Download Tamilnadu State Board Solutions for Class 12th Chapter 8 Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) PDF here. These Samacheer Kalvi Class 12th Chapter 8 Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) Questions and Answers will help you to improve your skills and score highest marks in the exams. Students can easily learn Chapter wise Samacheer Kalvi 12th Commerce Book Solutions Chapter 8 Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) by following the guide provided here.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Commerce Solutions Chapter 8 Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI)
Students can score good marks in the exam by preparing with Samacheer Kalvi Class 12th Commerce Solutions Chapter 8 Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) Questions and Answers. Your efforts can give you good results when you have the best resources. Samacheer Kalvi Class 12th Commerce Solutions Chapter 8 Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) is the best resource to learn Commerce. Have the best learning with Chapterwise Tamilnadu State Board Class 12th Commerce Solutions to have the best future ahead.
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Commerce Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers
I. Choose the Correct Answer
Question 1.
Securities Exchange Board of India was first established in the year _________
(a) 1988
(b) 1992
(c) 1995
(d) 1998
Answer:
(a) 1988
Question 2.
The headquarters of SEBI is _________
(a) Calcutta
(b) Bombay
(c) Chennai
(d) Delhi
Answer:
(b) Bombay
Question 3.
In which year SEBI was constituted as the regulator of capital markets in India?
(a) 1988
(b) 1992
(c) 2014
(d) 2013
Answer:
(a) 1988
Question 4.
Registering and controlling the functioning of collective investment schemes as _________
(a) Mutual Funds
(b) Listing
(c) Rematerialisation
(d) Dematerialization
Answer:
(d) Dematerialization
Question 5.
SEBI is empowered by the Finance ministry to nominate members on the Governing body of every stock exchange.
(a) 5
(b) 3
(c) 6
(d) 1
Answer:
(b) 3
Question 6.
The process of converting physical shares into electronic form is called _________
(a) Dematerialisation
(b) Delisting
(c) Materialisation
(d) Debarring
Answer:
(a) Dematerialisation
Question 7.
Trading in dematerialized shares commenced on the NSE in _________
(a) January 1996
(b) June 1998
(c) December 1996
(d) December 1998
Answer:
(c) December 1996
Question 8.
_________ was the first company to trade its shares in Demat form.
(a) Tata Industries
(b) Reliance Industries
(c) Infosys
(d) Birla Industries
Answer:
(b) Reliance Industries
Question 9.
_________ enables small investors to participate in the investment on the share capital of large companies.
(a) Mutual Funds
(b) Shares
(c) Debentures
(d) Fixed deposits
Answer:
(a) Mutual Funds
Question 10.
PAN stands for _________
(a) Permanent Amount Number
(b) Primary Account Number
(c) Permanent Account Number
(d) Permanent Account Nominee
Answer:
(c) Permanent Account Number
II. Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Write short notes on SEBI.
Answer:
- Securities and Exchange Board of India [SEBl] is an APEX body that maintains and Regulates Capital Market.
- It was established in 1988 as a supervisory body for regulating the securities market.
- It was made as an autonomous Body, on 12th May 1992.
- SEBI Act was passed in the Indian Parliament in the year 1992
Question 2.
Write any two objectives of SEBI.
Answer:
The first objective of SEBI is to regulate stock exchanges so that efficient services may be provided to all the parties operating there. Another objective is to supervise/check the activities of the brokers and other middlemen in order to control the capital market.
Question 3.
What is a Demat Account?
Answer:
- A Demat A /c holds all the shares that are purchased in Electronic form.
- Like a Bank A/c, Demat A/c holds the certificate of financial instruments like Shares, Bonds, Government Securities. Mutual Funds and Exchange Trader Funds.
- Purchases made by an investor is credited to his account and sail’s are debited to his account.
Question 4.
Mention the headquarters of SEBI.
