These Tamilnadu State Board Class 12th Economics Solutions Chapter 11 Economics of Development and Planning Questions and Answers help to enhance the skills. Download Solutions of Samacheer Kalvi 12th Economics Book Solutions Chapter Wise Pdf for free of cost. Refer Samacheer Kalvi Class 12th Economics Solutions pdf and kickstart your preparation. You can find the best Solutions for Samacheer Kalvi Class 12th Economics Solutions Chapterwise here.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Economics Solutions Chapter 11 Economics of Development and Planning
With the help of the Samacheer Kalvi Class 12th Economics Solutions Chapter 11 Economics of Development and Planning you can get an idea about the subject. The topics covered in Samacheer Kalvi Class 12th Economics Solutions Chapter 11 Economics of Development and Planning Solutions Questions and Answers. Tap the link and Download Samacheer Kalvi Class 12th Economics Solutions for Chapter 11 Economics of Development and Planning to cover all the topics.
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Economics Economics of Development and Planning Text Book Back Questions and Answers
Part – A
Multiple Choice Questions.
Question 1.
“Redistribution with Growth” became popular slogan under which approach?
(a) Traditional approach
(b) New welfare oriented approach
(c) Industrial approach
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(b) New welfare oriented approach
Question 2.
Which is not the feature of economic growth?
(a) Concerned with developed nations
(b) Gradual change
(c) Concerned with quantitative aspect
(d) Wider concept
Answer:
(d) Wider concept
![]()
Question 3.
Which among the following is a characteristic of underdevelopment?
(a) Vicious circle of poverty
(b) Rising mass consumption
(c) Growth of Industries
(d) High rate of urbanization
Answer:
(a) Vicious circle of poverty
Question 4.
The non – economic determinant of economic development ………………………..
(a) Natural resources
(b) Human resource
(c) Capital formation
(d) Foreign trade
Answer:
(b) Human resource
Question 5.
Economic growth measures the ………………………..
(a) Growth of productivity
(b) Increase in nominal income
(c) Increase in output
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(c) Increase in output
![]()
Question 6.
The supply side vicious circle of poverty suggests that poor nations remain poor because
(a) Saving remains low
(b) Investment remains low
(c) There is a lack of effective government
(d) a and b above
Answer:
(d) a and b above
Question 7.
Which of the following plan has focused on the agriculture and rural economy?
(a) People’s Plan
(b) Bombay Plan
(c) Gandhian Plan
(d) Vishveshwarya Plan
Answer:
(c) Gandhian Plan
![]()
Question 8.
Arrange following plans in correct chronological order ………………………..
(a) People’s Plan
(b) Bombay Plan
(c) Jawaharlal Nehru Plan
(d) Vishveshwarya Plan
Answer choices
(a) (i) (ii) (iii) (iv)
(b) (iv) (iii) (ii) (i)
(c) (i) (ii) (iv) (iii)
(d) (ii) (i) (iv) (iii)
Answer:
(b) (iv) (iii) (ii) (i)
Question 9.
M.N. Roy was associated with ………………………..
(a) Congress Plan
(b) People’s Plan
(c) Bombay Plan
(d) None of the above
(b) People’s Plan
Question 10.
Which of the following country adopts indicative planning?
(a) France
(b) Germany
(c) Italy
(d) Russia
Answer:
(b) Germany
![]()
Question 11.
Short – term plan is also known as ………………………..
(a) Controlling Plans
(b) De – controlling Plans
(c) Rolling Plans
(d) De – rolling Plans
Answer:
(a) Controlling Plans
Question 12.
Long – term plan is also known as ………………………..
(a) Progressive Plans
(b) Non – progressive Plans
(c) Perspective Plans
(d) Non – perspective Plans
Answer:
(c) Perspective Plans
Question 13.
The basic philosophy behind long – term planning is to bring ……………………….. changes in the economy?
(a) Financial
(b) Agricultural
(c) Industrial
(d) Structural
Answer:
(c) Industrial
![]()
Question 14.
Sarvodaya Plan was advocated by ………………………..
(a) Mahatma Gandhi
(b) J.P. Narayan
(c) S. N Agarwal
(d) Structural
Answer:
(b) J.P. Narayan
Question 15.
Planning Commission was set up in the year ………………………..
(a) 1950
(b) 1951
(c) 1947
(d) 1948
Answer:
(a) 1950
![]()
Question 16.
Who wrote the book ‘The Road to Serfdom’?
(a) Friedrich Hayek
(b) H.R. Hicks
(c) David Ricardo
(d) Thomas Robert Malthus
Answer:
(a) Friedrich Hayek
Question 17.
Perspective plan is also known as ………………………..
(a) Short – term plan
(b) Medium – term plan
(c) Long – term plan
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(c) Long – term plan
![]()
Question 18.
NITI Aayog is formed through ………………………..
(a) Presidential Ordinance
(b) Allocation of business rules by President of India
(c) Cabinet resolution
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(c) Cabinet resolution
Question 19.
Expansion of NITI Aayog?
(a) National Institute to Transform India
(b) National Institute for Transforming India
(c) National Institution to Transform India
(d) National Institution for Transforming India
Answer:
(d) National Institution for Transforming India
![]()
Question 20.
The Chair Person of NITI Aayog is ………………………..
(a) Prime Minister
(b) President
(c) Vice – President
(d) Finance Minister
Answer:
(a) Prime Minister
Part – B
Answer The Following Questions In One or Two Sentences.
Question 21.
Define economic development?
Answer:
- Economic development refers to the problems of underdeveloped countries and economic growth to those of developed countries.
- Economic development deals with the problems of UDCs. Change is discontinuous and spontaneous.
- Economic development is not determined by any single factor. Economic development depends on Economic, Social, Political and Religious factors.
![]()
Question 22.
Mention the indicators of development?
Answer:
Economic development refers to the systematic use of scientific and technical knowledge to meet specific objectives and requirements. It deals with the problem of underdeveloped countries.
