduction in number of __________
(a) helper T cells
(b) killer T cells
(c) superior T cells
(d) B-cells
Answer:
(a) helper T cells
Question 33.
Plague and malaria are caused by __________ and __________ respectively.
(a) bacteria and virus
(b) fungi and protozoa
(c) bacteria and protozoan
(d) fungi and bacteria
Answer:
(c) bacteria and protozoan
Question 34.
A pair of fungal disease __________
(a) Amoebiasis, Kala-azar
(b) Candidiasis, Athlete’s foot
(c) Ascariasis, Filariasis
(d) Poliomyelitis, Amoebiasis
Answer:
(b) Candidiasis, Athlete’s foot
Question 35.
Plant source of Heroin is __________
(a) Poppy plants
(b) Cannabis plants
(c) Datura species
(d) Atropa species
Answer:
(a) Poppy plants
Question 36.
The test that confirms HIV positive is __________
(a) Western blot
(b) Northern blot
(c) Southern blot
(d) all the above
Answer:
(a) Western blot
Question 37.
Bacillary dysentery is caused due to __________
(a) Salmonella
(b) Shigella
(c) Clostridium
(d) Yersinia
Answer:
(b) Shigellosis
Question 38.
Cocaine is a __________ potent.
(a) Sedative
(b) Hallucinogen
(c) pain reliever
(d) neurotransmitter
Answer:
(b) Hallucinogen
Question 39.
Alkaloid found in tobacco is __________
(a) Atropine
(b) cocaine
(c) heroin
(d) nicotine
Answer:
(d) nicotine
Question 40.
__________ is a chronic memory disorder due to alcohol misuse.
(a) Cushing’s syndrome
(b) Turners’ syndrome
(c) Klinefelters’ syndrome
(d) Korsakoff syndrome
Answer:
(d) Korsakoff syndrome
2 – Mark Questions
Question 1.
What steps should be taken to maintain good health?
Answer:
Personal hygiene, regular exercise and balanced diet are very important to maintain good health.
Question 2.
Define disease.
Answer:
Disease can be defined as a disorder or malfunction of the mind or body. It involves morphological, physiological and psychological disturbances which may be due to environmental factors or pathogens or genetic anomalies or life style changes.
Question 3.
According to the WHO, what is health?
Answer:
The World Health Organization [WHO] defines health as ‘a state of complete physical, mental and social wellbeing and not merely absence of diseases’.
Question 4.
Differentiate between infectious and non-infections disease.
Answer:
- Infectious disease: Disease which are transmitted form one person to another are called infectious disease, e.g. Common cold
- Non-infectious disease: Disease which do not transmitted form one person to another are called non-infectious disease, e.g. Anaemia.
Question 5.
Name any two fungal disease and helminthic disease.
Answer:
- Fungal disease : Candidiasis, Athlete’s foot
- Helminthic disease : Ascariasis, Filariasis
Question 6.
Mention the causative organism of the following.
- Tetanus
- Bubonic plague
- Pneumonia
- Cholera
Answer:
- Tetanus : Clostridium tetani
- Bubonic plague : Yersinia pestis
- Pneumonia : Streptococcus pneumoniae
- Cholera : Vibrio cholerae
Question 7.
Classify viral disease based on the organ of infection.
Answer:
- Pneumotropic diseases
- Dermotropic diseases
- Viscerotropic diseases
- Neurotropic diseases
Question 8.
Write the symptoms of viral hepatitis.
Answer:
- Liver damage
- jaundice
- nausea
- yellowish eyes
- fever and pain in the abdomen.
Question 9.
Name the different species of malarial parasites and also mention which is the fatal one?
Answer:
- Plasmodium vivax
- Plasmodium ovale
- Plasmodium malariae
- Plasmodium falciparum .
- Plasmodium falciparum causes fatal malaria.
Question 10.
Name the causative agent and confirmatory test for Typhoid.
Answer:
Typhoid is caused by Salmonella typhi. Widal test can be done to confirm typhoid.
Question 11.
Mention the three phases in the life of plasmodium parasite with their respective host.
Answer:
- Schizogony occurs in man.
- Gamogony occurs in man.
- Sporogony occurs in gut of mosquito.
Question 12.
What causes shivering in malarial patient?
Answer:
After infection of RBC with sporozoite, when the RBC ruptures a toxic substance haemozoin is released which causes shivering chills and high fever followed by sweating.
Question 13.
Malaria Eradication programme launched by WHO is a failure. Why?
Answer:
In the 1950’s the World Health Organisation (WHO) introduced the Malaria eradication programme. This programme was not successful due to the resistance of Plasmodium to the drugs used to treat it and resistance of mosquito’s to DDT and other insecticides.
Question 14.
