Download Tamilnadu State Board Solutions for Class 12th Chapter 27 Company Management PDF here. These Samacheer Kalvi Class 12th Chapter 27 Company Management Questions and Answers will help you to improve your skills and score highest marks in the exams. Students can easily learn Chapter wise Samacheer Kalvi 12th Commerce Book Solutions Chapter 27 Company Management by following the guide provided here.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Commerce Solutions Chapter 27 Company Management
Students can score good marks in the exam by preparing with Samacheer Kalvi Class 12th Commerce Solutions Chapter 27 Company Management Questions and Answers. Your efforts can give you good results when you have the best resources. Samacheer Kalvi Class 12th Commerce Solutions Chapter 27 Company Management is the best resource to learn Commerce. Have the best learning with Chapterwise Tamilnadu State Board Class 12th Commerce Solutions to have the best future ahead.
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Commerce Company Management Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers
I. Choose the Correct Answer
Question 1.
A person shall hold office as a director in ______ companies as per the Companies Act,2013.
(a) 5 companies
(b) 10 companies
(c) 20 companies
(d) 15 companies
Answer:
(c) 20 companies
Question 2.
Which Director is appointed by a Financial institution?
(a) Nominee
(b) Additional
(c) Women
(d) Shadow
Answer:
(a) Nominee
Question 3.
A Private Company shall have a minimum of ______
(a) Seven directors
(b) Five directors
(c) Three directors
(d) Two directors
Answer:
(d) Two directors
Question 4.
A Public Company shall have a minimum of ______ Directors.
(a) Twelve
(b) Seven
(c) Three
(d) Two
Answer:
(c) Three
Question 5.
A Public Company having a paid up Share Capital of Rs. ______ or more may have a Director, elected by such small shareholders.
(a) One
(b) Three
(c) Five
(d) Seven
Answer:
(c) Five
Question 6.
Under the companies Act, which one of the following powers can be exercised by the Board of Directors?
(a) Power to sell the company’s undertakings
(b) Power to make call
(c) Power to borrow money in excess of the paid up capital
(d) Power to reappoint an auditor
Answer:
(b) Power to make call
Question 7.
Which director need not hold qualifying shares?
(a) Directors appointed to Central Government
(b) Directors appointed to Shareholders
(c) Directors appointed to Managing Director
(d) Directors appointed to Board of Directors
Answer:
(a) Directors appointed to Central Government
Question 8.
What is the status of Directors who regulate money of the company?
(a) Banker
(b) Holder
(c) Agent
(d) Trustees
Answer:
(d) Trustees
Question 9.
According to Companies Act, the Directors must be appointed by the _______
(a) Central Government
(b) Company Law Tribunal
(c) Company in General Meeting
(d) Board of Directors
Answer:
(c) Company in General Meeting
Question 10.
The Board of Directors can exercise the power to appoint directors in the case of _______
(a) Additional Directors
(b) Filling up the Casual vacancy
(c) Alternate Directors
(d) All the above
Answer:
(d) All the above
II. Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What are the positions of a Director?
Answer:
- Director as an Agent: When a Director entered into a contract on behalf of the company he acts as an Agent.
- Director as Trustee: When he safeguards the money and property of the company he acts as a Trustee.
- Director as an officer: When he signs any statutory Documents he acts as a Chief Executive Officer.
- Director as Employee: Directors are professionals who manage the company for the benefit of themselves for the benefit of the shareholders.
- Director as partners: Directors are elected by shareholders are like partners to the shareholders.
Question 2.
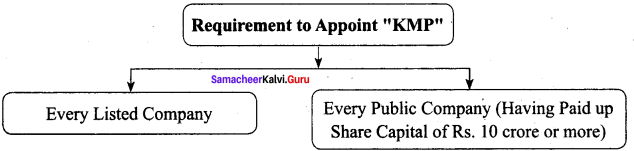
Name the companies required to appoint KMP.
Answer:
Following Companies are required to appoint KMP:
Question 3.
Who is the whole-time Director?
Answer:
- A Whole Time Director is one who devotes the whole of his time of working hours to the company.
- He has a significant personal interest in the company as the source of his income.
Question 4.
Who is called as Managing Director?
Answer:
A Managing Director is one who is employed by the company and has substantial powers of management over the affairs of the company subject to superintendence, direction, and control of the board.
Question 5.
Who can be Executive Director?
Answer:
An Executive Director is a Chief Executive Officer [C.E.O] or MD of an organisation or company or corporation, who is responsible for making decisions to complete the mission and for the success of the organisation.
III. Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Differentiate Executive and Non-Executive Directors.
Answer:
| Basis for Difference | Executive Director | Non-Executive Director |
| 1. Meaning | An Executive Director can be either a whole-time Director of the Company or a Managing Director. | A Non- Executive Director is a Director who is neither a Whole-time Director nor a Managing Director. |
Question 2.
What is a Casual Vacancy?
Answer:
A vacancy arises in the office of an Auditor or Director of the company before the term expired is known as “Casual Vacancy” due to
- Death of an Auditor or Director.
- Retirement of an Auditor or Director.
