Students can Download Computer Science Chapter 13 Python and CSV Files Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 12th Computer Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Computer Science Solutions Chapter 13 Python and CSV Files
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Computer Science Python and CSV Files Text Book Back Questions and Answers
PART – I
I. Choose The Correct Answer
Csv File Questions Class 12 Question 1.
A CSV file is also known as a
(a) Flat File
(b) 3D File
(c) String File
(d) Random File
Answer:
(a) Flat File
A Csv File Is Also Known As A 3d File Question 2.
The expansion of CRLF is ………………………
(a) Control Return and Line Feed
(b) Carriage Return and Form Feed
(c) Control Router and Line Feed
(d) Carriage Return and Line Feed
Answer:
(d) Carriage Return and Line Feed
Csv Files In Python Class 12 Questions Question 3.
Which of the following module is provided by Python to do several operations on the CSV files?
(a) py
(b) xls
(c) csv
(d) os
Answer:
(c) csv
Question 4.
Which of the following mode is used when dealing with non-text files like image or exe files?
(a) Text mode
(b) Binary mode
(c) xls mode
(d) csv mode
Answer:
Question 5.
The command used to skip a row in a CSV file is ……………………….
(a) next( )
(b) skip( )
(c) omit( )
(d) bounce( )
Answer:
(b) skip( )
Question 6.
Which of the following is a string used to terminate lines produced by writer( )method of csv module?
(a) Line Terminator
(b) Enter key
(c) Form feed
(d) Data Terminator
Answer:
(a) Line Terminator
Question 7.
What is the output of the following program?
import csv
d=csv.reader(open(‘c:\PYPRG\chl3\city.csv’))
next(d)
for row in d:
print(row)
if the file called “city.csv” contain the following details
chennai,mylapore
mumbai,andheri
(a) chennai,mylapore
(b) mumbai,andheri
(c) chennai, mumbai
(d) chennai,mylapore,mumbai,andheri
Answer:
(b) mumbai,andheri
Question 8.
Which of the following creates an object which maps data to a dictionary?
(a) listreader( )
(b) reader( )
(c) tuplereader( )
(d) DictReader( )
Answer:
(d) DictReader( )
Question 9.
Making some changes in the data of the existing file or adding more data is called
(a) Editing
(b) Appending
(c) Modification
(d) Alteration
Answer:
(c) Modification
Question 10.
What will be written inside the file test.csv using the following program import csv
D = [[‘Exam’],[‘Quarterly’],[‘Halfyearly’]]
csv.register_dialect(‘M’,lineterminator = ‘\n’)
with open(‘c:\pyprg\chl3\line2.csv’, ‘w’) as f:
wr = csv.writer(f,dialect=’M’)
wr.writerows(D)
f.close( )
(a) Exam Quarterly Halfyearly
(b) Exam Quarterly Halfyearly
(c) Q H
(d) Exam, Quarterly, Half early
Answer:
(d) Exam, Quarterly, Half early
PART – II
II. Answer The Following Questions
Question 1.
What is CSV File?
Answer:
- A CSV file is a human-readable text file where each line has a number of fields, separated by commas or some other delimiter.
- A CSV file is also called a Flat File.
Question 2.
Mention the two ways to read a CSV file using Python?
Answer:
Read a CSV File Using Python
There are two ways to read a CSV file.
- Use the csv module’s reader function
- Use the DictReader class.

Question 3.
Mention the default modes of the File?
Answer:
You can specify the mode while opening a file. In mode, you can specify whether you want to read ‘r’, write ‘w’ or append ‘a’ to the file. You can also specify “text or binary” in which the file is to be opened.
The default is reading in text mode. In this mode, while reading from the file the data would be in the format of strings.
Question 4.
What is use of next( ) function?
Answer:
The next() function returns the next item from the iterator. It can also be used to skip a row of the csv file.# skipping the first row(heading)
Example: next( reader)
Question 5.
How will you sort more than one column from a csv file? Give an example statement?
Answer:
To sort by more than one column you can use item getter with multiple indices: operator .itemgetter (1,2).
PART – III
III. Answer The Following Questions
Question 1.
Write a note on open( ) function of python. What is the difference between the two methods?
Answer:
- Python has a built-in function openQ to open a file.
- This function returns a file object also called a handle, as it is used to read or modify the file accordingly.
Method 1:
Syntax:
f = open(” test.txt”)
# perform file operations
f.close()
#since no mode is specified the default mode rt is used
Method 2:
Syntax:
with open(“test.txt”,’r’) as f:
- Method1 is not entirely safe.
- If an exception occurs when you are performing some operation with the file, the code exits without closing the file.
- The best way to do this is to use the “with” statement.
- This ensures that the file is closed when the block inside is exited. It is not necessary to explicitly call the close() method. It is done internally.
Question 2.
Write a Python program to modify an existing file?
Answer:
import csv
row= [‘3’, ‘Meena’, ‘Bangalore’]
with open(‘student.csv’, ‘r’) as readFile:
reader= csv.reader(readFile)
lines =list(reader) # list( ) – to store each row of data as a list
lines[3] =row
with open(‘student.csv’, ‘w’) as writeFile:
# returns the writer object which converts the user data with delimiter
writer= csv.writer(writeFile)
#writerows( )method writes multiple rows to a csv file
writer, writerows(lines)
readFile.close( )
writeFile.close( )
When we Open the student.csv file with text editor, then it will show:

Question 3.
Write a Python program to read a CSV file with default delimiter comma (,)?
Answer:
CSV file with default delimiter comma(,)
The following program read a file called “sample l.csv” with default delimiter cpmma(,) and print row by row.
#importing csv
import csv
#opening the csv fde which is in different location with read mode
with open(‘c:\ \pyprg\\sample l.csv’, V) as F:
#other way to open the file is f = (‘c:\\pyprg\\sample l.csv’, ‘r’)
reader = csv.reader(F)
Sprinting each line of the Data row by row print(row)
F.close( )
OUTPUT
[‘SNO’, ‘NAME’, ‘CITY’]
[12101’,’RAM’, ‘CHENNAI’]
[‘12102′,’LAVANYA’,’TIRUCHY’]
[‘12103′,’LAKSHMAN’,’MADURA’]
Question 4.
What is the difference between the write mode and append mode?
Answer:
Append mode writes the value of row after the last line of the “student.csv file:”
The ‘w’ write mode creates a new file. If the file is already existing ‘w’ mode over writs it. Where as ‘a’ append mode add the data at the end of the file if the file already exists otherwise creates a new one.
Question 5.
What is the difference between reader( ) and DictReader( ) function?
Answer:
Reading CSV File Into A Dictionary:
To read a CSV file into a dictionary can be done by using DictReader class of csv module which works similar to the reader( ) class but creates an object which maps data to a dictionary. The keys are given by the fieldnames as parameter. DictReader works by reading the first line of the CSV and using each comma-separated value in this line as a dictionary key.
The columns in each subsequent row then behave like dictionary values and can be accessed with the appropriate key (i.e. fieldname). The main difference between the csv.reader( ) and DictReader( ) is in simple terms csv. reader and csv.writer work with list/tuple, while csv.DictReader and csv.DictWriter work ‘ with dictionary. csv.DictReader and csv.DictWriter take additional argument fieldnames that are used as dictionary keys.
PART – IV
IV. Answer The Following Questions
Question 1.
Differentiate Excel file and CSV file?
Answer:
The difference between Comma-Separated Values (CSV) and eXceL Sheets(XLS) file formats is
Answer:
Excel:
- Excel is a binary file that holds information about all the worksheets in a file, including both content and formatting
- XLS files can only be read by applications that have been especially written to read their format, and can only be written in the same way.
- Excel is a spreadsheet that saves files into its own proprietary format viz. xls or xlsx
- Excel consumes more memory while importing data
CSV:
- CSV format is a plain text format with a series of values separated by commas.
- CSV can be opened with any text editor in Windows like notepad, MS Excel, OpenOffice, etc.
- CSV is a format for saving tabular information into a delimited text file with extension .csv
- Importing CSV files can be much faster, and it also consumes less memory
Question 2.
Tabulate the different mode with its meaning?
Python File Modes:
Answer:

Question 3.
Write the different methods to read a File in Python?
Answer:
Read a CSV File Using Python
There are two ways to read a CSV file.
- Use the csv module’s reader function
- Use the DictReader class.
CSV Module’s Reader Function:
You can read the contents of CSV file with the help of csv.reader( )method. The reader function is designed to take each line of the file and make a list of all columns. Then, you just choose the column you want the variable data for. Using this method one can read data from csv files of different formats like quotes (” “),pipe (|) and comma(,).
The syntax for csv.reader( ) is
csv. reader (fileobject, delimiter,fmtparams)
where
file object:- passes the path and the mode of the file
delimiter:- an optional parameter containing the standard dilects like, I etc can be omitted
fmtparams:- an optional parameter which help to override the default values of the dialects like skip initial space, quoting etc. Can be omitted

