Students can Download Computer Applications Chapter 16 Electronic Payment Systems Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 12th Computer Applications Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Computer Applications Solutions Chapter 16 Electronic Payment Systems
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Computer Applications Electronic Payment Systems Text Book Back Questions and Answers
PART – I
I. Choose The Correct Answer
Question 1.
Based on the monetary value e payment system can be classified into
(a) Mirco and Macro
(b) Micro and Nano
(c) Maximum and Minimum
(d) Maximum and Macro
Answer:
(a) Mirco and Macro
![]()
Question 2.
Which of the following is not a category of micropayment?
(a) Buying a movie ticket
(b) Subscription to e-journals
(c) Buying a laptop
(d) Paying for smartphone app
Answer:
(c) Buying a laptop
Question 3.
Assertion (A): Micro electronic payment systems support higher value payments.
Reason (R): Expensive cryptographic operations are included in macro payments
(a) Both (A) and (R) are correct and (R) is the correct explanation of (A)
(b) Both (A) and (R) are correct, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A)
(c) (A) is true and (R) is false
(d) (A) is false and (R) is true
Answer:
(d) (A) is false and (R) is true
![]()
Question 4.
Which of the following is correctly matched
(a) Credit Cards – pay before
(b) Debit Cards – pay now
(c) Stored Value Card – pay later
(d) Smart card – pay anytime
Answer:
(b) Debit Cards – pay now
Question 5.
ECS stands for
(a) Electronic Clearing Services
(b) Electronic Cloning Serivces
(c) Electronic Clearing Station
(d) Electornic Cloning Station
Answer:
(a) Electronic Clearing Services
![]()
Question 6.
Which of the following is not a Altcoin
(a) Litecoin
(b) Namecoin
(c) Ethereum
(d) Bitcoin
Answer:
(c) Ethereum
Question 7.
Which of the following is true about Virtual payment address (VPA)
(a) Customers can use their e-mail id as VPA
(b) VPA does not include numbers
(c) VPA is a unique ID
(d) Multiple bank accounts cannot have a single VPA
Answer:
(d) Multiple bank accounts cannot have a single VPA
![]()
Question 8.
Pick the odd one in the credit card transaction
(a) cardholder
(b) merchant
(c) marketing manager
(d) acquirer
Answer:
(c) marketing manager
Question 9.
Which of the following is true about debit card
(i) debit cards cannot be used in ATMs
(ii) debit cards cannot be used in online transactions
(iii) debit cards do not need bank accounts
(iv) debit cards and credit cards are identical in physical properties
(a) (i), (ii), (iii)
(b) (ii), (iii), (iv)
(c) (iii) alone
(d) (iv) alone
Answer:
(d) (iv) alone
![]()
Question 10.
Match the following.
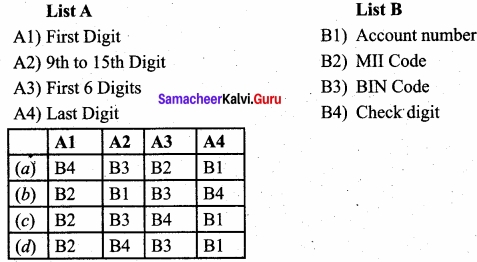
Answer:
(b) A1-B2, A2-B1, A3-B3, A4-B4
II. Short Answers
Question 1.
Define electronic payment system?
Answer:
The term electronic payment refers to a payment made from one bank account to another bank account using electronic methods for going the direct intervention of bank employees.
![]()
Question 2.
Distinguish microelectronic payment and macro electronic payment?
Answer:
Micro Electronic Payment System:
- Payments of small system amount
- Less Security
- Eg. Subscriptions of online games
Macro Electronic Payment System:
- Payments of higher value
- Highly Secured
- Electronic account transfer
![]()
Question 3.
List the types of microelectronic payments based on its algorithm?
Answer:
- Hash chain-based microelectronic payment systems.
- Hash collisions and hash sequences based microelectronic payment systems.
- Shared secrete keys-based microelectronic payment systems.
- Probability-based microelectronic payment systems.
Question 4.
Explain the concept of an e-wallet?
Answer:
Electronic wallets (e-wallets) or electronic purses allow users to make electronic transactions quickly and securely over the Internet through smartphones or computers.
![]()
Question 5.
What is a fork in cryptocurrency?
Answer:
Many cryptocurrencies operate on the basis of the same source code, in which the authors make only a few minor changes in parameters like time, date, distribution of blocks, number of coins, etc. These currencies are called a fork.
PART – III
III. Explain in Brief Answers
Question 1.
Define microelectronic payment and its role in E-Commerce?
Answer:
- It is an online payment system designed to allow efficient and frequent payments of small amounts.
- In order to keep transaction costs very low, the communication and computational costs are minimized here.
- The security of microelectronic payment systems is comparatively low
- The majority of microelectronic payment systems were designed to pay for simple goods on the Internet, e.g., subscriptions of online games, read journals, listen to a song or watch a movie online, etc.
