Download Tamilnadu State Board Solutions for Class 12th Chapter 22 The Negotiable Instruments Act 1881 PDF here. These Samacheer Kalvi Class 12th Chapter 22 The Negotiable Instruments Act 1881 Questions and Answers will help you to improve your skills and score highest marks in the exams. Students can easily learn Chapter wise Samacheer Kalvi 12th Commerce Book Solutions Chapter 22 The Negotiable Instruments Act 1881 by following the guide provided here.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Commerce Solutions Chapter 22 The Negotiable Instruments Act 1881
Students can score good marks in the exam by preparing with Samacheer Kalvi Class 12th Commerce Solutions Chapter 22 The Negotiable Instruments Act 1881 Questions and Answers. Your efforts can give you good results when you have the best resources. Samacheer Kalvi Class 12th Commerce Solutions Chapter 22 The Negotiable Instruments Act 1881 is the best resource to learn Commerce. Have the best learning with Chapterwise Tamilnadu State Board Class 12th Commerce Solutions to have the best future ahead.
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Commerce The Negotiable Instruments Act 1881 Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers
I. Choose the Correct Answer
Question 1.
Negotiable Instrument Act was passed in the year ________
(a) 1981
(b) 1881
(c) 1994
(d) 1818
Answer:
(b) 1881
Question 2.
Negotiable Instrument is freely transferable by delivery if it is a ________ instrument.
(a) Order
(b) Bearer
(c) Both a and b
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(b) Bearer
Question 3.
The transferee of a Negotiable Instrument is the one ________
(a) Who transfer the instrument
(b) On whose name it is transferred
(c) Who enchases it
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(b) On whose name it is transferred
Question 4.
Number of parties in a bill of exchange are ________
(a) 2
(b) 6
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer:
(c) 3
Question 5.
Section 6 of Negotiable Instruments Act 1881 deals with ________
(a) Promissory Note
(b) Bills of exchange
(c) Cheque
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(c) Cheque
Question 6.
________ cannot be a bearer instrument.
(a) Cheque
(b) Promissory Note
(c) Bills of exchange
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(a) Cheque
Question 7.
When crossing restrict further negotiation ________
(a) Not negotiable crossing
(b) General Crossing
(c) A/c payee crossing
(d) Special crossing
Answer:
(a) Not negotiable crossing
Question 8.
Which endorsement relieves the endorser from incurring liability in the event of dishonour?
(a) Restrictive
(b) Facultative
(c) Sans recourse
(d) Conditional
Answer:
(b) Facultative
Question 9.
A cheque will become stale after ________ months of its date.
(a) 3
(b) 4
(c) 5
(d) 1
Answer:
(a) 3
Question 10.
Document of title to the goods exclude ________
(a) Lorry receipt
(b) Railway receipt
(c) Airway bill
(d) Invoice
Answer:
(d) Invoice
II. Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What is meant by Negotiable Instrument?
Answer:
- The word “Negotiable” means “Transferable” from one person to another in return for consideration.
- It is a document which entitles a person to a certain sum of money and which is transferable from one person to another by mere delivery or by endorsement and delivery.
Question 2.
Define Bill of Exchange.
Answer:
According to section 5 of the Negotiable Instruments Act, “a bill of exchange is an instrument in writing containing an unconditional order, signed by the maker, directing a certain person to pay a certain sum of money only to, or to the order of a certain person or to the bearer of the – instrument”.
Question 3.
List three characteristics of a Promissory Note.
Answer:
- A Promissory Note must be in writing.
- It must contain a promise or undertaking to pay.
- The promise to pay must be unconditional.
- It must be signed by the maker.
Question 4.
What is meant by a cheque?
Answer:
According to section 6 of the Negotiable Instruments Act, 1881 defines a cheque is “a bill of exchange drawn on a specified banker and not expressed to be payable otherwise than on-demand”.
Question 5.
Define Endorsement.
Answer:
“Where the maker or the holder of the negotiable instrument signs the same, otherwise than as such maker/for the purpose of negotiation, on the back or face thereof, or on a slip of paper annexed thereto, he is said to endorse the same, and is called the endorser”. – NEGOTIABLE INSTRUMENT ACT 1881, SEC -15
III. Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Explain the nature of a Negotiable Instrument.
Answer:
Transferability:
- A negotiable instrument is transferable from one person to another without any formality, such as affixing stamp, registration etc.