CSV file with default delimiter comma(,)
The following program read a file called “sample l.csv” with default delimiter comma(,) and print row by row.
#importing csv
import csv
#opening the csv file which is in different location with read mode
with open(‘c:\ \pyprg\\sample l.csv’, ‘r’) as F:
#other way to open the file is f= (‘c:\\pyprg\\sample l.csv’, ’r)
reader = csv.reader(F)
#printing each line of the Data row by row
print( row)
F.close( )
OUTPUT
[‘SNO’, ‘NAME’, ‘CITY’]
[‘12101′,’RAM’,’CHENNAI’]
[‘12102’, ‘LAVANYA’, ‘TIRUCHY’]
[‘12103’, ‘LAKSHMAN’, ‘MADURAI’]
CSV files- data with Spaces at the beginning
Consider the following file “sample 2.csv” containing the following data when opened through notepad

The following program read the file through Python using “csv.reader( )”.
import csv
csv.register_dialect(‘myDialect’,delimiter = ‘,’,skipimtialspace=True)
F=open(‘c:\ \pyprg\ \sample 2.csv’,’r’)
reader= csv.reader(F, dialect=’myDialect’)
for row in reader:
print( row)
F.close( )
OUTPUT
[‘Topic 1’, ‘Topic 2’, ‘Topic 3′]
[!one’, ‘two’, ‘three’]
[‘Example 1’, ‘Example 2’, ‘Example 3’]
As you can see in “sample 2.csv” there are spaces after the delimiter due to which the output is also displayed with spaces.
These whitespaces can be removed, by registering new dialects using CSV.register_dialect( ) class of CSV module. A dialect describes the format of the CSV file that is to be read. In dialects, the parameter “skipinitialspace” is used for removing whitespaces after the delimiter.
CSV File-Data With Quotes
You can read the csv file with quotes, by registering new dialects using csv.register_dialect( ) class of csv module.
Here, we have a quotes.csv file with the following data.
SNO, Quotes
(a) “The secret to getting ahead is getting started.”
(b) “Excellence is a continuous process and not an accident.”
(c) “Work hard dream big never give up and believe yourself.”
(d) “Failure is the opportunity to begin again more intelligently.”
(e) “The successful warrior is the average man, with laser-like focus.”
The following Program read “quotes.csv” file, where delimiter is comma (,)but the quotes are within quotes (“”). import csv
csv.register_dialect(‘myDialect’,delimiter = ‘,’,quoting=csv.QUOTE_ALL,
skipinitialspace=True)
f=open(’c:\\pyprg\ \quotes.csv’,’r’)
reader= csv.reader(f, dialect-myDialect’)
for row in reader:
print (row)
OUTPUT
[‘SNO’, ’Quotes’]
[(a), ’The secret to getting ahead is getting started.’]
[(b), ’Excellence is a continuous process and not an accident.’]
[(c), ’Work hard dream big never give up and believe yourself.’]
[(d), ’Failure is the opportunity to begin again more intelligently.’]
[(e), ’The successful warrior is the average man, with laser-like focus. ’]
In the above program, register a dialect with name myDialect. Then, we used csv. QUOTE_ ALL to display all the characters after double-quotes.
CSV files with Custom Delimiters
You can read CSVfile having custom delimiter by registering a new dialect with the help of csv.register_dialect( ).
In the following file called “sample 4.csv”,each column is separated with | (Pipe symbol)

