Students can Download Computer Science Chapter 11 Database Concept Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 12th Computer Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Computer Science Solutions Chapter 11 Database Concept
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Computer Science Database Concept Text Book Back Questions and Answers
PART – 1
I. Choose The Best Answer
Question 1.
What is the acronym of DBMS?
Answer:
(a) DataBase Management Symbol
(b) Database Managing System
(c) DataBase Management System
(d) DataBasic Management System
Answer:
(c) DataBase Management System
Question 2.
A table is known as ……………………..
(a) tuple
(b) attribute
(c) relation
(d) entity
Answer:
(c) relation
![]()
Question 3.
Which database model represents parent-child relationship?
(a) Relational
(b) Network
(c) Hierarchical
(d) Object
Answer:
(c) Hierarchical
Question 4.
Relational database model was first proposed by ……………………..
(a) E F Codd
(b) E E Codd
(c) c) E F Cadd
(d) E F Codder
Answer:
(a) E F Codd
Question 5.
What type of relationship does hierarchical model represents?
(a) one-to-one
(b) one-to-many
(c) many-to-one
(d) many-to-many
Answer:
(b) one-to-many
![]()
Question 6.
Who is called Father of Relational Database from the following?
(a) Chris Date
(b) Hugh Darween
(c) Edgar Frank Codd
(d) Edgar Frank Cadd
Answer:
(c) Edgar Frank Codd
Question 7.
Which of the following is an RDBMS?
(a) Dbase
(b) Foxpro
(c) Microsoft Access
(d) SQLite
Answer:
(d) SQLite
Question 8.
What symbol is used for SELECT statement?
(a) σ
(b) π
(c) X
(d) Ω
Answer:
(a) σ
Question 9.
A tuple is also known as ………………………
(a) table
(b) row
(c) attribute
(d) field
Answer:
(b) row
![]()
Question 10.
Who developed ER model?
(a) Chen
(b) EF Codd
(c) Chend
(d) Chand
Answer:
(a) Chen
PART – II
II. Answer The Following Questions
Question 1.
Mention few examples of a database?
Answer:
dbase-III , dbase-III Plus, Foxbase , Foxpro ,SQL Server, Oracle Database, Sybase, Informix, MySQL are some examples of Database languages which are used to design ERP applications like Payroll, Railway Reservation System, Inventory Systems.
Question 2.
List some examples of RDBMS?
Answer:
SQL server, Oracle, mysql, MariaDB, SQLite.
![]()
Question 3.
What is data consistency?
Answer:
Data Consistency means that data values are the same at all instances of a database.
Question 4.
What is the difference between the Hierarchical and Network data model?
Answer:
A network database model is an extended form of the hierarchical data model. The difference between hierarchical and Network data model is :
- In a hierarchical model, a child record has only one parent node,
- In a Network model, a child may have many parent nodes. It represents the data in many-to-many relationships.
- This model is easier and faster to access the data.
![]()
Question 5.
What is normalization?
Answer:
- Normalization is a technique of organizing the data in the database.
- Database normalization was first proposed by Dr. Edgar F Codd as an integral part of RDBMS in order to reduce data redundancy (repetition) and improve data integrity (security from unauthorized users ).
PART – III
III. Answer The Following Questions
Question 1.
What is the difference between the Select and Project command?
Answer:
Select:
THE SELECT operation is used for selecting a subset with tuples according to a given condition. Select filters out all tuples that do not satisfy C.
Project:
The projection eliminates all attributes of the input relation but those mentioned in the projection list. The projection method defines a relation that contains a vertical subset of Relation.
![]()
Question 2.
What is the role of DBA?
Answer:
Database Administrator
- Database Administrator or DBA is the one who manages the complete database management system.
- DBA takes care of the security of the DBMS; managing the license keys, managing user accounts, and access.
![]()
Question 3.
Explain Cartesian Product with a suitable example?
PRODUCT OR CARTESIAN PRODUCT (Symbol: X)
Answer:
Cross product is a way of combining two relations. The resulting relation contains, both relations being combined.
A × B means A times B, where the relation A and B have different attributes.
This type of operation is helpful to merge columns from two relations.