Question 23.
Distinguish between economic growth and development?
Answer:
Economic Growth:
- Deals with the problems of Developed countries
- Change is gradual and steady
- Means more output
- Concerns Quantitative aspects i.e. increase in per capita income
- Narrow
Economic Development:
- Deals with the problems of UDCs
- Change is discontinuous and spontaneous
- Means not only more output but also its composition
- Quantitative as well as Qualitative
- Wider concept Development = Growth + Change
![]()
Question 24.
What is GNP?
Answer:
GNP is the total market value of all final goods and services produced within a nation in a particular year, Plus income earned by its citizens minus income of non-residents located in that country.
Question 25.
Define economic planning?
Answer:
- Economic Planning is “collective control or suppression of private activities of production and exchange”. – Robbins
- “Economic Planning in the widest sense is the deliberate direction by persons in – charge of large resources of economic activity towards chosen ends”. – Dalton
Question 26.
What are the social indicators of economic development?
Answer:
Social indicators are normally referred to as the basic and collective needs of the people. The direct provision of basic needs such as health, education, food, water, sanitation, and having facilities are called social indicators.
Question 27.
Write a short note on NITI Aayog?
Answer:
NITI Aayog (National Institution for Transforming India) was formed on January 1, 2015. It replaced the planning commission. NITI Aayog is a policy think-tank of the Government of India. The PM is its chairperson.
Part – C
Answer The Following Questions In One Paragraph.
Question 28.
Elucidate major causes of the vicious circle of poverty with diagram?
Answer:
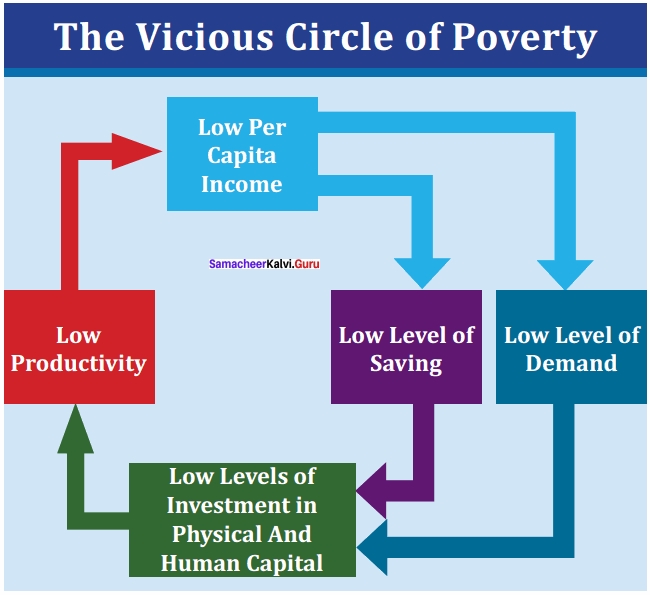
- There are circular relationships known as the ‘vicious circles of poverty’ that tend to perpetuate the low level of development in Less Developed Countries (LDCs).
- Nurkse explains the idea in these words: “It implies a circular constellation of forces tending to act and react upon one another in such a way as to keep a poor country in a state of poverty.
- For example, a poor man may not have enough to eat; being underfed, his health may be weak; being physically weak, his working capacity is low, which means that he is poor, which in turn means that he will not have enough to eat and so on.
- A situation of this sort relating to a country as a whole can be summed up in the proposition: “A county is poor because the country is poor”.
- The vicious circle of poverty operates both on the demand side and the supply side.
- On the supply side, the low level of real income means low savings.
- The low level of saving leads to low investment and to deficiency of capital.
- The deficiency of capital, in turn, leads to low levels of productivity and back to low income. Thus the vicious circle is complete from the supply side.
- The demand-side of the vicious circle is that the low level of real income leads to a low level of demand which, in turn, leads to a low rate of investment and hence back to deficiency of capital, low productivity and low income.
Question 29.
What are the non – economic factors determining development?
Answer:
The Non-Economic factors are:-
- Human Resource
- Technical know-how
- Political freedom
- Social organization
- Corruption free administration
- Desire for development
- Moral, ethical and social values
- Casino capitalism
- Patrimonial capitalism.
Non – Economic Factors:
‘Economic Development has much to do with human endowments, social attitudes, political conditions, and historical accidents. Capital is a necessary but not a sufficient condition of progress.’
(I) Human Resources:
- Human resource is named human capital because of its power to increase productivity and thereby national income.
- There is a circular relationship between human development and economic growth.
- A healthy, educated and skilled labour force is the most important productive asset.
- Human capital formation is the process of increasing knowledge, skills, and the productive capacity of people.
(II) Technical Know-how:
As scientific and technological knowledge advances, more and more sophisticated techniques steadily raise the productivity levels in all sectors.
(III) Political Freedom:
The process of development is linked with political freedom.
(IV) Social Organization:
People show interest in the development activity only when they feel that the fruits of development will be fairly distributed.
(V) Corruption free administration:
- Corruption is a negative factor in the growth process.
- Unless the countries root-out corruption in their administrative system, the crony capitalists and traders will continue to exploit national resources.
(VI) Desire for development:
The pace of economic growth in any country depends to a great extent on people’s desire for development.
(VII) Moral, ethical and social values:
- These determine the efficiency of the market, according to Douglas C. North.
- If people are not honest, market cannot function.
(VIII) Casino Capitalism:
If People spend larger propotion of their income and time on entertainment liquor and other illegal activities, productive activities may suffer, according to Thomas Piketty.
(IX) Patrimonial Capitalism:
If the assets are simply passed on to children from their parents, the children would not work hard, because the children do not know the value of the assets.
Question 30.
How would you break the vicious circle of poverty?
Answer:
Breaking the Vicious Circle of Poverty:
- The vicious circle of poverty is associated with low rate of saving and investment on the supply side.
