Students who wish to prepare the Samacheer Kalvi Class 12th Physics Solutions Subject Chapter 8 Atomic and Nuclear Physics can rely on the Tamilnadu State Board Solutions for Class 12th Physics Solutions Chapter 8 Atomic and Nuclear Physics Questions and Answers prevailing. Become perfect with the concepts of Samacheer Kalvi Class 12th Physics Solutions Chapter 8 Atomic and Nuclear Physics Questions and Answers and score better grades in your exams. Detailed Solutions are provided to the concepts by experts keeping in mind the latest edition textbooks and syllabus.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Physics Solutions Chapter 8 Atomic and Nuclear Physics
Ace up your preparation by referring to the Samacheer Kalvi Class 12th Physics Solutions Chapter 8 Atomic and Nuclear Physics and learn all the topics within. Click on the topic you want to prepare from the Class 12th Chapter 8 Atomic and Nuclear Physics Questions and Answers and prepare it easily. You can understand your strengths and weaknesses by practicing the Questions in Samacheer Kalvi Class 12th Physics Solutions PDF.
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Physics Atomic and Nuclear Physics Textual Evaluation Solved
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Physics Atomic and Nuclear Physics Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Suppose an alpha particle accelerated by a potential of V volt is allowed to collide with a nucleus whose atomic number is Z, then the distance of closest approach of alpha particle to the nucleus is
(a) 14.4\(\frac { Z }{ V }\) Å
(b) 14.4\(\frac { V }{ Z }\) Å
(c) 1.44\(\frac { Z }{ V }\) Å
(d) 14.4\(\frac { V }{ Z }\) Å
Answer:
(c) 1.44\(\frac { Z }{ V }\) Å
Question 2.
In a hydrogen atom, the electron revolving in the fourth orbit, has angular momentum equal to
(a) h
(b) \(\frac { h }{ π }\)
(c) \(\frac { 4h }{ π }\)
(d) \(\frac { 2h }{ π }\)
Answer:
(d) \(\frac { 2h }{ π }\)
Hint:
Angular momentum of an electron is an integral multiple of \(\frac { h }{ 2π }\)
According to Bohr atom model,
Angular momentum of an electron mvr = \(\frac { nh }{ 2π }\)
n = 4th orbit = \(\frac { 4h }{ 2π }\)
mvr = \(\frac { 2h }{ π }\)
Question 3.
Atomic number of H-like atom with ionization potential 122.4 V for n = 1 is
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer:
(c) 3
Hint:
The ionisation energy of a hydrogen atom is, IE = \(\frac {{ 13.6z }^{2}}{{ n }^{2}}\)
∴ z2 = \(\frac{I E \times n^{2}}{13.6}\) = \(\frac{122.4 \times(1)^{2}}{13.6}\) = 9
Question 4.
The ratio between the first three orbits of hydrogen atom is
(a) 1 : 2 : 3
(b) 2 : 4 : 6
(c) 1 : 4 : 9
(d) 1 : 3 : 5
Answer:
(c) 1 : 4 : 9
Hint:
En = \(\frac {{ -13.6×z }^{2}}{{ n }^{2}}\) eV / atom
n = 1; E1 = 13.6 eV / atom
n = 2; E2 = 3.4 eV / atom
n = 3; E3 = 151 eV / atom
The ratio of theree orbits
E1 : E2 : E3 = 13.6 : 3.4 : 1.51
= 1 : 4 : 9
Question 5.
The charge of cathode rays is
(a) positive
(b) negative
(c) neutral
(d) not defined
Answer:
(b) negative
Question 6.
In J.J. Thomson e/m experiment, a beam of the electron is replaced by that of muons (a particle with the same charge as that of electrons but mass 208 times that of electrons). No deflection condition is achieved only if
a) B is increased by 208 times
b) B is decreased by 208 times
c) B is increased by 14.4 times
d) B is decreased by 14.4 times
Answer:
c) B is increased by 14.4 times
Solution:
\(\frac{\mathrm{e}}{\mathrm{m}}\) = \(\frac{\mathrm{E}^{2}}{2 \mathrm{VB}^{2}}\)
In the condition of no deflection. If m is increased by 208 times then B should be increased \(\sqrt{208}\) = 14.4 times
Question 7.
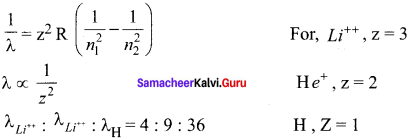
The ratio of the wavelengths for the transition from n =2 to n = 1 in Li++, He+ and H is
(a) 1 : 2 : 3
(b) 1 : 4 : 9
(c) 3 : 2 : 1
(d) 4 : 9 : 36
Answer:
(d) 4 : 9 : 36
Hint:
According to Rydberg formula, the wavelength
Question 8.
The electric potential between a proton and an electron is given by V = V0 In \(\left( \frac { r }{ { r }_{ 0 } } \right) \),
where r0 is a constant. Assume that Bohr atom model is applicable to potential, then variation of radius of nth orbit rn with the principal quantum number n is
(a) rn ∝\(\frac { 1 }{ n }\)
(b) rn ∝ n
(c) rn ∝ \(\frac { 1 }{{ n }^{2}}\)
(d) rn ∝ n2
Answer:
(b) rn ∝ n
Hint:
Electric potential between proton and electron in nth orbit is given as,
V = V0 In \(\left( \frac { { r }_{ n } }{ { r }_{ 0 } } \right) \)
Thus the coulomb force |Fc| = e \(\left( \frac { { dv } }{ dr } \right) \) = e \(\left( \frac { { V }_{ 0 } }{ { r }_{ n } } \right) \)
This coulomb force is balance by the centripetal force
\(\frac {{ mv }^{2}}{{r}_{n}}\) = e \(\left( \frac { { V }_{ 0 } }{ { r }_{ n } } \right) \left( \frac { { dv } }{ dr } \right) \) ⇒ V = \(\sqrt { \frac { e{ V }_{ 0 } }{ m } } \)
Now from
mvrn = \(\frac { nh }{2π}\)
rn ∝ n
Question 9.
If the nuclear radius of 27Al is 3.6 fermi, the approximate nuclear radius of 64Cu is
a) 2.4
b) 1.2
c) 4.8
d) 3.6
Answer:
c) 4.8
Solution:
R α A1/3
\(\frac{R_{2}}{R_{1}}\) = \(\left(\frac{A_{2}}{A_{1}}\right)^{1 / 3}\)
A1 = 27 = 33
A2 = 64 = 43
R1 = 3.6 F
\(\frac{R_{2}}{R_{1}}\) = \(\left(\frac{4^{3}}{3^{3}}\right)^{1 / 3}\)
R2 = 4/3 × 3.6F
R2 = 4.8 F
Question 10.
The nucleus is approximately spherical in shape. Then the surface area of the nucleus having mass number A varies as
(a) A2/3
(b) A4/3
(c) A1/3
(d) A5/3
Answer:
(a) A2/3
Hint:
The volume of the nucleus is proportional to mass number 4
\(\frac { 4 }{ 3 }\) πR3 ∝ A = R0 A1/3
So, πR2 = RR0 A2/3 ⇒ 4πR2 ∝ A2/3
Surface area is proportional to (mass number)2/3
Question 11.
The mass of a \(_{ 3 }^{ 7 }{ Li }\) nucleus is 0.042 u less than the sum of the masses of all its nucleons. The binding energy per nucleon of \(_{ 3 }^{ 7 }{ Li }\) nucleus is nearly
(a) 46 MeV
(b) 5.6 MeV
(c) 3.9 MeV
(d) 23 MeV
Answer:
(b) 5.6 MeV
Hint:
If w = 1 u, C = 3 x 108 ms-1 then, E = 931 MeV
1 u = 931 Mev
Binding energy = 0. 042 x 931
= 39. 10 MeV
∴ B.E 39.10
Binding energy per nucleon = \(\frac { B.E }{ A }\) = \(\frac { 39.10 }{ 7 }\) = 5.58 = 5.6 MeV
Question 12.
Mp denotes the mass of the proton and Mn denotes mass of a neutron. A given nucleus of binding energy B, contains Z protons and N neutrons. The mass M (N,Z) of the nucleus is given by (where c is the speed of light)
a) M (N,Z) = NMn + ZMp – Bc2
b) M (N,Z) = NMn + ZMp + Bc2
c) M (N,Z) = NMn + ZMp – B/c2
d) M (N,Z) = NMn + ZMp + B/c2
Answer:
c) M (N,Z) = NMn + ZMp – B/c2
Solution:
BE = [ZMp+ (A-Z)Mn – M(N,Z)]C2
M (N,Z) = ZMp + NMn – B/C2
Question 13.
A radioactive nucleus (initial mass number A and atomic number Z) emits 2α and 2 positrons. The ratio of number of neutrons to that of proton in the final nucleus will be
(a) \(\frac { A-Z-4 }{ Z-2 }\)
(b) \(\frac { A-Z-2 }{ Z 6 }\)
(c) \(\frac { A-Z-4 }{ Z-6 }\)
(d) \(\frac { A-Z-12 }{ Z-4 }\)
Answer:
(b) \(\frac { A-Z-2 }{ Z 6 }\)
Question 14.
The half-life period of radioactive element A is same as the mean lifetime of another radioactive element B. Initially both have the same number of atoms. Then
(a) A and B have the same decay rate initially
(b) A and B decay at the same rate always
(c) B will decay at faster rate than A
(d) A will decay at faster rate than B.
Answer:
(c) B will decay at faster rate than A
Hint:
(t1/2)A = (tmean )B
\(\frac { 0.6931 }{{ λ }_{A}}\) = \(\frac { 1 }{{ λ }_{B}}\)
λA = 0.6931 λB
λA < λB
Question 15
A system consists of N0 nucleus at t = 0. The number of nuclei remaining after half of a half-life (that is, at time t =\(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) T\(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\))
(a) \(\frac {{ N }_{0}}{ 2 }\)
(b) \(\frac {{ N }_{0}}{ √2 }\)
(c) \(\frac {{ N }_{0}}{ 4 }\)
(d) \(\frac {{ N }_{0}}{ 8 }\)
Answer:
(b) \(\frac {{ N }_{0}}{ √2 }\)
Hint:

Samacheer Kalvi 12th Physics Atomic and Nuclear Physics Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What are cathode rays?
Answer:
When the pressure reaches to around 0.01 mm of Hg, positive column disappears. At this time, a dark space is formed between anode and cathode which is often called Crooke’s dark space and the walls of the tube appear with green colour. At this stage, some invisible rays emanate from the cathode called cathode rays, which are later found be a beam of electrons.
Question 2.
Write the properties of cathode rays.
Answer:
- Cathode rays possess energy and momentum and travel in a straight line with high speed of the order of 107 m s-1
- It can be deflected by application of electric and magnetic fields.
- When the cathode rays are allowed” to fall on matter, they produce heat.
- They affect the photographic plates and also produce fluorescence when they fall on certain crystals and minerals.
- When the cathode rays fall on a material of high atomic weight, x-rays are produced.
- Cathode rays ionize the gas through which they pass.
- The speed of cathode rays is up to( \(\frac { 1 }{ 10 }\))th
Question 3.
Give the results of Rutherford alpha scattering experiment.
Answer:
- Most of the alpha particles are undeflected through the gold foil and went straight.
- Some of the alpha particles are deflected through a small angle.
- A few alpha particles (one in thousand) are deflected through the angle more than 90°.
- Very few alpha particles returned back (back scattered) -that is, deflected back by 180°.
Question 4.
Write down the postulates of Bohr atom model.
Answer:
Postulates of Bohr atom model:
- The electron in an atom moves around nucleus in circular orbits under the influence of Coulomb electrostatic force of attraction. This Coulomb force gives necessary centripetal force for the electron to undergo circular motion.
- Electrons in an atom revolve around the nucleus only in certain discrete orbits called stationary orbits where it does not radiate electromagnetic energy. Only those discrete orbits allowed are stable orbits.
Question 5.
What is meant by excitation energy?
Answer:
The energy required to excite an electron from lower energy state to any higher energy state is known as excitation energy.
Question 6.
Define the ionization energy and ionization potential.