![]()
Question 2.
Compare and contrast the credit card and debit card?
Answer:
Credit Card:
A credit card is different from a debit card where the credit card issuer lends money to the customer instead of deducting it from customer’s bank account instantly.
Debit Card:
Credit card is an electronic payment system normally used for retail transactions. A credit card enables the bearer to buy goods or services from a vendor, based on the cardholder’s promise to the card issuer to pay back the value later with the agreed interest.
Question 3.
Explain briefly the Anatomy of a credit card?
Answer:
- All Payment cards (including debit cards) are usually plastic cards of size 85.60 mm width × 53.98 mm height, rounded corners with a radius of 2.88 mm to 3.48 mm, and thickness of 0.76 mm.
- These standards dimensions are maintained universally in accordance with ISO/IEC 7810#ID-1.
![]()
Question 4.
Briefly explain the stored value card and its types?
Answer:
(i) Closed-loop (single purpose):
In closed-loop cards, money is metaphorically stored on the card in the form of binary-coded data. e.g. Chennai metro rail travel card.
(ii) Open-loop (multipurpose):
It is also called as prepaid-debit cards, e.g. Visa gift cards.
![]()
Question 5.
Write a note on mining in cryptocurrency?
Answer:
- The cryptocurrency units are created by the solution of cryptographic tasks called mining.
- The miners not only generate new monetary units but also initiate new transactions to the blockchain.
- As a reward, they will receive new Bitcoins. In terms of trade, the creation of cryptocurrencies may be related to the ICO (Initial Coin Offer) procedure, i.e. the ICO, aimed at gathering the initial capital necessary for the further develop¬ment of the system.
- The initial value of a cryptographic currency is just the cost of consumed electricity. The second¬ary value is determined by the demand for the cryptocurrency.
PART – IV
IV. Explain in detail
Question 1.
What is credit card? Explain the key players of a credit card payment system and bring out the merits of it?
Answer:
Credit Card:
Credit card is an electronic payment system normally used for retail transactions. A credit card enables the bearer to buy goods or services from a vendor, based on the cardholder’s promise to the card issuer to payback the value later with an agreed interest. Every credit card account has a purchase limit set by the issuing bank or the firm. A credit card is different from a debit card where the credit card issuer lends money to customer instead of deducting it from customer’s bank account instantly.
The term credit card was first mentioned in 1887 in the sci-fi novel “Looking Backward” by Edward Bellamy. The modem credit cards concept was bom in the U.S.A, in the 1920s, when private companies began to issue cards to enable their customers to purchase goods on credit within their own premises.
Advantages of credit card:
- Most credit cards are accepted worldwide.
- It is not necessary to pay physical money at the time of purchase. The customer gets an extra period to pay the purchase.
- Depending on the card, there is no need to pay an annuity.
- Allows purchases over the Internet in installments.
- Some issuers allow “round up” the purchase price and pay the difference in cash to make the transactions easy.
Key players in operations of credit card:
1. Bearer:
The holder of the credit card account who is responsible for payment of invoices in full (transactor) or a portion of the balance (revolver) the rest accrues interest and carried forward.
2. Merchant:
Storekeeper or vendor who sells or providing service, receiving payment made by its customers through the credit card.
3. Acquirer:
Merchant’s bank that is responsible for receiving payment on behalf of merchant sends authorization requests to the issuing bank through the appropriate channels.
4. Credit Card Network:
It acts as the intermediate between the banks. The Company is responsible for communicating the transaction between the acquirer and the credit card issuer. These entities operate
the networks that process credit card payments worldwide and levy interchange fees. E.g. Visa, MasterCard, Rupay
5. Issuer:
Bearer’s bank, that issue the credit card, set a limit of purchases, decides the approval of transactions, issue invoices for payment, charges the holders in case of default and offer card-linked products such as insurance, additional cards, and rewards plan.
![]()
Question 2.
Briefly explain Electronic Account transfer and its types?
Answer:
With the advent of computers, network technologies, and electronic communications a large number of alternative electronic payment systems have emerged. These include ECS (Electronic Clearing Services), EFT (Electronic funds transfers), Real-Time Gross Settlement system (RTGS), etc.
1. Electronic Clearing Services (ECS):
Electronic Clearing Service can be defined as a repeated transfer of funds from one bank account to multiple bank accounts or vice versa using computer and Internet technology. Advantages of this system are bulk payments, guaranteed payments, and no need to remember payment dates. ECS can be used for both credit and debit purposes i.e. for making bulk payments or bulk collection of amounts.
2. ECS credit:
ECS Credit is used for making bulk payments of amounts. In this mode, a single account is debited and multiple accounts are credited. This type of transaction is Push transactions. Example: If a company has to pay a salary to its 100 employees it can use the ECS credit system than crediting every employees’ account separately.