- In UDCs the rate of investment and capital formation can be stepped up without reduction in consumption. For this, the marginal rate of savings is to be greater than average rate of savings.
- To break the vicious circle on the demand side, Nurkse suggested the strategy of balanced growth.
- If investment is made in several industries simultaneously the workers employed in various industries will become consumers of each other’s products and will create demand for one another.
- The balanced growth i.e. simultaneous investment in large number of industries creates mutual demand. Thus, through the strategy of balanced growth, vicious circle of poverty operating on the demand side of capital formation can be broken.
Question 31.
Trace the evolution of economic planning in India?
Answer:
The evolution of planning in India is stated below:
- Sir M. Vishveshwarya (1934)He laid the foundation for economic planning in India in 1934 through his book, “Planned Economy of India”. It was a 10 year plan.
- Jawaharlal Nehru (1938): Set up “National planning commission”.
- Bombay plan 1940 : The 8 leading industrialists of Bombay represented it. It was a 15 year Investment plan.
- S. N. Agarwal (1944) : Gandhian plan.
- M. N. Roy (1945): People’s Plan
- J. P Narayan : Sarvodaya Plan.
Question 32.
Describe the case for planning?
Answer:
The economic planning is justified on the following grounds.
(I) To accelerate and strengthen market mechanism:
The market mechanism works imperfectly in underdeveloped countries because of the ignorance and unfamiliarity with it. A large part of the economy comprises the non-monetized sector.
(II) To remove unemployment:
Capital being scarce and labour being abundant, the problem of providing gainful employment opportunities to an ever-increasing labour force is a difficult task.
(III) To achieve balanced development:
In the absence of sufficient enterprise and initiative, the planning authority is the only institution for planning the balanced development of the economy.
(a) Development of Agriculture and Industrial Sectors:
The need for developing the agriculture sector along with the industrial sector arises from the fact that agriculture and industry are interdependent.
(b) Development of Infrastructure:
The agriculture and industrial sectors cannot develop in the absence of economic and social overheads. The building of canals, roads, railways, power stations, etc., is indispensable for agricultural and industrial development.
(c) Development of Money and Capital Markets:
The expansion of domestic and foreign trade requires not only the development of agricultural and industrial sectors along with social and economic overheads but also the existence of financial institutions.
(IV) To remove poverty and inequalities:
Planning is the only path open to underdeveloped countries, for raising national and per capita income, reducing inequalities and poverty and increasing employment opportunities.
Question 33.
Distinguish between functional and structural planning?
Answer:
Functional planning:
Functional planning refers to that planning which seeks to remove economic difficulties by directing all the planning activities within the existing economic and social structure.
Structural planning:
Structural planning refers to a good deal of changes in the socio-economic framework of the country. This type of planning is adopted mostly in underdeveloped countries.
Question 34.
What are the functions of NITI Aayog?
Answer:
- Cooperative and competitive federalism.
- Shared National Agenda
- Decentralized planning
- Vision and scenario planning
- Network of expertise
- Harmonization
- Conflict Resolution
- coordinating Interface with the world.
- Internal consultancy
- Capacity Building
- Monitoring and Evaluation
Part – D
Answer The Following Questions In About A Page.
Question 35.
Discuss the economic determinants of economic development?
Answer:
Determinants of Economic Development:
Economic development is not determined by any,single factor. Economic development depends on Economic, Social, Political and Religious factors.
Economic and Non – Economic Factors:
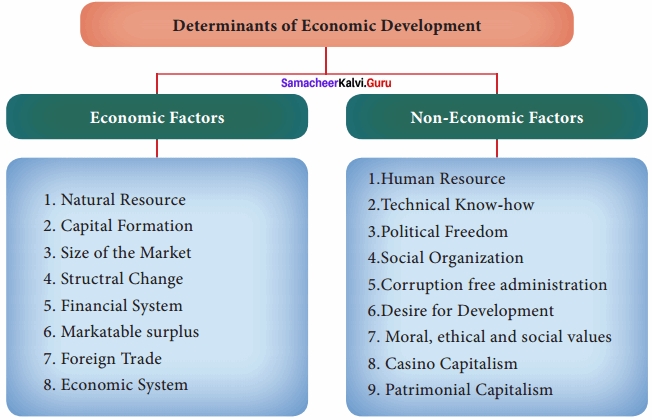
Economic Factors:
1. Natural Resource:
The principal factor affecting the development of an economy is the availability of natural resources. The existence of natural resources in abundance is essential for development.
2. Capital Formation:
Capital formation is the main key to economic growth. Capital formation refers to the net addition to the existing stock of capital goods which are either tangible like plants and machinery or intangible like health, education and research.
3. Size of the Market:
Large size of the market would stimulate production, increase employment and raise the National per capita income. That is why developed countries expand their market to other countries through WTO.
4. Structural Change:
Structural change refers to change in the occupational structure of the economy. Any economy of the country is generally divided into three basic sectors: Primary sector such as agricultural, animal husbandry, forestry, etc; Secondary sector such as industrial production, constructions and Tertiary sector such as trade, banking and commerce.
5. Financial System:
Financial system implies the existence of an efficient and organized banking system in the country.
6. Marketable Surplus:
Marketable surplus refers to the total amount of farm output cultivated by farmers over and above their family consumption needs. This is a surplus that can be sold in the market for earning income.
7. Foreign Trade:
The country which enjoys favorable balance of trade and terms of trade is always developed. It has huge forex reserves and stable exchange rate.
8. Economic System:
The countries which adopt free market mechanism (laissez faire) enjoy better growth rate compared to controlled economies.
Non – Economic Factors:
‘Economic Development has much to do with human endowments, social attitudes, political conditions and historical accidents. Capital is a necessary but not a sufficient condition of progress.’
1. Human Resources:
Human resource is named as human capital because of its power to increase productivity and thereby national income. There is a circular relationship between human development and economic growth. A healthy, educated and skilled labour force is the most important productive asset. Human capital formation is the process of increasing knowledge, skills and the productive capacity of people.