Answer:
The ionization energy and ionization potential are:
- Ionization energy: The minimum energy required to remove an electron from an atom in the ground state is known as binding energy or ionization energy.
- Ionization potential: Ionization potential is defined as ionization energy per unit charge.
Question 7.
Write down the drawbacks of Bohr atom model.
Answer:
The following are the drawbacks of Bohr atom model
- Bohr atom model is valid only for hydrogen atom or hydrogen like – atoms but not for complex atoms.
- When the spectral lines are closely examined, individual lines of hydrogen spectrum is accompanied by a number of faint lines. These are often called fine structure. This is not explained by Bohr atom model.
- Bohr atom model fails to explain the intensity variations in the spectral lines.
- The distribution of electrons in atoms is not completely explained by Bohr atom model.
Question 8.
What is distance of closest approach?
Answer:
The minimum distance between the centre of the nucleus and the alpha particle just before it gets reflected back through 180° is defined as the distance of closest approach r0 (also known as contact distance).
Question 9.
Define impact parameter.
Answer:
The impact parameter is defined as the perpendicular distance between the centre of the gold nucleus and the direction of velocity vector of the alpha particle when it is at a large distance.
Question 10.
Write a general notation of nucleus of element X. What each term denotes?
Answer:
The nucleus of any element, we use the following general notation \(_{ Z }^{ A }X\)
where X is the chemical symbol of the element, A is the mass number and Z is the atomic number.
Question 11.
What is isotope? Give an example.
Answer:
Isotopes are atoms of the same element having same atomic number Z, but different mass number A. For example, hydrogen has three isotopes and they are represented as \(_{ 1 }^{ 1 }H\) (hydrogen), \(_{ 1 }^{ 2 }H\) (deuterium),and \(_{ 1 }^{ 3 }H\) (tritium).
Question 12.
What is isotone? Give an example.
Answer:
Isotones are the atoms of different elements having same number of neutrons. \({ }_{5}^{12} \mathrm{B}\) and \({ }_{6}^{13} \mathrm{C}\) are examples of isotones with 7 neutrons.
Question 13.
What is isobar? Give an example.
Answer:
1. Isobar: Isobars are the atoms of different elements having the same mass number A, but different atomic number Z.
2. For example \(_{ 16 }^{ 40 }S\), \(_{ 17 }^{ 40 }Cl\), \(_{ 18 }^{ 40 }Ar\),\(_{ 19 }^{ 40 }K \) and \(_{ 20 }^{ 40 }Ca\) are isobars having same mass number 40 and different atomic number.
Question 14.
Define atomic mass unit u.
Answer:
One atomic mass unit (u) is defined as the 1/12th of the mass of the isotope of carbon \({ }_{6}^{12} \mathrm{C}\). In other words
1u = \(\frac{\text { mass of }_{6}^{12} \text { Catom }}{12}\)
= \(\frac{1.9926 \times 10^{-26}}{12}\)
= 1.660 × 10-27 kg
Question 15.
Show that nuclear density is almost constant for nuclei with Z > 10.
Answer:
Nuclear density,

The expression shows that the nuclear density is independent of the mass number A. In other words, all the nuclei (Z > 10) have the same density and it is an important characteristic of the nuclei.
Question 16.
What is mass defect?
Answer:
The mass of any nucleus is always less than the sum of the mass of its individual constituents. The difference in mass Am is called mass defect.
∆m = (Zmp + Nmn) – M.
Question 17.
What is binding energy of a nucleus? Give its expression.
Answer:
Mass energy relation (E = mc2)
When the protons and neutrons combine to form a nucleus, mass equal to mass defect disappears and the corresponding energy is released. This is called the binding energy of the nucleus.
BE = (∆m)c2
BE = (Zmp +Nmn – M)c2
The binding energy of a nucleus may be defined as the energy required to breakup a nucleus into its protons and neutrons and to seperate them to such a large distance that they may not interact with each other.
Question 18.
Calculate the energy equivalent of 1 atomic mass unit.
Answer:
We take, m = 1 amu = 1.66 x 10-27 kg
c = 3 x 108ms-1
Then, E = mc2 = 1.66 x 10-27 x (3 x 108)2 J
\(\frac{1.66 \times 10^{-27} \times\left(3 \times 10^{8}\right)^{2}}{1.6 \times 10^{-19}} e \mathrm{V}\)
E ≈ 981 MeV
∴ 1 amu = 931 MeV.
Question 19.
Give the physical meaning of binding energy per nucleon.
Answer:
The average binding energy per nucleon is the energy required to separate single nucleon from the particular nucleus.
Question 20.
What is meant by radioactivity?
Answer:
The phenomenon of spontaneous emission of highly penetrating radiations such as α β and γ rays by an element is called radioactivity and the substances which emit these radiations are called radioactive elements.
Question 21.
Give the symbolic representation of alpha decay, beta decay and gamma decay.
Answer:
1. Alpha decay:
The alpha decay process symbolically in the following way
\(_{ Z }^{ A }X\) → \(_{ Z-2 }^{ A-4 }Y\) + \(_{ 2 }^{ 4 }He\)
2. Beta decay:
β decay is represented by \(_{ Z }^{ A }X\) → \(_{ Z-1 }^{ A }Y\) +e+ + v
3. Gamma decay:
The gamma decay is given by \(_{ Z }^{ A }{{ X }^{ * }}\) → \(_{ Z }^{ A }X\) + gamma (γ ) rays
Question 22.
In alpha decay, why the unstable nucleus emits \(_{ 2 }^{ 4 }He\) He nucleus? Why it does not emit four separate nucleons?
Answer:
After all \(_{ 2 }^{ 4 }He\) He consists of two protons and two neutrons. For example, if \(_{ 92 }^{ 238 }U\) nucleus decays into \(_{ 90 }^{ 234 }U\) Th by emitting four separate nucleons (two protons and two neutrons), then the disintegration energy Q for this process turns out to be negative. It implies that the total mass of products is greater than that of parent (\(_{ 92 }^{ 238 }U\)) nucleus. This kind of process cannot occur in nature because it would violate the conservation of energy. In any decay process, the conservation of energy, conservation of linear momentum and conservation of angular momentum must be obeyed.
Question 23.
What is mean life of nucleus? Give the expression.
Answer:
The mean life time of the nucleus is the ratio of sum or integration of life times of all nuclei to the total number nuclei present initially.
Question 24.
What is half-life of nucleus? Give the expression.
Answer:
The half-life T1/2 is defined as the time required for the number of atoms initially present to reduce to one half of the initial amount.
T1/2 = \(\frac { In 2 }{ λ }\) = \(\frac { 0.6931 }{ λ }\).
Question 25.
What is meant by activity or decay rate? Give its unit.
Answer:
The activity (R) or decay rate is defined as the number of nuclei decayed per second and it is denoted as R = \(\left| \frac { dN }{ dt } \right| \)
The SI unit of activity R is Becquerel.
Question 26.
Define curie.
Answer:
One curie was defined as number of decays per second in 1 g of radium and it is equal to 3.7 × 1010 decays / s
Question 27.
What are the constituent particles of neutron and proton?
Answer:
Protons and neutrons are Baryon which are made up of three Quarks. According to quark model, proton is made up of two up quarks and one down quark and neutron is made up of one up quark and two down quarks.
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Physics Atomic and Nuclear Physics Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
Explain the J.J. Thomson experiment to determine the specific charge of electron.
Answer:
In 1887, J. J. Thomson made a remarkable improvements in the scope of study of gases in discharge tubes. In the presence of electric and magnetic fields, the cathode rays are deflected. By the variation of electric and magnetic fields, mass normalized charge or the specific charge (charge per unit mass) of the cathode rays is measured.
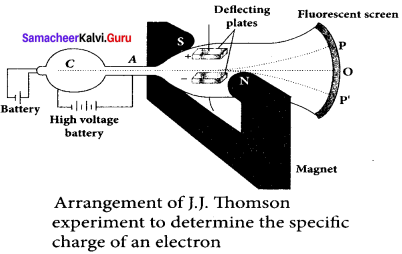
A highly evacuated discharge tube is used and cathode rays (electron beam) produced at cathode are attracted towards anode disc A. Anode disc is made with pinhole in order to allow only a narrow beam of cathode rays. These cathode rays are now allowed to pass through the parallel metal plates, maintained at high voltage.
Further, this gas discharge tube is kept in between pole pieces of magnet such that both electric and magnetic fields are perpendicular to each other. When the cathode rays strike the screen, they produce scintillation and hence bright spot is observed. This is achieved by coating the screen with zinc sulphide.
(i) Determination of velocity of cathode rays:
For a fixed electric field between the plates, the magnetic field is adjusted such that the cathode rays (electron beam) strike at the original position O.
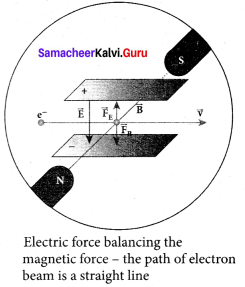
This means that the magnitude of electric force is balanced by the magnitude of force due to magnetic field. Let e be the charge of the cathode rays, then
eE = eBv
⇒ v = \(\frac { E }{ B }\) ….. (1)
(ii) Determination of specific charge:
Since the cathode rays (electron beam) are accelerated from cathode to anode, the potential energy of the electron beam at the cathode is converted into kinetic energy of the electron beam at the anode. Let V be the potential difference between anode and cathode, then the potential energy is eV. Then from law of conservation of energy,
eV = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) mv2 ⇒ \(\frac { e }{ m }\) = \(\frac {{ v }^{ 2 }}{ 2V }\)
Substituting the value of velocity from equation (1), we get
\(\frac { e }{ m }\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2V }\) = \(\frac {{ E }^{ 2 }}{{ B }^{ 2 }}\) …… (2)
Substituting the values of E, B and V, the specific charge can be determined as
\(\frac { e }{ m }\) = 1.7 x 1011 C kg-1
(iii) Deflection of charge only due to uniform electric field:
When the magnetic field is turned off, the deflection is only due to electric field. The deflection in vertical direction is due to the electric force.
Fe = eE ….. (3)
Let m be the mass of the electron and by applying Newton’s second law of motion, acceleration of the electron is
ae = \(\frac { 1 }{ m }\) Fe …. (4)
Substituting equation (4) in equation (3),
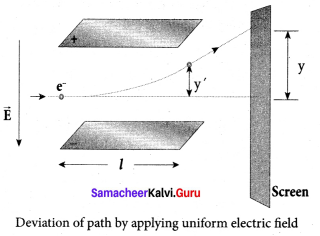
ae = \(\frac { 1 }{ m }\) eE = \(\frac { e }{ m }\) E
Lety be the deviation produced from original position on the screen. Let the initial upward velocity of cathode ray be u = 0 before entering the parallel electric plates. Let t be the time taken by the cathode rays to travel in electric field. Let t be the length of one of the plates, then the time taken is
t = \(\frac { 1 }{ v }\) ….. (5)
Hence, the deflection y’ of cathode rays is (note : u = 0 and ae = \(\frac { e }{ m }\) E)
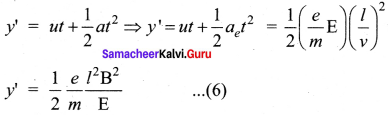
Therefore, the deflection y on the screen is
y ∝ y’ ⇒ y = Cy’
where C is proportionality constant which depends on the geometry of the discharge tube and substituting y’ value in equation (6), we get
y = C\(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) \(\frac { e }{ m }\) \(\frac{l^{2} B^{2}}{E}\) …… (7)
Rerranging equation (7) as
\(\frac { e }{ m }\) = \(\frac{2 y E}{C l^{2} B^{2}}\) ……. (8)
Substituting the values on RHS, the value of specific charge is calculated as
\(\frac { e }{ m }\) = 1.7 x 1011 Ckg-1
(iv) Deflection of charge only due to uniform magnetic field:
Suppose that the electric field is switched off and only the magnetic field is switched on. Now the deflection occurs only due to magnetic field. The force experienced by the electron in uniform magnetic field applied perpendicular to its path is
Fm = evB (in magnitude)
Since this force provides the centripetal force, the electron beam undergoes a semicircular path. Therefore, we can equate Fm to centripetal force
\(\frac {{ mv }^{2}}{ R }\)
Fm = evB = m \(\frac {{ v }^{2}}{ R }\)
where v is the velocity of electron beam at the point where it enters the magnetic field and R is the radius of the circular path traversed by the electron beam.
eB = m \(\frac { v }{ R }\) ⇒ \(\frac { e }{ m }\) = \(\frac { v }{ BR }\) …… (9)
Further, substituting equation (1) in equation (9), we get
\(\frac { e }{ m }\) = \(\frac{E}{B^{2} R}\) ……. (10)
By knowing the values of electric field, magnetic field and the radius of circular path, the value of specific charge\(\left( \frac { e }{ m } \right) \) can be calculated.