Question 4.
Explain the Object Model with an example?
Answer:
Object Model
- Object model stores the data in the form of objects, attributes and methods, classes, and Inheritance.
- O This model handles more complex applications, such as Geographic Information System (GIS), scientific experiments, engineering design, and manufacturing.
- It is used in the file Management System.
- It represents real-world objects, attributes, and behaviors. It provides a clear modular structure.
- It is easy to maintain and modify the existing code.

An example of the Object model is Shape, Circle, Rectangle, and Triangle are all objects in this model.
- The circle has the attribute radius.
- Rectangle has the length and breadth of the attribute.
- Triangle has the attributes base and height.
- The objects Circle, Rectangle, and Triangle inherit from the object Shape.
![]()
Question 5.
Write a note on different types of DBMS users?
Answer:
Types of DBMS Users:
1. Database Administrators:
- Database Administrator or DBA is7 the one who manages the complete database management system.
- DBA takes care of the security of the DBMS, managing the license keys, managing user accounts and access etc.
2. Application Programmers or Software Developers:
This user group is involved in developing and designing the parts of DBMS.
3. End User:
- All modern applications, web or mobile, store user data.
- Applications are programmed in such a way that they collect user data and store the data on DBMS systems running on their server.
- End users are the one who store, retrieve, update and delete data.
4. Database Designers:
Database Designers are responsible for identifying the data to be stored in the database for choosing appropriate structures to represent and store the data.
PART – IV
IV. Answer The Following Questions
Question 1.
Explain the different types of data models?
Answer:
Types of Data Model
Following are the different types of a Data Model
- Hierarchical Model
- Relational Model
- Network Database Model
- Entity-Relationship Model
- Object Model
1. Hierarchical Model
Hierarchical model was developed by IBM as Information Management System.
In Hierarchical model, data is represented as a simple tree like structure form. This model represents a one-to-many relationship i.e. parent-child relationship. One child can have only one parent but one parent can have many children. This model is mainly used in IBM Main Frame computers.

2. Relational Model
The Relational Database model was first proposed by E.F. Codd in 1970 . Nowadays, it is the most widespread data model used for database applications around the world.
The basic structure of data in relational model is tables (relations). All the information’s related to a particular type is stored in rows of that table. Hence tables are also known as relations in a relational model. A relation key is an attribute which uniquely identifies a particular tuple (row in a relation (table)).

3. Network Model
Network database model is an extended form of hierarchical data model. The difference between hierarchical and-Network data model is:
- In hierarchical model, a child record has only one parent node,
- In a Network model, a child may have many parent nodes. It represents the data in many-to-many relationships.
- This model is easier and faster to access the data.

The school represents the parent node
Library, Office, and Staffroom is a child to school (parent node)
The student is a child to the library, office, and staff room (one to many relationships)
4. Entity-Relationship Model. (ER model)
In this database model, relationships are created by dividing the object into the entity and its characteristics into attributes.
It was developed by Chen in 1976. This model is useful in developing a conceptual design for the database. It is very simple and easy to design a logical view of data. The developer can easily understand the system by looking at ER Model constructed. The rectangle represents the entities. E.g. Doctor and Patient.
Ellipse represents the attributes E.g. D-id, D-name, P-id, P-name. Attributes describe the characteristics and each entity becomes a major part of the data stored in the database. The diamond represents the relationship in ER diagrams E.g. Doctor diagnosis the Patient

5. Object Model
Object model stores the data in the form of objects, attributes, and methods, classes, and Inheritance. This model handles more complex applications, such as Geographic Information System (GIS), scientific experiments, engineering design, and manufacturing. It is used in the File Management System. It represents real-world objects, attributes, and behaviors. It provides a clear modular structure. It is easy to maintain and modify the existing code.
![]()
Question 2.
Explain the different types of relationship mapping?
Answer:
Types of Relationships:
Following are the types of relationships used in a database.
- One-to-One Relationship
- One-to-Many Relationship
- Many-to-One Relationship
- Many-to-Many Relationship

1. One-to-One Relationship
In One-to-One Relationship, one entity is related to only one other entity. One row in a table is linked with only one row in another table and vice versa.
For example, A student can have only one exam number.
2. One-to-Many Relationship
In a One-to-Many relationship, one entity is related to many other entities. One row in table A is linked to many rows in table B, but one row in table B is linked to only one row in table A. For example, One Department has many staff members.