3. ECS debit:
ECS debit is an inverse of ECS credit. It is used for the bulk collection of amounts. In this mode, multiple accounts are debited and then a single account is credited. This type of transaction is a Pull transaction. Example: The insurance premium of bulk number of customers
4. Electronic Funds Transfer:
Electronic Funds Transfer (EFT) is the “electronic transfer” of money over an online network. The amount sent from the sender’s bank branch is credited to the receiver’s bank branch on the same day in batches.
5. Real Time Gross Settlement:
Real-Time Gross Settlement system (RTGS) is a payment system particularly used for the settlement of transactions between financial institutions, especially banks.
Real-time gross settlement transactions are:
- Unconditional – the beneficiary will receive funds regardless of whether the 242 fulfills his obligations to the buyer or whether he would deliver the goods or perform a service of a quality consistent with the order.
- Irrevocable – a correctly processed transaction cannot be reversed and its money cannot get refunded (the so-called settlement finality).
![]()
Question 3.
Write a note on
(a) Internet banking
(b) Mobile banking
Answer:
a) Internet banking
- Internet banking is a collective term for E-banking, online banking, virtual banking (operates only on the Internet with no physical branches), direct banks, web banking, and remote banking.
- Internet banking allows customers of a financial institution to conduct various financial transactions on a secure website operated by the banking institutions.
- This is a very fast and convenient way of performing any banking transactions.
- It enables customers of a bank to conduct a wide range of financial transactions through its website. In fact, it is like a branch exclusively operating on an individual customer.
- The online banking system will typically connect to the core banking system operated by customers themselves (Self-service banking).
b) Mobile banking
Mobile banking is another form of net banking.
- The term mobile banking (also called m-banking) refers to the services provided by the bank to the customer to conduct banking transactions with the aid of mobile phones.
- These transactions include balance checking, account transfers, payments, purchases, etc. Transactions can be done at any time and anywhere.
- The WAP protocol installed on a mobile phone qualifies the device through an appropriate application for mobile session establishment with the bank’s website.
- In this way, the user has the option of permanent control over the account and remote management of his own finances.
Question 4.
What is cryptocurrency? Explain the same?
Answer:
Cryptocurrency:
- People have always valued unique and irreplaceable things. A unique thing always has a demand and acclaims a price.
- A cryptocurrency is a unique virtual (digital) asset designed to work as a medium of exchange using a cryptographic algorithm.
- This algorithm secures the transactions by recording it in blockchain and controls the creation of additional units of the currency.
- Cryptocurrency is also called as crypto coins, e-cash, alternative currencies, or virtual currencies and is classified as a subset of digital currencies.
- Cryptocurrency can be defined as distributed accounting system based on cryptography, storing information about the state of ownership in conventional units.
- The state of ownership of a cryptocurrency is related to individual system blocks called “portfolios”.
- Only the holder of the corresponding private key would have control over a given portfolio and it is impossible to issue the same unit twice.
- The function of cryptocurrency is based on technologies such as Mining, Blockchain, Directed Acyclic Graph, Distributed register (ledger), etc. The information about the transaction is usually not encrypted and is available in cleartext.
Bitcoin:
Bitcoin is the most popular and the first decentralized cryptocurrency. Bitcoin is the most popular cryptocurrency, but there are many other cryptocurrencies, which are referred to as “altcoins”.
Altcoins:
- Altcoins is the collective name for all cryptocurrencies that appeared after Bitcoin. The early Altcoins Litecoin and Namecoin appeared in 2011.
- From 2014, the 2nd generation of cryptocurrencies appeared, such as Monero, Ethereum, and Nxt. These crypto-coins have advanced features such as hidden addresses and smart contracts.
- In terms of trade, the creation of cryptocurrencies may be related to the ICO (Initial Coin Offer) procedure.
Blockchain:
- Blockchains are open distributed books that record transactions of cryptocurrencies between any two parties in an efficient and verifiable manner.
- It is a continuously growing list of records, called blocks, which are linked to each other and protected using an encryption algorithm.
- Each block typically contains a hash pointer as a link to a previous block. It records data about every transaction with its date and time.
- Once recorded, the data in any given block cannot be altered without the alteration of all subsequent blocks.
![]()
Question 5.
Explain in detail: Unified payments interface?
Answer:
- Unified Payments Interface (UPI) is a re¬al-time payment system developed by the National Payments Corporation of India (NCPI) to facilitate inter-bank transactions.
- It is a simple, secure, and instant payment facility.
- This interface is regulated by the Reserve Bank of India and used for transferring funds instant¬ly between two bank accounts through mobile (platform) devices, http://www.npci.org.in/.
- Unlike traditional e-wallets, which take a specified amount of money from the user and store it in its own account, UPI withdraws and deposits funds directly from the bank account whenever a transaction is requested.
- It also provides the “peer Peer” collect request which can be scheduled and paid as per require¬ment and convenience,
- UPI is developed on the basis of Immediate Payment Service (IMPS). To initiate a transaction, UPI applications use two types of addresses – global and local.
