These Tamilnadu State Board Class 12th Economics Solutions Chapter 6 Banking Questions and Answers help to enhance the skills. Download Solutions of Samacheer Kalvi 12th Economics Book Solutions Chapter Wise Pdf for free of cost. Refer Samacheer Kalvi Class 12th Economics Solutions pdf and kickstart your preparation. You can find the best Solutions for Samacheer Kalvi Class 12th Economics Solutions Chapterwise here.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Economics Solutions Chapter 6 Banking
With the help of the Samacheer Kalvi Class 12th Economics Solutions Chapter 6 Banking you can get an idea about the subject. The topics covered in Samacheer Kalvi Class 12th Economics Solutions Chapter 6 Banking Solutions Questions and Answers. Tap the link and Download Samacheer Kalvi Class 12th Economics Solutions for Chapter 6 Banking to cover all the topics.
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Economics Banking Text Book Back Questions and Answers
Part – A
Multiple Choice Questions.
Question 1.
A Bank is a …………………………
(a) Financial institution
(b) Corporate
(c) An Industry
(d) Service institutions
Answer:
(a) Financial institution
Question 2.
A Commercial Bank is an institution that provides services …………………………
(a) Accepting deposits
(b) Providing loans
(c) Both a and b
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(c) Both a and b
Question 3.
The Functions of commercial banks are broadly classified into …………………………
(a) Primary Functions
(b) Secondary functions
(c) Other functions
(d) a, b, and c
Answer:
(d) a, b, and c
Question 4.
Bank credit refers to …………………………
(a) Bank Loans
(b) Advances
(c) Bank loans and advances
(d) Borrowings
Answer:
(c) Bank loans and advances
Question 5.
Credit creation means …………………………
(a) Multiplication of loans and advances
(b) Revenue
(c) Expenditure
(d) Debt
Answer:
(a) Multiplication of loans and advances
Question 6.
NBFI does not have …………………………
(a) Banking license
(b) Government approval
(c) Money ministry approval
Answer:
(a) Banking license
Question 7.
Central bank is …………………………….. authority of any country.
(a) Monetary
(b) Fiscal
(c) Wage
(d) National Income
Answer:
(a) Monetary
Question 8.
Who will act as the banker to the Government of India?
(a) SBI
(b) NABARD
(c) ICICI
(d) RBI
Answer:
(d) RBI
Question 9.
Lender of the last resort is one of the functions of …………………………
(a) Central Bank
(b) Commercial banks
(c) Land Development Banks
(d) Co – operative banks
Answer:
(a) Central Bank
Question 10.
Bank Rate means …………………………
(a) Re – discounting the first class securities
(b) Interest rate
(c) Exchange rate
(d) Growth rate
Answer:
(a) Re – discounting the first class securities
Question 11.
Repo Rate means …………………………
(a) Rate at which the Commercial Banks are willing to lend to RBI
(b) Rate at which the RBI is willing to lend to commercial banks
(c) Exchange rate of the foreign bank
(d) Growth rate of the economy
Answer:
(b) Rate at which the RBI is willing to lend to commercial banks
Question 12.
Moral suasion refers …………………………
(a) Optimization
(b) Maximization
(c) Persuasion
(d) Minimization
Answer:
(c) Persuasion
Question 13.
ARDC started functioning from …………………………
(a) June 3, 1963
(b) July 3, 1963
(c) June 1, 1963
(d) July 1, 1963
Answer:
(d) July 1, 1963
Question 14.
NABARD was set up in …………………………
(a) July 1962
(b) July 1972
(c) July 1982
(d) July 1992
Answer:
(c) July 1982
Question 15.
EXIM bank was established in …………………………
(a) June 1982
(b) April 1982
(c) May 1982
(d) March 1982
Answer:
(d) March 1982
Question 16.
The State Financial Corporation Act was passed by …………………………
(a) Government of India
(b) Government of Tamilnadu
(c) Government of Union Territories
(d) Local Government.
Answer:
(a) Government of India
Question 17.
Monetary policy is formulated by …………………………
(a) Co – operative banks
(b) Commercial banks
(c) Central Bank
(d) Foreign banks
Answer:
(c) Central Bank
Question 18.
Online Banking is also known as …………………………
(a) E – Banking
(b) Internet Banking
(c) RTGS
(d) NEFT
Answer:
(b) Internet Banking
Question 19.
Expansions of ATM.
(a) Automated Teller Machine
(b) Adjustment Teller Machine
(c) Automatic Teller mechanism
(d) Any Time Money
Answer:
(a) Automated Teller Machine
Question 20.
2016 Demonetization of currency includes denominations of …………………………
(a) ₹ 500 and ₹ 1000
(b) ₹ 1000 and ₹ 2000
(c) ₹ 200 and ₹ 500
(d) All the above
Answer:
(a) ₹ 500 and ₹ 1000
Part – B
Answer The Following Questions In One or Two Sentences.
Question 21.
Define Commercial banks?
Answer:
“Commercial Banks are the institutions that make short term loans to business and in the process create money” – Culbertson.
Question 22.
What is credit creation?
Answer:
- Credit Creation means the multiplication of loans and advances.
- Commercial banks receive deposits from the public and use these deposits to give loans.
- However, loans offered are many times more than the deposits received by banks.
- This function of banks is known as ‘Credit Creation’.
Question 23.
Define Central bank?
Answer:
- A central bank, reserve bank, or monetary authority is an institution that manages a state’s currency, money supply, and interest rates.
- Central banks also usually oversee the commercial banking system of their respective countries.
Question 24.
Distinguish between CRR and SLR?
Answer:
CRR:
- The Central Bank controls credit by changing the Cash Reserves Ratio.