3. Many-to-One Relationship
In Many-to-One Relationship, many entities can be related with only one in the other entity. For example A number of staff members working in one Department. Multiple rows in staff members table are related with only one row in Department table.

4. Many-to-Many Relationship
A many-to-many relationship occurs when multiple records in a table are associated with multiple records in another table.
Example 1: Customers and Product:
Customers can purchase various products and Products can be purchased by many customers
Example 2: Students and Courses:
A student can register for many Courses and a Course may include many students
Example 3: Books and Student:
Many Books in students.

Question 3.
Differentiate DBMS and RDBMS?
Answer:

Question 4.
Explain the different operators in Relational algebra with suitable examples?
Answer:
Relational Algebra Operations from Set Theory
- UNION (∪)
- INTERSECTION (∩)
- DIFFERENCE (-)
- CARTESIAN PRODUCT (X)
SELECT (symbol: σ)
General form σ<sub>c</sub> ( R) with a relation R and a condition C on the attributes of R.
The SELECT operation is used for selecting a subset with tuples according to a given condition. Select filters out all tuples that do not satisfy C.

PROJECT (symbol: II)
The projection eliminates all attributes of the input relation but those mentioned in the projection list.
Example 1 using Table A
π<sub>course</sub> (STUDENT)
Result
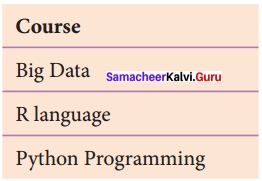
Course Big Data R language PythonProgramming
Note: duplicate row is removed in the result UNION (Symbol:u)
It includes all tuples that are in tables A or in B. It also eliminates duplicates. Set A Union Set B would be expressed as AuB
Example 2:
Consider the following tables

Result

SET DIFFERENCE ( Symbol: -)
The result of A – B, is a relation which includes all tuples that are in A but not in B. The attribute name of A has to match with the attribute name in B.
Example 4:
( using Table B)
Result

INTERSECTION (symbol: ∩) A∩B
Defines a relation consisting of a set of all tuple that is in both A and B. However, A and B must be union-compatible
Example 5:
(using Table B)

PRODUCT OR CARTESIAN PRODUCT (Symbol: X)
Cross-product is a way of combining two relations. The resulting relation contains, both relations being combined.
A × B means A times B, where the relation A and B have different attributes.
This type of operation is helpful to merge columns from two relations.


Cartesian product : Table A × Table B

![]()
Question 5.
Explain the characteristics of DBMS?
Characteristics of Database Management System
Answer:

Samacheer Kalvi 12th Computer Science Database Concept Additional Questions and Answers
PART – I
I. Choose The Correct Answer
Question 1.
………………….is an organized collection of data.
a) Word Processor
b) Spreadsheet
c) Programming language
d) Database
Answer:
d) Database
Question 2.
……………………. gives meaningful information
(a) data
(b) Information
(c) row
(d) tuple
Answer:
(b) Information
![]()
Question 3.
Data contain ………………….
a) Character
b) text
c) Word
d) All of these
Answer:
d) All of these
Question 4.
……………………… is a software that allows us to create, define and manipulate databases
(a) data
(b) Information
(c) DBMS
(d) Tuple
Answer:
(c) DBMS
![]()
Question 5.
Which one of the following is not a characteristic of DBMS?
(a) Redundancy
(b) consistency
(c) Normalization
(d) Insecure
Answer:
(d) Insecure
Question 6.
…………………. is not an example of DBMS.
a) Foxpro
b) Dbase
c) COBOL
d) Ms-Access
Answer:
c) COBOL
Question 7.
How many major components of DBMS are there?
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 5
Answer:
(d) 5
![]()
Question 8.
Which one of the following is not a component of DBMS?
(a) Data
(b) Methods
(c) DataBase Access Language
(d) Modules
Answer:
(d) Modules
Question 9.
…………………. makes the data more meaningful and connected in the database?
a) Ingress
b) ) DBMS
c) Relationship
d) Data models
Answer:
c) Relationship
Question 10.
A column is known as an ……………………….
Answer:
Attribute
![]()
Question 11.
The entire collection of related data in one table is referred to as ……………………… or …………………………
Answer:
File or Table
Question 12.
Each table ………………………. represents a Field
Answer:
column
Question 13.
Each ……………………… in the table represents a record.
Answer:
row
![]()
Question 14.
How many different types of data models are there?
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 5
Answer:
(d) 5
Question 15.
Which of the following in a table represents a field?
a) row
b) column
c) data
d) files
Answer:
b) column
![]()
Question 16.
Which database Model is the extended form of hierarchical data Model?
(a) Network
(b) Relational
(c) Flat File
(d) Object
Answer:
(a) Network
Question 17.
1. Relational – (i) classes
2. object model – (ii) Mainframe
3. ER model – (iii) key
4. Hierarchical – (iv) Entity
(a) 1-iii, 2-i, 3-iv, 4-ii
(b) 1-i, 2-ii, 3-iii, 4-iv
(c) 1-iv, 2-iii, 3-i, 4-ii
(d) 1-iv, 2-ii, 3-i, 4-iii
Answer:
(a) 1-iii, 2-i, 3-iv, 4-ii
![]()
Question 18.
…………………. model is mainly used in IBM Main Frame computers.
a) ER model
b) Hierarchical model
c) Network database model
d) Object model
Answer:
b) Hierarchical model
Question 19.
…………………… uniquely identifies a particular tuple in a table
Answer:
Relation key
Question 20.
Which model establishes many to many relationships?
(a) Network
(b) Relational
(c) Hierarchical
(d) Object
Answer:
(a) Network
![]()
Question 21.
…………………. is the one who manages the complete database management system.
a) Database Designer
b) Database Administrator
c) Database Architect
d) Data Analyst
Answer:
b) Database Administrator
Question 22.
ER Model was developed in the year …………………….
(a) 1978
(b) 1972
(c) 1976
(d) 1975
Answer:
(c) 1976
Question 23.
In ER Model, objects are said to be ……………………..
Answer:
entity
![]()
Question 24.
A column in the database is known as an ………………….
a) Attribute
b) Relation
c) Tuple
d) Data
Answer:
a) Attribute
Question 25.
…………………….. represents the relationship in ER diagrams.
Answer:
Diamonds
Question 26.
GIS stands for ………………………
Answer:
Geographic Information System
![]()
Question 27.
Which model is used in file management systems?
(a) object
(b) Hierarchical
(c) Network
(d) ER
Answer:
(a) object
Question 28.
DBA means ………………….
Answer:
Database Administrators
Question 29.
………………….. is one who manages the complete database management system
(a) Manager
(b) Engineer
(c) DBA
(d) Service Person
Answer:
(c) DBA
Question 30.
……………………. are the ones who stores, retrieve, update and delete data.
Answer:
End-User
![]()
Question 31.
Choosing appropriate structures to represent and store the data are the task of ……………………..
Answer:
database designer
Question 32.
RDBMS means ………………………..
(a) Relational Database Manipulation System
(b) Relational Database Management system
(c) Rapid DataBase Management Server
Answer:
(b) Relational Database Management system
![]()
Question 33.
Pick the odd out.
Oracle, Foxpro, MariaDB, SQLite
Answer:
Foxpro
Question 34.
Find the true statement
(a) Data redundancy is exhibited by DBMS
(b) Data redundancy is not present in DBMS
Answer:
(a) Data redundancy is exhibited by DBMS
Question 35.
Find the false statement
(a) Distributed Databases supported by DBMS
(b) Distributed Databases supported by RDBMS
Answer:
(a) Distributed Databases supported by DBMS
![]()
Question 36.
……………………. Model of data storage is used in DBMS.
Answer:
Navigational
Question 37.
In which database systems, transaction management is efficient?
(a) DBMS
(b) RDBMS
(c) ERDMS
(d) DBMS
Answer:
(b) RDBMS
![]()