2. Technical Know-how:
As scientific and technological knowledge advances, more and more sophisticated techniques steadily raise the productivity levels in all sectors.
3. Political Freedom:
The process of development is linked with political freedom.
4. Social Organization:
People show interest in the development activity only when they feel that the fruits of development will be fairly distributed.
5. Corruption free administration:
Corruption is a negative factor in the growth process. Unless the countries root-out corruption in their administrative system, the crony capitalists and traders will continue to exploit national resources.
6. Desire for development:
The pace of economic growth in any country depends to a great extent on people’s desire for development.
7. Moral, ethical and social values:
These determine the efficiency of the market, according to Douglas C. North. If people are not honest, market cannot function.
8. Casino Capitalism:
If People spend larger propotion of their income and time on entertainment liquor and other illegal activities, productive activities may suffer, according to Thomas Piketty.
9. Patrimonial Capitalism:
If the assets are simply passed on to children from their parents, the children would not work hard, because the children do not know the value of the assets.
Question 36.
Describe different types of Planning?
Answer:
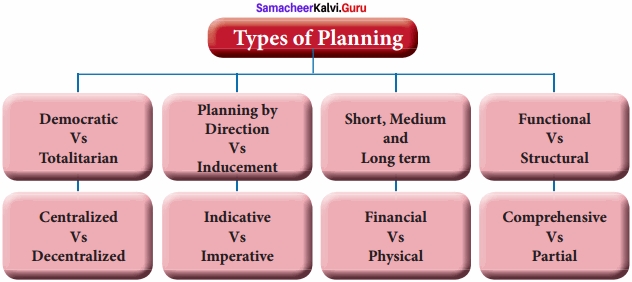
- Democratic planning:- Democratic planning implies planning within democracy. People are associated at every step in the formulation and implementation of the plan.
- Totalitarian Planning:- Here, there is central control and direction of all economic activities in accordance with a single plan. In authoritarian planning, the planning authority is the supreme body.
- Centralized Planning:- It means the power of planning and decision making are exclusively in the hands of top management.
- Decentralized Planning:- Here local organizations and institutions formulate, adopt, execute and supervise the plan without interference by the central authorities.
- Planning by Direction:- There is a central authority which plans, directs and orders the execution of the plan in accordance with pre-determined targets and priorities.
- Planning by Inducement:- The people are induced to act in a certain way through various monetary and fiscal measures.
- Indicative Planning:- Under this plan, the outline of plan is prepared by the Government. Then it is discussed with the representatives of private management, trade unions, consumer groups, financial institutions and other experts. The essential function is coordination of different economic units.
- Imperative planning:- The state is all-powerful in the operation and implementation of the plan. Once a plan is drawn up, its implementation is a matter of enforcement.
- Short term Plan:- They are also known as ‘controlling plans’. They encompass the period of one year, they are also known as ‘annual plans’.
- Medium-term Plans:- They last for the period of 3 to 7 years. But normally, the period should be 5 years. It deals with the allocation of both financial and physical resources.
- Long- term Plan:- It is considered for a time period-over 10 years. It is strategic planning.
- Financial Planning:- It refers to the technique in which resources are allocated in terms of money .
- Physical planning: It pertains to the allocation of resources in terms of men, materials and machinery.
- Functional Planning: It refers to that planning which seeks to remove economic difficulties.
- Structural planning: It refers to a good deal of changes in the socio-economic framework of the country.
- Comprehensive planning: It concerns with the major issues of the whole economy.
- Partial planning: It considers only a few important sectors of the economy.
Question 37.
Bring out the arguments against planning?
Answer:
The arguments against planning are discussed below.
(I) Loss of freedom:
- The absence of freedom in decision-making may act as an obstacle for economic growth.
- Regulations and restrictions are the backbones of a planned economy.
- Economic freedom comprises freedom of consumption, freedom of choice of occupation, freedom to produce and the freedom to fix prices for the products.
- Under planning, the crucial decisions are made by the Central Planning Authority.
(II) Elimination of Initiative:
Under centralized planning, there will be no incentive for initiatives and innovations.
(a) The absence of private ownership and profit motive discourages entrepreneurs from taking bold decisions and risk taking. Attractive profit is the incentive for searching new ideas, new lines and new, methods.
(b) As all enjoy equal reward under planned economy irrespective of their effort, efficiency and productivity.
(c) The bureaucracy and red-tapism which are the features of the planned economy cripple the initiative as they cause procedural delay and time loss.
(III) High cost of Management:
- No doubt the fruits of planning such as industrialization, social justice and regional balance are good.
- But the cost of management of economic affairs outweighs the benefits of planning.
- Plan formulation and implementation involve the engagement of an army of staff for data collection and administration.
(IV) Difficulty in advance calculations:
- Price mechanism provides for the automatic adjustment among price, demand and supply in a Laissez-Faire economy.
- The producers and consumers adjust their supply and demand based on price changes.
- The arguments against planning are mostly concerned with centralized and totalitarian planning.
- Democratic planning, planning by inducement and decentralized planning especially under mixed economies give an equal role for the private sector and public sector.
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Economics Economics of Development and Planning Additional Questions and Answers
Part – A
I. Multiple Choice Questions.
Question 1.
………………………. defines development strictly in Economic terms.
(a) Traditional approach
(b) New welfare oriented approach
(c) Development approach
(d) Under development approach
Answer:
(a) Traditional approach
Question 2.
New welfare oriented approach is called ……………………….
(a) Economic growth
(b) Economic Development
(c) Redistribution with growth
(d) New Welfare Development
Answer:
(c) Redistribution with growth
Question 3.
Under development refers to that state of an economy is very low levels of Per Capita Income and ……………………….
(a) Low level of productivity
(b) Low level of people
(c) Low level of distribution
(d) Low level of unemployment
Answer:
(a) Low level of productivity
Question 4.
………………………. leads to a higher quality of living all other thing being equal.