Answer:
SEBI has its headquarters at the business district of Bandra Kurla Complex in Mumbai and has Northern, Eastern, Southern, and Western Regional Offices in New Delhi, Kolkata, Chennai, and Ahmedabad, respectively.
Question 5.
What are the various ID proofs?
Answer:
- PAN – card
- Voter ID
- Driving License
- Bank Pass Book
- Government-issued card with photo ID
- Passport
- Electricity Bill
- Telephone Bill
III. Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What is meant by Dematerialization?
Answer:
Dematerialization is the process by which physical share certificates of an investor are taken back by the company/registrar and destroyed. Then an equivalent number of securities in the electronic form are credited to the investor’s account with his Depository Participant.
Question 2.
What are the documents required for a Demat account?
Answer:
- You need to submit proof of Identity and Address along with a passport size photo and an account opening form.
- Only xerox copies of the documents are required for submission, but original copies are also required for verification.
Documents Proof of Identity and Address:
- PAN – card
- Voter ID
- Driving License
- Bank Pass Book
- Government-issued card with photo ID
- Passport
- Electricity Bill
- Telephone Bill
- All the documents with addresses issued by Both the Governments at their departments. [Legal – Education – PSU’s]
Question 3.
What is the power of SEBI under the Securities Contract Act?
Answer:
For effective regulation of stock exchange, the Ministry of Finance issued a Notification on 13 September 1994 delegating several of its powers under the Securities Contracts (Regulations) Act to SEBI is also empowered by the Finance Ministry to nominate three members on the Governing Body of every stock exchange.
Question 4.
What is meant by Insider trading?
Answer:
Insider Trading means the buying and selling of securities by Directors, Promoters, etc. Who has access to some – Confidential information about the company and who wish to take advantage of this confidential information. This affects the interests of the general investors.
Question 5.
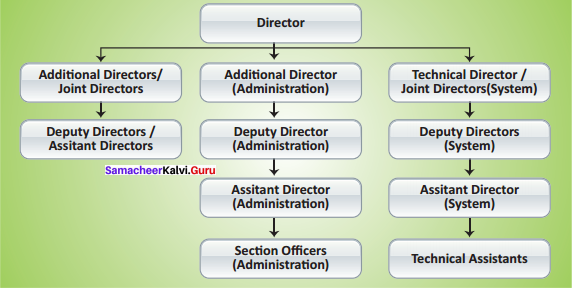
Draw the organizational structure of SEBI.
Answer:
The SEBI is managed by its members, which consists of the following.
IV. Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
What are the functions of SEBI?
Answer:
SEBI performs three key functions: quasi-legislative, quasi-judicial, and quasi-executive.
- Safeguarding the interests of investors by means of adequate education and guidance.
- Regulating and controlling the business on stock markets.
- Conduct inspection and inquiries of stock exchanges, intermediaries, and self-regulating organizations.
- Barring insider trading in securities.
- Prohibiting deceptive and unfair methods used by financial intermediaries operating in the securities market.
- Registering and controlling the functioning of stockbrokers, sub-brokers, share transfer agents, bankers, trustees, underwriters who are linked to the securities market.
- SEBI issues Guidelines and Instructions to businesses organisation for the issue of shares,
- Registering and controlling the functioning of collective investment schemes such as mutual funds.
Question 2.
Explain the powers of SEBI
Answer:
Powers of SEBI:
Stock Exchanges and Intermediaries :
- SEBI has wide powers regarding the Stock Exchange and – intermediaries dealing in securities.
- SEBI can inspect and ask for information from the stock exchange and intermediaries.
Monetary Penalties:
SEBI has been empowered to impose monetary penalties on capital market intermediaries and other participants for a range of violations.
Actions in Functions Assigned:
- SEBI has the power to initiate actions in regard to functions assigned.
- Can issue guidelines and rules for the protection of the interest of the investors.
Regulate Business of Stock Exchange:
- SEBI is empowered to regulate the business of stock exchanges.