The following program read the file “sample4.csv” with user defined delimiter “|”
import csv
csv.register_dialect(‘myDialect’, delimiter ‘|’)
with open(‘c:\\pyprg\\sample 4.csv’, ‘r’) as f:
reader= csv.reader(f, dialect-myDialect’)
for row in reader:
print(row)
f.close( )
OUTPUT
[‘RollNo’, ‘Name’, ‘City’]
[‘12101’, ‘Arun’, ‘Chennai’]
[‘12102’, ‘Meena’, ‘Kovai’]
[T21031,’Ram’,’Nellai’]
Reading CSV File Into A Dictionary:
To read a CSV file into a dictionary can be done by using DictReader class of csv module which works similar to the reader() class but creates an object which maps data to a dictionary. The keys are given by the fieldnames as parameter. DictReader works by reading the first line of the CSV and using each comma-separated value in this line as a dictionary key. The columns in each subsequent row then behave like dictionary values and can be accessed with the appropriate key (i.e. fieldname).
If the first row of your CSV does not contain your column names, you can pass a fieldnames parameter into the DictReader’s constructor to assign the dictionary keys manually. The main difference between the csv.reader( ) and DictReader( ) is in simple terms csv. reader and csv.writer work with list/tuple, while csv.DictReader and csv.DictWriter work with dictionary. csv.DictReader and csv.DictWriter take additional argument field names that are used as dictionary keys.
For Example:
Reading “sample 8.csv” file into a dictionary
import csv
filename= ‘c:\ \pyprg\ \sample 8.csv’
input_file =csv.DictReader(open(filename;’r’))
for row in input_file:
print(dict(row))
print (data(row)) #dict( ) to print data
OUTPUT
{‘ItemName ‘^Keyboard’, ‘Quantity’: ’48’}
{‘ItemName VMonitor’, ‘Quantity’: ’52’}
{‘ItemName VMouse’, ‘Quantity’: ’20’}
In the above program, DictReader( ) is used to read “sample 8.csv” file and map into a dictionary. Then, the function dict( ) is used to print the data in dictionary format without order. Remove the dict( ) function from the above program and use print(row). Check you are getting
the following output
OrderedDict([(‘ItemName Keyboard’), (‘Quantity’, ’48’)])
OrderedDict([(‘ltemName ‘,’Monitor’), (‘Quantity’, ’52’)])
OrderedDict([(‘ItemName ‘,’Mouse’), (‘Quantity’, ’20’)])
Question 4.
Write a Python program to write a CSV File with custom quotes?
CSV File with quote characters
Answer:
You can write the CSV file with custom quote characters, by registering new dialects using csv.register_dialect( ) class of csv module,
import csv
csvData = [[‘SNO’,Items’], [‘l’,’Pen’], [‘2′,’Book’], [‘3′,’Pencil’]]
csv.register_dialect(‘myDialect’, delimiter = ‘|’,quotechar = “”,
quoting=csv.QUOTE_ALL)
with open(‘c:\\pyprg\ \chl3\\quote.csv’, ‘w’) as csvFile:
writer= csv.writer(csvFile, dialect-myDialect’)
writer, write rows(csvData)
print(“writing completed”)
csvFile.close( )
When you open the “quote.csv” file in notepad, we get following output:

In the above program, myDialect uses pipe (|) as delimiter and quotechar as doublequote “” to write inside the file.
Question 5.
Write the rules to be followed to format the data in a CSV file?
Answer:
Rules to be followed to format data in a CSV file:
(i) Each record (row of data) is to be located on a separate line, delimited by a line break by pressing the enter key. For example:
xxx,yyy
denotes enter Key to be pressed
(ii) The last record in the file may or may not have an ending line break. For example:
PPP, qqq
yyy, xxx
(iii) There may be an optional header line appearing as the first line of the file with the same format as normal record lines. The header will contain names corresponding to the fields in the file and should contain the same number of fields as the records in the rest of the file. For example: field_ name 1,field_name 2,field_name_3 aaa,bbb,ccc
zzz,yyy,xxx CRFF( Carriage Return and Line feed)
(iv) Within the header and each record, there may be one or more fields, separated by commas. Spaces are considered part of a field and should not be ignored. The last field in the record must not be followed by a comma. For example Red, Blue
(v) Each field may or may not be enclosed in double-quotes. If fields are not enclosed with double quotes, then double quotes may not appear inside the fields. For example: “Red”,”Blue”,”Green” #Field data with double quotes
Black, White, Yellow #Field data without double quotes
(vi) Fields containing line breaks (CRLF), double quotes, and commas should be enclosed in double-quotes. For example:
Red, “;:Blue CRLF #comma itself is a field value, so it is enclosed with double quotes Red, Blue, Green
(vii) If double-quotes are used to enclose fields, then a double-quote appearing inside a field must be preceded with another double quote. For example:
“Red,” “Blue1: “Green”, #since double quotes is a field value it is enclosed with another double quote,, White
Practice Programs
Question 1.
Write a Python program to read the following Namelist.csv file and sort the data in alphabetically order of names in a list and display the output

import csv.operator
data = csv.reader(open(‘c:\\PYPRG\\NameList.scv’))
next(data)
sorted list = sorted(data, key = operator.itemgetter(1))
for row in sorted list:
print(row)
Output:

Question 2.
Write a Python program to accept the name and five subjects mark of 5 students. Find the total and store all the details of the students in a CSV file?
Answer:
import csv
csvData = [[‘student’, ‘ml Vm2′,’m3′,’m4′,’m5′,’total’],
[‘Ram’, ’90’,’90’,”90′,”90′,”90′,”450′],
[‘Hari’,’100′,’100′,’100′,’10’,’90’,’490′],
[‘Sai’, ’90’,’90’,’ 100′,’ 100′,’ 100′,’480′],
[‘Viji’, ’ 100′,’90’,’90’,’90’,’ 100′,’470′],
[‘Raja’, ’80’,’’80’,”80′,’ 100′,’ 100′,’440′]]
with open(‘c:\\pyprg\\chl3\\st.csv’,’w’)as CF:
writer = csv.writer(CF) writer. writerows(csvData)
CF.close( )
Output:

Samacheer Kalvi 12th Computer Science Python and CSV Files Additional Questions and Answers
PART – 1
I. Choose The Correct Answer
Question 1.
Which of the following gives the python programmer the ability to parse CSV files?
a) sys module
b) CSV module
c) parse module
d) CSV flat file
Answer:
b) CSV module
Question 2.
The file extension to save excel files are
(a) xls Civdsx
(b) XL
(c) exc or XL
(d) XL or xlx
Answer:
(a) xls Civdsx
Question 3.
……………….. is a human-readable text file where each line has a number of fields, separated by commas or some other delimiter.
a) CSV file
b) Column separated values
c) CSV sheet
d) Condition systematic values
Answer:
a) CSV file
Question 4.
Identify the wrong statement
(a) Excel is a binary file
(b) csv is a plain text
(c) Excel is a plain text
(d) csv has tabular information
Answer:
(c) Excel is a plain text
Question 5.
Identify the statement which is correct.
(a) csv consumes less memory and faster
(b) Excel consumes less memory and slower
Answer:
(a) csv consumes less memory and faster
Question 6.
There are ……………. ways to read a CSV file.
a) 2
b) 3
c) 4
d) Only one
Answer:
a) 2
Question 7.
…………………… file is used to store tabular data such as spreadsheet or database.
Answer:
csv
Question 8.
How will you open a new file in Notepad?
(a) File → New
(b) Ctrl + N
(c) both a and b
(d) shift + N
Answer:
(c) both a and b
Question 9.
If the fields of data in the csv file have commas, then it should be given with …………………..
(a) ,
(b) ”
(c) ‘
(d) :
Answer:
(b) ”
Question 10.
The CSV file contents can be read with the help of the method
a) read ()
b) open ()
c) with open ()
d) reader ()
Answer:
d) reader ()
Question 11.
If the fields contain double quotes as part of the data, the internal quotation marks need to be
(a) same
(b) quarter
(c) doubled
(d) tripled
Answer:
(c) doubled
Question 12.
The line white indicates
(a) the first two fields of the row are empty
(b) It can be deleted
(c) comma not necessary
(d) only one field is there and, can be deleted
Answer:
(a) the first two fields of the row are empty
Question 13.
……………………….. allows creating, store and re-use various formatting parameters for CSV file in reading and writing.
a) class
b) dialect
c) write()
d) read()
Answer:
b) dialect
Question 14.
Identify the wrong statement from the following.
(a) Each field may or may not be enclosed in double-quotes.
(b) If the fields are not enclosed with double quotes, then double quotes may not appear inside the fields
(c) Fields containing line breaks, double quotes, and commas should be enclosed in single quotes.
(d) the last field in the record must not be followed by a comma
Answer:
(c) Fields containing line breaks, double quotes, and commas should be enclosed in single quotes.
Question 15.
There are ……………………. ways to read a csv file.
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer:
(b) 2
Question 16.
……………… method returns a writer object which converts the user’s data into delimited strings on the given file-like object.
a) csv.writer()
b) csv.write user ()
c) csv.writes ()
d) csv_writer ()
Answer:
a) csv.writer()
Question 17.
open( ) returns a file called ………………………… which is used to read or modify the file accordingly.
Answer:
handle
Question 18.
The default reading mode is ………………….. mode.
Answer:
text
Question 19.
The default mode when you open a file is
(a) r
(b) w
(c) x
(d) a
Answer:
(a) r
Question 20.
Excel files are saved with extension ………………
a) xlsx
b) CSV
c) Wordpad
d) Notepad
Answer:
a) xlsx
Question 21.
What will happen when you open a file for writing and a file already exists there?
(a) creates a new file
(b) truncates the file
(c) overwrite the file
(d) append the contents
Answer:
(b) truncates the file
Question 22.
To open the file updating data, click ……………………
(a) a
(b) b
(c) t
(d) +
Answer:
(d) +
Question 23.
…………………… opens a file for exclusive creation.
(a) r
(b) w
(c) x
(d) +
Answer:
(c) x
Question 24.
………………….. opens the file for read and write in binary mode.
(a) r
(b) b
(c) x + b
(d) r + b
Answer:
(d) r + b
Question 25.
Python has a ……………………… collector to clean up unreferenced objects.
Answer:
garbage
Question 26.
closing a file will free up the resources that were tied with the file and is done by ……………………. method.
(a) Exit
(b) close
(c) Quit