(a) GNP
(b) NNP
(c) GDP
(d) NDP
Answer:
(a) GNP
Question 5.
GNP relates to increase in the ………………………. of the Economy.
(a) Per Capita Real Income
(b) Per Capita Finance
(c) Per Capita Economy
(d) Per Capita Natural Resource
Answer:
(a) Per Capita Real Income
Question 6.
………………………. is defined as a sustained improvement in health, literacy and standard of living.
(a) Economic level
(b) Economic welfare
(c) Economic development
(d) Economic goods
Answer:
(c) Economic development
Question 7.
………………………. is called basic needs such as health, education, food, water, sanitation, and housing facilities and social backwardness.
(a) Economic Indicators
(b) Social Indicators
(c) Welfare Indicators
(d) State Indicators
Answer:
(b) Social Indicators
Question 8.
Economic development depends on Economic, Social, Political and ………………………. factors.
(a) Real
(b) Religion
(c) Religious
(d) Welfare
Answer:
(c) Religious
Question 9.
Low level of Development is called ……………………….
(a) Developed countries
(b) Less developed countries
(c) Developed nation
(d) Underdeveloped nation
Answer:
(b) Less developed countries
Question 10.
Price mechanism provides for the automatic adjustment among price, demand, and supply in a ………………………. Economy.
(a) Laissez-Faire
(b) Developed
(c) Underdeveloped
(d) Planned
Answer:
(a) Laissez Faire
Question 11.
Centralized planning the entire planning process in a country is under a ………………………. authority.
(a) Imperative planning
(b) Planning by direction
(c) Central planning
(d) Long term planning
Answer:
(c) Central planning
Question 12.
………………………. planning by Inducement the people are induced to act in a certain way through various monetary and fiscal measures.
(a) Centralized planning
(b) Planning by direction
(c) Imperative planning
(d) Short term planning
Answer:
(b) Planning by direction
Question 13.
Short term plans are also known as ……………………….
(a) Long term plans
(b) Planning by direction
(c) Centralised planning
(d) Controlling plans
Answer:
(d) Controlling plans
Question 14.
………………………. planning is peculiar to the mixed economies.
(a) Centralised planning
(b) Indicative planning
(c) Planing by direction
(d) Imperative short term planning
Answer:
(b) Indicative planning
Question 15.
………………………. the state is all-powerful in the preparation and implementation of the plan.
(a) Centralized planning
(b) Planning by direction
(c) Indicative planning
(d) Imperative planning
Answer:
(d) Imperative planning
Question 16.
………………………. planning refers to the technique of planning in which resources are allocated in terms of money.
(a) Financial
(b) Physical
(c) Structural
(d) Functional
Answer:
(a) Financial
Question 17.
………………………. planning pertains to the allocation of resources in terms of men, materials, and machinery.
(a) Financial
(b) Physical
(c) Functional
(d) Structural
Answer:
(b) Physical
Question 18.
………………………. planning refers to a good deal of changes in the socio-economic framework of the country.
(a) Financial
(b) Physical
(c) Functional
(d) Structural
Answer:
(d) Structural
Question 19.
General planning concerns itself with the major issues for the whole economy is known as ………………………. planning.
(a) comprehensive
(b) Partial
(c) Functional
(d) Structural
Answer:
(a) comprehensive
Question 20.
NITI Aayog was formed on through a ……………………….
(a) Financial resolution
(b) Functional resolution
(c) Comprehensive resolution
(d) Union cabinet
Answer:
(d) Union cabinet
Question 21.
……………………… is a policy think tank of the Government of India.
(a) Comprehensive planning
(b) Partial planning
(c) NITI Aayog
(d) Functional planning
Answer:
(c) NITI Aayog
Question 22.
……………………… to central and state governments on policy and programmes.
(a) Internal consultancy
(b) Interface consultancy
(c) Conflict consultancy
(d) Monitoring consultancy
Answer:
(a) Internal consultancy
Question 23.
A shared vision of national development priorities and strategies with the active involvement of states is called ………………………
(a) Competitive federalism
(b) Shared national agenda
(c) Scenario planning
(d) Network of expertise
Answer:
(b) Shared national agenda
Question 24.
To restructure the planning process into a bottom-up model is called ………………………
(a) Decentralized planning
(b) Scenario planning
(c) Partial planning
(d) Comprehensive planning
Answer:
(a) Decentralized planning
Question 25.
To enable the states to have active participation in the formulation of national policy is called cooperative and ………………………
(a) Competitive federalism
(b) Comprehensive federalism
(c) Partial federalism
(d) Comprehensive federalism
Answer:
(a) Competitive federalism
II. Match The Following And Choose The Correct Answer By Using the Codes Given Below.
Question 1.
A. UDC – (i) Economic terms
B. Traditional approach – (ii) Low Per Capita Income
C. Economic Development – (iii) Higher level of living
D. GNP – (iv) Economic growth
Codes:
(a) A (ii) B (i) C (iv) D (iii)
(b) A (i) B (ii) C (i) D (ii)
(c) A (iii) B (iv) C (ii) D (i)
(d) A (iv) B (iii) C (i) D (ii)
Answer:
(a) A (ii) B (i) C (iv) D (iii)
Question 2.
A. Capital formation – (i) Organised banking system
B. Size of the market – (ii) Economic growth
C. Occupational structure – (iii) Increase employment
D. Financial system – (iv) Structural change
Codes:
(a) A (i) B (ii) C (iii) D (iv)
(b) A (iii) B (iv) C (i) D (ii)
(c) A (iv) B (i) C (ii) D (iii)
(d) A (ii) B (iii) C (iv) D (i)
Codes:
Answer:
(d) A (ii) B (iii) C (iv) D (i)
Question 3.