Question 2.
Discuss the Millikan’s oil drop experiment to determine the charge of an electron.
Answer:
Millikan’s oil drop experiment is another important experiment in modem physics which is used to determine one of the fundamental constants of nature known as a charge of an electron. By adjusting the electric field suitably, the motion of oil drop inside the chamber can be controlled – that is, it can be made to move up or down or even kept balanced in the field of view for a sufficiently long time.
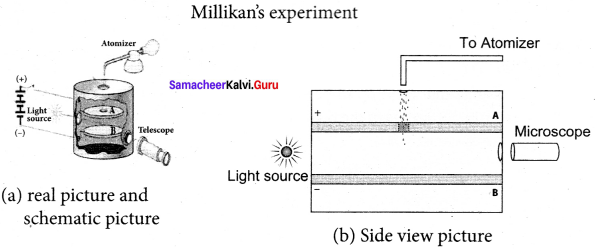
1. The apparatus consists of two horizontal circular metal plates A and B each with diameter around 20 cm and are separated by a small distance 1.5 cm. These two parallel plates are enclosed in a chamber with glass walls. Further, plates A and B are given a high potential difference around 10 kV such that electric field acts vertically downward.
2. A small hole is made at the centre of the upper plate A and atomizer is kept exactly above the hole to spray the liquid. When a fine droplet of highly viscous liquid (like glycerine) is sprayed using atomizer, it falls freely downward through the hole of the top plate only under the influence of gravity.
3. Few oil drops in the chamber can acquire electric charge (negative charge) because of friction with air or passage of x-rays in between the parallel plates. Further the chamber is illuminated by light which is passed horizontally and oil drops can be seen clearly using microscope placed perpendicular to the light beam. These drops can move either upwards or downward.
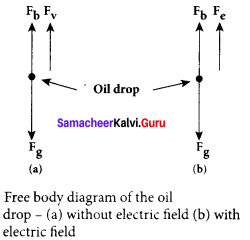
4. Let m be the mass of the oil drop and q be its charge. Then the forces acting on the droplet are
(a) gravitational force Fg = mg
(b) electric force Fe = qE
(c) buoyant force Fb
(a) Determination of radius of the droplet: When the electric field is switched off, the oil drop accelerates downwards. Due to the presence of air drag forces, the oil drops easily attain its terminal velocity and moves with constant velocity. This velocity can be carefully measured by nothing down the time taken by the oil drop to fall through a predetermined distance. The free body diagram of the oil drop), we note that viscous force and buoyant force balance the gravitational force.
Let the gravitational force acting on the oil drop (downward) be Fg = mg.
Let us assume that oil drop to be spherical in shape. Let ρ be the density of the oil drop, and r be the radius of the oil drop, then the mass of the oil drop can be expressed in terms of its density as
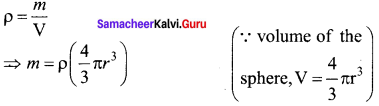
The gravitational force can be written in terms of density as
Fg = mg ⇒ Fg = ρ \(\left( \frac { 4 }{ 3 } \pi { r }^{ 3 } \right) \)g
Let σ be the density of the air, the upthrust force experienced by the oil drop due to displaced air is
Fb = σ \(\left( \frac { 4 }{ 3 } \pi { r }^{ 3 } \right) \)g
Once the oil drop attains a terminal velocity υ, the net downward force acting on the oil drop is equal to the viscous force acting opposite to the direction of motion of the oil drop. From Stokes law, the viscous force on the oil drop is
Fr = 6πr vη
From the free body diagram as shown in Figure (a), the force balancing equation is Fg = Fb + Fv
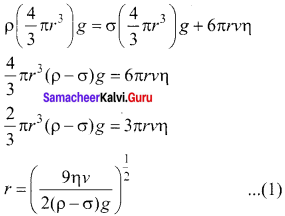
Thus, equation (1) gives the radius of the oil drop.
(b) Determination of electric charge: When the electric field is switched on, charged oil drops experience an upward electric force (qE). Among many drops, one particular drop can be chosen in the field of view of the microscope and the strength of the electric field is adjusted to make that particular drop to be stationary. Under these circumstances, there will be no viscous force acting on the oil drop. Then, from the free body diagram, the net force acting on the oil droplet is
Fe = Fb + Fg

Substituting equation (1) in equation (2), we get
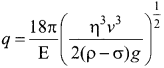
Millikan repeated this experiment several times and computed the charges on oil drops. He found that the charge of any oil drop can be written as an integral multiple of a basic value, -1.6 x 10-19C, which is nothing but the charge of an electron.
Question 3.
Derive the energy expression for hydrogen atom using Bohr atom model.
Answer:
The energy of an electron in the nth orbit
Since the electrostatic force is a conservative force, the potential energy for the nth orbit is

The kinetic energy for the nth orbit is
KEn = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) \({ mv }_{ n }^{ 2 }\) \(\frac{m e^{4}}{8 \varepsilon_{0}^{2} h^{2}}\) \(\frac{Z^{2}}{n^{2}}\)This implies that Un = -2 KEn. Total energy in the nth orbit is
En = kEn + Un = KEn – 2KEn = – KEn
En = \(\frac{m e^{4}}{8 \varepsilon_{0}^{2} h^{2}}\) \(\frac{Z^{2}}{n^{2}}\)
For hydrogen (Z = 1),
En = \(\frac{m e^{4}}{8 \varepsilon_{0}^{2} h^{2}}\) \(\frac { 1 }{{ n }^{ 2 }}\) joule ….. (1)
where n stands for principal quantum number. The negative sign in equation (1) indicates that the electron is bound to the nucleus.
Substituting the values of mass and charge of an electron (m and e), permittivity’ of free space ε0and Planck’s constant h and expressed in terms of eV, we get
En = -13.6 \(\frac { 1 }{{ n }^{ 2 }}\) eV
For the first orbit (ground state), the total energy of the electron is E1 = – 13.6 eV. For the second orbit (first excited state), the total energy of the electron is E2 = -3.4 eV. For the third orbit (second excited state), the total energy of electron is E3 = -1.51 eV and so on.
Notice that the energy of the first excited state is greater than the ground state, second excited state is greater than the first excited state and so on. Thus, the orbit which is closest to the nucleus (r1) has lowest energy (minimum energy compared with other orbits). So, it is often called ground state energy (lowest energy state). The ground state energy of hydrogen (-13.6 eV ) is used as a unit of energy called Rydberg (1 Rydberg = -13.6 eV). The negative value of this energy is because of the way the zero of the potential energy is defined. When the electron is taken away to an infinite distance (very far distance) from nucleus, both the potential energy and kinetic energy terms vanish and hence the total energy also vanishes.
Question 4.
Discuss the spectral series of the hydrogen atom.
Answer:
The spectral lines of hydrogen are grouped in separate series. In each series, the distance of separation between the consecutive wavelengths decreases from higher wavelength to the lower wavelength, and also wavelength in each series approaches a limiting value known as the series limit. These series are named as Lyman series, Balmer series, Paschen series, Brackett series, Pfund series, etc. The wavelengths of these spectral lines perfectly agree with the equation derived from the Bohr atom model.
\(\frac { 1 }{ λ }\) R \(\left(\frac{1}{n^{2}}-\frac{1}{m^{2}}\right)\) = \(\bar { v } \) … (1)
where \(\bar { v } \) is known as wave number which is inverse of wavelength, R is known as Rydberg constant whose value is 1.09737 x 107 m-1 and m and n are positive integers such that m > n. The various spectral series are discussed below:
(a) Lyman series:
Put n = 1 and m = 2, 3, 4 …..in equation (1). The wave number or wavelength of spectral lines of Lyman series which lies in ultra-violet region is
\(\bar { v } \) \(\frac { 1 }{ λ }\) R \(\left(\frac{1}{n^{2}}-\frac{1}{m^{2}}\right)\) = \(\bar { v } \)
(b) Balmer series:
Put n = 2 and m = 3, 4, 5 …. in equation (1). The wave number or wavelength of spectral lines of Balmer series which lies in visible region is
\(\bar { v } \) \(\frac { 1 }{ λ }\) R \(\left(\frac{2}{n^{2}}-\frac{1}{m^{2}}\right)\) = \(\bar { v } \)
(c) Paschen series:
Put n = 3 and m = 4, 5, 6…. in equation (1). The wave number or wavelength of spectral lines of Paschen series which lies in infra-red region (near IR) is
\(\bar { v } \) \(\frac { 1 }{ λ }\) R \(\left(\frac{3}{n^{2}}-\frac{1}{m^{2}}\right)\) = \(\bar { v } \)
(d) Brackett series:
Put n = 4 and m = 5, 6, 7 ….in equation (1). The wave number or wavelength of spectral lines of Brackett series which lies in infra-red region (middle IR) is
\(\bar { v } \) \(\frac { 1 }{ λ }\) R \(\left(\frac{4}{n^{2}}-\frac{1}{m^{2}}\right)\) = \(\bar { v } \)
(e) Pfund series:
Put n = 5 and m = 6, 7, 8 …. in equation (1). The wave number or wavelength of spectral lines of Pfund series which lies in infra-red region (far IR) is
\(\bar { v } \) \(\frac { 1 }{ λ }\) R \(\left(\frac{5}{n^{2}}-\frac{1}{m^{2}}\right)\) = \(\bar { v } \)
Question 5.
Explain the variation of average binding energy with the mass number by graph and discuss its features.
Answer:
We can find the average binding energy per nucleon \(\overline { BE } \). It is given by
\(\overline { BE } \) = \(\frac{\left[Z m_{H}+N m_{n}-M_{\mathrm{A}}\right] c^{2}}{\mathrm{A}}\)
The average binding energy per nucleon is the energy required to separate single nucleon from the particular nucleus. \(\overline { BE } \) is plotted against A of all known nuclei.
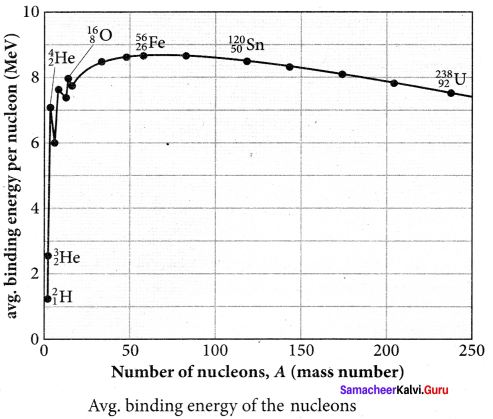
Important inferences from of the average binding energy curve:
(i) The value of \(\overline { BE } \) rises as the mass number increases until it reaches a maximum value of 8.8 MeV for A = 56 (iron) and then it slowly decreases.
(ii) The average binding energy per nucleon is about 8.5 MeV for nuclei having a mass number between A = 40 and 120. These elements are comparatively more stable and not radioactive.
(iii) For higher mass numbers, the curve reduces slowly, and BE for uranium is about 7.6 MeV. They are unstable and radioactive.
If two light nuclei with A < 28 combine with a nucleus with A < 56, the binding energy per nucleon is more for final nucleus than the initial nuclei. Thus, if the lighter elements combine to produce a nucleus of medium value A, a large amount of energy will be released. This is the basis of nuclear fusion and is the principle of the hydrogen bomb.
(iv) If a nucleus of the heavy element is split (fission) into two or more nuclei of medium value A, the energy released would again be large. The atom bomb is based on this principle and the huge energy of atom bombs comes from this fission when it is uncontrolled.