- Commercial Banks have excessive cash reserves on the basis of which they are creating too much of credit, this will be harmful for the larger interest of the economy.
- So it will raise the cash reserve ratio which the Commercial Banks are required to maintain with the Central Bank.
SLR:
- Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR) is the amount which a bank has to maintain in the form of cash, gold or approved securities.
- The quantum is specified as some percentage of the total demand and time liabilities.
- The liabilities of the bank which are payable on demand anytime, and those liabilities which are accruing in one month’s time due to maturity.
Question 25.
Write the meaning of Open market operations?
Answer:
The sale and purchase of Government securities and other proper eligible securities like bills and securities of private concerns in the money market are called open market operations.
Question 26.
What is rationing of credit?
Answer:
- This is the oldest method of credit control. Rationing of credit as an instrument of credit control was first used by the Bank of England by the end of the 18th Century.
- It aims to control and regulate the purposes for which credit is granted by commercial banks.
- It is generally of two types.
Question 27.
Mention the functions of the agriculture credit department?
Answer:
- To maintain an expert staff to study all questions on agricultural credit.
- To finance the rural sector through eligible institutions engaged in the business of agricultural credit and to coordinate their activities.
Part – C
Answer The Following Questions In One Paragraph.
Question 28.
Write the mechanism of credit creation by commercial banks?
Answer:
Mechanism / Technique of Credit Creation by Commercial Banks:
- Bank credit refers to bank loans and advances.
- Money is said to be created when the banks, through their lending activities, make a net addition to the total supply of money in the economy.
- Money is said to be destroyed when the loans are repaid by the borrowers to the banks and consequently the credit already created by the banks is wiped out in the process.
- Banks have the power to expand or contract demand deposits and they exercise this power through granting more or less loans and advances and acquiring other assets.
- This power of commercial bank to create deposits through expanding their loans and advances is known as credit creation.
Question 29.
Give a brief note on NBFI?
Answer:
- A non-banking financial institution is a financial institution that does not have a full banking license or is not supervised by the central bank.
- The NBFTs do not carry on pure banking business, they are institutions that undertake borrowing and lending. They operate in both the money and the capital markets.
- NBFIs are classified into 1) stock Exchange and 2) other Financial Institutions.
Question 30.
Bring out the methods of credit control?
Answer:
Methods of Credit Control:
I. Quantitative or General Methods:
1. Bank Rate Policy:
The bank rate is the rate at which the Central Bank of a country is prepared to rediscount the first-class securities.
2. Open Market Operations:
- In a narrow sense, the Central Bank starts the purchase and sale of Government securities in the money market.
- In Broad Sense, the Central Bank purchases and sells not only Government securities but also other proper eligible securities like bills and securities of private concerns.
3. Variable Reserve Ratio:
(I) Cash Reserves Ratio:
- Under this system, the Central Bank controls credit by changing the Cash Reserves Ratio.
- For example, if the Commercial Banks have excessive cash reserves on the basis of which they are creating too much of credit,this will be harmful for the larger interest of the economy.
- So it will raise the cash reserve ratio which the Commercial Banks are required to maintain with the Central Bank.
(II) Statutory Liquidity Ratio:
- Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR) is the amount which a bank has to maintain securities.
- The quantum is specified as some percentage of the total demand and time liabilities (i.ethe liabilities of the bank which are payable on demand anytime, and those liabilities which are accruing in one month’s time due to maturity) of a bank.
Question 31.
What are the functions of NABARD?
Answer:
- NABARD acts as a refinancing institution for all kinds of production and investment credit to various industries with a view to promoting integrated rural development.
- It provides short, medium and long term Credits to state Co-operative Banks, RRBS, LDBS and other financial institutions approved by RBI.
- NABARD gives long-term loans to state Governments to enable them to subscribe to the share capital of co-operative credit societies.
- NABARD gives long – term loans to any institution approved by the central Government or contribute to the share capital or invests in securities of any institution concerned with agriculture and rural development.
Question 32.
Specify the functions of IFCI?
Answer:
- Long – term loans; both in rupees and foreign currencies.
- Underwriting of equity, preference and debenture issues.
- Subscribing to equity, preference and debenture issues.
- Guaranteeing the deferred payments in respect of machinery imported from abroad or purchased in India; and
- Guaranteeing of loans raised in foreign currency from foreign financial institutions.
Question 33.
Distinguish between money market and capital market?
Answer:
Money Market:
- Money market is the mechanism through which short term funds are loaned and. borrowed. It designates financial institutions which handle the purchase, sale and transfer of short term credit instruments.
- Commercial banks, acceptance houses, Non Banking Financial Institutions and the Central Bank are the institutions catering to the requirements of short term funds in the money Market.
Capital Market:
- Capital Market is a part of the financial system which is concerned with raising capital by dealing in shares, bonds, and other long term investments.
- The market where investment instruments like bonds, equities, and mortgages are traded is known as the capital market.
Question 33.
Mention the objectives of demonetizations?
Answer:
The objectives of Demonetization are:
- Removing Black money from the country
- Stopping of corruption
- Stopping Terror Funds
- Curbing Fake notes.
Part – D
Answer The Following Questions In About A Page.
Question 34.
Explain the role of Commercial Banks in economic development?
Answer:
1) Capital Formation:
Banks mobilize the small savings of the people scattered over a wide area and make it available for productive purposes.
2) Creation of credit:
Banks create credit for the purpose of providing more funds for development projects, credit creation brings about faster economic development.
3) Channelizing the Funds towards productive Investment:
Bank invest the savings mobilized by them for productive purposes, pooled savings should be allocated to various sectors of the economy with a view to increase the productivity.
