You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Solutions Term 2 Chapter 6 Human Organ Systems
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Human Organ Systems Textual Evaluation
I. Choose the appropriate answer:
Question 1.
Circulatory system transports these throughout the body
(a) Oxygen
(b) Nutrient
(c) Hormones
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d) All of these
Question 2.
Main organ of respiration in human body is
(a) Stomach
(b) Spleen
(c) Heart
(d) Lungs
Answer:
(d) Lungs
Question 3.
Breakdown of food into smaller molecules in our body is known as
(a) Muscle contraction
(b) Respiration
(c) Digestion
(d) Excretion
Answer:
(c) Digestion
![]()
II. Fill in the blanks:
- A group of organs together make up an _______ system.
- The part of the skeleton that protects the brain is _______
- The process by which the body removes waste is _______
- The _______ is the largest sense organ in our body.
- The endocrine glands produce chemical substances called _______
Answers:
- organ
- skull
- Excretion
- skin
- hormones
![]()
III. True or False. If False, give the correct statement:
Question 1.
Blood is produced in the bone marrow.
Answer:
False, Red Blood Corpuscles are produced in the bone marrow.
Question 2.
All the waste products of the body are excreted through the circulatory system.
Answer:
False, All the waste products of the body are excreted through the excretory system.
Question 3.
The other name of food pipe is alimentary canal.
Answer:
False. The other name of food pipe is called oesophagus.
Question 4.
Thin tube like structures which are the component of circulatory system are called blood vessels.
Answer:
False, The tube like structure which are the component of circulatory system are called blood capillaries.
Question 5.
The brain, the spinal cord and nerves form the nervous system.
Answer:
True
![]()
IV. Match the following:
| 1. Ear | Cardiac muscle |
| 2. Skeletal System | Flat muscle |
| 3. Diaphragm | Sound |
| 4. Heart | Air sacs |
| 5. Lungs | Protection of internal organs |
Answer:
| 1. Ear | Sound |
| 2. Skeletal System | Protection of internal organs |
| 3. Diaphragm | Flat muscle |
|
4. Heart |
Cardiac muscle |
| 5. Lungs | Air sacs |
![]()
V. Arrange in Correct sequence:
Question 1.
Stomach → Large intestine → Oesophagus → Pharynx → Mouth → Small Intestine → Rectum → Anus.
Answer:
Mouth → Pharynx → Oesophagus → Stomach → Small Intestine → Large intestine → Rectum → Anus.
Question 2.
Urethra → Ureter → Urinary Bladder → Kidney.
Answer:
Kidney → Ureter → Urinary Bladder → Urethra.
![]()
VI. Analogy:
Question 1.
Arteries : Carry blood from the heart:: _______ :carry blood to the heart.
Answer:
Veins.
Question 2.
Lungs: Respiratory system:: _______ : Circulatory system.
Answer:
Heart
Question 3.
Enzymes: Digestive glands:: _______ : Endocrine glands.
Answer:
Hormones
![]()
VII. Give very short answer:
Question 1.
Write about skeletal system.
Answer:
- The skeletal system consists of bones, cartilages and joints.
- Bones provide a framework for the body.
- Bones along with muscles help in movements such as walking, running, chewing and dancing etc.
Question 2.
Write the functions of epiglottis.
Answer:
The function of Epiglottis is to prevent the entry of food into the wind pipe.
Question 3.
What are the three types of blood vessels?
Answer:
- Arteries
- Veins
- Capillaries
Question 4.
Define the term “Trachea”.
Answer:
Trachea is commonly called as windpipe. It is a tube supported by cartilaginous rings that connects the pharynx and larynx to the lungs, allowing the passage of air. The trachea divides into right and left bronchi and enter into the lungs.
Question 5.
Write any two functions of digestive system?
Answer:
- Digestive system is involved in the conversion of complex food substances into simple forms.
- Absorption of digested food.
Question 6.
Name the important parts of the eye.
Answer:
The important parts of eye are cornea, iris, lens and pupil.
Question 7.
Name the five important sense organs?
Answer:
- Eyes
- Ears
- Nose
- Tongue
- Skin
![]()
VIII. Give short answer:
Question 1.
Write a short note on rib cage.
Answer:
Rib cage
The rib cage is made up of 12 pairs of curved, flat rib bones. It protects the delicate vital organs such as heart and lungs.
Question 2.
List out the functions of the human skeleton.
Answer:
- The skeletal system gives shape to the body.
- Bones provide a framework for the body.
- Bones along with muscles help in movements such as walking, running, chewing and dancing etc.
- It protects, the soft internal organs.
Question 3.
Differentiate between the voluntary muscles and involuntary muscles.
Answer:
Voluntary muscles:
- They are attached to the bones.
- They can be controlled by our will. Example: Muscles of arm.