Filarial worm and Plasmodium both are digenic parasites. Man is a common host for both parasites. Name the other host.
Answer:
The other host of filarial worm is female Culex mosquito The other host of plasmodium is female Anopheles mosquito
Question 15.
Name the causative organism of filariasis and mention the site of infection of parasite.
Answer:
Causative organisms of filariasis is Wuchereria bancrofti (filarial worm). The site of infection is lymph vessels and lymph nodes.
Question 16.
What do you mean by the term personal hygiene?
Answer:
Personal hygiene refers to maintaining one’s body clean by bathing, washing hands, trimming fingernails, wearing clean clothes and also includes attention to keeping surfaces in the home and workplace, including toilets, bathroom facilities, clean and pathogen-free.
Question 17.
Define Immunity and Susceptibility.
Answer:
The overall ability of body to fight against the disease causing pathogen is called immunity. It is also called disease resistance and the lack of immunity is known as susceptibility.
Question 18.
How skin and mucus membrane act as barriers for infections?
Answer:
Skin prevents the entry of microbes. Its acidic environment (pH 3-5) retards the growth of microbes.
Question 19.
Mucus membrane entraps foreign microorganisms and competes with microbes for attachment. What is diapedesis?
Answer:
Tissue damage and infection induce leakage of vascular fluid, containing chemotactic signals like serotonin, histamine and prostaglandins. They influx the phagocytic cells into the affected area. This phenomenon is called diapedesis.
Question 20.
Write any two differences between CMI and AMI.
Answer:
Cell Mediated Immunity (CMI):
- In CMI, pathogens are destroyed by cells without producing antibodies.
- It is carried out by T cells, Macrophages, NK cells
Antibody Mediated Immunity (AMI):
- In AMI, pathogens are destroyed by antibodies.
- It is carried out by B cells, T helper cells, APC cells.
Question 21.
Define haematopoiesis.
Answer:
The process of production of blood cells in the bone marrow is called haematopoiesis.
Question 22.
Which is the primary lymphoid organs of birds? Mention its location and role.
Answer:
Bursa of Fabricius is a primary lymphoid organ of birds. It is attached to the dorsal side of the cloaca. B lymphocytes mature in the bursa and bring about humoral immunity.
Question 23.
What are the primary lymphoid organs of mammals?
Answer:
Bone marrow and thymus gland.
Question 24.
What are Peyer’s patches?
Answer:
Peyer’s patches are oval-shaped areas of thickened tissue that are embedded in the mucus- secreting lining of the small intestine of humans and other vertebrate animals. Peyer’s patches contain a variety of immune cells, including macrophages, dendritic cells, T cells, and B cells.
Question 25.
Point out any four peripheral lymphoid organs.
Answer:
Lymph nodes, spleen, tonsils, MALT.
Question 26.
Write a brief note on GALT.
Answer:
Gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT) is a component of the mucosa associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) which works in the immune system to protect the body from invasion in the gut.
Question 27.
Why secondary immune response is more effective than primary immune response?
Answer:
Due to the establishment of immunological memory of the first encounter, the secondary immune response highly intense and effective.
Question 28.
Name the Agranulocytes involved in immune response.
Answer:
- Lymphocyte
- Monocytes
Question 29.
Why dendritic cells are called so?
Answer:
Dendritic cells are called so because its covered with long, thin membrane extensions that resemble dendrites of nerve cells. These cells present the antigen to T-helper cells.
Question 30.
How many dendritic cells are identified? Name them.
Answer:
Four types of dendritic cells are known. They are langerhans, interstitial cells, myeloid and lymphoid cells.
Question 31.
What are Haptens?
Answer:
Haptens are substance that are non-immunogenic but can react with the products of a specific immune response.
Question 32.
Distinguish between Epitope and Paratope.
Answer:
- Epitope: Epitope is an antigenic determinant and is ‘ the active part of an antigen.
- Paratope: A paratope is the antigen – binding site and is a part of an antibody which recognizes and binds to an antigen.
Question 33.
Draw a simplified diagram of immunoglobulin.
Answer:
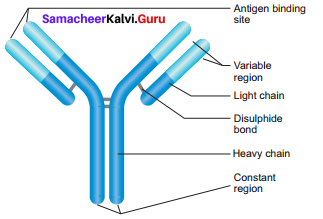
Question 34.
On which basis, the antibodies are classified? Name them.
Answer:
The antibodies are classified into five major categories, based on their physiological and biochemical properties. They are IgG (gamma), IgM(mu), IgA (alpha), IgD(delta) and IgE (epsilon).
Question 35.
Name any four functions of antibodies.
Answer:
The functions of immunoglobulin are agglutination, precipitation, opsonisation, neutralization.
Question 36.
Which type of bonds are developed between an antigen and antibody? Name them.