A. Human resource – (i) Technical knowledge
B. Technical know-how – (ii) Crony capitalism
C. Political freedom – (iii) Increase productivity
D. Social organization – (iv) Development linked
Codes:
(a) A (i) B (ii) C (iii) D (iv)
(b) A (iii) B (i) C (iv) D (ii)
(c) A (iv) B (iii) C (ii) D (i)
(d) A (ii) B (iii) C (iv) D (i)
Answer:
(b) A (iii) B (i) C (iv) D (ii)
Question 4.
A. Casino capitalism – (i) 1948
B. First five year plan – (ii) 1950
C. Industrial policy – (iii) 1951 – 1956
D. Plan era – (iv) Illegal activities
Codes:
(a) A (i) B (ii) C (iii) D (iv)
(b) A (ii) B (iv) C (iii) D (i)
(c) A (iii) B (iv) C (ii) D (i)
(d) A (iv) B (iii) C (i) D (ii)
Answer:
(d) A (iv) B (iii) C (i) D (ii)
Question 5.
A. Patrimonial capitalism – (i) Collective control
B. Vicious circle of poverty – (ii) LDC
C. Economic planning – (iii) Solved union econokic planning
D. Industrial super power – (iv) Children would not work hard
Codes:
(a) A (i) B (iii) C (ii) D (i)
(b) A (ii) B (iv) C (iii) D (i)
(c) A (iv) B (ii) C (i) D (iii)
(d) A (iii) B (i) C (iv) D (ii)
Answer:
(d) A (iii) B (i) C (iv) D (ii)
III. State Whether The Statements Are True or False.
Question 1.
(i) There are two main approaches to the concept of development viz
(1) The traditional approach
(2) The new welfare-oriented approach.
(ii) The traditional approach defines development strictly in economic terms.
(a) Both (i) and (ii) are true
(b) Both (i) and (ii) are false
(c) (i) is true but (ii) is false
(d) (i) is false but (ii) is true
Answer:
(a) Both (i) and (ii) are true
Question 2.
(i) Economic development was redefined in terms of reduction of poverty, inequality, and unemployment within the context of a growing economy.
(ii) New welfare-oriented approach is “Redistribution with growth”.
(a) Both (i) and (ii) are true
(b) Both (i) and (ii) are false
(c) (i) is true but (ii) is false
(d) (i) is false but (ii) is true
Answer:
(a) Both (i) and (ii) are true
Question 3.
(i) GNP is the total market value of all final goods and services.
(ii) GNP leads the low level of living.
(a) Both (i) and (ii) are true
(b) (i) is true but (ii) is false
(c) Both (i) and (ii) are false
(d) (i) is false but (ii) is true
Answer:
(b) (i) is true but (ii) is false
Question 4.
(i) Social Indicators are the basic and collective needs of the people.
(ii) The basic needs are agriculture and Industry.
(a) Both (i) and (ii) are true
(b) (i) is true but (ii) is false
(c) Both (i) and (ii) are false
(d) (i) is false but (ii) is true
Answer:
(b) (i) is true but (ii) is false
Question 5.
(i) Capital formation is the main key to economic growth.
(ii) Capital formation helps to increase the population.
(a) (i) is true but (ii) is false
(b) Both (i) and (ii) are false
(c) Both (i) and (ii) are true
(d) (i) is false but (ii) is true
Answer:
(a) (i) is true but (ii) is false
IV. Which of The Following is Correctly Matched.
Question 1.
(a) Sir M. Vishveshwarya – 1940
(b) Jawaharlal Nehru – 1934
(c) Bombay plan – 1938
(d) S.N. Agarwal – 1944
Answer:
(d) S.N. Agarwal – 1944
Question 2.
(a) Planned Economy of India – S.N. Agarwal
(b) National planning commission – Jawaharlal Nehru
(c) Bombay plan – Sir M. Vishveshwarya
(d) Gandhianplan – Investment plan
Answer:
(c) Bombay plan – Sir M. Vishveshwarya
Question 3.
(a) NITI Aayog – Union cabinet resolution
(b) Financial planning – Controlling plans
(c) Short term plans – Technique planning
(d) Indicative planning – Capitalist economy
Answer:
(a) NITI Aayog – Union cabinet resolution
Question 4.
(a) UDC – Vicious circle of poverty
(b) Rural economy – Peoples plan
(c) Redistribution with growth – Industrial approach
(d) Controlling plans – Polling plans
Answer:
(a) UDC – Vicious circle of poverty
Question 5.
(a) H.R. Hicks – The road to serfdom
(b) Sarvodaya plan – M.N. Roy
(c) Perspective plan – Long term plan
(d) Modernisation – Industrialization
Answer:
(c) Perspective plan – Long term plan
V. Which of The Following is Not Correctly Matched.
Question 1.
(a) Structural changes – Modernization
(b) Functional planning – Remove Economic difficulties
(c) Capitalist economy – Partial planning
(d) People’s plan – N.S.C. Bose
Answer:
(d) People’s plan – N.S.C. Bose
Question 2.
(a) Market economy – Capitalist economy
(b) Industry – Socialist economy
(c) J.P. Narayan – Bombay plan
(d) S.N. Agarwal – Gandhian plan
Answer:
(c) J.P. Narayan – Bombay plan
Question 3.
(a) 1934 – Jawaharlal Nehru
(b) 1950 – J.P. Narayan
(c) 1945 – M.N. Roy
(d) 1944 – S.N. Agarwal
Answer:
(a) 1934 – Jawaharlal Nehru
Question 4.
(a) Centralized planning – Planning from above
(b) Indicative planning – Mixed economies
(c) Imperative planning – China and Russia
(d) Totalitarian planning – Inducement planning
Answer:
(d) Totalitarian planning – Inducement planning
Question 5.
(a) Financial planning – Technique of planning
(b) NITI Aayog – Union cabinet resolution
(c) Seven pillars of effective governance – NITT
(d) Physical planning – Techniques of planning
Answer:
(c) Seven pillars of effective governance – NITT
VI. Pick The Odd One Out.
Question 1.