4) Encouraging Right type of Industries :
Many banks help in the development of the right type of industries by extending loan to right type of persons. They grant loans and advances to manufacturers whose product are in great demand.
5) Banks monetize Debt:
Commercial banks transform the loan to be repaid after a certain period into cash, which can be immediately used for business activities, Banks lend money by discounting bills of exchange, business concerns are able to carry¬out the economic activities without any interruption
6) Finance to Government:
Banks provide long – term credit to Government by investing their funds in Government securities and short – term finance by purchasing Treasury Bills.
7) Employment Generation:
After the nationalization. Bank’s branches are opened frequently, which leads to the creation of new employment opportunities.
8) Banks promote Entrepreneurship :
Banks provide 100% credit for worth while projects, which is also technically feasible and economically viable, there by developing entrepreneurship.
Question 36.
Elucidate the functions of Commercial Banks?
Answer:
The functions of commercial banks are broadly classified into primary functions and secondary functions.
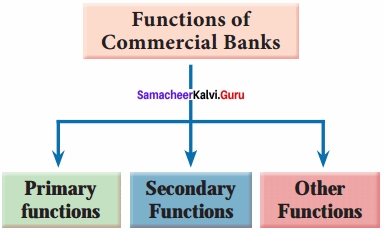
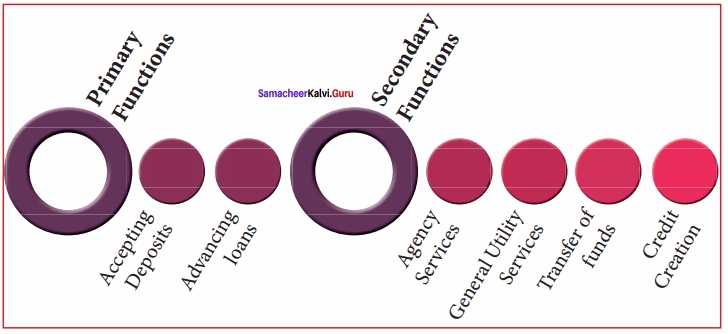
Functions of Commercial Banks
(a) Primary Functions:
1. Accepting Deposits:
It implies that commercial banks are mainly dependent on public deposits.
There are two types of deposits
(I) Demand Deposits:
It refers to deposits that can be withdrawn by individuals without any prior notice to the bank. In other words, the owners of these deposits are allowed to withdraw money anytime by writing a withdrawal slip or a cheque at the bank counter or from ATM centres using debit card.
(II) Time Deposits:
It refers to deposits that are made for certain committed period of time. Banks pay higher interest on time deposits. These deposits can be withdrawn only after a specific time period by providing a written notice to the?bank.
2. Advancing Loans:
(a) It refers to granting loans to individuals and businesses. Commercial banks grant loans in the form of overdraft, cash credit, and discounting bills of exchange.
(b) Secondary Functions:
The secondary functions can be classified under three heads, namely, agency functions, general utility functions, and other functions.
1. Agency Functions:
It implies that commercial banks act as agents of customers by performing various functions.
(I) Collecting Cheques:
Banks collect cheques and bills of exchange on the behalf of their customers through clearing house facilities provided by the central bank.
(II) Collecting Income:
Commercial banks collect dividends, pension, salaries, rents, and interests on investments on behalf of their customers. A credit voucher is sent to customers for information when any income is collected by the bank.
(III) Paying Expenses:
Commercial banks make the payments of various obligations of customers, such as telephone bills, insurance premium, school fees, and rents.
2. General Utility Functions:
It implies that commercial banks provide some utility services to customers by performing various functions.
(I) Providing Locker Facilities:
Commercial banks provide locker facilities to its customers for safe custody of jewellery, shares, debentures, and other valuable items. This minimizes the risk of loss due to theft at homes. Banks are not responsible for the items in the lockers.
(II) Issuing Traveler’s Cheques:
Banks issue traveler’s cheques to individuals for traveling outside the country. Traveler’s cheques are the safe and easy way to protect money while traveling.
(III) Dealing in Foreign Exchange:
Commercial banks help in providing foreign exchange to businessmen dealing in exports and imports. However, commercial banks need to take the permission of the Central Bank for dealing in foreign exchange.
3. Transferring Funds:
It refers to transferring of funds from one bank to another. Funds are transferred by means of draft, telephonic transfer, and electronic transfer.
4. Letter of Credit:
Commercial banks issue letters of credit to their customers to certify their creditworthiness.
(I) Underwriting Securities:
Commercial banks also undertake the task of underwriting securities. As public has full faith in the credit worthiness of banks, public do not hesitate in buying the securities underwritten by banks.
(II) Electronic Banking:
It includes services, such as debit cards, credit cards, and Internet banking.
(c) Other Functions:
(I) Money Supply:
It refers to one of the important functions of commercial banks that help in increasing money supply.
(II) Credit Creation:
Credit Creation means the multiplication of loans and advances. Commercial banks receive deposits from the public and use these deposits to give loans.
Question 37.
Describe the functions of the Reserve Bank of India?
Answer:
- Monetary Authority : It controls the supply of money in the economy to stabilize exchange rate, maintain healthy balance of payment, attain financial stability, control inflation, strengthen banking system.
- The issuer of currency : The objective is to maintain the currency and credit system of the country. It is the sole authority to issue currency.
- The issuer of Banking license : As per sec 22 of Banking Regulation Act, every bank has to obtain a banking license from RBI to conduct banking business in India.
- Banker to the Government: It acts as banker both to the central and the state government.
- Banker’s Bank : It provides loan to banks, accept the deposit of banks, and re-discount the bills of banks.
- Lender of Last resort: The banks can borrow from the RBI by keeping eligible securities as collateral at the time of need or crisis, when there is no other source.