- The global address includes bank account numbers and IF5C.
- The local address is a virtual payment address.
- Virtual payment address (VPA) also called UPI-ID, is a unique ID similar to email id (e.g. name@bankname) that enables us to send and receive money from multiple banks and prepaid payment issuers.
- Bank or the. the financial institution allows the customer to generate VPA using a phone number associated with the Aadhaar number and bank account number.
- VPA replaces bank account details thereby completely hides critical information.
- The MPIN (Mobile banking Personal Identification Number) is required to confirm each payment. UPI allows operating multiple bank accounts in a single mobile application.
- Some UPI application also allows customers to initiate the transaction using only Aadhaar number in absence VPA.
Advantages
- Immediate money transfers through mobile devices round the clock 24 x 7.
- Can use a single mobile application for accessing multiple bank accounts.
- Single Click Authentication for transferring of the fund.
- It is not required to enter the details such as Card no, Account number, IFSC, etc. for every transaction.
- Electronic payments will become much easi¬er without requiring a digital wallet or credit or debit card.
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Computer Applications Electronic Payment Systems Additional Questions and Answers
I. Choose The Best Answer
Question 1.
…………. is an essential part of a company’s financial operations.
a) mobile Banking
b) Internet Banking
c) E-Banking
d) payment system
Answer:
d) payment system
![]()
Question 2.
The electronic payment systems are classified into …………………….. types
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 5
Answer:
(a) 2
Question 3.
The term credit card was coined by …………..
a) Edward Bellamy
b) Netin
c) Flemming
d) Robert Lake
Answer:
a) Edward Bellamy
Question 4.
Pick the odd one out
(a) read journals
(b) listen to a song
(c) watch a movie online
(d) Internet payment systems
Answer:
(d) Internet payment systems
![]()
Question 5.
…………………….. are plastic cards that enable cashless payments.
Answer:
Payment Cards
Question 6.
………………. is used in contactless transactions
a) BIN
b) UNF
c) CVC2
d) UDI
Answer:
c) CVC2
![]()
Question 7.
How many microelectronic payments systems are there based on simple cryptographic algorithms?
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 5
Answer:
(c) 4
Question 8.
The term that refers to a business that has a physical store; opposite of an online Store is
a) E-banking
b) Brick and mortar
c) NetBanking
d) None of these
Answer:
b) Brick and mortar
Question 9.
The term credit card was first mentioned in the novel by ……………………..
Answer:
Edward Bellamy
![]()
Question 10.
The term credit card was first mentioned in the sci-fi novel ………………………
(a) Looking Backward
(b) Arrival
(c) Interstellar
(d) the Altered States
Answer:
(a) Looking Backward
Question 11.
………….. is s magnetic stripe or chip card that holds the value of money to offer as a gift by an E-business.
a) E-card
b) Gift card
c) E-buy
d) E-wallets
Answer:
d) E-wallets
![]()
Question 12.
The plastic cards were introduced in the year ……………………..
(a) 1957
(b) 1597
(c) 1955
(d) 1855
Answer:
(c) 1955
Question 13.
Who created Diners Club Card?
(i) Frank McNamara
(ii) Ralph Schneider
(iii) Edward Bellamy
(a) (i), (iii)
(b) (ii), (iii)
(c) (i), (ii)
(d) (i), (ii), (iii)
Answer:
(c) (i), (ii)
![]()
Question 14.
The Diners Club Card was created in the year …………………………
(a) 1950
(b) 1955
(c) 1960
(d) 1965
Answer:
(a) 1950
Question 15.
Initially, the Diners Club Card was made of ……………………..
(a) paper-cardboard
(b) plastic
(c) wood
(d) metal
Answer:
(a) paper-cardboard
![]()
Question 16.
(I) The Diners Club Card was accepted only in 25 restaurants (initially).
(II) From 1965, the card was made of plastic.
(a) I-True, II-False
(b) I-False, II-True
(c) I, II-both True
(d) I, II-both are false
Answer:
(d) I, II-both are false
Question 17.
How many key players are there in the operation of credit cards?
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 5
Answer:
(d) 5
![]()
Question 18.
The ……………………. is the holder of the credit card account.
Answer:
Bearer
Question 19.
……………………. Network acts as the Intermediate between the banks.
Answer:
Credit Card
Question 20.
The credit card limit, approval of transactions, default charges are issued by
(a) issuer
(b) Merchant
(c) Acquirer
(d) Bearer
Answer:
(a) issuer
![]()
Question 21.