Question 6.
Explain in detail the nuclear force.
Answer:
The nucleus contains protons and neutrons. From electrostatics, we learned that like charges repel each other. In the nucleus, the protons are separated by a distance of about a few Fermi (1 0-15 m), they must exert on each other a very strong repulsive force. For example, the electrostatic repulsive force between two protons separated by a distance 10-15 m
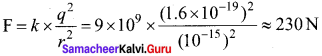
The acceleration experienced by a proton due to the force of 230 N is
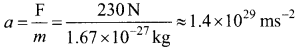
This is nearly 1028 times greater than the acceleration due to gravity. So if the protons in the nucleus experience only the electrostatic force, then the nucleus would fly apart in an instant. From this observation, it was concluded that there must be a strong attractive force between protons to overcome the repulsive Coulomb’s force. This attractive force which holds the nucleus together is called strong nuclear force. A few properties of strong nuclear force are
(i) The strong nuclear force is of very short range, acting only up to a distance of a few Fermi. But inside the nucleus, the repulsive Coulomb force or attractive gravitational forces between two protons are much weaker than the strong nuclear force between two protons. Similarly, the gravitational force between two neutrons is also much weaker than strong nuclear force between the neutrons. So nuclear force is the strongest force in nature.
(ii) The strong nuclear force is attractive and acts with an equal strength between proton-proton, proton-neutron, and neutron – neutron.
(iii) Strong nuclear force does not act on the electrons. So it does not alter the chemical properties of the atom.
Question 7.
Discuss the alpha decay process for example.
Answer:
When unstable nuclei decay by emitting an α-particle (\(_{ 2 }^{ 4 }{ He }\) nucleus), it loses two protons and two neutrons. As a result, its atomic number Z decreases by 2, the mass number decreases by 4. We write the alpha decay process symbolically in the following way
\(_{ Z }^{ A }{ X }\) → \(_{ Z-2 }^{ A-4 }{ Y}\) +\(_{ 2 }^{ 4 }{ He }\)
Here X is called the parent nucleus and Y is called the daughter nucleus.
Example:
Decay of Uranium \(_{ 92 }^{ 238 }{ U }\) to thorium \(_{ 92 }^{ 234 }{ Th }\)with the emission of \(_{ 2 }^{ 4 }{ He }\) nucleus (α-particle)
\(_{ 92 }^{ 238 }{ U }\) → \(_{ 92 }^{ 234 }{ Th }\) + \(_{ 2 }^{ 4 }{ He }\)
As already mentioned, the total mass of the daughter nucleus and \(_{ 2 }^{ 4 }{ He }\) nucleus is always less than that of the parent nucleus. The difference in mass Q = (∆mx – my – mα) is released as energy called disintegration energy Q and is given by Q = (∆mx – my – mα) c2
Note that for spontaneous decay (natural radioactivity) Q > 0. In alpha decay process, the disintegration energy is certainly positive (Q > 0). In fact, the disintegration energy Q is also the net kinetic energy gained in the decay process or if the parent nucleus is at rest, Q is the total kinetic energy of daughter nucleus and the 2 He nucleus. Suppose Q < 0, then the decay process cannot occur spontaneously and energy must be supplied to induce the decay.
Question 8.
Discuss the beta decay process with examples.
Answer:
β– decay:
1. In β– decay, the atomic number of the nucleus increases by one but mass number remains the same. This decay is represented by
\({ }_{Z}^{A} \mathrm{X}\) → \({ }_{Z+1}^{A} \mathrm{Y}\) + e– + \(\bar{v}\)
2. It implies that the element X becomes Y by giving out an electron and antineutrino (\(\bar{v}\)). In other words, in each β– decay, one neutron in the nucleus of X is converted into a proton by emitting an electron (e–) and an antineutrino. It is given by
3. n —> p + e– + \(\bar{v}\)
4. where p – proton \(\bar{v}\) – antineutrino.
5. Example:
Carbon \(\left(\begin{array}{c}
14 \\
6
\end{array} \mathrm{C}\right)\) is converted into nitrogen \(\left(\begin{array}{c}
14 \\
7
\end{array} \mathrm{~N}\right)\) through β– decay.
β+ decay:
1. In β+ decay, the atomic number is decreased by one and the mass number remains the same. This decay is represented by
\(\stackrel{\mathrm{A}}{\mathrm{Z}} \mathrm{X} \rightarrow{ }_{\mathrm{Z}-1}^{\mathrm{A}} \mathrm{Y}+\mathrm{e}^{+}+\mathrm{v}\)
2. It implies that the element X becomes Y by giving out a positron and neutrino (ν). In other words, for each β+ decay, a proton in the nucleus of X is converted into a neutron by emitting a positron e+ and a neutrino. It is given by
p → n + e+ + v
3. However a single proton (not inside any nucleus) cannot have β+ decay due to energy conservation, because neutron mass is larger than proton mass. But a single neutron (not inside any nucleus) can have β– decay.
4. Example:
Sodium (\({ }_{11}^{22} \mathrm{Na}\)) is converted into neon (\({ }_{10}^{22} \mathrm{Ne}\)) through β+ decay.
5. It is important to note that the electron or positron which comes out from nuclei during beta decay never present inside the nuclei rather they are produced during the conversion of a neutron into proton of a proton into neutron inside the nucleus.
Question 9.
Discuss the gamma decay process for an example.
Answer:
In a and p decay, the daughter nucleus is in the excited state most of the time. The typical lifetime of the excited state is approximately 10-11 s. So this excited state nucleus immediately returns to the ground state or lower energy state by emitting highly energetic photons called 7 rays. In fact, when the atom is in the excited state, it returns to the ground state by emitting photons of energy in the order of a few eV. But when the excited state nucleus returns to its ground state, it emits a highly energetic photon (γ rays) of energy in the order of MeV. The gamma decay is given by
\(_{ Z }^{ A }{ { X }^{ * } }\) → \(_{ Z }^{ A }{ X}\) + gamma (γ) rays
Here the asterisk (*) means excited state nucleus. In gamma decay, there is no change in the mass number or an atomic number of the nucleus.
Boron (\(_{ 5 }^{ 12 }{ B }\)) has two beta decay modes:
(i) it undergoes beta decay directly into ground state carbon by emitting an electron of the maximum of energy 13.4 MeV.
(ii) it undergoes beta decay to an excited state of carbon (\(_{ 6 }^{ 12 }{{ C}^{ * }}\)) by emitting an electron of maximum energy 9.0 MeV followed by gamma decay to ground state by emitting a photon of energy 4.4 MeV.
It is represented by
\(_{ 5 }^{ 12 }{ B }\) → \(_{ 6 }^{ 12 }{ C }\) + e+ + \(\bar { v } \)
\(_{ 6 }^{ 12 }{{ C }^{ * }}\) → \(_{ 6 }^{ 12 }{ C }\) + γ
Question 10.
Obtain the law of radioactivity.
Answer:
Law of radioactive decay:
At any instant t, the number of decays per unit time, called rate of decay \(\left( \frac { dN }{ dt } \right) \) is proportional to the number of nuclei (N) at the same instant.
\(\frac { dN }{ dt } \) ∝ N
By introducing a proportionality constant, the relation can be written as
\(\frac { dN }{ dt } \) = -λN …… (1)
Here proportionality constant λ is called decay constant which is different for different radioactive sample and the negative sign in the equation implies that the N is decreasing with time. By rewriting the equation (1), we get
dN = -λNdt …… (2)
Here dN represents the number of nuclei decaying in the time interval dt. Let us assume that at time t =0 s, the number of nuclei present in the radioactive sample is N0. By integrating the equation (2), we can calculate the number of undecayed nuclei N at any time t. From equation (2), we get
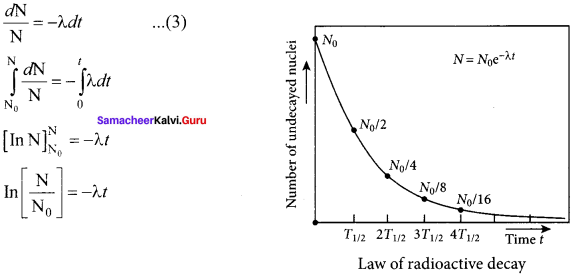
Taking exponentials on both sides, we get
N = N0 e-λt ….. (4)
[Note: eInx = ey ⇒ x = ey]
Equation (4) is called the law of radioactive decay. Here N denotes the number of undecayed nuclei present at any time t and N0 denotes the number of nuclei at initial time t = 0. Note that the number of atoms is decreasing exponentially over the time. This implies that the time taken for all the radioactive nuclei to decay will be infinite. Equation (4) is plotted.
We can also define another useful quantity called activity (R) or decay rate which is the number of nuclei decayed per second and it is denoted as R = \(\left| \frac { dN }{ dt } \right| \).
Note: that activity R is a positive quantity. From equation (4), we get
R = \(\left| \frac { dN }{ dt } \right| \) = λ N0 e-λt ….. (5)
R = R0 e-λt ….. (6)
Where R = λ N0
The equation (6) is also equivalent to radioactive law of decay. Here R0 is the activity of the sample at t = 0 and R is the activity of the sample at any time t. From equation (6), activity also shows exponential decay behavior. The activity R also can be expressed in terms of number of undecayed atoms present at any time t. From equation (6), since N = N0 e-λtwe write
R = λ N …… (7)
Equation (4) implies that the activity at any time t is equal to the product of decay constant and number of undecayed nuclei at the same time t. Since N decreases over time, R also decreases.
Question 11.
Discuss the properties of neutrino and its role in beta decay.
Answer:
Role of neutrino:
- During beta decay, a neutron in the parent nucleus is converted to the daughter nuclei by emitting only electron as given by
\({ }_{Z}^{A} X \rightarrow{ }_{z+1}^{A} Y+e^{-}\) - But the kinetic energy of electron coming out of the nucleus did not match with the experimental results.
- In β– decay, it was found that the β partice have a continuous range of energies.
- But the conservation of energy and momentum gives specific single values for electron energy and the recoiling nucleus Y.
- In 1931 W. Pauli proposed a third particle which must be present in beta decay away missing energy and momentum. Fermi later named this particle the neutrino.
- The neutrino was detected experimentally in 1956 by Fredrick Reines and Clyde Cowan
- Later Reines received Nobel prize in physics in the year 1995 for his discovery.
The neutrino has the following properties:
- It has zero charge.
- It has an antiparticle called anti – neutrino.
- Recent experiments showed that the neutrino has very tiny mass.
- It interacts very weakly with the matter.
- Therefore, it is very difficult to defect. In fact, in every second, trillions of neutrinos coming from the sun are passing through our body without any interaction.
Question 12.
Explain the idea of carbon dating.
Answer:
Carbon dating:
1. The interesting application of beta decay is radioactive dating or carbon dating. Using this technique, the age of an ancient object can be calculated. All living organisms absorb carbon dioxide (CO2) from air to synthesize organic molecules. In this absorbed CO2, the major part is \(_{ 6 }^{ 12 }{ C }\) and very small fraction (1.3 x 10-12) is radioactive \(_{ 6 }^{ 14 }{ C }\) whose half-life is 5730 years.
Carbon-14 in the atmosphere is always decaying but at the same time, cosmic rays from outer space are continuously bombarding the atoms in the atmosphere which produces \(_{ 6 }^{ 14 }{ C }\). So the continuous production and decay of \(_{ 6 }^{ 14 }{ C }\) in the atmosphere keep the ratio of
\(_{ 6 }^{ 14 }{ C }\) to \(_{ 6 }^{ 12 }{ C }\) always constant.
2. Since our human body, tree or any living organism continuously absorb CO2 from the atmosphere, the ratio of \(_{ 6 }^{ 14 }{ C }\) to \(_{ 6 }^{ 12 }{ C }\) in the living organism is also nearly constant. But when the organism dies, it stops absorbing C2.
3. Since \(_{ 6 }^{ 14 }{ C }\) starts to decay, the ratio of \(_{ 6 }^{ 14 }{ C }\) to \(_{ 6 }^{ 12 }{ C }\) in a dead organism or specimen decreases over the years. Suppose the ratio of \(_{ 6 }^{ 14 }{ C }\) to \(_{ 6 }^{ 14 }{ C }\) in the ancient tree pieces excavated is known, then the age of the tree pieces can be calculated.