- Act as clearing house For settlement of banking transactions, RBI manages 14 clearing houses. It facilitates the exchange of instruments and processing of payment instructions. .
- Custodian of foreign exchange reserves : It acts as a custodian of FOREX. It administers and enforces the provision of FEMA, 1999. RBI buys and sells foreign currency to maintain the exchange rate of Indian rupee v/s foreign currencies.
- Regulator of Economy : It controls the money supply in the system, monitors different key indicators like GDP, Inflation etc.,
- Managing Government securities: RBI administers investment in institutions when they invest specified minimum proportions of their total assets/ liabilities in government securities.
- Banking ombudsman scheme : RBI introduced the Banking ombudsman scheme in 1995. Under this scheme, the complainants can file their complaints in any form, including online and can also appeal to the ombudsman against the awards and the other decisions of the Bank.
Question 38.
What are the objectives of Monetary Policy? Explain?
The specific objectives of monetary policy are Objectives of monetary policy:
- Neutrality of Money
- Stability of Exchange Rates
- Price Stability
- Full Employment
- Economic Growth
- Equilibrium in the Balance of Payments
1. Neutrality of Money:
- Economists like Wicksteed, Hayek and Robertson are the chief exponents of neutral money.
- They hold the view that monetary authority should aim at neutrality of money in the economy.
- Monetary changes could be the root cause of all economic fluctuations.
- According to neutralists, the monetary change causes distortion and disturbances in the proper operation of the economic system of the country.
2. Exchange Rate Stability:
- Exchange rate stability was the traditional objective of monetary authority.
- This was the main objective under Gold Standard among different countries.
- When there was disequilibrium in the balance of payments of the country, it was automatically corrected by movements.
3. Price Stability:
- Economists like Crustave Cassel and Keynes suggested price stabilization as a main objective of monetary policy.
- Price stability is considered the most genuine objective of monetary policy.
- Stable prices repose public confidence.
- It promotes business activity and ensures equitable distribution of income and wealth.
4. Full Employment:
- During world depression, the problem of unemployment had increased rapidly.
- It was regarded as socially dangerous, economically wasteful and morally deplorable.
- Thus, full employment was considered as the main goal of monetary policy.
5. Economic Growth:
- Economic growth is the process whereby the real per capita income of a country increases over a long period of time.
- It implies an increase in the total physical or real output, production of goods for the satisfaction of human wants.
- Monetary policy should promote sustained and continuous economic growth by maintaining equilibrium between the total demand for money and total production capacity and further creating favourable conditions for saving and investment.
6. Equilibrium in the Balance of Payments: Equilibrium in the balance of payments is another objective of monetary policy which emerged significant in the post war years.
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Economics Banking Additional Questions and Answers
Part – A
I. Multiple Choice Questions.
Question 1.
“Commercial Banks are the institutions that make short term loans to business and in the process create money” said by …………….
a) Culbertson
b) Milton Fried man
c) Marshall
d) Keynes
Answer:
a) Culbertson
Question 2.
Overdraft is a facility offered by commercial banks to …………………………
(a) Exporters
(b) Importers
(c) Farmers
(d) Businessmen
Answer:
(d) Businessmen
Question 3.
Current account deposites are operated by …………………………
(a) Agriculturists
(b) Business men
(c) Goverment servants
(d) Labourers
Answer:
(b) Business men
Question 4.
Bank makes loans and advances to its customers out of …………………………………….. deposits.
a) Demand Deposits
b) Time Deposits
c) Recurring Deposits
d) Primary Deposits.
Answer:
d) Primary Deposits
Question 5.
The first bank in India was established in …………………………
(a) 1670
(b) 1770
(c) 1870
(d) 1872
Answer:
(b) 1770
Question 6.
The RBI was nationalized on …………
a) January 1,1949
b) April 1,1935
c) April 1,1934
d) January 1,1937
Answer:
a) January 1,1949
Question 7.
The amount of cash kept by commercial banks to meet the day to day transactions is known as …………………………
(a) Bank cash
(b) Commercial bank cash
(c) Reserve cash
(d) Cheque
Answer:
(c) Reserve cash
Question 8.
In India, Central bank is known as –
(a) SBI
(b) RBI
(c) Commercial bank
(d) IDBI
Answer:
(b) RBI
Question 9.
The rate at which the RBI is willing to lend to commercial banks is called ……………….
a) Reserve Repo Rate
b) Repo Rate
c) Cash Reserve Ratio
d) Bank Rate
Answer:
b) Repo Rate
Question 10.
………………………… Bank Finance the Import and Export trade.
(a) Industrial Bank
(b) Exim Bank
(c) Co-operative Bank
(d) RBI
Answer:
(b) Exim Bank
Question 11.
Commercial Banks create credit in favour of the …………………………
(a) Consumers
(b) Businessmen
(c) Customers
(d) Agriculturists
Answer:
(c) Customers
Question 12.
………………………… is a non-profit making financial institution of the country.
(a) Central Bank
(b) Commercial Bank
(c) Co-operative Bank
(d) Industrial Bank
Answer:
(a) Central Bank
Question 13.
Extending banking facilities to the rural and semi-urban areas is the promotional activity of the …………………………
(a) Co-operative Bank
(b) Commercial Bank
(c) RBI
(d) State Bank
Answer:
(a) Co-operative Bank
Question 14.
The book General Theory of Employment, Interest and Money ” was written by ……………..
a) Milton Fried man
b) Culbertson
c) Keynes
d) Marshall
Answer:
c) Keynes
Question 15.
Withdraw money more than deposit is called …………………………
(a) Cash credit
(b) Discounting bill
(c) Current account
(d) Over draft
Answer:
(d) Over draft
Question 16.