Answer:
The bonds that hold the antigen to the antibody combining site are all non-covalent in nature. These include hydrogen bonds, electrostatic bonds, Van der Waals forces and hydrophobic bonds.
Question 37.
What is antibody affinity?
Answer:
Antibody affinity is the strength of the reaction between a single antigenic determinant and a single combining site on the antibody.
Question 38
What do you mean by third generation vaccine?
Answer:
Third generation vaccine contains the purest and the highest potency vaccines which are synthetic in generation. The latest revolution in vaccine is DNA vaccine or recombinant vaccine.
Question 39
Define vaccination.
Answer:
Vaccination is the process of administrating a vaccine into the body or the act of introducing a vaccine into the body to produce immunity to a specific disease.
Question 40.
Define allergy and allergen.
Answer:
The exaggerated response of the immune system to certain antigens present in the environment is called allergy (allo-altered, erg-reaction). The substances to which such an immune response is produced are called allergens.
Question 41.
What is Anaphylaxis?
Answer:
Anaphylaxis is the classical immediate hypersensitivity reaction. It is a sudden, systematic, severe and immediate hypersensitivity reaction occurring as a result of rapid generalized mast-cell degranulation.
Question 42.
Expand
- MALT
- NACO
Answer:
- MALT – Mucosal-Associated Lymphoid Tissue
- NACO – National AIDS Control Organisation
Question 43.
How will you define Autoimmunity?
Answer:
Autoimmunity is due to an abnormal immune response in which the immune system fails to properly distinguish between self and non-self and attacks its own body.
Question 44.
What do you mean by drug abuse?
Answer:
The intake of certain drugs for a purpose other than their normal clinical use in an amount and frequency that impair one’s physical, physiological and psychological functions is called drug abuse.
Question 45.
Name any 4 natural cannabinoids.
Answer:
Marijuana, Ganja, Hashish and Charas.
Question 46.
Mention any two drugs to treat insomnia patient.
Answer:
- methamphetamine
- Lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD)
Question 47.
Name the antibody responsible for allergic reaction. Also mention two chemicals released during allergic response.
Answer:
IgE (epsilon) antibody is responsible for allergic reaction. Histamine and serotonin are the chemicals released during allergic reaction.
Question 48.
Name an opioid drug and its source plant. How it is useful in medical field?
Answer:
- Morphine is an opioid drug which is extracted from flowers of the poppy plant.
- It is used as a strong pain killer during surgery.
Question 49.
What is withdrawal symptom? Name any two symptoms.
Answer:
If the intake of the drug or alcohol is abruptly stopped, he or she would develop withdrawal symptoms. In a sense, the body becomes confused and protests against the absence of the drug. The withdrawal symptoms are nervousness and insomnia.
Question 50.
Name the plant source of Cocaine and Heroin.
Answer:
- Cocaine is obtained from Erythroxylum coca.
- Heroin is obtained from poppy plant.
Question 51.
What is Liver cirrhosis?
Answer:
Alcohol interferes with the ability of the liver to break down fat. Over time fat accumulation and high levels of alcohol destroy the liver cells and a scar tissue grows in the place of dead cells. This scarring of the liver is called “Liver cirrhosis”.
Question 52.
Define Korsakoff syndrome.
Answer:
Korsakoff syndrome, a chronic memory disorder is most commonly caused by alcohol misuse.
Question 53.
What are the benefits of exercising our body?
Answer:
Participating in an exercise programme can:
- Increase self-esteem
- Boost self-confidence
- Create a sense of empowerment
- Enhance social connections and relationships
3 – Mark Questions
Question 54.
Write the name of causative agent, infection site, mode of transmission and any two symptoms of Chikungunya.
Answer:
- Causative agent – Alpha virus
- Infection site – Nervous system
- Mode of transmission – Aedes aegypti (Mosquito)
- Symptoms – Fever, headache, joint pain and swelling.
Question 55.
Draw and label the parts of Entamoeba histolytica.
Answer:
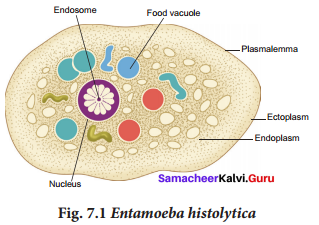
Question 56.
Give a brief account of Kala-azar.
Answer:
Kala – azar or visceral leishmaniasis is caused by Leishmania donovani, which is transmitted by the vector Phlebotomus (sand fly). Infection may occur in the endothelial cells, bone marrow, liver, lymph glands and blood vessels of the spleen. Symptoms of Kala azar are weight loss, anaemia, fever, enlargement of spleen and liver.
Question 57.
Comment on Malaria vaccine.