- Resignation of an Auditor or Director.
- Insolvency.
- Retirement by Rotation.
Question 3.
Who is a shadow director?
Answer:
- A person who is not the member [Director] of the Board but has some power to run it can be appointed as the Director but according to his/her wish.
- He is known as “Shadow Director”.
Question 4.
What is a causal vacancy?
Answer:
If a director is absent from India, for a period which is not less than three months, then it is called a casual vacancy. It may be filled by the appointment of an alternate director. The appointment ’must be authorized by the articles of association by passing a resolution in the meeting.
Question 5.
State the minimum number of Directors for a private company.
Answer:
- One Person Company [OPC] – ONE
- Private Companies – TWO
- Public limited company – THREE
IV. Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
What are the Rights of Directors?
Answer:
Individual Rights:
- To inspect books of Accounts.
- To receive the notice of board meeting.
- To participate and cast vote.
- To inspect minutes.
- To receive circular resolutions proposed to be passed.
Collective Rights:
- To refuse to transfer shares.
- To Elect a Chairman.
- To Appoint an MD.
- To recommend Dividend.
Question 2.
Explain the composition of the board of directors.
Answer:
Composition of the Board of Directors:
- General Optimum Combination: Board of Directors shall have an optimum combination of executive and non-executive directors with at least one woman director.
- When the non-executive Director is the Chairperson: In this case, at least one-third of the board of directors shall comprise of independent directors.
- When the non-executive chairperson is a promoter or is related to any promoter or person occupying management positions at the level of board of director or at one level below the Board of Directors: In this case, at least one half of the board of directors of the company shall consist of Independent Directors.
Question 3.
Briefly explain different types of Directors.
Answer:
Types of Directors as per Companies Act 2013:
i) Residential Director – [Section 149 (3)]:
- Every company should appoint a Director who has stayed in India for a total, period of not less than 182 days. in the previous calendar years.
ii) Additional Director:
- Any Individuals can be appointed (required number) as” Additional Directors” by the. Board of Directors.
iii) Small Shareholders Directors:
- “Small Shareholders” can appoint a Single Director in a Listed company,
- Atleast 1000 shareholders or 1/10th of the total shareholders follow proper procedure and give notice.
iv) Independent Directors: [Section 149(6)]:
- An “Independent Director” is an Alternate Director other than MD
- The following companies have to appoint TWO IDs.
- Public Company Having Paid up share capital – ₹ 10 crores or more
- Public Company -Having – Turnover ₹ 100 crores and’ more.
- Public Company – Having .- Total outstanding Loans, Debentures, and Deposits. ₹ 50 ‘crores or more.
v) Alternate Director:
- Alternate Director” appointed as a substitute to. the (original) Director who may be absent from India for a period, which is not less than 3 months.
vi) Nominee Director:
- He should be Nominated by any: Financial Institutions in pursuance of. any Law or in terms of an agreement entered into by the company.
- He could be appointed by the government or by any other person.
- He shall represent the interests of the organisation which he represents.
Question 4.
State the qualification of directors.
Answer:
A Director Shall possess the appropriate knowledge, skills and experience in the fields of [SMART – FLM] Sales, Management, Administration, Research, Technical operations, Finance, Law, Marketing, Corporate Governance, and other discipline related to Business.
Qualifications:
- He must be an Individual.
- He should be solvent.
- He must be a person of sound mind. [Sane]
- He must hold Qualification Shares.
- He should not be convicted by the Court for any Offence.
Question 5.
List the DisQualification of a Director.
Answer:
- A person of unsound mind [Insane or Lunatic]
- An undischarged Insolvent.
- Call money not yet paid by him for shares held by him.
- Disqualified by the court to act as a Director.
- He has been convicted of the offense of dealing with related party transactions under section 188.
- He has not got the Director Identification Number.
- He has been convicted by a court for any offense involving moral turpitude and sentenced in respect thereof to imprisonment for not less than six months.
Question 6.
Explain how the director of a company can be removed from the office.
Answer:
A Director of Company can be removed from his office before the expiry of his term by ‘
- the Shareholders
- the Central Government
- the Company Law Board
(i) Removal by shareholders (Sec- 169): A company may, by giving a special notice and passing an ordinary resolution, remove a director before the expiry of his period of office.
(ii) Removal by the Central Government: The Central Government has been empowered to remove managerial personnel from office on the recommendation of the Company Law Board under the following situations:
- Where a person concerned in the conduct and management of the affairs of a company has been guilty of fraud and negligence.
- If the business is managed by a person without sound business principles.
- Where the business of a company has been managed by such a person, who likes to cause injury or damage to the business.
(ii) Removal by the Company Law Board: If an application has been made to the Company Law Board against the oppression and mismanagement of the company’s affairs by a director, then the Company Law Board may order to terminate the director.
Question 7.
What is the maximum limit for Managerial remuneration?
Answer:
Managerial Remuneration: The Managerial remuneration is payable to a person’s appointed u/s 196 of the Act. The Term remuneration means any money or its equivalent given for their services.