Match the following (description of payment cards)
(i) width – 1.2.88 mm – 3.48 mm
(ii) height – 2. 53.98 mm
(iii) radius – 3. 85.60 mm
(iv) thickness – 4.0.76 mm
(a) (i)-3, (ii)-2, (iii)-1, (iv)-4
(b) (i)-1, (ii)-2, (iii)-3, (iv)-4
(c) (i)-4, (ii)-2, (iii)-1, (iv)-3
(d) (i)-2, (ii)- 1, (iii)-4, (iv)-3
Answer:
(a) (i)-3, (ii)-2, (iii)-1, (iv)-4
Question 22.
The credit card number has ……………………. digit unique identification number
(a) 8
(b) 16
(c) 15
(d) 20
Answer:
(b) 16
Question 27.
EMV means ………………………
Answer:
euro pay, Mastercard, Visa
![]()
Question 28.
EMV is categorized into ………………………
Answer:
chip and signature, chip and PIN
Question 29.
How many curved lines are there in the RFID symbol?
(a) 4
(b) 8
(c) 12
(d) 16
Answer:
(a) 4
Question 30.
……………………. is an Indian domestic open-loop card.
Answer:
Rupay
![]()
Question 31.
Rupay was launched in the year
(a) 2001
(b) 2003
(c) 2009
(d) 2012
Answer:
(d) 2012
Question 32.
Which is a credit card security feature to prevent duplication?
(a) logo
(b) Hologram
(c) signature
(d) CW
Answer:
(b) Hologram
![]()
Question 33.
CVC/CW means ………………….
Answer:
Card Verification Code/ Value
Question 34.
Which is used in contactless transactions.
(a) CVC2
(b) EMV
(c) RFID
(d) PIN
Answer:
(a) CVC2
Question 35.
……………………… is a 3 digit code printed to the left of the signature pane to validate the card.
Answer:
CVC/CVV
![]()
Question 36.
How many ways of processing debit card transactions are there?
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 5
Answer:
(b) 3
Question 37.
Which card is an electronic payment card where the transaction amount is deducted from the cardholder’s Bank account?
(a) Credit card
(b) Debit card
(c) Smart card
(d) Paytm card
Answer:
(b) Debit card
Question 38.
Which is also known as online debit or PIN debit?
(a) EFTPOS
(b) POSEFT
(c) FETPOS
(d) FETSOP
Answer:
(a) EFTPOS
![]()
Question 39.
……………………. is a type of debit card that is preloaded with a certain amount.
Answer:
Stored value card
Question 40.
Which is true regarding stored value cards?
(i) It has to default monetary value onto it.
(ii) The card may be disposed of when the value is used.
(iii) It is used to make offline purchases
(a) (i), (ii), (iii)
(b) (ii), (iii)
(c) (i), (ii)
(d) (iii) alone
Answer:
(a) (i), (ii), (iii)
![]()
Question 41.
How many varieties of the stored-value card are there?
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 5
Answer:
(a) 2
Question 42.
Pick the odd one out.
(a) closed-loop cards
(b) open-loop cards
(c) prepaid-debit cards
(d) visa gift cards
Answer:
(a) closed-loop cards
![]()
Question 43.
In which of the following cards in binary coded metaphorically stored on the card in binary coded data form?
(a) open-loop cards
(b) prepaid-debit cards
(c) closed-loop cards
(d) visa gift cards
Answer:
(c) closed-loop cards
Question 44.
Which of the following is not the advantage of smart cards?
(a) Identification
(b) RFID
(c) datastorage
(d) application processing
Answer:
(b) RFID
![]()
Question 45.
Smart cards are classified into ……………………. types.
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 5
Answer:
(a) 2
Question 46.
The two classifications of smart cards are ……………………… and ………………….. smart cards.
Answer:
contact and contactless
Question 47.
POS stands for ………………………
Answer:
Point of Sale
Question 48.
Contact smart cards have a contact area of approximately ……………………….
(a) 1 cms2
(b) 10 cms2
(c) 1 mm2
(d) 1 hectares
Answer:
(a) 1 cms2
![]()
Question 49.
Find the statements which are not true?
(I) contact smart cards use RF induction Technology
(II) smarts have Internal power Source
(III) Inductor is used to capture radio-frequency signal
(a) I, II
(b) II, III
(c) I, II
(d) III
Answer:
(c) I, II
Question 50.
Which technology is used in contactless smart cards?
(a) UV Induction
(b) RF Induction
(c) RFID
(d) IRID
Answer:
(b) RF Induction
![]()
Question 51.
EFT means ………………………
Answer:
Electronic Funds Transfers
Question 52.
RTGS means …………………….
Answer:
Real-Time Gross Settlement System
Question 53.
ECS ………………….. is used for making bulk payment of amounts.
Answer:
credit
![]()
Question 54.
ECS ………………….. is used for bulk collection of amounts.
Answer:
debit
Question 55.
Identify the wrongly matched pair.
(a) EFPOS – PIN debit
(b) Offline debit – Signature debit
(c) ECS credit – Push transactions
(d) ECS debit – Pull transactions
Answer:
(a) EFPOS – PIN debit
Question 56.