Question 13.
Discuss the process of nuclear fission and its properties.
Answer:
1. When uranium nucleus is bombarded with a neutron, it breaks up into two smaller nuclei of comparable masses with the release of energy.
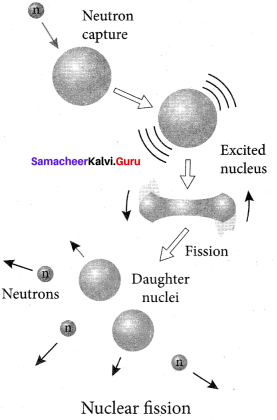
2. The process of breaking up of the nucleus of a heavier atom into two smaller nuclei with the release of a large amount of energy is called nuclear fission.
3. The fission is accompanied by the release of neutrons. The energy that is released in the nuclear fission is of many orders of magnitude greater than the energy released in chemical reactions.
4. Uranium undergoes fission reaction in 90 different Neutrons ways. The most common fission reactions of \(_{ 92 }^{ 235 }{ U }\) nuclei are shown here.
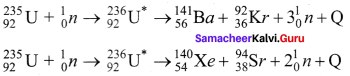
5. Here Q is energy released during the decay of each uranium nuclei. When the slow neutron is absorbed by the uranium nuclei, the mass number increases by one and goes to an excited state \(_{ 92 }^{ 236 }{{ U}^{ * }}\). But this excited state does not last longer than 10-12s and decay into two daughter nuclei along with 2 or 3 neutrons. From each reaction, on average, 2.5 neutrons are emitted.
Question 14.
Discuss the process of nuclear fusion and how energy is generated in stars.
Answer:
Nuclear Fusion:
1. When two or more light nuclei (A < 20) combine to form a heavier nucleus, then it is called nuclear fusion. In nuclear fusion, the mass of the resultant nucleus is less than the sum of the masses of original light nuclei.
2. The mass difference appears as energy.
Necessary conditions for nuclear fusion:
1. The high temperature is necessary for the light nuclei to have sufficient kinetic energy so that they can overcome their mutual coulombic repulsions and corne closer than the range of nuclear force.
2. This can be achieved if the temperature is very much greater than the value 107 K.
3. Nuclear fusion reaction is also called thermonuclear fusion reaction.
4. nuclear fusion never occurs at room temperature unlike nuclear fission.
Energy generation in stars:
1. The early stage of a star is in the form of clouds and dust.
2. Due to their own gravitational pull, these clouds fall inward.
3. As a result, its gravitational potential energy is converted to kinetic energy and finally into heat.
4. When the temperature is high enough to initiate the thermonuclear fusion, they start to release enormous energy which tends to stabilize the star and prevents it from further collapse.
5. The sun’s interior temperature is around 1.5 × 107 K
6. The sun is converting 6 × 1011 kg hydrogen into helium every second.
7. It has enough hydrogen such that this fusion lasts for another 5 billion years.
8. According to Hans Bethe, the sun is powered by the proton-proton cycle of fusion reaction.
9. This cycle consists of three steps
10. The first two steps are as follows:
\({ }_{1}^{1} \mathrm{H}+{ }_{1}^{1} \mathrm{H} \rightarrow{ }_{1}^{2} \mathrm{H}+\mathrm{e}^{+}+v\)
\({ }_{1}^{1} \mathrm{H}+{ }_{1}^{2} \mathrm{H} \rightarrow{ }_{2}^{3} \mathrm{He}+\gamma\)
A number of reactions are possible in the third step.
But the dominant one is
\({ }_{2}^{3} \mathrm{He}+{ }_{2}^{3} \mathrm{He} \rightarrow{ }_{2}^{4} \mathrm{He}+{ }_{1}^{1} \mathrm{H}+{ }_{1}^{1} \mathrm{H}\)
11. Note that the first two reactions should occur twice to produce two \({ }_{2}^{3} \mathrm{He}\) nuclei and initiate the third reaction.
12. The overall reaction of the above cycle is given as
\(4_{1}^{1} \mathrm{H} \rightarrow_{2}^{4} \mathrm{He}+2 \mathrm{e}^{+}+2 v+2 \gamma\)
13. The overall energy production in the above reactions is about 27 MeV.
14. The radiation energy received from the sun is due to these fusion reactions.
15. When the hydrogen is burnt out, the sun will enter into new phase called red gaint where helium will fuse to become carbon.
Question 15.
Describe the working of a nuclear reactors with a block diagram.
Answer:
Nuclear reactor:
1. Nuclear reactor is a system in which nuclear fission takes place in a self-sustained controlled manner and the energy produced is used either for research purposes or for power generation.
2. The main parts of a nuclear reactor are fuel, moderator and control rods. In addition to this, there is a cooling system which is connected with power generation setup.
Fuel:
1. The fuel is fissionable material, usually uranium or plutonium. Naturally occurring uranium contains only 0.7% of \(_{ 92 }^{ 235 }{ U }\) and 99.3% are only If \(_{ 92 }^{ 238 }{ U }\). So the \(_{ 92 }^{ 238 }{ U }\) must be enriched such that it contains at least 2 to 4% of \(_{ 92 }^{ 235 }{ U }\).
2. In addition to this, a neutron source is required to initiate the chain reaction for the first time. A mixture of beryllium with plutonium or polonium is used as the neutron source. During fission of \(_{ 92 }^{ 235 }{ U }\), only fast neutrons are emitted but the probability of initiating fission by it in another nucleus is very low. Therefore, slow neutrons are preferred for sustained nuclear reactions.
Moderators:
1. The moderator is a material used to convert fast neutrons into slow neutrons. Usually the moderators are chosen in such a way that it must be very light nucleus having mass comparable to that of neutrons. Hence, these light nuclei undergo collision with fast neutrons and the speed of the neutron is reduced
2. Most of the reactors use water, heavy water (D2O) and graphite as moderators. The blocks of uranium stacked together with blocks of graphite (the moderator) to form a large pile.
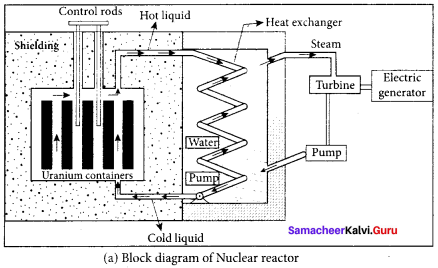
Control rods:
1. The control rods are used to adjust the reaction rate. During each fission, on an average 2.5 neutrons are emitted and in order to have the controlled chain reactions, only one neutron is allowed to cause another fission and the remaining neutrons are absorbed by the control rods.
2. Usually cadmium or boron acts as control rod material and these rods are inserted into the uranium blocks. Depending on the insertion depth of control rod into the uranium, the average number of neutrons produced per fission is set to be equal to one or greater than one.
3. If the average number of neutrons produced per fission is equal to one, then the reactor is said to be in critical state. In fact, all the nuclear reactors are maintained in a critical state by suitable adjustment of control rods. If it is greater than one, then reactor is said to be in super-critical and it may explode sooner or may cause massive destruction.
Shielding:
1. For protection against harmful radiations, the nuclear reactor is surrounded by a concrete wall of thickness of about 2 to 2.5 m.
Cooling system:
2. The cooling system removes the heat generated in the reactor core. Ordinary water, heavy water and liquid sodium are used as coolant since they have very high specific heat capacity and have large boiling point under high pressure.
3. This coolant passes through the fuel block and carries away the heat to the steam generator through heat exchanger. The steam runs the turbines which produce electricity in power reactors.
Question 16.
Explain in detail the four fundamental forces.
Answer:
1. Gravitational, electromagnetic, strong and weak forces are called fundamental forces of nature.
2. It is very interesting to realize that, even for our day – to – day life, we require these four fundamental forces.
Gravitational force:
The gravitational force between two masses and it is universal in nature. Our planets are bound to the sun through the gravitational force of the sun.
Electromagnetic force:
Between two charges there exists electromagnetic force and it plays major role in most of our day – to day events.
Strong nuclear force:
1. Between two nucleons, there exists a strong nuclear force and this force is responsible for stability of the nucleus.
2. This force holds the protons and neutrons together in the nucleus of an atom.
Week nuclear force:
1. In addition to these three forces, there exists another fundamental force of nature called the weak force.
2. Weak force is even shorter in range than nuclear force.
3. We are in the Earth because of Earth’s gravitational attraction on our body.
4. We are standing on the surface of the earth because of the electromagnetic force between atoms of the surface of the earth with atoms in our foot.
5. The atoms in our body are stable because of strong nuclear force
6. Finally, the lives of species in the earth depend on the solar energy from the sun and it is due to weak force which plays vital role during nuclear fusion reactions going on in the core of the sun.
Question 17.
Briefly explain the elementary particles of nature.
Answer:
Elementary particles:
1. An atom has a nucleus surrounded by electrons and nuclei is made up of protons and neutrons. Till 1960s, it was thought that protons, neutrons and electrons are fundamental building blocks of matter.
2. In 1964, physicist Murray Gellman and George Zweig theoretically proposed that protons and neutrons are not fundamental particles; in fact they are made up of quarks. These quarks are now considered elementary particles of nature. Electrons are fundamental or elementary particles because they are not made up of anything.
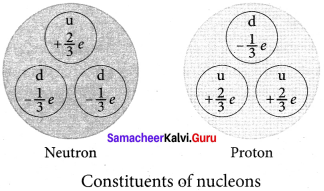
In the year 1968, the quarks were discovered experimentally by Stanford Linear Accelerator Center (SLAC), USA. There are six quarks namely, up, down, charm, strange, top and bottom and their antiparticles. All these quarks have fractional charges.
For example, charge of up quark is +\(\frac { 2 }{ 3 }\)e and that of down quark is –\(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\)e.
3. According to quark model, proton is made up of two up quarks and one down quark and neutron is made up of one up quark and two down quarks.
4. The study of elementary particles is called particle physics.
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Physics Atomic and Nuclear Physics Exercises
Question 1.
Consider two hydrogen atoms HA and HB in ground state. Assume that hydrogen atom HA is at rest and hydrogen atom HB is moving with a speed and make head-on collide on the stationary hydrogen atom HA. After the strike, both of them move together. What is minimum value of the kinetic energy of the moving hydrogen atom HB, such that any one of the hydrogen atoms reaches one of the excitation state.
Solution:
Collision between hydrogen HA and hydrogen HB atom will be inelastic if a part of kinetic energy is used to excite atom.
If u1 and u2 are speed of HA and HB atom after collision, then
mu = mu1 + mu2 …… (1)
\(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) mu2 = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) \({ mu }_{ 1 }^{ 2 }\) + \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) \({ mu }_{ 2 }^{ 2 }\) + ∆ E …… (2)
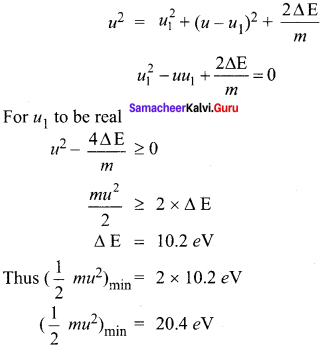
The minimum K.E of the moving hydrogen atom HB is 20.4 eV.
Question 2.
In the Bohr atom model, the frequency of transitions is given by the following expression υ = Rc \(\left(\frac{1}{n^{2}}-\frac{1}{m^{2}}\right)\), Where n < m,
Consider the following transitions:
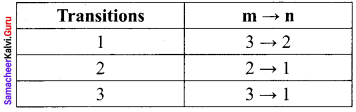
Show that the frequency of these transitions obey sum rule (which is known as Ritz combination principle)
Solution:
In the Bohr atom model, the frequency of transition
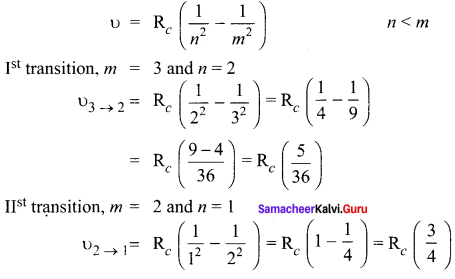
IIIrd transition, m = 3 and n = 1
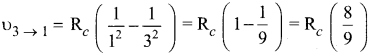
According to Ritz combination principle, the frequency transition of single step is the sum of frequency transition in two steps
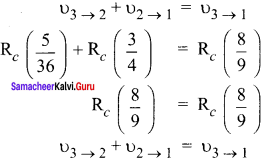
Question 3.