Answer:
Malaria vaccine is used to prevent malaria. The only approved vaccine as of 2015 is RTS,S(Mosquirix). It requires four injections and has relatively low efficacy (26-50%). Due to this low efficacy, WHO does not recommend the use of RTS,S vaccine in babies between 6 lr and 12 weeks of age.
Question 58.
What is innate immunity?
Answer:
Innate immunity is the natural phenomenon of resistance to infection which an individual possesses right from the birth. The innate defense mechanisms are non-specific in the sense that they are effective against a wide range of potentially infectious agents. It is otherwise known as non-specific immunity or natural immunity
Question 59.
Explain
- Cell Mediated Immunity
- Antibody Mediated Immunity
Answer:
- Cell-mediated immunity: When pathogens are destroyed by cells without producing antibodies, then it is known as cell mediated immune response or cell mediated immunity. This is brought about by T cells, macrophages and natural killer cells.
- Antibody mediated immunity or humoral immunity: When pathogens are destroyed by the production of antibodies, then it is known as antibody mediated or humoral immunity. This is brought about by B cells with the aid of antigen presenting cells and T helper cells. Antibody production is the characteristic feature of vertebrates only.
Question 60.
Secondary response is a booster response – Explain.
Answer:
The secondary immune response occurs when a person is exposed to the same antigen again. During this time, immunological memory has been established and the immune system can start producing antibodies immediately. Within hours after recognition of the antigen, a new army of plasma cells are generated. Within 2 to 3 days, the antibody concentration in the blood rises steeply to reach much higher level than primary response. This is also called as “booster response”.
Question 61.
What are lymphoid organs? Mention its types.
Answer:
The organs involved in the origin, maturation and proliferation of lymphocytes are called lymphoid organs. Based on their functions, they are classified into primary or central lymphoid organs and secondary or peripheral lymphoid organs.
Question 62.
Classify antigens based on origin.
Answer:
On the basis of origin, antigens are classified into exogenous antigens and endogenous antigens. The antigens which enter the host from the outside in the form of microorganisms, pollens, drugs, or pollutants are called exogenous antigens. The antigens which are formed within the individual are endogenous antigens. The best examples are blood group antigens.
Question 63.
Point out the factors that determine the binding force between antigen – antibody reactions.
Answer:
The binding force between antigen and antibody is due to three factors. They are closeness between antigen and antibody, noncovalent bonds or intermolecular forces and affinity of antibody.
Question 64.
Why it is important to study antigen – antibody interaction?
Answer:
The chief application of antigen – antibody reactions are to determine blood groups for transfusion, to study serological ascertainment of exposure to infectious agents, to develop immunoassays for the quantification of various substances, to detect the presence or absence, of protein in serum and to determine the characteristics of certain immunodeficiency diseases.
Question 65.
Explain opsonisation property of antibodies.
Answer:
Opsonisation or enhanced attachment is the process by which a pathogen is marked of ingestion and destruction by a phagocyte. Opsonisation involves the binding of an opsonin i.e antibody, to a receptor on the pathogen’s cell membrane. After opsonin binds to the membrane, phagocytes are attracted to the pathogen. So, opsonisation is a process in which pathogens are coated with a substance called an opsonin, marking the pathogen out for destruction by the immune system. This results in a much more efficient phagocytosis.
Question 66.
Give an example for
- First generufkmvaccine
- Second generation vaccine
- Third generation vaccine
Answer:
- First generation vaccine – MMR vaccine
- Second generation vaccine – Hepatitis-B vaccine
- Third generation vaccine – DNA Vaccine
Question 67.
Name the diseases for which vaccines were developed by Louis Pasteur.
Answer:
Cholera, Anthrax and Rabies
Question 68.
How AIDS patient fail to develop immunity?
Answer:
AIDS is caused by Human Immuno Deficiency Virus (HIV). It selectively infects helper T cells. The infected helper T cells will not stimulate antibody production by B-cells resulting in loss of natural defence against viral infection.
Question 69.
Suggest few methods to prevent AIDS.
Answer:
Prevention of AIDS is the best option. Advocating safe sex and promoting regular check-up, safe blood for transfusion, use of disposable needles, use of condoms during sexual contact, prevention of drug abuse, AIDS awareness programme by NACO (National AIDS Control Organisation), NGOs (Non-Governmental Organisations) and WHO are to prevent the spreading of AIDS.
Question 70.
State immunological surveillance theory.
Answer:
The concept of immunological surveillance postulates that the primary function of the immune system is to “seek and destroy” malignant cells that arise by somatic mutation. The efficiency of the surveillance mechanism reduces either as a result of ageing or due to congenital or acquired immunodeficiencies, leads to increased incidence of cancer. Thus, if immunological surveillance is effective, cancer should not occur. The development of tumour represents a lapse in surveillance.
Question 71.