EFT means
(a) National Electronic Fund Transactions
(b) National Electronic Fund Transfer
(c) National Electronic Finance Technology
(d) National Electronic Financial Transactions
Answer:
(b) National Electronic Fund Transfer
![]()
Question 57.
RBI means ……………………..
Answer:
Reserve Bank of India
Question 58.
IDRBT stands for ……………………
Answer:
Institute for Development and Research in Banking Technology
Question 59.
NEFT initiated in the year ……………………..
(a) 2001
(b) 2003
(c) 2005
(d) 2009
Answer:
(c) 2005
![]()
Question 60.
Which one of the following enables a bank customers to transfer funds between any two banks?
(a) EFT
(b) NEFT
(c) EMI
(d) ECS
Answer:
(b) NEFT
Question 61.
…………………… payments are generally large-value payments
Answer:
RTGS
Question 62.
…………………… is the electronic transfer of money over an online network
Answer:
EFT
Question 63.
Which one of the following is the currency that flows in the form of data?
(a) RTGS
(b) EFT
(c) ECS
(d) E-cash
Answer:
(d) E-cash
![]()
Question 64.
Cryptocurrency is also called as …………………..
(a) Crypto coins
(b) e-cahs
(c) virtual currencies
(d) all of these
Answer:
(d) all of these
Question 65.
The state of ownership of a cryptocurrency is related to individual system blocks called ………………………
(a) portfolios
(b) virtual asset
(c) cryptography
(d) none of these
Answer:
(a) portfolios
![]()
Question 66.
What are the technologies used in cryptocurrency?
(a) Mining
(b) blockchain
(c) Directed Acyclic Graph
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d) All of these
Question 67.
The first form of cryptocurrency is ……………………….
(a) Digicash
(b) D-cash
(c) E-cash
(d) Crypto cash
Answer:
(a) Digicash
Question 68.
“Digicash” was invented by …………………….
Answer:
David Chaum
Question 69.
Digicash was invented in the year ………………………
(a) 1978
(b) 1980
(c) 1985
(d) 1989
Answer:
(d) 1989
![]()
Question 70.
Identify the wrongly matched pair.
(a) Digicash- 1989
(b) Bitcoin- 2009
(c) SHA-254-crytographic Hash function
(d) Altcoin – 2011
Answer:
(c) SHA-254-crytographic Hash function
Question 71.
Which is the most popular and the first decentralized cryptocurrency?
(a) Digicash
(b) Bitcoin
(c) Altcoins
(d) blockchain
Answer:
(b) Bitcoin
Question 72.
The bitcoin payment system was developed under the pseudonym ……………………….
Answer:
Satoshi Nakamoto
![]()
Question 73.
………………….. was developed to build alternative root DNS servers.
Answer:
Namecoin
Question 74.
Which cryptocurrency has a higher transaction rate?
(a) Altcoin
(b) Litecoin
(c) Bitcoin
(d) Namecoin
Answer:
(b) Litecoin
Question 75.
Making few minor changes in the parameters of cryptocurrency is called ………………………..
(a) altoin
(b) Block
(c) Blockchain
(d) Fork
Answer:
(d) Fork
![]()
Question 76.
As the value of altcoins becomes ………………….. it is considered as dead.
(a) Null
(b) 0
(c) infinity
(d) negative
Answer:
(b) 0
Question 77.
Pick the odd one out.
(a) Bitshares
(b) Mastercoin
(c) Ripple
(d) Nxt
Answer:
(c) Ripple
Question 78.
Pick the odd one out.
(a) Monera
(b) Nxt
(c) Ethereum
(d) Mastercoin
Answer:
(d) Mastercoin
![]()
Question 79.
The Cryptocurrency units are created by the solution of cryptographic tasks called ………………………..
(a) mining
(b) Blockchain
(c) Hash
(d) Brick and Mortar
Answer:
(a) mining
Question 80.
Find the statements which are not true.
(i) The miners generate new monetary units
(ii) Miners doesn’t initiate new transactions
(iii) Miners receive new Bitcoins
(a) (i)
(b) (iii)
(c) (ii)
(d) All are true
Answer:
(c) (ii)
Question 81.
ICO means ……………………….
Answer:
Initial coin offer
![]()
Question 82.
Which one of the following is an open distributed book that records transactions of cryptocurrencies?
(a) mining
(b) e-wallets
(c) ICO
(d) Blockchains
Answer:
(d) Blockchains
Question 83.
Each block in the blockchain contains ………………….. pointer.
(a) dash
(b) hash
(c) memory
(d) link
Answer:
(b) hash
![]()
Question 84.
Which one of the following is an electronic wallet service?
(a) PayPal
(b) blockchain
(c) mining
(d) hash
Answer:
(a) PayPal
Question 85.
The term mobile banking is also called ………………………
Answer:
m-banking
Question 86.
……………………. operates only on the Internet with no physical branches.
Answer:
virtual banking
Question 87.