Adequate profits: A Public Company can pay remuneration to its directors including the Managing Director and Whole-time Directors, and its managers which shall not exceed 11% of the net profit.
Maximum Remuneration Payable by a Company to its Managerial Personnel – No adequate Profits: Remuneration Payable by a company in a case where there is no profit or inadequacy of
| Where Effective Capital is | Limit of yearly Remuneration payable shall not exceed (Rupees) | |
| (i) | less than ₹ 5 Crore | ₹ 30 lakh |
| (ii) | Above ₹ 5 Crore and less than ₹ 100 Crore | ₹ 42 lakh |
| (iii) | ₹ 5 Crore and above but less than ₹ 100 Crore | ₹ 60 lakh |
| (iv) | ₹ 250 Crore and above | ₹ 60 lakh plus 9.91% of the effective capital in excess of ₹ 250 Crore |
Question 8.
What are the Duties of a Director?
Answer:
Collective Duties:
- Approval and Authentication of Annual Accounts.
- Highlighting the performance of the company, Reserves, Investment of Surplus Funds, Borrowings.
- Appointment of First Auditors.
General Duties:
- Acting in accordance with the AOA.
- Act in good faith in order to promote the objects of the company.
- Perform duties with due and reasonable care and diligence.
- Appointing MD, Manager, Secretary and other employees.
Specific Duties:
- To disclose him – name – address – occupation particulars.
- To hold Qualification shares within 2 months after his appointment.
- To issue prospectus and fix the minimum subscription.
- To take care that prospectus should not contain any false or misleading statement.
- To file Return of Allotment of securities with the Registrar.
- To Forfeit and Transfer shares.
- To arrange for making payment of Divided declared.
Question 9.
State the powers of the directors.
Answer:
Powers of Directors: The directors must have powers to carry on objectives of the company. The powers may be of four types:
- Statutory Powers of Directors
- Managerial Powers of Directors
- Powers only with a resolution
- Other Powers
Statutory Powers: The following powers must be used in the Board meeting:
- Power to make calls on shareholders in respect of money unpaid on their shares
- Power to issue debentures
- Power to borrow money other than on debentures
- Power to invest the funds of the company
- Power to approve financial statement and Board report Managerial Powers:
- Power to allot, forfeit or transfer shares of company
- Power to decide the terms and conditions to issue debentures
- Power to appoint Managing Director, Manager and Secretary of the company.
Powers only with a resolution:
- To sell or lease any asset of the company
- To issue bonus shares
- To allow time to the director for repayment of the loan
Other Powers:
- Power to fill casual vacancy
- Power to appoint the first auditor of the company
- Power to appoint alternative directors, additional directors
- Power to remove key managerial personnel
Question 10.
State the Criminal liabilities of Directors.
Answer:
Directors will be liable with a fine and imprisonment or both for fraud of non-compliance of any statutory provisions in the following situations:
- Mis – Statement in the prospectus.
- Failure to file a return on the allotment with the registrar.
- Failure to give notice to the registrar for the conversion of shares into stock.
- Failure to issue share certificate and Debentures Certificate.
- Failure to maintain a register of the shareholders and Debenture holders.
- Default in holding Annual General Meeting.
- Failure to Provide Financial Statements.
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Commerce Company Management Additional Questions and Answers
I. Choose the Correct Answer
Question 1.
A company may appoint more than 15 directors after passing a ______ resolution.
(a) special
(b) ordinary
(c) usual
(d) commanding
Answer:
(a) special
Question 2.
A person can hold the position of Directorship in different companies up to the maximum of ______
(a) 15
(b) 10
(c) 18
(d) 20
Answer:
(d) 20
Question 3.
An ______ can be either a whole-time director of the company or a Managing Director.
(a) Executive Director
(c) Non-Executive Director
(b) First Director
(d) Residential Director
Answer:
(a) Executive Director
II. Very Short Answer Questions.
Question 1.
Write a note on the independent director.
Answer:
According to Section 149 (6), an independent director is an alternate director other than a Managing Director, who is known as Whole Time Director or Nominee Director.
Question 2.
Who is a ‘First Director’?
Answer:
A ‘First Director’ means a director who holds office from the date of incorporation of the company. The first directors are usually named in the Articles of Association.
III. Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
How a director is removed by the Company Law Board?
Answer:
There are three methods of removal of directors from the company.
They are:
- Removal by shareholders- If the shareholders feel that the policies pursued by the director are not appropriate, then they can remove the director by passing an ordinary resolution in a general meeting.
- Removal by the Central Government- The Central Government has been empowered to remove managerial personnel from office on the recommendation of the Company Law Board.
- Removal by the Company Law Board- If an application has been made to the Company Law Board against the oppression and mismanagement of the company’s affairs by a director, then the Company Law Board may order for the termination of the director’s tenure.
We hope the information prevailed in this article is helpful for all the students of Class 12th. The Tamilnadu State Board Solutions for Class 12th Chapter 27 Company Management Questions and Answers And Pdf enhance your skills and score good marks in the exams. Stay tuned to get the latest information about the Samacheer Kalvi Class 12th Chapter 27 Company Management Solutions.