What is contact inhibition? How it is related to tumours growth?
Answer:
Normal cells show a property called contact inhibition, which inhibits uncontrolled growth. Cancer cells do not have this property. As a result, cancerous cells divide continuously giving rise to mass of tissues called tumours.
Question 72.
Differentiate between normal cells and cancer cells.
Answer:
Normal Cells:
- Small uniformly shaped nuclei Relatively large cytoplasmic volume
- Conformity in cell size and shape Cells arranged into discrete tissue
- May possess differentiated cell structures Normal presentation of cell surface markers
- Lower levels of dividing cells Cell tissues clearly demarcated
Cancer Cells:
- Large, variable shaped nuclei Relatively small cytoplasmic volume
- Variation in cell size and shape Disorganised arrangement of cells
- Loss of normal specialised features Elevated expression of certain cell markers
- Large number of dividing cells Poorly defined tumor boundaries
Question 73.
Write a note on Heroin.
Answer:
Heroin (smack) is chemically diacetyl morphine, which is white, odourless and bitter crystalline compound. It is obtained by acetylation of morphine, which is extracted from flowers of the poppy plant.
Question 74.
“Smoking and Tobacco chewing is injurious to health” – Comment on the statement.
Answer:
Tohacco is smoked, chewed and used as snuff. It increases the carbon monoxide content of blood and reduces the concentration of haem bound oxygen, thus causing oxygen deficiency in the body. Tobacco contains nicotine, carbon monoxide and tars, which cause problems in the heart, lung and nervous system. Adrenal glands are stimulated by nicotine to release adrenaline and nor adrenaline which increases blood pressure and heart beat.
Question 75.
Point out the symptoms of mental depression.
Answer:
Signs and symptoms of mental depression:
- Loss of self confidence and self esteem
- Anxiety
- Not being able to enjoy things that are usually pleasurable or interesting.
5-Mark Questions
Question 76.
Name any five viral diseases, their causative agents, infection site, mode of transmission and their symptoms.
Answer:
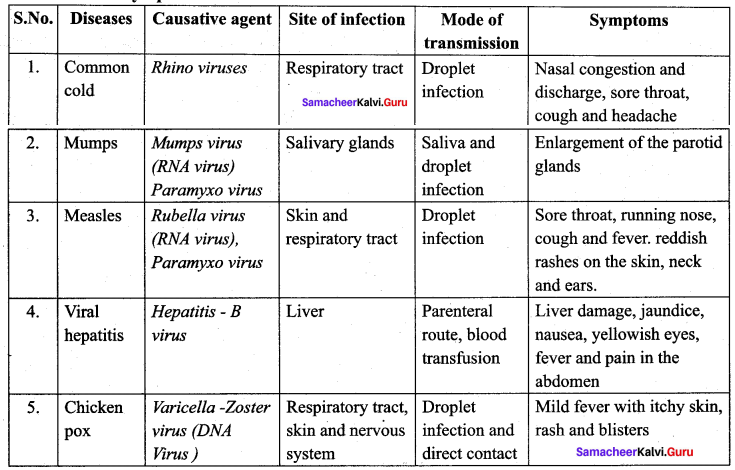
Question 77.
Describe the life cycle of plasmodium parasite.
Answer:
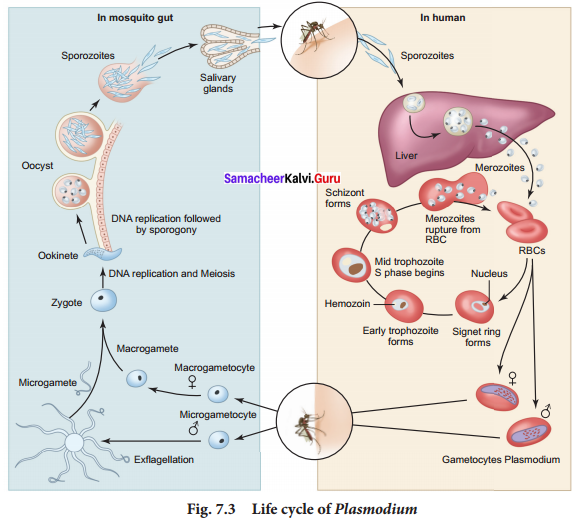
Plasmodium vivax is a digenic parasite, involving two hosts, man as the secondary host and female Anopheles mosquito as the primary host. The life cycle of Plasmodium involves three phases namely schizogony, gamogony and sporogony.
The parasite first enters the human blood stream through the bite of an infected female Anopheles mosquito. As it feeds, the mosquito injects the saliva containing the sporozoites. ‘The sporozoite within the blood stream immediately enters the hepatic cells of the liver. Further in the liver they undergo multiple asexual fission (schizogony) and produce merozoites. After being released from liver cells, the merozoites penetrate the RBC’s.