………………………… help in proper allocation of funds among different regions of the economy.
(a) Central banks
(b) Co-operative banks
(c) Commercial banks
(d) Agriculture banks
Answer:
(c) Commercial banks
Question 17.
Lowering the Bank rate offsets ……………………….. tendencies.
(a) Deflationary
(b) Inflationary
(c) Stagflationary
(d) Hyper inflationary
Answer:
(a) Deflationary
Question 18.
The main aim of the Central bank is …………………………
(a) Full employment
(b) Economic stability
(c) Balance of payment
(d) International capital movement
Answer:
(b) Economic stability
Question 19.
………………………… Bank regulates the credit and currency according to the economic situation of the country.
(a) State
(b) Commercial
(c) RBI
(d) Agriculture
Answer:
(b) Economic stability
Question 20.
………………………… credit control method mean the Regulation and control of the supply of the credit among its possible users.
(a) Quantitative
(b) Qualitative
(c) General
(d) Possible
Answer:
(b) Qualitative
Question 21.
The issue of paper money is the most important function of a …………………………
(a) Commercial Bank
(b) Central Bank
(c) ICICI Bank
(d) State Bank
Answer:
(b) Central Bank
Question 22.
………………………… stimulate saving and investment.
(a) Credit
(b) Bank
(c) Debit
(d) Cheque
Answer:
(b) Bank
Question 23.
The commercial banks only deal in foreign exchange under the directions of the …………………………
(a) State bank
(b) Central bank
(c) Commercial bank
(d) Co – operative bank
Answer:
(b) Central bank
Question 24.
Fixed Deposits are otherwise known as …………………………
(a) Bank Deposits
(b) Customer’s Deposits
(c) Time Deposits
(d) Money Deposits
Answer:
(c) Time Deposits
Question 25.
The rate of interest of every Central bank is known as …………………………
(a) Interest rate
(b) Credit rate
(c) Debit rate
(d) Bank rate
Answer:
(d) Bank rate
II. Match the following and choose the correct answer by using codes given below.
Question 1.
A. Saving Deposits – (i) Official minimum rate
B. Cash credit – (ii) Cheque facilities
C. Bank rate – (iii) Facility to businessman
D. Overdraft – (iv) Collateral security
Codes:
(a) A (ii) B (iv) C (i) D (iii)
(b) A (i) B (ii) C (iii) D (iv)
(c) A (iii) B (i) C (iv) D (ii)
(d) A (iv) B (iii) C (ii) D (i)
Answer:
(a) A (ii) B (iv) C (i) D (iii)
Question 2.
A. Transfer of funds – (i) Buying and selling
B. Commercial bank – (ii) Clearing
C. Open market operation – (iii) Interest not given
D. Demand deposits – (iv) Profit making
Codes:
(a) A (ii) B (iv) C (i) D (iii)
(b) A (i) B (iii) C (ii) D (iv)
(c) A (iii) B (ii) C (iv) D (i)
(d) A (iv) B (i) C (iii) D (ii)
Answer:
(a) A (ii) B (iv) C (i) D (iii)
Question 3.
A. NBFI – (i) Monetary policy
B. Per Capita Income – (ii) Minimum amount of fund
C. Inflation – (iii) Economic growth
D. RTGS – (iv) Non – bank Financial Institution
Codes:
(a) A (iii) B (ii) C (iv) D (i)
(b) A (iv) B (iii) C (i) D (ii)
(c) A (ii) B (i) C (iii) D (iv)
(d) A (i) B (iv) C (ii) D (iii)
Answer:
(b) A (iv) B (iii) C (i) D (ii)
Question 4.
A. UTI – (i) Quantitative credit control
B. Open market operation – (ii) Mutual fund
C. Bank – (iii) Automatic Teller mechine
D. ATM – (iv) Financial Institution
Codes:
(a) A (i) B (ii) C (iii) D (iv)
(b) A (iii) B (iv) C (ii) D (i)
(c) A (iv) B (iii) C (i) D (ii)
(d) A (ii) B (i) C (iv) D (iii)
Answer:
(d) A (ii) B (i) C (iv) D (iii)
Question 5.
A. NABARD – (i) Internet banking
B. SFC – (ii) Short term seasonal credit
C. Rationing of credit – (iii) State level institution
D. Online banking – (iv) Qualitative credit control of RBI
Codes:
(a) A (i) B (ii) C (iii) D (iv)
(b) A (iii) B (iv) C (i) D (ii)
(c) A (ii) B (iii) C (iv) D (i)
(d) A (iv) B (i) C (ii) D (iii)
Answer:
(c) A (ii) B (iii) C (iv) D (i)
III. State whether the statements are true or false.
Question 1.
(i) Businessmen operate the current account deposits.
(ii) State Bank organization established EXIM Bank
(a) Both (i) and (ii) are true
(b) Both (i) and (ii) are false
(c) (i) is true but (ii) is false
(d) (i) is false but (ii) is true
Answer:
(c) (i) is true but (ii) is false
Question 2.
(i) The Central bank of a country acts as the banker, fiscal agent, and advisor to the government.
(ii) The banks expand their loans resulting in the expansion of investment employment production and prices.
(a) Both (i) and (ii) are true
(b) Both (i) and (ii) are false
(c) (i) is true but (ii) is false
(d) (i) is false but (ii) is true
Answer:
(a) Both (i) and (ii) are true
Question 3.
(i) NABARD provides agriculture finance to medium and long term basis.
(ii) Bank observed that credit is the lubricant of all commerce and trade.
(a) Both (i) and (ii) are true
(b) Both (i) and (ii) are false
(c) (i) is true but (ii) is false
(d) (i) is false but (ii) is true
Answer:
(a) Both (i) and (ii) are true
Question 4.