Question 38.
How many types of relationships are there?
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer:
(d) 4
Question 39.
Identify which one of the following is an example for many to one relationship?
(a) a student with exam number
(b) many staff members in one department
(c) customer, products
(d) Books and students
Answer:
(b) many staff members in one department
![]()
Question 40.
…………………… is a procedural query language used to query the database tables using SQL
Answer:
Relational Algebra
Question 41.
Find the wrong pair
(a) Union U
(b) cartesian product P
(c) project n
(d) select o
Answer:
(b) cartesian product P
![]()
Question 42.
Which method defines a relation that contains a vertical subset of relations?
(a) project
(b) select
(c) difference
(d) union
Answer:
(a) project
Question 43.
The duplicate row is removed in ……………………….
(a) o
(b) π
(c) x
(d) –
Answer:
(b) π
Question 44.
…………………. is used to merge columns from two relations.
(a) σ
(b) π
(c) x
(d) –
Answer:
(c) x
![]()
Question 45.
…………………. is security from unauthorized users.
Answer:
Data Integrity
Question 46.
…………………. means duplication of data in a database.
Answer:
Redundancy.
PART- II
II. Answer The Following Questions
Question 1.
Differentiate data from Information?
Answer:
Data:
Data are raw facts stored in a computer. Data may contain any character, text, word, or number.
Example:
600006, DPI Campus, SCERT, Chennai, College Road
Information:
Information is formatted data, which allows being utilized in a significant way. It gives meaningful information.
Example:
SCERT
College Road
DPI Campus
Chennai 600006
![]()
Question 2.
Define database?
Answer:
Database is a repository collection of related data organized in a way that data can be easily accessed, managed and updated. Database can be a software or hardware based, with one sole purpose of storing data.
Question 3.
Name the components of DBMS?
Answer:
Components of DBMS:
The Database Management System can be divided into five major components as follows:
- Hardware
- Software
- Data
- Procedures/Methods
- Database Access Languages
Question 4.
What is DBMS?
Answer:
- DBMS is software that allows us to create, define and manipulate databases, allowing users to store, process, and analyze data easily.
- Example: dbase, Foxbase, Foxpro
![]()
Question 5.
Define row and column?
Answer:
Each row in a table represents a record, which is a set of data for each database entry. Each table column represents a Field, which groups each piece or item of data among the records into specific categories or types of data. Eg. StuNo., StuName, StuAge, StuClass, StuSec.
Question 6.
What are the components of DBMS?
Answer:
Components of DBMS:
- Hardware
- Software
- Data
- Procedures / Methods
- Database Access Languages
Question 7.
What is meant by the data model?
Answer:
Data Model:
- A data model describes how the data can be represented and accessed from the software after complete implementation
- It is a simple abstraction of a complex real-world data gathering environment.
- The main purpose of the data model is to give an idea as to how the final system or software will look after development is completed.
PART – III
III. Answer The Following Questions
Question 1.
Define DBMS?
Answer:
A DBMS is software that allows us to create, define and manipulate databases, allowing users to store, process and analyze data easily. DBMS provides us with an interface or a tool, to perform various operations to create a database, storing of data and for updating data, etc. DBMS also provides protection and security to the databases. It also maintains data consistency in the case of multiple users.
![]()
Question 2.
What are the advantages of DBMS?
Answer:
Advantages of DBMS
- Segregation of application program
- Minimal data duplication or Data Redundancy
- Easy retrieval of data using the Query Language
- Reduced development time and maintenance
PART – IV
IV. Answer The Following Questions
Question 1.
Explain the Various Components of DBMS?
Answer:
Components of DBMS:
The Database Management System can be divided into five major components as follows:
- Hardware
- Software
- Data
- Procedures/Methods
- Database Access Languages

1. Hardware:
The computer, hard disk, I/O channels for data, and any other physical component involved in storage of data
2. Software:
This main component is. a program that controls everything. The DBMS software is capable of understanding the Database Access Languages and interprets into database commands for execution.
3. Data:
It is that resource for which DBMS is designed. DBMS creation is to store and utilize data.
4. Procedures/Methods:
They are general instructions to use a database management system such as the installation of DBMS, manage databases to take backups, report generation, etc.
5. DataBase Access Languages:
They are the languages used to write commands to access, insert, update and delete data stored in any database.