OTP means ……………………….
Answer:
One-Time Password
Question 88.
PJN means ……………………
Answer:
Personal Identification Number
![]()
Question 89.
ACHmeans …………………….
Answer:
Automated Clearing Home
Question 90.
IFSC stands for ……………………
Answer:
Indian Financial System Code
Question 91.
……………………… is an 11 digit alpha-numeric code issued Reserve Bank of India.
(a) IIT
(b) IIM
(c) IFSC
(d) IFCS
Answer:
(c) IFSC
Question 92.
UPI means ………………………
Answer:
Unified Payments
![]()
Question 93.
NCPI means …………………..
Answer:
National Payments Corporation of India
Question 94.
Unified Payments Interface is a real-time payment system developed by NCPI to facilitate inter-bank transactions.
Answer:
Unified Payments Interface
Question 95.
IMPS stands for ………………………
Answer:
Immediate Payment Service
Question 96.
UPI applications …………………………. types of address.
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 5
Answer:
(a) 2
![]()
Question 97.
UPI applications are classified into two types of addresses like …………………….. and ……………………
Answer:
global and local
Question 98.
Which address in UPI is a virtual payment address?
(a) Global
(b) local
(c) private
(d) public
Answer:
(b) local
Question 99.
………………… also called as UPI-ID.
Answer:
Virtual Payment Address(VPA)
Question 100.
MPIN means ……………………..
Answer:
Mobile Banking Personal Identification Number
![]()
Question 101.
USSD means …………………..
Answer:
Unstructured Supplementary Service Data
Question 102.
COD means …………………..
Answer:
Cash on Delivery
Question 103.
BHIM stands for …………………….
Answer:
Bharat Interface for Money
Question 104.
NPCI means …………………….
Answer:
National Payments Corporation of India
Question 105.
BHIM is an exclusive mobile app for UPI developed by ……………………..
(a) 2014
(b) 2015
(c) 2016
(d) 2017
Answer:
(c) 2016
![]()
Question 106.
……………………. is a type of fraud where the same cryptocurrency is spent in more than one transactions.
Answer:
Double Spend
Question 107.
RThs are …………………. and ……………………
Answer:
Unconditional, Irrevocable
II. Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Write a note on Modern payment systems.
Answer:
- Modern payment systems may be physical or electronic and each has its own procedures and protocols that guide the financial institution with payment mechanisms and legal systems.
- Standardization has allowed some of these systems to grow globally.
![]()
Question 2.
Give some examples of macro online payment systems?
Answer:
Some of the popular macro online payment systems are mentioned below:
- Card-based payment systems
- Electronic account transfer
- Electronic cash payment systems
- Mobile payment systems and internet payment systems
Question 3.
Write a note on E-cash?
Answer:
Electronic cash is (E-Cash) is a currency that flows in the form of data. It converts the cash value into a series of encrypted sequence numbers and uses these serial numbers to represent the market value of various currencies in reality.
![]()
Question 4.
Mention the advantages of UPI?
Answer:
- Immediate money transfers through mobile devices round the clock 24 × 7.
- Can use single mobile application for accessing multiple bank accounts,
- Single Click Authentication for transferring of the fund.
- It is not required to enter the details such as Card no, Account number, IFSC etc. for every transaction.
- Electronic payments will become much easier without requiring a digital wallet or credit or debit card.
Question 5.
How are payment systems classified?
Answer:
Payment system are classified based on
- Money transactions
- Processing time
- Processing requirements
- Security issues
- Usability
![]()
Question 6.
Define BHIM?
Answer:
Bharat Interface for Money (BHIM) is an exclusive mobile app for UPI developed by the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) and launched on 30 December 2016. It is intended to facilitate e-payments directly through banks and drive towards cashless transactions.
III. Explain in Brief Answer
Question 1.
Explain briefly about Electronic Funds Transfer?
Answer:
- Electronic Funds Transfer (EFT) is the “electronic transfer” of money over an online network.
- The amount sent from the sender’s bank branch is credited to the receiver’s bank branch on the same day in batches.
- Unlike traditional processes, EFT saves the effort of sending a demand draft through the post and the inherent delay in reaching the money to the receiver.
- Banks may charge a commission for using this service. EFT is a widely used method of moving funds from one account to another in B2B business models.
![]()
Question 2.
Mention the three types of card-based payment systems?
Answer:
Based on the transaction settlement method there are three widely used card-based payment systems. They are:
- Credit card-based payment systems (pay later)
- Debit card-based payment systems (pay now)
- Stored value card-based payment systems (pay before)
Question 3.
What are the two methods of Real-time gross settlement transactions?
Answer:
- Unconditional – the beneficiary will receive funds regardless of whether he fulfills his obligations to the buyer or whether he would deliver the goods or perform a service of a quality consistent with the order.
- Irrevocable – a correctly processed transaction cannot be reversed and its money cannot get refunded (these-called settlement finality).