(i) State Bank is the financial advisor to the government.
(ii) Central Bank possesses the monopoly of note issue.
(a) Both (i) and (ii) are true
(b) Both (i) and (ii) are false
(c) (i) is true but (ii) is false
(d) (i) is false but (ii) is true
Answer:
(d) (i) is false but (ii) is true
Question 5.
(i) For maintaining saving deposits, cheque facilities can be enjoyed.
(ii) Fixed Deposits are otherwise known as time deposits.
(a) Both (i) and (ii) are true
(b) Both (i) and (ii) are false
(c) (i) is true but (ii) is false
(d) (i) is false but (ii) is true
Answer:
(a) Both (i) and (ii) are true
IV. Which of the following is correctly matched.
Question 1.
(a) EXIM Bank – Export and Import
(b) NABARD – Industrial finance
(c) Bank – Excess money
(d) Fixed Deposits – Bank saving
Answer:
(a) EXIM Bank – Export and Import
Question 2.
(a) CRR – Current Reserve Ratio
(b) Saving deposits – Cheque facilities
(c) Bank rate policy – High interest
(d) Adviser to the government – SBI
Answer:
(b) Saving deposits – Cheque facilities
Question 3.
(a) ICICI Bank – Three-tier Export Bank
(b) NABARD – Agriculture Finance
(c) IDBI – Co-operative Bank
(d) IFCI – State Bank
Answer:
(b) NABARD – Agriculture Finance
Question 4.
(a) South African Reserve Bank – 1921
(b) The Central bank of China – 1934
(c) The Reserve Bank of Newzealand – 1928
(d) The Reserve Bank of India – 1935
Answer:
(d) The Reserve Bank of India – 1935
Question 5.
(a) Forex cards – Smart card
(b) Paper currency – Legal tender
(c) Medium of Exchange – Functions of money
(d) CRR – Credit Reserve Ratio
Answer:
(c) Medium of Exchange – Functions of money
V. Which of the following is not correctly matched.
Question 1.
(a) RBI – Reserve Bank of India
(b) SBI – State Bank of India
(c) IMF – International Monetary Fund
(d) ATM – Any Time Money
Answer:
(d) ATM – Any Time Money
Question 2.
(a) Qualitative credit-control of RBI – Rationing of credit
(b) Agricultural credit department – To finance the rural sector
(c) NABARD – Short term seasonal credit
(d) UTI – Mutual fund
Answer:
(d) UTI – Mutual fund
Question 3.
(a) RBI – Central Bank of SBI
(b) ARDC – The agricultural refinance development corporation
(c) Bank Credit – Bank loans and advances
(d) Moral suasion – Persuasion
Answer:
(a) RBI – Central Bank of SBI
Question 4.
(a) Traveler’s cheques – Group of people
(b) Credit creation – Multiplication of loans and advances
(c) Primary deposits – Passive deposits
(d) Bank – Financial Institution
Answer:
(a) Traveler’s cheques – Group of people
Question 5.
(a) RBI – Monetary authority
(b) Bank rate – Re – discounting
(c) Recession – Monetary policy
(d) Keynes – Economic growth
Answer:
(d) Keynes – Economic growth
Question 6.
(a) RTGS – Real Time Gross Settlement
(b) NEFT – National Electronic Fund Transfer
(c) ATM – Any Time Money
(d) SIDCO – Small Industrial Development Corporation
Answer:
(c) ATM – Any Time Money
VI. Pick the odd one out.
Question 1.
1. Commercial Bank Secondary Functions
(a) Agency functions
(b) General utility services
(c) Transfer of bank
(d) Credit creation
Answer:
(c) Transfer of bank
Question 2.
Functions of Central Bank
(a) Monetary Authority
(b) The issuer of currency
(c) Banker to the foreign level
(d) Banker’s Bank
Answer:
(c) Banker to the foreign level
Question 3.
The frequent methods of credit control under the Selective method are called ……………………..
(a) Rationing of credit
(b) Direct Action of Industries
(c) Method of publicity
(d) Moral persuasion
Answer:
(b) Direct Action of Industries
Question 4.
Functions of ICICI is called ……………………..
(a) Assistance to Industries
(b) Merchant banking
(c) Credit bank operation
(d) Project promotion
Answer:
(c) Credit bank operation
Question 5.
The main objectives of Demonetisation ……………………..
(a) Removing black money from the country
(b) Stopping of corruption
(c) Stopping Terror Funds
(d) Fake notes given
Answer:
(d) Fake notes given
VII. Assertion and Reason.
Question 1.
Assertion (A): Commercial banks provide some utility services to the customers.
Reason (R): Credit creation leads to increased production, employment, sales and prices.
(a) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true and ‘R’ is the correct explanation to ‘A’
(b) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true but ‘R’ is not the correct explanation for ‘A’
(c) ‘A’ is true but ‘R’ is false
(d) ‘A’ is false but ‘R’ is true
Answer:
(a) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true and ‘R’ is the correct explanation to ‘A’
Question 2.
Assertion (A): Bank rate means rediscounting the first-class securities.
Reason (R): Credit creation means not given loans and advances.
(a) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true and ‘R’ is the correct explanation to ‘A’
(b) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true but ‘R’ is not the correct explanation for ‘A’
(c) ‘A’ is true but ‘R’ is false
(d) ‘A’ is false but ‘R’ is true
Answer:
(c) ‘A’ is true but ‘R’ is false
Question 3.
Assertion (A): Bank is a service institution.
Reason (R): Commercial Bank is an institution that provides accepting deposits and providing loans to the public.