Involuntary muscles:
- They are found in the walls of digestive tract, urinary bladder, arteries and other internal organs.
- They cannot be controlled by our will.
![]()
IX. Answer in detail:
Question 1.
List out the functions of Endocrine system and Nervous system.
Answer:
- Endocrine system regulates various functions of the body and maintain the internal environment.
- Endocrine glands produce chemical substances called “Hormones’ which control various activities of the body.
Eg. Growth hormone controls growth, Adrenalin hormone acts at the time of fear stress etc.
Functions of nervous system:
- Sensory input: The conduction of signals from sensory receptors.
- Integration : The interpretation of the sensory signals and the formulation of responses.
- Motor output: The conduction of signals from the brain and spinal card to effectors such as muscle and gland cells.
Question 2.
Label the diagram given below to show the four main parts of the urinary system and answer the following questions.
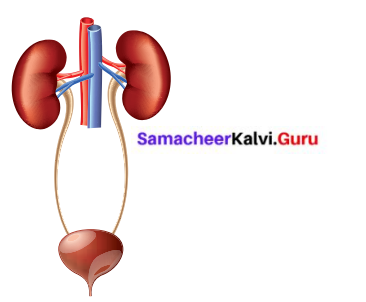
A. Which organ removes extra salts and ws
B. Where is the urine stored?
C. What is the tube through which urine is body?
D. What are the tubes that transfer urine fi the urinary bladder called?
Answers:
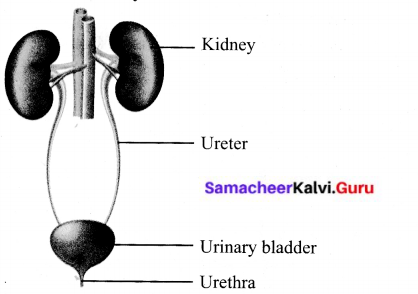
A. Kidney removes extra salts and water from the blood.
B. Urine is stored in urinary bladder.
C. Urine is excreted out of the body through urethra.
D. Ureter transfers urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder.
![]()
X. Questions based on Higher Order Thinking Skills.
Question 1.
What will happen if the diaphragm shows no movement?
Answer:
- The diaphragm is the primary organ of breathing.
- The movement of the diaphragm expands the lungs and creates a vacuum.
- Due to this the air is sucked in.
- If the diaphragm does not move the lungs do not expand or contract and breathing stops.
- The person will die.
Question 2.
Why is the heart divided into two halves by a thick muscular wall?
Answer:
The oxygenated and deoxygenated blood are separately circulated. So the heart is divided into two halves by a thick muscular wall.
Question 3.
Why do we sweat more in summer?
Answer:
- Sweating plays an important health role as it helps to maintain constant body temperature by cooling us down.
- When it is hot and we sweat that moisture evaporates and cools us immediately.
- This is why we sweat more when the summer is very hot.
Question 4.
Why do we hiccup and cough sometimes when we swallow food?
Answer:
Normally, the entry of food into the windpipe is prevented by a flap like structure called Epiglottis. But when we eat in a hurry, the flab gets lesser time to close the windpipe. Thus some of the food particles enter into the windpipe. It creates a hindrance in the movement of air in the windpipe and results in coughing or hiccup.
![]()
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Human Organ Systems Intext Activities
Activity 1
Question 1.
Sit absolutely still. Observe the movements taking place in your body. You must K be blinking your eyes time to time. Observe the movements in your body as you I breathe. Write down the movements in your note book.
We are able to move a few parts of our body easily in various directions and some, ft only in one direction. Why we are not able to move some parts at all directions?
Answer:
We are able to bend or rotate our body in places where two parts of our body seem to be joined together – like elbow, shoulder or neck. These places are called joints. If ft our body has no joints, it would not be possible for us to move in any way at all.
Bones cannot be bent. But we can bend our elbow. It is not one long bone from ft the upper arm to our wrist. It is different bones joined together at the elbow. Similarly, there are many bones present in each part of the body.
We can bend or move our body only at those points where bones meet. There are different types of joints in our body to help us carry out different movements and activities. Let us see the function / movements of some of the joints in our body.
Fixed joints which do not allow movement are called fixed joint.
Gliding joints allow only a limited amount of movement of sliding nature of cartilage. For example, the joints of back bone.
Hinge joint allows movement only in one plane. For example, fingers, knees. Elbow joint is composed of hinge joint. These joints allow movement in one plane and up to 180° only. Hence, we cannot move our elbows backwards.
Piyotal joint allows movement in all planes, i.e. up and down, side and other planes. For example, head.
Ball and socket joint allows movement in all directions. The rounded end of one bone fits into the cavity (hollow space) of other bone. Such a joint only allows movements in all directions. For example, joint between upper arm.