Inside the RBC, the merozoite begins to develop as unicellular trophozoites. The trophozoite grows in size and a central vacuole develops pushing them to one side of cytoplasm and becomes the signet ring stage. The trophozoite nucleus then divides asexually to produce the schizont. The large schizont shows yellowish – brown pigmented granules called Schuffners granules. The schizont divides and produces mononucleated merozoites. Eventually the erythrocyte lyses, releasing the merozoites and haemozoin toxin into the blood stream to infect other erythrocytes.
Lysis of red blood cells results in cycles of fever and other symptoms. This erythrocytic stage is cyclic and repeats itself approximately every 48 to 72 hours or longer depending on the species of Plasmodium involved. The sudden release of merozoites triggers an attack on the RBCs.
Occasionally, merozoites differentiate into macrogametocytes and microgametocytes. When these are ingested by a mosquitoe, they develop into male and female gametes respectively. In the mosquito’s gut, the infected erythrocytes lyse and male and female gametes fertilize to form a diploid zygote called ookinete. The ookinete migrates to the mosquito’s gut wall and develop into an oocyte.
The oocyte undergoes meiosis by a process called sporogony to form sporozoites. These sporozoites migrate to the salivary glands of the mosquito. The cycle is now completed and when the mosquito bites another human host, the sporozoites are injected and the cycle begins a new.
The pathological changes caused by malaria, affects not only the erythrocytes but also the spleen and other visceral organs. Incubation period of malaria is about 12 days. The early symptoms of malaria are headache, nausea and muscular pain. The classic symptoms first develop with the synchronized release of merozoites, haemozoin toxin and erythrocyte debris into the blood stream resulting in malarial paroxysms – shivering chills, high fever followed by sweating. Fever and chills are caused partly by malarial toxins that induce macrophages to release tumour necrosis factor (TNF-a) and interleukin.
Question 78.
Give an account of helminthic disease.
Answer:
Helminthes are mostly endoparasitic in the gut and blood of human beings and cause diseases called helminthiasis. The two most prevalent helminthic diseases are Ascariasis and Filariasis. Ascaris is a monogenic parasite and exhibits sexual dimorphism. Ascariasis is a disease caused by the intestinal endoparasite Ascaris lumbricoides commonly called the round worms. It is transmitted through ingestion of embryonated eggs through contaminated food and water.
Children playing in contaminated soils are also prone to have a chance of transfer of eggs from hand to mouth. The symptoms of the disease are abdominal pain, vomiting, headache, anaemia, irritability and diarrhoea. A heavy infection can cause nutritional deficiency and – severe abdominal pain and causes stunted growth in children. It may also cause enteritis, hepatitis and bronchitis.
Filariasis is caused by Wuchereria bancrofti, commonly called filarial worm. It is found in the lymph vessels and lymph nodes of man. Wuchereria bancrofti is sexually dimorphic, viviparous and digenic. The life cycle is completed in two hosts, man and the female Culex mosquitoe. The female filarial worm gives rise to juveniles called microfilariae larvae. In the lymph glands, the juveniles develop into adults. The accumulation of the worms block the lymphatic system resulting in inflammation of the lymph nodes. In some cases, the obstruction of lymph vessels causes elephantiasis or filariasis of the limbs, scrotum and mammary glands.
Question 79.
Tabulate the various types of innate immunity and their action mechanism.
Answer:
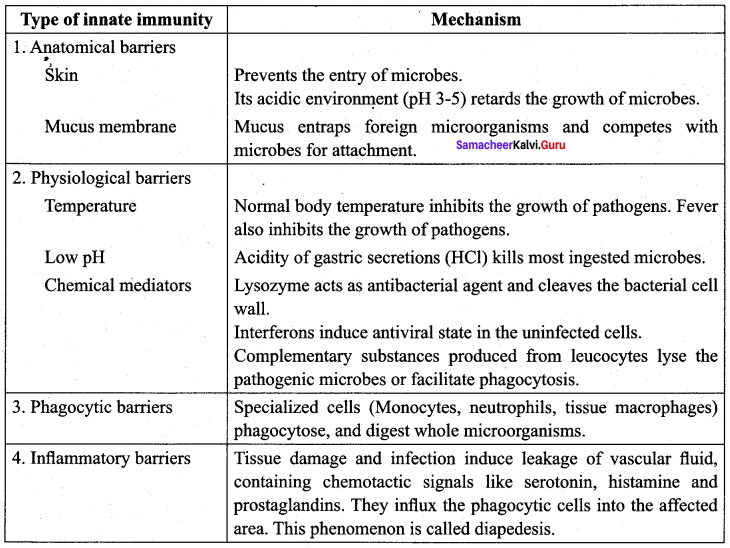
Question 80.