![]()
Question 4.
Write a note on ‘The Dinner Club Card’?
Answer:
In February 1950, Frank McNamara and Ralph Schneider created The Diners Club card which was made of paper-cardboard. Initially, The card was accepted in only 27 restaurants From 1955, the card was made of plastic. The Diners Club still exists today under the name Diners Club International.
Question 5.
Write a note on the Anatomy of a Credit Card?
Answer:
All Payment cards (including debit cards) are usually plastic cards of size 85.60 mm width x 53.98 mm height, rounded comers with a radius of 2.88 mm to 3.48 mm and thickness of 0.76 mm.
Question 6.
Write a note on the Credit Card number?
Answer:
Credit card number:
The modem credit card number has a 16-digit unique identification number.
![]()
Question 7.
Mention the three ways of processing debit card transactions?
Answer:
There are three ways of processing debit card transactions:
- EFTPOS (also known as online debit or PIN debit)
- Offline debit (also known as signature debit)
- Electronic Purse Card System
Question 8.
Mention the major advantage of stored-value cards?
Answer:
The major advantage of the stored-value cards is that customers don’t need to have a bank account to get prepaid cards.
![]()
Question 9.
Write note on Smart Card?
Answer:
Smart cards along with the regular features of any card-based payment system holds a EMV chip. This chip is similar to well-known sim card in appearance.
Question 10.
Mention the advantages of Smart Cards?
Answer:
The advantage of Smart cards is that it can provide identification, authentication, data storage and application processing.
Question 11.
Write note on ECS debit?
Answer:
ECS debit:
ECS debit is an inverse of ECS credit. It is used for the bulk collection of amounts. In this mode, multiple accounts are debited and then a single account is credited. This type of transaction is a Pull transactions. Example: The insurance premium of a bulk number of customers.
![]()
Question 12.
Write a note on NEFT?
Answer:
(NEFT) is an electronic funds transfer system initiated by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) in – November 2005. NEFT enables a bank customer to transfer funds between any two NEFT- enabled bank accounts on a one-to-one basis. It is done via electronic messages.
Question 13.
Write in brief about EMV chip.
Answer:
- It is an integrated chip in addition to a magnetic stripe to store cardholder information.
- EMV stands for Europay, MasterCard, Visa.
- These three names correspond to the names of the companies which are responsible to develop this technology.
- It is categorized into Chip-and-Signature and Chip-and-PIN.
![]()
Question 14.
How are the Mobile Banking operations implemented?
Answer:
Mobile Banking operations can be implemented in the following ways:
- Contacting the call center.
- Automatic IVR telephone service.
- Using a mobile phone via SMS.
- WAP technology
- Using smartphone applications.
Question 15.
Mention advantages of Internet Banking?
Answer:
1. The advantages of Internet banking are that the payments are made at the convenience of the account holder and are secured by user name and password, i.e. with Internet access it can be used from anywhere in the world and at any time.
2. Any standard browser (e.g. Google Chrome) is adequate. Internet banking does not need installing any additional software.
![]()
Question 16.
Explain the two types of addresses in UPI applications?
Answer:
UPI applications use two types of addresses – global and local.
- The global address includes bank account numbers and IFSC.
- The local address is a virtual payment address.
IV. Explain in detail
Question 1.
Explain the advantages of a Credit card.
Answer:
- Most credit cards are accepted worldwide.
- It is not necessary to pay physical money at the time of purchase.
- The customer gets an extra period to pay the purchase.
- Depending on the card, there is no need to pay an annuity.
- Allows purchases overthe Internet in installments.
- Some issuers allow “round up” the purchase price and pay the difference
- In cash to make the transactions easy.
![]()
Question 2.
Explain Smart Card?
Answer:
Smart card:
The modem version of card-based payment is smart cards. Smart cards along with the regular features of any card-based payment system holds an EMV chip.
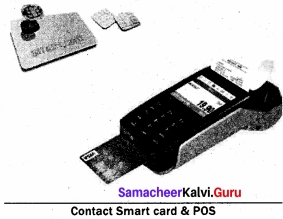
This chip is similar to well-known sim card in appearance but differ in its functionalities. The advantage of Smart cards is that it can provide identification, authentication, data storage and application processing. Smart cards can be classified into Contact smart cards and Contactless smart, Contact Smart card & POS cards.
(i) Contact smart cards:
Contact smart cards have a contact area of approximately 1 square centimeter, comprising several gold-plated contact pads. These pads provide electrical connectivity only when inserted into a reader, which is also used as a communications medium between the smart card and a host. e.g. a point of sale terminal(POS).
(ii) Contactless smart cards:
Contactless smart card is empowered by RF induction technology. Unlike contact smart cards, these cards require only near proximity to an antenna to communicate. Smart cards, whether they are contact or contactless cards do not have an internal power source. Instead, they use an inductor to capture some of the interrupting radio-frequency signal, rectify it and power the card’s processes.