Economic development
(a) State of development
(b) Nature and level of change
(c) Scope of change
(d) Growth change
Answer:
(d) Growth change
Question 2.
Economic factors
(a) Natural resource
(b) Capital formation
(c) Size of the market
(d) Social change
Answer:
(d) Social change
Question 3.
Non – Economic factors
(a) Human resource
(b) Technical know-how
(c) Foreign trade
(d) Political freedom
Answer:
(c) Foreign trade
Question 4.
UDC characteristics are
(a) Low Per Capita Income
(b) Widespread poverty
(c) Low population
(d) Low rate of capital formation
Answer:
(c) Low population
Question 5.
The economic planning is justified on the following grounds.
(a) To accelerate and strengthen the market mechanism
(b) To remove unemployment
(c) To remove agriculture
(d) To achieve balanced development
Answer:
(c) To remove agriculture
VII. Assertion And Reason.
Question 1.
Assertion (A): The traditional approach defines development strictly in economic terms.
Reason (R): The increase in GNP is accompanied by a decline in the share of agriculture in output and employment.
(a) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true and ‘R’ is the correct explanation to ‘A’
(b) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true but ‘R’ is not the correct explanation for ‘A’
(c) ‘A’ is true but ‘R’ is false
(d) ‘A’ is false but ‘R’ is true
Answer:
(a) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true and ‘R’ is the correct explanation to ‘A’
Question 2.
Assertion (A): Economic development depends on economic, social, political, and religious factors.
Reason (R): Economic development is determined by a single factor.
(a) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true and ‘R’ is the correct explanation to ‘A’
(b) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true but ‘R’ is not the correct explanation for ‘A’
(c) ‘A’ is true but ‘R’ is false
(d) ‘A’ is false but ‘R’ is true
Answer:
(c) ‘A’ is true but ‘R’ is false
Question 3.
Assertion (A): Social Indicators are normally referred to as basic and collective needs of the people.
Reason (R): The basic needs such as health, education, food, water, sanitation, and housing facilities check social backwardness.
(a) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true and ‘R’ is the correct explanation to ‘A’
(b) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true but ‘R’ is not the correct explanation to ‘A’
(c) ‘A’ is true but ‘R’ is false
(d) ‘A’ is false but ‘R’ is true
Answer:
(a) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true and ‘R’ is the correct explanation to ‘A’
Question 4.
Assertion (A): Capital is a necessary but sufficient condition of progress.
Reason (R): Economic development has much to do with human endowments, social attitudes, political conditions, and historical accidents.
(a) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true and ‘R’ is the correct explanation to ‘A’
(b) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true but ‘R’ is not the correct explanation to ‘A’
(c) ‘A’ is true but ‘R’ is false
(d) ‘A’ is false but ‘R’ is true
Answer:
(d) ‘A’ is false but ‘R’ is true
Question 5.
Assertion (A): The countries which adopt free-market mechanism [Laissez faire] enjoy better growth rate compared to controlled economies.
Reason (R): It may be true for some countries but not every country.
(a) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true and ‘R’ is the correct explanation to ‘A’
(b) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true but ‘R’ is not the correct explanation to ‘A’
(c) ‘A’ is true but ‘R’ is false
(d) ‘A’ is false but ‘R’ is true
Answer:
(a) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true and ‘R’ is the correct explanation to ‘A’
Part – B
Answer The Following Questions In One or Two Sentences.
Question 1.
Name the approaches to Economic Development.
Answer:
- The traditional Approach
- The new welfare-oriented Approach
Question 2.
What is the meaning of New Welfare oriented Approach?
Answer:
New Welfare oriented Approach:
- During the 1970s, economic development was redefined in terms of reduction of poverty, ‘inequality’, and unemployment within the context of a growing economy.
- In this phase, ‘Redistribution with Growth’ became the popular slogan.
Question 3.
What is ‘Totalitarianism’?
Answer:
A form of rule in which the government attempts to maintain total control over society, including all aspects of the public and private lives of its citizens.
Question 4.
What is the meaning of underdevelopment?
Answer:
Meaning of Underdevelopment:
The term underdevelopment refers to that state of an economy where levels of living of masses are extremely low due to very low levels of Percapita income, resulting from low levels of productivity and high growth rate of population.
Question 5.
What is economic growth?
Answer:
Economic growth refers to an increase in real GDP, which means an increase in the value of national output\ National expenditure.
Question 6.
Define “FOREX”?
Answer:
Foreign Trade:
- A country which enjoys a favorable balance of trade and terms of trade is always developed.
- It has huge forex reserves and a stable exchange rate.
Question 7.
Write casino capitalism?
Answer:
Casino Capitalism:
If People spend a larger proportion of their income and time on entertainment liquor and other illegal activities, productive activities may suffer, according to Thomas Piketty.
Question 8.
Define “Planning”?
Answer:
- Planning is a technique, a means to an end is the realization of certain pre-determined and well-defined aims and objectives laid down by central planning authority.
- The end may be to achieve economic, social, political, or military objectives.
Question 9.
What is Capital Formation?
Answer:
Capital Formation refers to the net addition to the existing stock of capital goods
which are either tangible like plants and machinery or intangible like health, education, and research.
Question 10.
Write Gandhian plan and Bombay plan?
Answer:
- S.N Agarwal (1944) gave the “Gandhian Plan” focusing on the agricultural and rural economy.
- Bombay Plan (1940): The 8 leading industrialists of Bombay presented the “Bombay Plan”. It was a 15 Year Investment Plan.
Part – C
Answer The Following Questions In One Paragraph.
Question 1.
Explain the approaches to economic development.
Answer:
1. Traditional approach: The traditional approach defines development strictly in economic terms. The increase in GNP is accompanied by a decline in the share of agricultural output and employment while those of manufacturing and service sectors increase. It emphasizes the importance of industrialization. It was assumed that growth in GNP per capita would trickle down to people at the bottom.