- In case it is payable to Bearer – mere delivery.
- In case it is payable in Order – Endorsement delivery.
Title of the holder free from all defects :
When the instrument is held by the holder in due course in the process of negotiation, it cured of ail defects in the instrument with respect to ownership.
Right of the transferee to sue:
Though a Bill or a promissory note or a cheque represents a debt, the transferee is entitled to sue on the instrument in his own name in case of dishonour without giving notice to the debtor that he has become its holder.
Question 2.
Distinguish between Negotiability and Assignability.
Answer:
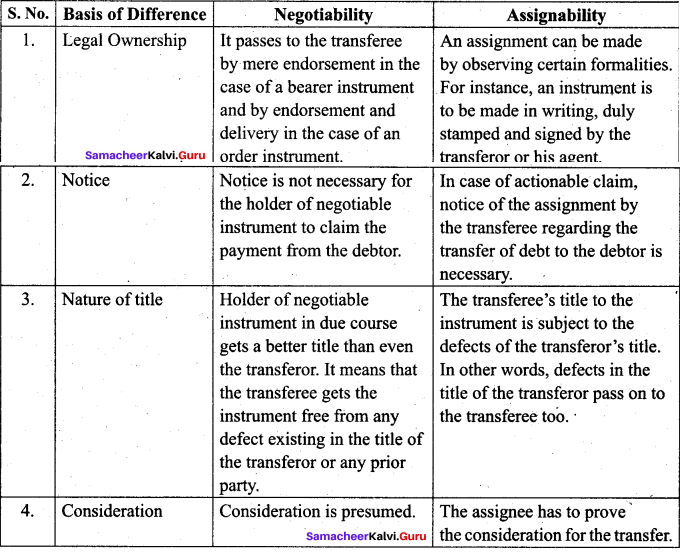
Question 3.
What are the characteristics of a bill of exchange?
Answer:
- The instrument must be in writing.
- Signed by the maker [Drawer].
- Order must be unconditional.
- The amount payable must be certain.
- The person to whom the bill is drawn must be specified.
- Drawer, Drawee, and Payee must ail be certain.
Question 4.
Distinguish between Bill of Exchange and Promissory Note.
Answer:
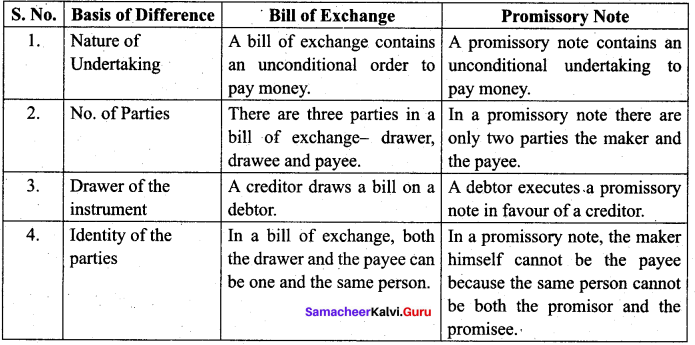
IV. Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
Mention the presumptions of Negotiable Instruments.
Answer:
Negotiable Instruments presumed to have been.
- Drawn, Accepted, etc. for consideration.
- Reasonable time (Accepted within them) after the date and before its maturity.
- The endorsement made in the order to which they appear thereon.
- Accepted.
- Made before maturity.
- Stamped duly.
Question 2.
Distinguish a cheque and a bill of exchange.
Answer:
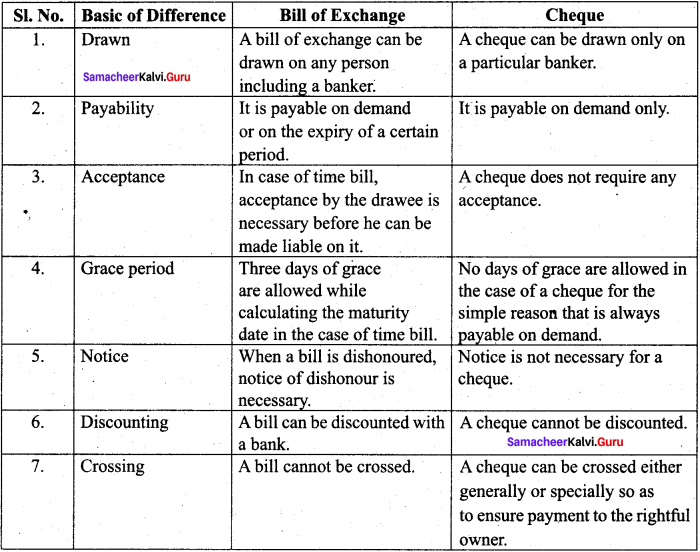
Question 3.