(a) A hydrogen atom is excited by radiation of wavelength 97.5 nm. Find the principal quantum number of the excited state.
(b) Show that the total number of lines in emission spectrum is \(\frac { n(n-1) }{ 2 }\) and compute the total number of possible lines in emission spectrum.
Solution:
(a) Wavelength, λ = 97.5 nm = 97.5 x 10-9 m
Principle quantum number n = ?
According to Bohr atom model,
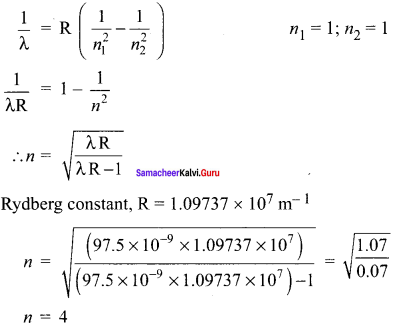
(b) A hydrogen atom initially in the ground level absorbs a photon, which excites it to the n = 4 level
So total number of lines in emission spectrum is \(\frac { n(n-1) }{ 2 }\)
= \(\frac { (4(4-1) }{ 2 }\) = \(\frac { 4×3) }{ 2 }\) = 6
So the total number of possible lines in emission spectrum is 6.
Question 4.
Calculate the radius of the earth if the density of the earth is equal to the density of the nucleus. [mass of earth 5.97 x 1024 kg].
Solution:
The density of the nucleus of an atom
ρN = 2.3 x 1017 kg m-3
ρN = ρE = 2.3 x 1017 kg m-3
Mass of the earth ME = 5.97 x 1024 kg
Density of the earth,

r3 = 0.62155 x 107 m3
r3 = 183.85 m
r ≈ 180 m.
Question 5.
Calculate the mass defect and the binding energy per nucleon of the \(_{ 47 }^{ 108 }{ Ag }\) nucleus, [atomic mass of Ag = 107.905949]
Solution:
Mass of proton, mp = 1.007825 amu
Mass of neutron, mn = 1.008665 amu
Mass defect, ∆m = Zmp + Z mN – MN
= 47 x 1.007825 + 61 x 1.008665 – 107.905949
= 108.89634- 107.905949
∆m = 0.990391 u
Binding energy per nucleon of the \(_{ 47 }^{ 108 }{ Ag }\) nucleus

Question 6.
Half lives of two radioactive elements A and B are 20 minutes and 40 minutes respectively. Initially, the samples have equal number of nuclei. Calculate the ratio of decayed numbers of A and B nuclei after 80 minutes.
Solution:
80 minutes = 4 half lives of A = 2 half live of B
Let the initial number of nuclei in each sample be N.
NN after 80 minutes = \(\frac { N }{{ 2 }^{ 4 }}\)
Number of A nuclides decayed = \(\frac { 15 }{16}\)N
NB after 80 minutes = \(\frac { N }{{ 2 }^{ 4 }}\)
Number of B nuclides decayed = \(\frac { 3 }{4}\)N
Required ratio = \(\frac { 15 }{16}\) x \(\frac { 4 }{3}\) = \(\frac { 5 }{4}\)
NN : NB = 5 : 4.
Question 7.
On your birthday, you measure the activity of the sample 210Bi which has a half-life of 5.01 days. The initial activity that you measure is lμCi . (a) What is the approximate activity of the sample on your next birthday? Calculate (b) the decay constant (c) the mean life (d) initial number of atoms.
Solution:
(a) A year of 365 days is equivalent to 365 d/5.01 d ≈ 73 half-lives. Thus, the activity will be reduced after one year to approximately (1/2)73 (1.000 μCi) ~ 10-22 μCi.
(b) Initial measure R0 = 1.000 μCi
= 10-6 x 3.7 x 1010
= 3.7 x 104 Bq
After 1 year, the measure R = 10-22 μCi.
= 10-22 x 10-6 x 3.7 x 1010
= 3.7 x 10-18 Bq
decay constant,
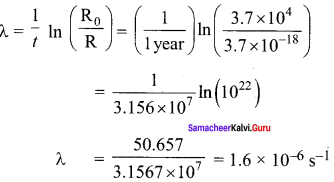
(c) Mean life
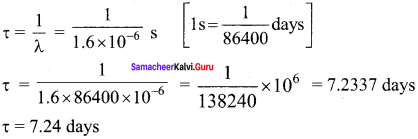
(d) Initial number of atoms
R0 = λN ; N = \(\frac {{ R }_{ 0 }}{ λ }\)
= \(\frac{3.7 \times 10^{4}}{1.6 \times 10^{-6}}\) ; N = 2.31 x 1010
Question 8.
Calculate the time required for 60% of a sample of radon undergo decay. Given T1/2 of radon = 3.8 days.
Solution:
Here consider Rn – 222 with a half life of 3.823 days.
From decay equation,
Current amount = Initial amount x (2)-n
N = N0 (2)-n
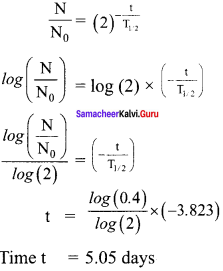
Question 9.
Assuming that energy released by the fission of a single \(_{ 92 }^{ 235 }{ U }\) nucleus is 200MeV, calculate the number of fissions per second required to produce 1 watt power.
Solution:
The fission of a single \(_{ 92 }^{ 235 }{ U }\) nucleus releases 200 MeV of energy
Energy released in the fission is given by the formula,
E = \(\frac { Pt }{ n }\) ⇒ \(\frac { n }{ t }\) = \(\frac { P }{ E }\)
E = 200 MeV = 200 x 106 x 1.6 x 10-19
E = 3.2 x 10-11 J
\(\frac { n }{ t }\) = \(\frac { P }{ E }\) = \(\frac{1}{3.2 \times 10^{-11}}\) = 0.3125 x 1011 = 3.125 x 1010
\(\frac { n }{ t }\) = 3.125 x 1010
Question 10.
Show that the mass of radium (\(_{ 88 }^{ 226 }{ Ra }\)) with an activity of 1 curie is almost a gram. Given T1/2 = 1600 years.
Solution:
The activity of the sample at any time t
R = λN
Here, λ = \(\frac{0.6931}{\mathrm{T}_{1 / 2}}\)
R = 1 Ci = 3.7 x 1010 dis s-1
T1/2 = 1600 year = 1600 x 3.16 x 107 dis
∴ The amount of radium,

= 26990.62 x 1017
N = 2.7 x 1021 atoms
As 226 g of radium contains 6.023 x 1023 atoms so the amount of required strength.
= \(\frac{226 \times 2.7 \times 10^{21}}{6.023 \times 10^{23}}\)
= 101.311 x 10-2
= 1.013 g ≈ 1 g.
Question 11.
Characol pieces of tree is found from an archeological site. The carbon-14 content of this characol is only 17.5% that of equivalent sample of carbon from a living tree. What is the age of tree?
Solution:
R0 = 100%
R = 17.5%
λ = \(\frac{0.6931}{\mathrm{T}_{1 / 2}}\)
T1/2 = 5730 years
According to radioactive law
R = R0 e-λt
e-λt = \(\frac {{ R }_{ 0 }}{ R }\)
Talking log on both sides
t = \(\frac {1}{ λ }\) in \(\left( \frac { { R }_{ 0 } }{ R } \right) \)
Half life of carbon, T1/2 = 5730 years
t = \(\frac{\mathrm{T}_{1 / 2}}{0.6931}\) In \(\left(\frac{1}{0.175}\right)\)
= \(\frac { 5730 years }{ 0.6931 }\) x 1.74297
= 14409.49 years
t = 1.44 x 104 years.
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Physics Atomic and Nuclear Physics Additional Questions
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Physics Atomic and Nuclear Physics Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Electron was discovered by ________.
a) Thomas Alva Edison
b) Michael Faraday
c) Flemming
d) J.J. Thomson
Answer:
d) J.J. Thomson
Question 2.
The allowed energy for the particle for a particular value of n is proportional to
(a) a-2
(b) a-3/2
(c) a-1
(d) a2
Answer:
(a) a-2
Hint:
For the standing wave, a = n \(\frac { λ }{ 2 }\) or λ= \(\frac { 2a }{ n }\)
P = \(\frac {h}{ λ }\) = \(\frac { nh }{ 2a }\) ; E = \(\frac {{ p }^{2}}{ 2m}\) = \(\frac{n^{2} h^{2}}{2 a^{2} m}\) ; E ∝ a-2.
Question 3.
A diatomic molecular has a moment of inertia I. By Bohr’s quantization condition its rotational energy in the nth level (n = 0 is not allowed) is
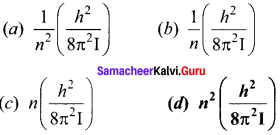
Answer:
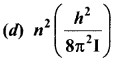
Hint:
Angular momentum, L = \(\frac { nh }{ 2π }\)
Rotation K.E = \(\frac {{ L }^{2}}{ 2I}\) = \(\frac{n^{2} h^{2}}{8 \pi^{2} I}\).
Question 4.
Hydrogen bomb involves the principle of _______.
a) Nuclear fission
b) Nuclear fusion
c) Newtons law
d) Coulomb law
Answer:
b) Nuclear fusion
Question 5.
If 13.6 eV energy is required to 10 is the hydrogen atom, then energy required to remove an electron from n = 2 is
(a) 10.2 eV
(b) 0 eV
(c) 3.4 eV
(d) 6.8 eV
Answer:
(c) 3.4 eV
Hint:
En = \(\frac { 13.6 }{ n }^{2}\)eV
∴ ∆E = E∝ – E2 = 0 + \(\frac { 13.6 }{ n }^{2}\) = 3.4 eV.
Question 6.
Which of the following transitions in hydrogen atoms emits photons of highest frequency?
(a) n = 1 to n = 2
(b) n = 2 to n = 6
(c) n = 6 to n = 2
(d) n = 2 to n = 1
Answer:
(d) n = 2 to n = 1
Hint:
The energy difference E2 – E1 is maximum as calculated in the above problem.
Question 7.
The wavelengths involved in the spectrum of deuterium \(_{ 1 }^{ 2 }{ H }\) are slightly different from that of the hydrogen spectrum because
(a) sizes of the two nuclei are different
(b) masses of the two nuclei are different
(c) the attraction between the electron and the nucleus is different in the two cases
(d) nuclear forces are different in the two cases
Answer:
(b) masses of the two nuclei are different
Hint:
It is because the masses of the two nuclei are different.
Question 8.
_________ is the difference between the mass of the nucleus and the sum of the masses of its individual nucleons.
a) Mass defect
b) Binding energy
c) Binding energy per nucleon
d) None of the above
Answer:
a) Mass defect
Question 9.
The minimum energy required to take out the only one electron from the ground state of He+ is
(a) 13.6 eV
(b) 54.4 eV
(c) 27.2 eV
(d) 6.8 eV
Answer:
(b) 54.4 eV
Hint:
Ionisation energy, E = 13.6 Z2 eV
Fe He+, Z = 2
∴ E= 13.6 x (2)2 = 13.6 x 4 = 54.4 eV.
Question 10.
Energy of characteristic X-ray is a consequence of
(a) energy of projectile electron
(b) thermal energy of target
(c) transition in target atoms
(d) none of the above
Answer:
(c) transition in target atoms.
Question 11.
How much energy is needed to excite an electron in H-atom from the ground state to first excited state?
(a) -13.6 eV
(b) -10.2 eV
(c) +10.2 eV
(d) +13.6 eV
Answer:
(c) + 10.2 eV
Hint:
E1 = – 13.6 eV,
E2 = – 13.6/222 = – 3.4 eV
Required excitation energy
= E2 – E2 = – 3.4 + 13.6 = + 10.2 eV.