2. New welfare-oriented Approach. During the 1970s, economic development was redefined in terms of reduction of poverty, inequality unemployment within the contrast of a growing economy In this phase, Redistribution with Growth become the population slogan.
Question 2.
Explain Economic growth changes?
Answer:
(I) State of Development:
Generally speaking, economic development refers to the problems of underdeveloped countries and economic growth to those of developed countries.
(II) Nature and Level of Change:
Development is a discontinuous and spontaneous change while growth is a gradual and steady change in the long run.
(III) Scope of Change:
- Growth simply means more output.
- But development refers to efficiency in production i.e. output per unit of input.
- It also implies changes in the composition of output and in the allocation of resources, reduction of poverty, inequality, and unemployment.
(IV) Extent of change:
Economic development (a wider concept than economic growth) is taken to mean growth plus structural change.
Question 3.
Explain economic factors capital formation?
Answer:
Capital Formation:
- Capital formation is the main key to economic growth.
- Capital formation refers to the net addition to the existing stock of capital goods which are either tangible like plants and machinery or intangible like health, education, and research.
- Capital formation helps to increase the productivity of labour and thereby production and income.
- It facilitates the adoption of advanced techniques of production.
- It leads to better utilization of natural resources, industrialization, and expansion of markets which are essential for economic progress.
Question 4.
Explain short, medium, and Long term planning:
Answer:
- Short-term plans are also known as controlling plans. They encompass the period of one year, therefore, they are also known as annual plans.
- Medium-term planning is considered for a time period of 5 years. It is tactical planning
- Long-term plans last for a period of 10 to 30 years. They are also known as ‘perspective plans’. It brings structural changes to the economy.
Question 5.
Write Development of Infrastructure?
Answer:
Development of Infrastructure:
- The agriculture and industrial sectors cannot develop in the absence of economic and social overheads.
- The building of canals, roads, railways, power stations, etc., is indispensable for agricultural and industrial development.
- Infrastructure involves huge capital investment long gestation period and low rate of return.
- The state alone can provide strong infrastructural bases through planning.
Question 6.
What is called crony capitalism?
Answer:
Mass participation in development programs is a pre-condition for accelerating the development process, whenever the defective social organization allows some groups to appropriate the benefits of growth. The majority of the poor people do not participate in the process of development. This is called crony capitalism.
Part – D
Answer The Following Questions In About A Page.
Question 1.
Explain the criteria of measurement of Economic Development.
Answer:
Economic Development is measured on the basis of four criteria.
Gross national product (GNP):
GNP is the total market value of all final goods and services provided within a nation in a particular year, plus income earned by its citizens minus income of non-residents located in that country. GNP is one measure of the economic condition of a country, under the assumption that a higher GNP leads to a high quality of living, all other things being equal.
GNP per capita: This relates to an increase in the per capita real income of the economy over the long period. This indicator of economic growth emphasizes that for economic development the rate of increase in real per capita income should be higher than the growth rate of the population.
Welfare: Economic development is regarded as a process whereby there, is an increase in the consumption of goods and services by individuals. From a welfare perspective, economic development is defined as a sustained improvement in health, literacy, and standard of living.
Social Indicators: Social indicators are normally referred to as the basic and collective needs of the people. The direct provision of basic needs such as health, education, food, water, sanitation, and housing facilities check social backwardness.
Question 2.
Explain the Human Resource of Economic Development?
Answer:
Human Resources:
- Human resource is named human capital because of its power to increase productivity and thereby national income.
- There is a circular relationship between human development and economic growth.
- A healthy, educated and skilled labour force is the most important productive asset.
- Human capital formation is the process of increasing knowledge, skills, and the productive capacity of people.
- It includes expenditure on health, education, and social services.
- If labor is efficient and skilled, its capacity to contribute to growth will be high. For example Japan and China.
Question 3.
Discuss the Economic planning of Democratic planning and Totalitarian planning?
Answer:
Democratic Vs Totalitarian:

- Democratic planning implies planning within a democracy.
- People are associated at every step in the formulation and implementation of the plan.
- A democratic plan is characterized by the widest possible consultations with the various state governments and private enterprises at the stage of preparation.
- The plan prepared by the Planning Commission is not accepted as such.
- It can be accepted, rejected or modified by the Parliament of the country.
- Under totalitarian planning, there is central control and direction of all economic activities in accordance with a single plan.
- Consumption, production, exchange, and distribution are all controlled by the state. In authoritarian planning, the planning authority is the supreme body.
- It decides about the targets, schemes, allocations, methods, and procedures of implementation of the plan.
Question 4.
Describe the functions of NITI Aayog.
Answer:
- Cooperative and competitive Federalism: To enable the states to have active participation in the formulation of national policy
- Shared National Agenda: To evolve a shared vision of national development priorities and strategies with the active involvement of states.
- Decentralized planning: To restructure the planning process into a bottom-up model.
- Vision and scenario planning: To design medium and long-term strategic frameworks towards India’s future.
- The network of Expertise: To mainstream external ideas and expertise into government policies and programmes through collective participation.
- Harmonization: To facilitate harmonization of actions across different layers of Government.
- Conflict Resolution: To provide a platform for mutual consensus to inter-sectoral, inter-departmental, inter-state as well as center-state issues for all speedy execution of the government programmes.
- Coordinating Interface with the world: It will act as a nodal point to harness global expertise and resources coming from the international organisation for India’s developmental process.
- Internal consultancy: It provides internal consultancy to central and state governments on policy and programmes
- Capacity Building: It enables to provide capacity building and technology up-gradation across government, benchmarking with latest global trends and providing managerial and technical know-how.
- Monitoring and Evaluation: It will monitor the implementation of policies and programmes and evaluate the impacts.
The main aim is to provide quality education for the students of Class 12th is very important for the students in their career. We hope the information provided in this Samacheer Kalvi Class 12th Economics Solutions Chapter 11 Economics of Development and Planning Questions and Answers is satisfactory for all. Bookmark our site to get the latest information about the solutions.