Discuss in detail the features of a cheque.
Answer:
Signed by the Drawer:
- A Cheque is to be signed by the drawer.
- Further, it should tally with the specimen signature furnished to the bank at the time of opening the Account.
A certain sum of money only :
- The order must be for payment of money only.
- Further, the sum of money must be certain.
Unconditional order:
- The order must be unconditional.
- A Cheque is an order to pay and is not a request.
- Pay itself denotes a command and words like ‘please’ or ‘kindly’ are dispensed with in a cheque.
Drawn on a Specified Banker Only:
- The cheque is always drawn on a specified Banker.
- The customer of a Bank can draw the cheque only on the particular Bank (Branch) where he has an account.
The instrument in writing:
- A cheque must be an instrument in writing. (Ink)
- Though the Law does not prohibit a cheque from being written in Pencil, Bankers never accept it because of risks involved.
- Alteration is quite easy but detection is impossible in such cases.
Payee to be certain:
- The cheque must be payable to a certain person or to the order of a certain person or to
Payable on-demand: - A cheque is always payable on demand.
Question 4.
What are the requisites for a valid endorsement?
Answer:
Backside:
The endorsement is usually made on the backside of an instrument.
Allonge:
When there is no space for making further endorsements a piece of paper can be attached to the negotiable instrument for this purpose. This piece of paper is called “ALLONGE”.
Delivery:
The endorsement is complete only when delivery of the instrument is made.
Names:
The prefixes (Thiru, Mr., Mrs., Dr., etc….) or suffixes (Avargal, IAS, M.com, etc….) added to the names of the payees or endorsees must be omitted in the endorsement.
The endorsement in Ink:
The endorsement must be in Ink.
Wrongly spelled:
If the endorsee’s name is wrongly spelled [VIRAT – VEER AT] the endorser should sign the same spelled in the instrument and write the correct spelling in brackets.
Signing:
Signing in block letters [sign – RAAJA] does not constitute a regular endorsement.
Duly authorised:
A person who is duly authorised to endorse an instrument must indicate that he is signing in it on behalf of his principal by using such words “for”, or “on behalf of” or “per pro”.
Question 5.
Explain the different kinds of endorsements.
Answer:
When the person signs on the back of the instrument to transfer his interest, it is known as an endorsement. The endorsement are of various types:
(i) Blank or general endorsement:
When the endorser puts his mere signature on the back of an instrument without mentioning the name of the person to whom the endorsement is made, it is called Blank Endorsement
(ii) Endorsement in full or special endorsement:
If the endorser, in addition to his signature, mentions the name of the person to whom it is endorsed, is known as an endorsement in full or special endorsement.
(iii) Conditional endorsement:
When the endorser of a negotiable instrument makes his liability dependent upon the happening of an event which may or may not happen, it is called a conditional endorsement,
(iv) Restrictive endorsement:
When an endorsement restricts or prohibits further negotiability of the instrument, it is called Restrictive Endorsement.
(v) Partial Endorsement:
Where the endorsement seeks to transfer only a part of the amount payable under the instrument, the endorsement is called Partial Endorsement.
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Commerce The Negotiable Instruments Act 1881 Additional Questions and Answers
I. Choose the Correct Answer
Question 1.
Section ……………………….. defined the promissory Note.
a) 10
b) 15
c) 4
d) 6
Answer:
c) 4
Question 2.
Grace days allowed to a Bill of exchange for calculation of due date is
(a) 4
(b) 10
(c) 3
(d) 5
Answer:
(c) 3
We hope the information prevailed in this article is helpful for all the students of Class 12th. The Tamilnadu State Board Solutions for Class 12th Chapter 22 The Negotiable Instruments Act 1881 Questions and Answers And Pdf enhance your skills and score good marks in the exams. Stay tuned to get the latest information about the Samacheer Kalvi Class 12th Chapter 22 The Negotiable Instruments Act 1881 Solutions.