Question 12.
Relation between Half life and average_life of radioactivity is ________.
a) T1/2 = \(1 / \tau\)
b) T1/2 = \(0.6931 / \tau\)
c) T1/2 = \(=\tau / 2\)
d) T1/2 = \(0.6931 / \tau\)
Answer:
d) T1/2 = \(0.6931 / \tau\)
Question 13.
The total energy of an electron in the first excited state of a hydrogen atom is about -3.4 eV. Its kinetic energy in this state is
(a) 3.4 eV
(b) 6.8 eV
(c) – 3.4 eV
(d) – 6.8 eV
Answer:
(a) 3.4 eV
Hint:
K.E = – Total energy = +3.4 eV.
Question 14.
The energy of the ground electronic state of a hydrogen atom is 13.6 eV. The energy of the first excited state will be
(a) – 27.2 eV
(b) – 52.4 eV
(c) – 3.4 eV
(d) – 6.8 eV
Answer:
(c) – 3.4 eV
Hint:
For the first excited state, n = 2
∴ E2 = \(\frac {{ E }_{ 1 }}{{ E }_{ 2 }}\) = \(\frac {-13.6 eV}{4}\) = -3.4 eV.
Question 15.
The total energy of electron in the ground state of hydrogen atom is – 13.6 eV. The kinetic energy of an electron in the first excited state is
(a) 6.8 eV
(b) 13.6 eV
(c) 1.7 eV
(d) 3.4 eV
Answer:
(d) 3.4 eV
Hint:
Total energy in the first excited state,
E2 = \(\frac {{ E }_{ 1 }}{{ E }_{ 2 }}\) = \(\frac {{ E }_{ 1 }}{{ 2 }^{ 2 }}\) = \(\frac {-13.6 }{4}\) = -3.4 eV
K.E = -E2 = 3.4 eV.
Question 16.
Bohr’s theory of hydrogen atom did not explain fully
(a) diameter of H-atom
(b) emission spectra
(c) ionisation energy
(d) the fine structure of even hydrogen spectrum
Answer:
(d) the fine structure of even hydrogen spectrum
Hint:
Bohr theory could not explain the five structure of hydrogen spectrum.
Question 17.
In Bohr’s model of an atom, which of the following is an integral multiple of \(\frac { h }{ 2\pi } \) ?
(a) Kinetic energy
(b) Radius of an atom
(c) Potential energy
(d) Angular momentum
Answer:
(d) Angular momentum
Hint:
L = mvr = \(\frac { nh }{ 2\pi } \).
Question 18.
According to Bohr’s theory, relation between n and radius of orbit is:
(a) r ∝ \(\frac { 1 }{ n } \)
(b) r ∝ n
(c) r ∝ n2
(d) r ∝ \(\frac { 1 }{{ n }^{2}} \)
Answer:
(c) r ∝ n2
Hint:
r = \(\frac{n^{2} h^{2}}{4 \pi^{2} m K Z e^{2}}\) i.e., r ∝ n2.
Question 19.
A beam of electrons is moving with constant velocity in a region having electric and magnetic fields of strength 20 Vm-1 and 0.5T at right angles to the direction of motion of the electrons. What is the velocity of the electrons?
a) 20 m/s
b) 40 m/s
c) 8 m/s
d) 5.5 m/s
Answer:
b) 40 m/s
Solution:
ν = E/B
= \(\frac{20}{0.5}\)
= 40 m/s
Question 20.
In Bohr model of the hydrogen atom, which of the following is quantised?
(a) linear velocity of the electron
(b) angular velocity of electron
(c) linear momentum of electron
(d) angular momentum of electron
Answer:
(d) angular momentum of electron.
Question 21.
In Bohr’s model, the atomic radius of the first orbit is r0. Then, the radius of the third orbit is
(a) r0/9
(b) r0
(c) 9r0
(d) 3r0
Answer:
(c) 9r0
Hint:
rn = r1 n2, where r1 = r0
∴ v3 = r0 (3)2 9r0
Question 22.
What is ratio of Bohr magneton to the nuclear magneton?
(a) \(\frac {{ m }_{ p }}{{ m }_{ e }}\)
(b) \(\frac{m_{p}^{2}}{m_{e}^{2}}\)
(c) 1
(d) \(\frac {{ m }_{ e }}{{ m }_{ p }}\)
Answer:
(a) \(\frac {{ m }_{ p }}{{ m }_{ e }}\)
Hint:
Bohr magneton, μB = \(\frac {eh}{{ 2m }_{ e }}\)
Nuclear magneton, μN = \(\frac {eh}{{ 2m }_{ p }}\)
∴ \(\frac {{ μ }_{ B }}{{ μ }_{ N }}\) = \(\frac {{ m }_{ p }}{{ m }_{ e }}\).
Question 23.
According to the Rutherford atom model, the spectral lines emitted by an atom is ________.
a) line spectrum
b) continuous spectrum
c) continuous absorption spectrum
c) band spectrum.
Answer:
b) continuous spectrum
Solution:
Rutherford atom model result.
Question 24.
If an a-particle collides head-on with a nucleus, what is impact parameter?
(a) zero
(b) infinite
(c) 10-10 m
(d) 1010 m
Answer:
(a) zero
Question 25.
The spectral series of the hydrogen spectrum that lies in the ultraviolet region in the
a) Balmer series
b) Pfund series
c) Paschen series
d) Lyman series
Answer:
d) Lyman series
Solution:
Lyman series lies in the UV region.
Question 26.
Wavelength of Kα line of X-ray spectra varies with atomic number as
(a) λ ∝ Z
(b) λ ∝ √Z
(c) λ ∝ \(\frac { 1 }{{ Z }^{2}}\)
(d) λ ∝ \(\frac { 1 }{ √Z }\)
Answer:
(c) λ ∝ \(\frac { 1 }{{ Z }^{2}}\)
Hint:
ccording to moseley’s law, √V = a(Z – b) or V = \(\frac { c }{ λ }\) = a2 (Z – b)2
∴ (c) λ ∝ \(\frac { 1 }{{ Z }^{2}}\).
Question 27.
The shortest wavelength of X-rays, emitted from a X-ray tube, depend upon
(a) current in the tube
(b) voltage applied to the tube
(c) nature of glass material in the tube
(d) atomic number of the target material
Answer:
(b) voltage applied to the tube
Hint:
λmin = \(\frac { 12375 }{V (volt)}\) Å ; λmin ∝ \(\frac { 1 }{ V }\).
Question 28.
During X-ray formation, if voltage is increased
(a) minimum wavelength decreases
(b) minimum wavelength increases
(c) intensity decreases
(d) intensity increases
Answer:
(a) minimum wavelength decreases
Hint:
As λmin ∝ \(\frac { 1 }{ V }\) if a voltage is increased, the minimum wavelength of X-rays emitted decreases.
Question 29.
The half-life of an element is 25 years, then what percentage of a sample will be left over after 125 years and its lifetime are?
a) 3.125% & 1250
b) 3.125% & ∞
c) 6.25% & 1250
d) 6.25% & ∞
Answer:
a) 3.125% & 1250
Question 30.
The minimum wavelength of the X-rays produced by electrons accelerated through a potential difference of V volts is directly proportional to
(a) \(\frac { 1 }{ √V }\)
(b) \(\frac { 1 }{ V }\)
(c) √V
(d) V2
Answer:
(b) \(\frac { 1 }{ V }\)
Hint:
\(\frac { hc }{ λ }\) =eV or λ = \(\frac { hc }{ eV }\), i.e., λ ∝ \(\frac { 1 }{ V }\).
Question 31.
Which source is associated with a line emission spectrum?
(a) Electric fire
(b) Neon street sign
(c) Red traffic light
(d) Sun
Answer:
(b) Neon street sign
Question 32.
Which one of the relation is correct between time period and a number of orbits while an electron is revolving in an orbit?
(a) T ∝ \(\frac { 1 }{{ n }^{2}}\)
(b) T ∝ n2
(c) T ∝ n3
(d) T ∝ \(\frac { 1 }{{ n }^{2}}\)
Answer:
(c) T ∝ n3
Hint:
In Bohr’s atomic model, T ∝ n3.
Question 33.
The minimum energy required to excite the atom from ground state of hydrogen atom is _________.
a) 13.6 eV
b) 10.2 eV
c) 3.4 eV
d) 1.89 eV
Answer:
b) 10.2 eV
Solution:
For the first orbit (ground state) the total energy of electron is E1 = -13.6 eV.
For the second orbit (first excited state), the total energy of electron is E2 = -3.4 eV
E1 = E2 – E1
= -3.4 eV – (- 13.6eV) = 10.2 eV
Question 34.
If an electron jumps from 1st orbit to 3rd orbit, then it will
(a) not lose energy
(b) not given energy
(c) release energy
(d) absorb energy
Answer:
(d) absorb energy
Hint:
Only by absorbing energy, an electron jumps from first orbit to third orbit.
Question 35.
According to uncertainty principle for an electron, time measurement will become uncertain if following is measured with high certainty
(a) energy
(b) momentum
(c) location
(d) velocity
Answer:
(a) energy
Hint:
According to uncertainty principle, ∆E.∆t ≥ \(\frac { h }{ 2π }\).
Question 36.
According to Rutherford’s atomic model, the electrons inside an atom are
(a) stationary
(b) centralized
(c) non-stationary
(d) none of these
Answer:
(c) non-stationary
Hint:
According to the Rutherford model, the electron inside an atom cannot be stationary.
Question 37.
Wavelength of a light emitted from second orbit to first orbit in a hydrogen atom is
(a) 1.215 x 10-7 m
(b) 1.215 x 10-5 m
(c) 1.215 x 10-4 m
(d) 1.215 x 10-3 m
Answer:
(a) 1.215 x 10-7 m
Hint:
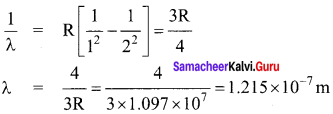
Question 38.
In terms of Rydberg constant R, the wave number of the first Balmer line is
(a) R
(b) 3R
(c) \(\frac { 5R }{ 36 }\)
(d) \(\frac { 8R }{ 9 }\)
Answer:
(c) \(\frac { 5R }{ 36 }\)
Hint:
For the first Balmer line, \(\bar { v } \) =\(\frac { 1 }{ λ }\) = R\(\left(\frac{1}{2^{2}}-\frac{1}{3^{2}}\right)\) =\(\frac { 5R }{ 36 }\).
Question 39.
The K∝ X-ray emission line of tungsten occurs at λ = 0.021 nm. The energy difference between K and L levels in this atom is about
(a) 0.51 MeV
(b)1.2MeV
(c) 59 keV
(d) 136
Answer:
(c) 59 keV
Hint:
E = \(\frac { hc }{ λ }\) = \(\frac{6.6 \times 10^{-34} \times 3 \times 10^{8}}{0.021 \times 10^{-9}}\) eV = 589.3 x 102 eV ≈ 59 KeV.
Question 40.
The radius of an electron orbit in a hydrogen atom is of the order of
(a) 10-8 m
(b) 10-9 m
(c) 10-11 m
(d) 10-13 m
Answer:
(c) 10-11 m
Question 41.
Which of the following atoms has the lowest ionisation potential?
(a) \(_{ 7 }^{ 14 }{ N }\)
(b) \(_{ 55 }^{ 133 }{ Cs }\)
(c) \(_{ 18 }^{ 40 }{ Ar }\)
(d) \(_{ 8 }^{ 16 }{ O }\)
Answer:
(b) \(_{ 55 }^{ 133 }{ Cs }\)
Hint:
In \(_{ 55 }^{ 133 }{ Cs }\), the outermost electron is farthest from the nucleus and so minimum energy is required to remove this electron from the atom. Hence \(_{ 55 }^{ 133 }{ Cs }\) has lowest concision potential.
Question 42.
The transition from the state n = 4 to n = 3 in a hydrogen like atom result in ultraviolet radiation. Infrared radiation will be obtained in the transition from
(a) 2 → 1
(b) 3 → 2
(c) 4 → 2
(d) 5 → 4
Answer:
(d) 5 → 4
Hint:
The energy gap between 4th and 3rd states is more than the gap between 5th and 4th states.