(a) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true and ‘R’ is the correct explanation to ‘A’
(b) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true but ‘R’ is not the correct explanation for ‘A’
(c) ‘A’ is true but ‘R’ is false
(d) ‘A’ is false but ‘R’ is true
Answer:
(d) ‘A’ is false but ‘R’ is true
Question 4.
Assertion (A): Credit creation leads to an increase in production.
Reason (R): Credit creation means the multiplication of loans and advances.
(a) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true and ‘R’ is the correct explanation to ‘A’
(b) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true but ‘R’ is not the correct explanation for ‘A’
(c) ‘A’ is true but ‘R’ is false
(d) ‘A’ is false but ‘R’ is true
Answer:
(a) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true and ‘R’ is the correct explanation to ‘A’
Question 5.
Assertion (A): The objectives of demonetization is called issuing currency notes.
Reason (R): Black money accepted.
(a) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true and ‘R’ is the correct explanation to ‘A’
(b) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true but ‘R’ is not the correct explanation to ‘A’
(c) ‘A’ is true but ‘R’ is false
(d) ‘A’ is false but ‘R’ is true
Answer:
(c) ‘A’ is true but ‘R’ is false
Question 6.
Assertion (A): Primary deposits are also called passive deposits.
Reason (R): Passive deposits are also called time deposits.
(a) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true and ‘R’ is the correct explanation to ‘A’
(b) Both ‘A’ and ‘R’ are true but ‘R’ is not the correct explanation for ‘A’
(c) ‘A’ is true but ‘R’ is false
(d) ‘A’ is false but ‘R’ is true
Answer:
(c) ‘A’ is true but ‘R’ is false
Part – B
Answer The Following Questions In One or Two Sentences.
Question 1.
What is the meaning of primary deposits and derived deposits?
Answer:
- The modem banks create deposits in two ways. They are primary deposits and derived deposits.
- When a customer gives cash to the bank and the bank creates a book debt in his name called a deposit, it is known as a “primary deposit”.
- But when such a deposit is created, without there being any prior payment of equivalent cash to the bank, it is called a ‘derived deposit’.
Question 2.
What are passive Deposits?
Answer:
- The bank makes loans and advances to its customer from its primary deposits.
- The initiative is taken by the customers themselves. In this case,/the role of the bank is passive.
- So these deposits are also called ” Passive Deposits”.
Question 3.
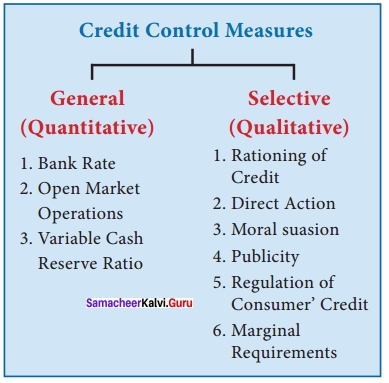
What are the credit control measures?
Answer:
Question 4.
Define RBI Rural credit?
Answer:
Reserve Bank of India and Rural Credit:
In a developing economy like India, the Central bank of the country cannot confine itself to the monetary regulation only, and it is expected that it should take part in development function in all sectors especially in agriculture and industry.
Question 5.
Write a note on Industrial Finance Corporation of India.
Answer:
IFCI is the first Financial Corporations to provide financial assistance for industrial development. This was established on July 1, 1948, under the Act of the parliament.
Question 6.
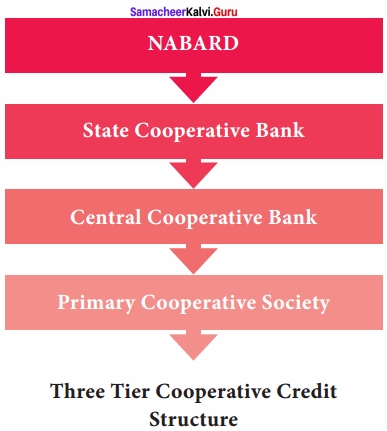
Define Three Tier cooperative credit structure?
Answer:
Part – C
Answer The Following Questions In One Paragraph.
Question 1.
Write a note on NABARD.
Answer:
- A National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD) was, therefore, set up in July 1982 by an act of parliament to take over the functions of ARDC and the refinancing functions of RBI in relation to co-operative banks and RRBs.
- NABARD performs all the functions performed by RBI with regard to agricultural credit.
- Deputy Governor of RBI is appointed as chairman of NABARD.
Question 2.
What are the ARDC – objectives?
Answer:
Objectives of the ARDC:
- To provide necessary funds by way of refinancing to eligible institutions such as the Central Land Development Banks, State Co-operative Banks, and Scheduled banks.
- To subscribe to the debentures floated by the Central Land Development banks, State Co-operative Banks, and Scheduled banks, provided they were approved by the RBI.
Question 3.
Describe the functions of IDBI?
Answer:
Functions of IDBI:
- The functions of IDBI fall into two groups
- Assistance to other financial institutions
- Direct assistance to industrial concerns either on its own or in participation with other institutions.
- The IDBI can provide refinance in respect of term loans to industrial concerns given by the IFC, the SFCs, other financial institutions notified by the Government, scheduled banks and state cooperative banks.
- A special feature of the IDBI is the provision for the creation of a special fund known as the Development Assistance Fund.
- The fund is intended to provide assistance to industries which require heavy investments with a low anticipated rate of return.
- Such industries may not be able to get assistance in the normal course.
- The financing of exports was also undertaken by the IDBI till the establishment of EXIM BANK in March 1982.
Question 4.
Difference between NEFT and RTGS?
Answer:
NEFT:
- National Electronic Fund Transfer
- Transactions happen in batches hence slow
- Timings: 8:00 am to 6:30 pm (12:30 pm on Saturday)
- No minimum limit
RTGS:
- Real-Time Gross Settlement
- Transactions happen in real-time hence fast
- Timings: 9:00 am to 4:30 pm (1:30 pm on Saturday)
- The minimum amount for RTGS transfer is ₹ 2 lakhs
Question 5.