Point out the differences between active and passive immunity.
Answer:
Active Immunity:
- Active immunity is produced actively by host’s immune system.
- It is produced due to contact with pathogen or by its antigen.
- It is durable and effective in protection.
- Immunological memory is present.
- Booster effect on subsequent dose is possible.
- Immunity is effective only after a short period.
Passive Immunity:
- Passive immunity is received passively and there is no active host participation.
- It is produced due to antibodies obtained from outside.
- It is transient and less effective.
- No memory.
- Subsequent dose is less effective.
- Immunity develops immediately.
Question 81.
How primary immune response differ from secondary immune response?
Answer:
Primary Immune Response:
- It occurs as a result of primary contact with an antigen.
- Antibody level reaches peak in 7 to 10 days.
- Prolonged period is required to establish immunity.
- There is rapid decline in antibody level.
- It appears mainly in the lymph nodes and spleen.
Secondary Immune Response:
- It occurs as a result of second and subsequent contacts with the same antigen.
- Antibody level reaches peak in 3 to 5 days.
- It establishes immunity in a short time.
- Antibody level remains high for longer period.
- It appears mainly in the bone marrow, followed by the spleen and lymph nodes.
Question 82.
Explain the structure and role of thymus in primary lymphoid organ.
Answer:
Thymus is most active during the neonatal and pre-adolescent periods. The thymus is a flat and bilobed organ located behind the stemun, above the heart. Each lobe of the thymus contains numerous lobules, separated from each other by connective tissue called septa. Each lobule is differentiate into an outer cortex and an inner medulla. Within each lobule, the devoloping T cells called thymocytes are arranged into outer cortex and inner medulla. The inner medulla contains immature thymocytes and outer cortex has matured thymocytes. One of its main secretions is the hormone thymosin. It stimulates the cell to become mature and immunocompetent. By the early teens, the thymus begins to atrophy and is replaced by adipose tissue.
Question 83.
Describe the structure of lymph node with a labelled diagram.
Answer:
Lymph node has three zones. They are the cortex, paracortex and medulla. The outer most layer of the lymph node is called cortex, which consists of B-lymphocytes, macrophages, and follicular dendritic cells. The paracortex zone is beneath the cortex, which is richly populated by lymphocytes and interdigitating dendritic cells. The inner most zone is called the medulla
which is sparsely populated by lymphocytes, but many of Afferentymiatic them are plasma cells, which actively secrete antibody molecules. As the lymph enters, it slowly percolates through the cortex, paracortex and medulla, giving sufficient chance for the phagocytic cells and dendritic cells to trap the antigen brought by the lymph.
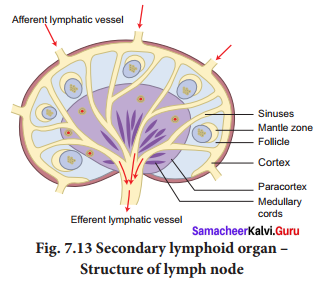
The lymph leaving a node carries enriched antibodies secreted by the medullary plasma cells against the antigens that enter the lymph node. Sometimes visible swelling of lymph nodes occurs due to active immune response and increased concentration of lymphocytes. Thus swollen lymph nodes may signal an infection. There are several groups of lymph nodes. The most frequently enlarged lymph nodes are found in the neck, under the chin, in the armpits and in the groin.
Question 84.
Explain the types of cells involved in immune system.
Answer:
Lymphocytes: About 20-30% of the white blood cells are lymphocytes. They have a large nucleus filling most of the cell, surrounded by a little cytoplasm. The two main types of lymphocytes are B and T lymphocytes. Both these are produced in the bone marrow. B lymphocytes (B cells) stay in the bone marrow until they are mature. Then they circulate around the body. Some remain in the blood, while others accumulate in the lymph nodes and spleen. T lymphocytes leave the bone marrow and mature in the thymus gland. Once mature, T cells also accumulate in the same areas of the body as B cells. Lymphocytes have receptor proteins on their surface. When receptors on a B cell bind with an antigen, the B cell becomes activated and divides rapidly to produce plasma cells. The plasma cells produce antibodies. Some B cells do not produce antibodies but become memory cells.
These cells are responsible for secondary immune response. T lymphocytes do not produce antibodies. They recognize antigen-presenting cells and destroy them. The two important types of T cells are Helper T cells and Killer T cells. Helper T cells release a chemical called cytokine which activates B cells. Killer cells more around the body and destroy cells which are damaged or infected. Apart from these cells neutrophils and monocytes destroy foreign cells by phagocytosis. Monocytes when they mature into large cells, they are called macrophages which performs phagocytosis on any foreign organism.