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) close
Question 27.
………………. is used to sort by more than one column.
a) Colsort
b) itemgetter ()
c) sor_ter ()
d) more_item ()
Ans :
b) itemgetter ()
Question 28.
How many arguments are there in csv.reader( ) functions?
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 5
Answer:
(b) 3
Question 29.
Which one of the following cannot be omitted in cav. reader?
(a) file object
(b) delimiter
(c) fmtparams
(d) space
Answer:
(a) file object
Question 30.
A ……………………. describes the format of the csv file that is to be read.
Answer:
dialect
Question 31.
In dialects, the parameter …………………… is used for the remaining whitespaces after the delimiter.
Answer:
skipintialspace
Question 32.
By default, what will be the value of skip initial space?
(a) True
(b) False
(c) 0
(d) 1
Answer:
(b) False
Question 33.
A ………………….. is a class of csv module which helps to define parameters for reading and writing csv.
Answer:
dialect
Question 34.
We can register for new dialects using class of csv module.
Answer:
csv.register-dialects
Question 35.
Which of the following is used to display all the characters after double-quotes.
(a) Quote
(b) Quote-all
(c) double quotes
(d) single quotes
Answer:
(b) Quote-all
Question 36.
Which one of the following is used to add the elements to the list.
(a) add
(b) insert
(c) append
(d) update
Answer:
(c) append
Question 37.
Which one of the following cannot be used as a column separator?
(a) delimiter
(b) pipe
(c) comma
(d) #
Answer:
(d) #
Question 38.
List literals are written using ………………………..
(a) [ ]
(b) ( )
(c) { }
(d) <>
Answer:
(a) [ ]
Question 39.
An ordered sequence of elements which are mutable or changeable are called ……………………..
(a) object
(b) tuple
(c) list
(d) dictionary
Answer:
(c) list
Question 40.
…………………….. command arranges a list value in ascending order.
Answer:
sort( )
Question 41.
……………………… is used to arrange a list in descending order.
Answer:
sort(reverse)
Question 42.
To sort by more than one column, we can use ………………………. with multiple indices.
Answer:
itemgetter
Question 43.
To sort the second column which option have to be selected?
(a) itemgetter(0)
(b) itemgetter(1)
(c) itemgetter(2)
(d) itemgetter(3)
Answer:
(b) itemgetter(1)
Question 44.
(I) csv.writer work with list/tuple
(II) csv.Dictwriter work with dictionary
(III) csv.DictReader work with list/tuple/dictionary.
(a) (I),(II) – True (III) – False
(b) (I) – True (II), (III) – False
(c) (I),(II),(III) – True
(d) (I),(II),(III) – False
Answer:
(a) (I),(II) – True (III) – False
Question 45.
The additional argument field names that are used with csv.DictReader and csv. Dictwriter is called as …………………………
Answer:
dictionary keys
Question 46.
Which function is used to print the data in dictionary format without order?
(a) dictionary
(b) print( )
(c) dict( )
(d) dictprint( )
Answer:
(c) dict( )
Question 47.
Which is a dictionary subclass that saves the order in whcih its contents are added?
(a) orderedDist
(b) SortDist
(c) DistSort
(d) Sorting
Answer:
(a) orderedDist
Question 48.
……………………. is used to remove the ordered Diet.
Answer:
Dist( )
Question 49.
…………………. method writes a row of data into the specified file.
Answer:
writerow( )
Question 50.
The number of parameters in csv.writer( ) …………………….
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 5
Answer:
(b) 3
Question 51.
Identify the wrong statement.
(a) The writerow( ) writes one row at a time
(b) The writerows( ) writes all the data at once
(c) No such writerows( ) function in csv
Answer:
(c) No such writerows( ) function in csv
Question 52.
Identify the true statement.
(a) writerow( ) takes 1 dimensional data
(b) writerows( ) takes 2 dimensional data
(c) both are true
(d) both are false
Answer:
(c) both are true
Question 53.
By default, csv files open automatically in ……………………..
Answer:
Excel.
PART – II
II. Answer The Following Questions
Question 1.
How can you handle CSV file data contains comma?
Answer:
- If the fields of data in your CSV file contain commas, we can protect them by enclosing those data fields in double-quotes (“).
- The commas that are part of your data will then be kept separate from the commas which delimit the fields themselves.
PART – III
III. Answer The Following Questions
Question 1.
How will you create a csv file?
Answer:
Creating CSV Normal File
To create a CSV file in Notepad, First open a new file using
File → New or Ctrl +N.
Then enter the data you want the file to contain, separating each value with a comma and each row with a new line.
For example consider the following details
Topic 1,Topic 2,Topic 3
one,two,three
Example 1,Example 2,Example 3
Save this content in a file with the extension .csv . You can then open the same using Microsoft Excel or any other spreadsheet program. Here we have opened using Microsoft Excel. It would create a table of data similar to the following:

Question 2.
How will you create csv file that contains comma with data?
Answer:

To retain the commas in “Address” column, you can enclose the fields in quotation marks.
For example:
RollNo, Name, Address
12101, Nivetha, “Mylapore, Chennai”
12102, Lavanya, “Adyar, Chennai”
12103, Ram, “Gopalapuram, Chennai”
As you can see, only the fields that contain commas are enclosed in quotes. If you open this in MS Excel, It looks like as follows

Question 3.
How will you create csv file that contains double quotes with data?
Answer:
Creating CSV File That contains Double Quotes With Data
If your fields contain double-quotes as part of their data, the internal quotation marks need to be doubled so that they can be interpreted correctly. For Example, given the following data:
Answer:

It should be written in csv file as RollNo, Name, FavoriteSports, Address
12101,Nivetha””” Cricket’”‘”, FootballMylapore chennai 12102, Lavanya,””” Basketball Cricket “””, Adyar chennai 12103, Ram,””” Soccer”””,”” Hockey”””, Gopalapuram chennai
The output will be

Question 4.
How will you create csv file using MS-Excel?
Answer:
Create A CSV File Using Microsoft Excel:
To create a CSV file using Microsoft Excel, launch Excel and then open the file you want to save in CSV format. For example, below is the data contained in our sample Excel worksheet:

Item Name, Cost-Rs, Quantity, Profit
Keyboard,480, 12,1152 ,
Monitor, 5200, 10, 10400
Mouse,200,50,2000
Total Profit = 13552
Question 5.
Define: Ordered Diet?
Answer:
- DictReader () gives OrderedDict by default in its output.
- An OrderedDict is a dictionary subclass which saves the order in which its contents are added.
- To remove the OrderedDict use diet ().
Question 6.
Write a program create csv files data with sapces at the beginning?
Answer:
import csv
csv.register_dialect(‘myDialect’,delimiter = 7,skipinitialspace=True)
F=open(‘c:\ \pyprg\ \sample2.csv’,’r’)
reader= csv.reader(F, dialect=’myDialect’)
for row in reader:
print( row)
F.close( )
OUTPUT
[‘Topic 1’, ‘Topic2’, ‘Topic3’]
[‘one’, ‘two’, ‘three’]
[‘Example 1’, ‘Example2’, ‘Example3’]
Question 7.
Write a program to read csv files with custom delimiters?
Answer:
import csv
csv.register_dialect(‘myDialect’, delimiter ‘|’)
with open(‘c:\\pyprg\\sample4.csv’, ‘r’) as
f: reader= csv.reader(f, dialect=’myDialect’)
for row in reader: print(row)
F.close( )
Output
[‘RollNo’, ‘Name’, ‘City’]
[‘12101’, ‘Arun’, ‘Chennai’]
[‘12102’, ‘Meena’, ‘Kovai’]
[‘12103’, ‘Ram’, ‘Nellai’]
Question 8.
Give the syntax for csv.writer( )
Answer:
The syntax for csv.writer( ) is
csv. writerffileobject, delimiter,fmtparams)
where
fileobject : passes the path and the mode of the file.
delimiter : an optional parameter containing the standard dilects like , | etc can be omitted.
fmtparams : optional parameter which help to override the default values of the dialects like skipinitialspace,quoting etc. can be omitted.
Question 9.
Give the program to add new row to the csv file?
Answer:
import csv
row= [‘6’, ‘Sajini’Madurai’]
with open(‘student.csv’, ‘a’) as CF: # append mode to add data at the end
writer= csv.writer(CF)
writer.writerow(row) # writerow( ) method write a single row of data in file
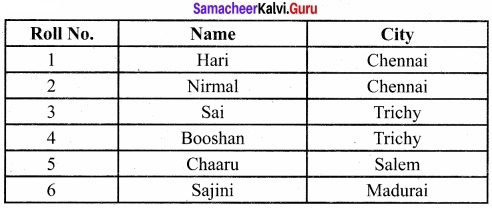
CF.close( )
Output
Question 10.
Give a program for csv file with a line terminator?
import csv
Answer:
Data= [[‘Fruit’, ‘Quantity’], [‘Apple’, ‘5’], [‘Banana’, ‘7’], [‘Mango’, ‘8’]] csv.register_dialect(‘myDialect’, delimiter= ‘|’, lineterminator = ‘\n’) with open(‘c:\\pyprg\ \chl3\\line.csv’, ‘w’) as f:
writer= csv.writer(f, dialect=’myDialect’) writer.writerows(Data)
f.close( )
Output