Explain Expansionary vs Contractionary Monetary policy.
Answer:
- Expansionary policy is a cheap money policy when a monetary authority uses its tools to stimulate the economy.
- An Expansionary policy maintains short-term interest rates at a lower than usual rate or increases the total supply of money in the economy more rapidly than usual.
- The contractionary monetary policy is dear money policy, which maintains short-term interest rates higher than usual or slows the rate of growth in the money supply or even shrinks it.
Part – D
Answer The Following Questions In One Page.
Question 1.
Describe the frequent methods of selective method credit control?
Answer:
Qualitative or Selective Method of Credit Control:
- The qualitative or the selective methods are directed towards the diversion of credit into particular uses or channels in the economy.
- Their objective is mainly to control and regulate the flow of credit into particular industries or businesses.
- The following are the frequent methods of credit control under selective method:
- Rationing of Credit:
- Direct Action
- Moral Persuasion
- Method of Publicity
- Regulation of Consumer’s Credit
- Regulating the Marginal Requirements on Security Loans
- Rationing of Credit:
1. Rationing of Credit:
- This is the oldest method of credit control.
- Rationing of credit as an instrument of credit control was first used by the Bank of England by the end of the 18th Century.
- It aims to control and regulate the purposes for which credit is granted by commercial banks. It is generally of two types.
(I) The variable portfolio ceiling:
It refers to the system by which the central bank fixes ceiling or maximum amount of loans and advances for every commercial bank.
(II) The variable capital asset ratio:
It refers to the system by which the central bank fixes the ratio which the capital of the commercial bank should have to the total assets of the bank.
2. Direct Action:
Direct action against the erring banks can take the following forms.
- The central bank may refuse to altogether grant discounting facilities to such banks.
- The central bank may refuse to sanction further financial accommodation to a bank whose existing borrowing are found to be in excess of its capital and reserves.
- The central bank may start charging penal rate of interest on money borrowed by a bank beyond the prescribed limit.
3. Moral Suasion:
- This method is frequently adopted by the Central Bank to exercise control over the Commercial Banks.
- Under this method Central Bank gives advice, then requests and persuades the Commercial Banks to co-operate with the Central Bank in implementing its credit policies.
4. Publicity:
- Central Bank in order to make their policies successful, take the course of the medium of publicity.
- A policy can be effectively successful only when an effective public opinion is created in its favour.
5. Regulation of Consumer’s Credit:
- The down payment is raised and the number of installments reduced for the credit sale
6. Changes in the Marginal Requirements on Security Loans:
- This system is mostly followed in U.S.A.
- Under this system, the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System has been given the power to prescribe margin requirements for the purpose of preventing excessive use of credit for stock exchange speculation.
Question 2.
Describe the Merger of Banks?
Answer:
The merger of Banks:
- Union Cabinet decided to merge all the remaining five associate banks of State Bank Group with State Bank of India in 2017.
- After Parliament passed the merger Bill, the subsidiary banks have ceased to exist.
- Five associates and the Bharatiya Mahila Bank have become part of the State Bank of India (SBI) beginning April 1, 2017.
- This has placed the State Bank of India among the top 50 banks in the world.
- The five associate banks that were merged are State Bank of Bikaner and Jaipur (SBBJ), State Bank of Hyderabad (SBH), State Bank of Mysore (SBM), State Bank of Patiala (SBP), and State Bank of Travancore (SBT).
- The other two Associate Banks namely State Bank of Indore and State Bank of Saurashtra had already been merged with State Bank of India.
- After the merger, the total customer base of SBI increased to 37 crores with a branch network of around 24,000 and around 60,000 ATMs across the country.
Question 3.
Briefly describe the ATM?
Answer:
ATM (Automated Teller Machine):
- ATMs transformed the bank tech system when they were first introduced in 1967.
- The next revolution in ATMs is likely to involve contactless payments.
- Much like Apple Pay or Google Wallet, soon we will be able to conduct contactless ATM transactions using a smartphone.
- Some ATM innovations are already available overseas.
- For example, biometric authentication is already used in India, and its recognition is in place at Qatar National Bank ATMs.
- These technologies can help overall bank security by protecting against ATM hacks.
Question 4.
Explain the State Industrial Development Corporations?
Answer:
State Industrial Development Corporations (SIDCOs):
- The Industrial Development Corporations have been set up by the state governments and they are wholly owned by them.
- These institutions are not merely financing agencies; they are entrusted with the responsibility of accelerating the industrialization of their states.
SIDCO (Small Industrial Development Corporation):
- SIDCOs provide financial assistance to industrial concerns by way of loans guarantees and underwriting of or direct subscriptions to shares and debentures.
- In addition to these, they undertake various promotional activities, such as conducting techno-economic surveys, project identification, preparation of feasibility studies, and selection and training of entrepreneurs.
- They also promote joint sector projects in association with the private promoters in such types of projects.
- SIDCOs take 26 percent, private co-promoter takes 25 percent of the equity, and the rest is offered to the investing public.
- SIDCOs undertake the development of industrial areas by providing all infrastructural facilities and initiation of new growth centers.
- They also administer various State government incentive schemes.
- SIDCOs get refinance facilities from IDBI.
- They also borrow through bonds and accept deposits.
The main aim is to provide quality education for the students of Class 12th is very important for the students in their career. We hope the information provided in this Samacheer Kalvi Class 12th Economics Solutions Chapter 6 Banking Questions and Answers is satisfactory for all. Bookmark our site to get the latest information about the solutions.