Dendritic cells are called so because its covered with long, thin membrane extensions that resemble dendrites of nerve cells. These cells present the antigen to T-helper cells. Four types of dendritic cells are known. They are langerhans, interstitial cells, myeloid and lymphoid cells.
Question 85.
Write in detail about various types of antigen-antibody reactions.
Different types of antigen and antibody reactions:
Answer:
The reaction between soluble antigen and antibody leads to visible precipitate formation, which is Called precipitin reaction. Antibodies that bring about precipitate formation on reacting with antigens are called as precipitins. Whenever a particulate antigen interacts with its antibody, it would result in clumping or agglutination of the particulate antigen, which is called agglutination reaction. The antibody involved in bringing about agglutination reaction is called agglutinin.
Opsonisation or enhanced attachment is the process by which a pathogen is marked of ingestion and destruction by a phagocyte. Opsonisation involves the binding of an opsonin antibody, to a receptor on the pathogen’s cell membrane. After opsonin binds to the membrane, phagocytes are attracted to the pathogen. So, opsonisation is a process in which pathogens are coated with a substance called an opsonin, marking the pathogen out for destruction by the immune system. This results in a much more efficient phagocytosis.
The neutralization reactions are the reactions of antigen-antibody that involve the elimination of harmful effects of bacterial exotoxins or a virus by specific antibodies. These neutralizing substances i.e. antibodies are known as antitoxins. This specific antibody is produced by a host cell in response to a bacterial exotoxin or corresponding toxoid (inactivated toxin).
Question 86.
Describe the structure of HIV with a diagram.
Answer:
The human immunodeficiency virus belongs to the genus Lentivirus. When observed under the electron microscope, HIV is seen as a spherical virus, 100-120 nm in diameter, containing a dense .core surrounded by a lipoprotein envelope.The envelope has glycoprotein (gp) spikes termed gp 41 and gp 120. At the core, there are two large single stranded RNA. Attached to the RNA are molecules of reverse transcriptase.
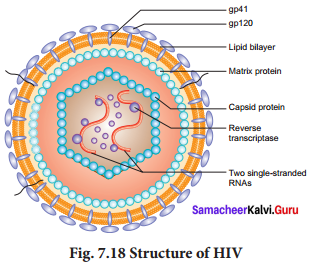
It also contains enzymes like protease and ribonuclease.The core is covered by a capsid made of proteins. This is followed by another layer of matrix proteins as shown above.
Question 95.
Suggest some of the ways to prevent drug and alcohol abuse.
Answer:
- Effectively dealing with peer pressure: The biggest reason for teens to start on drugs is due to their friends / peer groups imposing pressure on them. Hence, it is important to have a better group of friends to avoid such harmful drugs and alcohol.
- Seeking help from parents and peers: Help from parents and peer group should be sought immediately so that they can be guided appropriately. Help may even be sought from close and trusted friends. Getting proper advice to sort out their problems would help the young to vent their feelings of anxiety and guilt.
- Education and counselling: Education and counselling create positive attitude to deal with many problems and to accept disappointments in life.
- Looking for danger signs: Teachers and parents need to look for sign that indicate tendency to go in for addiction.
- Seeking professional and medical assistance: Assistance is available in the form of highly qualified psychologists, psychiatrists and de addiction and rehabilitation programmes to help individuals to overcome their problems.
Higher Order Thinking Skills (HOTs) Questions
Question 1.
Identify the mismatched pair and give reason.
(a) Plague – Yersinia pestis
(b) Filariasis – Wuchereria bancrofti
(c) Dermatomycosis – Trypanosoma gambiense
(c) Common cold – Rhino virus
Answer:
(c) Dermatomycosis – Trypanosoma gambiense is the mismatched pair. Dermatomycosis is a cutaneous infection caused by fungus.
Question 2.
In which form does the malarial parasite enter the human body through mosquito? What is the target site of parasite immediately after entering the host body?
Answer:
- Sporozoites.
- After entering the blood stream of host it finally reaches the liver cell.
Question 3.
A boy of ten years had suffered from chicken-pox. His grand mother consoled him that he is not expected to have it for the rest of his life. Whether his grandmother is right? If so how it happens?
Answer:
The infection produces not only antibodies but also generates memory in the lymphocytes. These cells recognize the pathogen on subsequent attack and generate antibodies to neutralize the pathogen, so his grandmother is right and the boy will not get the disease for rest of his life.
The data given about Chapterwise Samacheer Kalvi Class 12th Bio Zoology Solutions Chapter 7 Human Health and Diseases Questions and Answers will help the students to score good marks in the exam. Contact us for more updated information and also to clear your queries. Keep every single update by bookmarking our website. Get advanced skills by referring to Samacheer Kalvi Class 12th Bio Zoology Solutions Chapter 7 Human Health and Diseases solutions pdf.