- It regulates fraudulent and unfair trade practices.
Insider Trading:
SEBI has the power to regulate insider trading and the functions of Merchant Bankers.
Question 3.
What are the benefits of Dematerialisation?
Answer:
- The risks pertaining to physical certificates like loss, theft, forgery and damage are eliminated completely with a DEMAT A/c.
- The lack of paperwork enables quicker transactions and higher efficiency in trading.
- Without the need of visiting the Broker, one can trade through computers at any location.
- The shares that are created through mergers and consolidation of companies are credited automatically in the DEMAT A/c.
- As all the transactions occur through the DP, a trader does not have to communicate individually with each and every company.
- There is no need for stamp duty for the transfer of securities.
- Certain Banks are also permitted the holding of both equity and debentures in a single account.
- Bank provide Trained and Dedicated CCD’s to assist in all the procedures.
- A DEMAT account holder can buy or sell any amount of shares.
- The holder can take a loan against securities in the DEMAT account.
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Commerce Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) Additional Questions and Answers
I. A. Choose the Correct Answer:
Question 3.
DEMAT is done at the request of ……..
a) Investors
b)Brokers
c) Speculators
d) NDTA
Answer:
a) Investors
B. Fill in the blanks
Question 1.
The first objective of SEBI is to regulate ______
Answer:
Stock exchanges
II. Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Mention the documents required for a Demat A/c.
a) Address proof
b) ID proof
c) Photo
d) All of these
Answer:
d) All of these
Question 2.
What is meant by PAN?
Answer:
- PAN – Permanent Account Number.
- It is a unique 10 digit alpha numeric identity number.
- It also serves as identity proof.
Case Study
Question (a)
Koushikaa’s father has gifted her the shares of a large cement company with which he had been working. The securities were in physical form. She already has a bank account and does not possess any other forms of securities. She wishes to sell the shares and approached a registered broker for the purpose. Mention one mandatory detail which she will have to provide with the broker.
Answer:
Mandatory Detail:
- The shares can be sold by opening a Demat account.
- She has to mention the no of shares of the cement company.
- Without the paperwork, shares can be transferred through dematerialization.
- Shares can be transferred to the person who wants to purchase.
- Also mention the name of the company, Type of share, amount of share capital.
Question (b)
Mr. Kulandaivel was the Chairman of Thangam Bank. The bank was earning good profits. Shareholders were happy as the bank was paying regular dividends. The market price of their share was also steadily rising. The bank was about to announce taking over the ‘Trinity Bank’. Mr. Kulandaivel knew that the share price of Thangam Bank would rise on this announcement. Being a part of the bank, he was not allowed to buy shares of the bank. He called one of his rich friends Mr. Chandrasekaran and asked him to invest 5 crores in shares of his bank promising him the capital gains.
As expected, the share prices went up by 40% and the market price of Chandrasekaran’s shares was now 2 crores. He earned a profit of 2 crores. He gave 1 crore to Mr. Kulandaivel and kept 1 crore with himself. On regular inspection and by conducting enquires of the brokers involved, the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) was able to detect this irregularity. The SEBI imposed a heavy penalty on Mr. Kulandaivel. By quoting the lines from the above paragraph, identify and state any two functions that were performed by SEBI in the above case.
Answer:
Functions performed by SEBI in this case:
- The market price of their share was informed and controlled by SEBI.
- On regular inspection and conducting enquiries, the Exchange Board of India was able to detect this irregularity.
- The SEBI imposed a heavy penalty on Mr. Kulandaivel.
We hope the information prevailed in this article is helpful for all the students of Class 12th. The Tamilnadu State Board Solutions for Class 12th Chapter 8 Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) Questions and Answers And Pdf enhance your skills and score good marks in the exams. Stay tuned to get the latest information about the Samacheer Kalvi Class 12th Chapter 8 Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) Solutions.