PART – IV
IV. Answer The Following Questions
Question 1.
Write a program to read a specific column in a file?
Answer:
Read a specific column In a File:
To get the specific columns like only Item Name and profit for the “sampleS.csv” file. Then you have to do the following:
import csv
#opening the csv file which is in different location with read mode
f=open(“c:\ \pyprg\ \chl3sample5.csv”,’r’)
#reading the File with the help of csv.reader( )
readFile=csv.reader(f)
#printing the selected column for col in readFile :
print col[0],col[3]
f.close( )

Question 2.
Write a python program to read a csv file and store it in a list?
Answer:
Read A CSV File And Store It In A-List
In this topic you are going to read a CSV file and the contents of the file will be stored as a list. The syntax for storing in the List is
list = [ ] # Start as the empty list
list.append(element) # Use append( ) to add elements
For example all the row values of “sample.csv” file is stored in a list using the following
program
import csv
# other way of declaring the filename
inFile= ‘c:\ \pyprg\\sample.csv’
F=open(inFile,’r’)
reader= csv.reader(F)
# declaring array
arrayValue = [ ]
# displaying the content of the list
for row in reader:
array Value, appendfrow)
print(row)
F.close( )

Question 3.
Write a python program to read a csv file and store a column value in a list for sorting?
Answer:
python file
F=open(inFile;’r’)
# reading the File with the help of csv.reader( )
reader = csv.reader(F)
# skipping the first row(heading) next( reader)
# declaring a list array Value = [ ]
a= int(input (“Enter the column number 1 to 3:-“))
# sorting a particular column-cost for row in reader:
array Value. append(row[a]) array Value.sorif) for row in array Value: print (row)
F.close( )
OUTPUT
Enter the column number 1 to 3:- 2
50
12
10
Question 4.
Write a python program to get data at runtime and write it in a csv file?
Answer:
import csv
with open(‘c:\ \pyprg\ \chl3\\dynamicfile.csv’, ‘w’) as f:
w = csv. writer (f)
ans=’y’
while (ans= =’y’):
name= input(“Name?: “)
date = input(“Date of birth: “)
place = input(“Place: “) w.writerow([name, date, place])
ans=input(“Do you want to enter more y/n?: “)
F=open(‘c:\ \pyprg\ \chl3\\dynamiefde.csv,’r’)
reader = csv.reader(F)
for row in reader:
print(row)
F.close( )
OUTPUT
Name?: Nivethitha
Date of birth: 12/12/2001
Place: Chennai
Do you want to enter more y/n?: y
Name?: Leena
Date of birth: 15/10/2001
Place: Nagercoil
Do you want to enter more y/n?: y
Name?: Padma
Date of birth: 18/08/2001
Place: Kumbakonam
Do you want to enter more y/n?: n
[‘Nivethitha’, ’12/12/2001′, ‘Chennai’]
[ ]
[’Leena’, ’15/10/2001′, ‘Nagercoil’]
[ ]
[‘Padma’, ’18/08/2001′, ‘Kumbakonam’]