Question 43.
The number of waves, contained in unit length of the medium, is called
(a) elastic wave
(b) wave number
(c) wave pulse
(d) electromagnetic wave
Answer:
(b) wave number
Hint:
The number of waves contained in a unit length of the medium is called a wave number.
Question 44.
When hydrogen atom is in its first excited level, its radius is
(a) sarhe
(b) half
(c) twice
(d) four times
Answer:
(d) four times
Hint:
r2 = r1 (2)2 = 4r1
Question 45.
The ground state energy of hydrogen atom is -13.6 eV. What is the potential energy of the electron in this state?
(a) 0 eV
(b) -27.2 eV
(c) 1 eV
(d) 2 eV
Answer:
(b) -27.2 eV
Hint:
PE = 2 x Total energy = 2 x (-13.6) = – 27.2 eV.
Question 46.
For ionising an excited hydrogen atom, the energy required (in eV) will be
(a) a little less than 13.6
(b) 13.6
(c) more than 13.6 eV
(d) 3.4 or less
Answer:
(d) 3.4 or less
Hint:
The energy of the electron is – 3.4 eV in first excited state and the its magnitude is less for higher excited state.
Question 47.
What is the energy of He+ electron in first order?
(a) 40.8 eV
(b) -27.2 eV
(c) -54.4 eV
(d)-13.6eV
Answer:
(c) -54.4 eV
Hint:
For hydrogen like atoms or ions, En = \(\frac{-13.6 Z^{2}}{n^{2}}\) eV
For He+, Z = 2 and n = 1
E1 = \(\frac{-13.6 \times 2^{2}}{12}\) 54.4 eV.
Question 48.
If voltage across on X-ray tube is doubled, then energy of X-ray emitted by
(a) be doubled
(b) be quadrupled
(c) become half
(d) remain the same
Answer:
(d) remain the same
Hint:
The energy of the X-rays depends on the nature of the target material. Thus the energy of the X-rays remain the same.
Question 49.
When hydrogen atom is in its first excited level, its radius is of the Bohr radius.
(a) twice
(b) 4 times
(c) same
(d) half
Answer:
(b) 4 times
Hint:
For first excited level, n = 2
r2 = (2)2 r0 = 4r0
Question 50.
The ionisation energy of hydrogen atom is 13.6 eV, the ionisation energy of a singly ionsed helium atom would be
(a) 13.6 eV
(b) 27.2 eV
(c) 6.8 eV
(d) 54.4 eV
Answer:
(d) 54.4 eV
Hint:
\({ E }_{ 2 }^{ 1 }\) = (2)2 E1 = 4 x 13.6 = 54.4 eV.
Question 51.
When an electron makes transition from n = 4 to n = 2, then emitted line spectrum will be
(a) first line of lyman series
(b) second line of Balmer series
(c) first line of paschen series
(d) second line of paschen series
Answer:
(b) second line of Balmer series
Hint:
The transition from n = 4 to n = 2 emits second line of Balmer series.
Question 52.
Maximum frequency of emission is obtained for the transition
(a) n = 2 to n = 1
(b) n = 6 to n = 2
(c) n = 1 to n = 2
(d) n = 2 to n = 6
Answer:
(a) n = 2 to n = 1
Hint:
The energy difference E2 – E1 is maximum, so photon of maximum frequency is emitted in transition n = 2 to n = 1.
Question 53.
Hydrogen atoms are excited from ground state to the state of principle quantum number 4. Then the number of spectral lines observed will be
(a) 3
(b) 6
(c) 5
(d) 2
Answer:
(b) 6
Hint:
Here n = 4
∴ The number of spectral lines emitted \(\frac { n(n-1) }{ 2 }\) = \(\frac { 4×3 }{ 2 }\) = 6
Question 54.
The radius of hydrogen atom, in the ground state is of the order of
(a) 10-18 cm
(b) 10-7 cm
(c) 10-6 cm
(d) 10-4 cm
Answer:
(a) 10-18 cm
Hint:
Radius of first orbit of H-atom = 0.53 Å ≈ 10-8 cm.
Question 56.
According to Bohr’s theory of the hydrogen atom, the speed vn of the electron in a stationary orbit is related to the principal quantum number n as (c is a constant)
(a) vn = c/n2
(b) vn = c/n
(c) vn = c x n
(d) vn = c x n2
Answer:
(b) vn = c/n
Hint:
Speed of electron in nth orbit, υn= c/n.
Question 57.
Out of the following which one is not possible energy for a photon to be emitted by hydrogen atom according to Bohr’s atomic model?
(a) 13.6 eV
(b) 0.65 eV
(c) 1.9 eV
(d) 11.1 eV
Answer:
(d) 11.1 eV
Hint:
For no two energy levels of hydrogen atom, E2 – E1 = 11.1 eV.
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Physics Atomic and Nuclear Physics Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Write down the drawbacks of the Rutherford model.
Answer:
1. Drawbacks of Rutherford model:
Rutherford atom model helps in the calculation of the diameter of the nucleus and also the
2. Size of the atom but has the following limitations:
(a) This model fails to explain the distribution of electrons around the nucleus and also the stability of the atom. According to classical electrodynamics, any accelerated charge emits electromagnetic radiations. Due to emission of radiations, it loses its energy.
Hence, it can no longer sustain the circular motion. The radius of the orbit, therefore, becomes smaller and smaller (undergoes spiral motion) and finally the electron should fall into the nucleus and the atoms should disintegrate. But this does not happen. Hence, the Rutherford model could not account for the stability of atoms.
(b) According to this model, emission of radiation must be continuous and must give a continuous emission spectrum but experimentally we observe only line (discrete) emission spectrum for atoms.
Question 2.
What is a discharge tube?
Answer:
A simple and convenient device used to study the conduction of electricity through gases is known as a gas discharge tube.
Question 3.
What is meant by atomic number?
Answer:
The number of protons in the nucleus is called the atomic number and it is denoted by Z.
Question 4.
What is meant by neutron number?
Answer:
The number of neutrons in the nucleus is called neutron number (N).
Question 5.
What is meant by mass number?
Answer:
The total number of neutrons and protons in the nucleus is called the mass number and it is denoted by A. Hence, A = Z + N.
Question 6.
Write the principle of Millikan’s oil drop experiment.
Answer:
- This method is based on the study of the motion of uncharged oil drop under free fall due to gravity and charged oil drop in a uniform electric field.
- By adjusting the electric field suitably, the motion of oil drop inside the chamber can be controlled that is, it can be made to move up or down or even kept balanced in the field of view for a sufficiently long time.
Samacheer Kalvi 12th Physics Atomic and Nuclear Physics Numerical Problems
Question 1.
What is the distance of closest approach when a 5 MeV proton approaches a gold nucleus.
Solution:
q1 = ze
q2 = e
At the distance r0 of closest approach,
K.E of a Proton = P.E. of proton and the gold nucleus
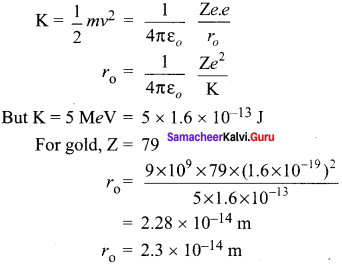
Question 2.
Calculate the impact parameter of a 5 MeV particle scattered by 90° when it approaches.
Solution:
KE = 5 MeV = 5 x 106 x 1.6 x 10-19 J
θ = 90°
For gold, Z = 79
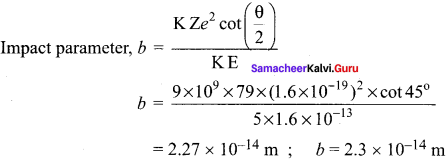
Question 3.
What is the angular momentum of an electron in the third orbit of an atom?
Solution:
Here n = 3; h = 6.6 x 10-34 Js
Angular momentum,
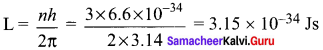
Question 4.
Write down the expression for the radii of orbits of hydrogen atom. Calculate the radius of the smallest orbit.
Solution:
The radius of the nth orbit of a hydrogen atom is given by
r = \(\frac{n^{2} h^{2}}{4 \pi^{2} m K e^{2}}\)
Radius of innermost orbit, called Bohr’s radius, is obtained by putting n = 1. It is denoted by r0
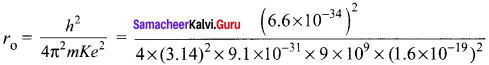
r0 = 0.53 x 10-10 m = 0.53 A°.
Question 5.
Calculate the frequency of the photon, which can excite the electron to – 3.4 eV from -13.6 eV.
Solution:
Energy of photon, hυ = E2 – E1

υ = 2.47 x 1015 Hz
Question 6.
In a nuclear fission 0.1% mass is converted into energy. Calculate the energy released by the fission of 1kg mass.
Solution:
E = (∆m) C2
= (\(\frac{0.1}{100}\) × 1) (3 × 108)2
E = 9 × 1013 J
Question 7.
Express 16 rag mass into equivalant energy in eV.
Solution:
Here m = 16 mg = 16 x 10-16 kg, C = 3 x 108 ms-1
Equivalent energy, E = mc2
= 16 x 10-16 x (3 x 108)2 J
= \(\frac{16 \times 10^{-6} \times\left(3 \times 10^{8}\right)^{2}}{1.6 \times 10^{-19}} \mathrm{eV}\)
E = 9 x 1030 eV.
Question 8.
The nuclear mass of \(_{ 26 }^{ 56 }{ Fe }\) is 55.85 amu. Calculate its nuclear density.
Solution:
Here MFe = 55.85 amu = 55.85 x 1.66 x 10-27 kg
= 9.27 x 10-26 kg
Nuclear Mass = R0 A1/3 = 1.1 x 10-15 x (56)1/3 m
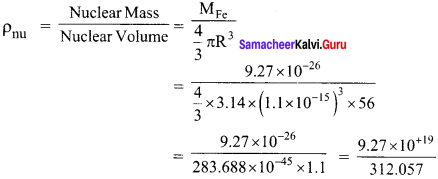
ρnu = 2.9 x 1017 kg m-3.
Question 9.
Calculate the density of hydrogen nuclear in SI units. Given R0 = 1.1 fermi and mp = 1.007825 amu.
Solution:
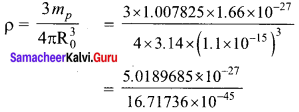
ρ = 2.98 x 1017 kg m-3.
Question 10.
Calculate the shortest wavelength of Lyman series. Given Rydberg’s constant
R = 1.09737 × 107 m-1
Solution:
Data:
R = 1.09737 × 107 m-1
For shortest wavelength of Lyman series.
n1 = 1, n2 = ∞
1/λS = R [\(\frac{1}{1}\) – \(\frac{1}{\infty}\)] = R
λS = 1/R
= \(\frac{1}{1.09737 \times 10^{7}}\)
λS = 911.6 Å
Question 11.
The decay constant, for a given redioactive sample is 0.3465 / day. What percentage of this sample will get decayed in a period of 4 years?
Solution:
Here λ, = 0.3465/day; t = 4 years

Hence sample left undecayed after a period of 4 years,
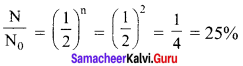
Question 12.
If 50% of a radioactive sample decays in 5 days, how much of the original sample will be left over after 20 days?
Solution:
Data:
T1/2 = 5 days
initial sample = 100%
n = \(\frac{t}{\mathrm{~T}_{1} / 2}\) = \(\frac{20}{5}\) = 4
Amount left over n = 4
N = N0 e-λt
\(\frac{N}{N_{o}}=\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)^{n}\)
N = 100 × (\(\frac{1}{2}\))4 = 100 × \(\frac{1}{16}\)
N = 6.25%
Hope the data shared has shed some light on you regarding the Samacheer Kalvi Class 12th Physics Solutions Chapter 8 Atomic and Nuclear Physics Questions and Answers. Do leave us your queries via the comment section and we will guide you at the earliest with help seeked. Stay connected with our website and avail the latest information in a matter of seconds.