Activity 2
To show that we can bend or move our body only at those points where the bones meet.

Materials required; A wooden scale and string.
Method Ask your friend to tie a wooden scale and your arm together. So that the elbow is at the centre. Even if you try hard, you cannot bend your elbow.
Conclusion: A single bone cannot bend. The different bones joined together at the elbow, help the elbow to bend.
![]()
Activity 3
Question 1.
Move your lower arm up and down gently. Feel the contraction and relaxation of your biceps and triceps muscles. The muscles present in the upper arm help in the contraction of front biceps muscles (become short and thick), and also relaxation of rear triceps muscles (become long and thin). You can feel the muscles on top that go stiff. When the arm is moved downwards, the front muscles relax and the rear muscles contract.
Answer:
Activities to be done by the students themselves
![]()
Activity 5
Air? To prove that exhaled air is rich in carbon- dioxide
Materials required Two glass jars with lime water and a straw
Procedure: Leave the first jar with lime water undisturbed, blow air in to the second jar with the help of a straw
Observation: Lime water turns milky in few seconds in the second jar. The CO? gas alone can change the lime water into milky white.
Conclusion: Carbon-di-oxidc is present in the air that we exhale.
Activity 6
Question 1.
Place the middle and index fingers of your right hand on the inner side of your left wrist. Can you feel a throbbing movement. Why do you feel the throbbing? This throbbing is called the pulse and it is due to the blood flowing in the arteries. Count the number of pulse in one minute.

How many pulse beats could you count in one minute? The number of beats per minute is called the Pulse rate. A resting person usually has a pulse rate between 72 to 80 beats per minute.
Find other places in your body where you can feel the pulse. Record your own pulse beats and your classmates as beats per minute; Compare the values.
Answer:
Activities to be done by the students themselves
![]()
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Human Organ Systems Additional Questions
I. Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
A group of organs that work together to perform a particular function is known as _______
(a) Skeletal system
(b) Muscular system
(c) Nervous system
(d) Organ system
Answer:
(d) Organ system
Question 2.
………. is the largest and strongest bone in the human face.
(a) Hyoid bone
(b) Stapes
(c) Cranial bones
(d) Lower jaw bone
Answer:
(d) Lower jaw bone
Question 3.
_______ bone is the largest and strongest bone in the human face.
(a) Nasal
(b) Temporal
(c) Lower jaw
(d) Parietal
Answer:
(c) Lower jaw
Question 4.
The heart is surrounded by a double-layered membrane called
(a) Pleura
(b) Alveolar membrane
(c) Pericardium
(d) Iris
Answer:
(c) Pericardium
Question 5.
_______ is a major organ for digestion of food materials.
(a) Heart
(b) Oesophagus
(c) Stomach
(d) Kidney
Answer:
(c) Stomach
Question 6.
The _______ is a complex organ which is placed inside the cranium.
(a) Kidney
(b) Heart
(c) Lungs
(d) Brain
Answer:
(d) Brain
Question 7.
Skin helps us to synthesize using sun light.
(a) vitamin A
(b) vitamin B
(c) vitamin C
(d) vitamin D
Answer:
(d) vitamin D
Question 8.
_______ gland is located in the neck region.
(a) Pituitary
(b) Thyroid
(c) Adrenal
(d) Thymus
Answer:
(b) Thyroid
Question 9.
Pituitary gland is located at _______ in our body.
(a) Neck region
(b) base of brain
(c) Abdomen region
(d) above the kidney
Answer:
(b) base of brain
Question 10.
The functional units of the kidney are called _______
(a) Nephrons
(b) Neuron
(c) bladder
(d) urethra
Answer:
(a) Nephrons
![]()
II. Fill in the blanks.
- The adult human skeletal system consists of _______ bones
- _______ help in connecting bone to bone.
- Vertebral column is formed by a number of serially arranged small bones called _______
- The rib cage is made up of _______ of curved flat rib bones.
- The digestive gland associated with alimentary canal is _______
- _______ are located within the chest cavity.
- The lungs are covered by a double layered _______
- The heart is _______ chambered.
- The heart is surrounded by a double layered membrane called _______
- _______ are produced in the bone marrow.
- Nervous system is we,11 developed in human and is composed of _______ or _______
- _______ is the controlling centre of the body.
- The outer ear in human beings is made up of an external flap called _______
- _______ gland is located above the kidney.
- Our body contains _______ % of water.
- Our stomach consists of _______ acid.
Answers:
- 206
- Ligaments
- vertebrae
- 12 pairs
- salivary gland
- Lungs
- pleura
- four
- pericardium
- Red Blood Carpuscles
- neurons or nerve cells
- Brain
- pinna
- Adrenal
- 70
- Hydro choloric
![]()
III. Find whether the following sentences are true or false. If false Correct the statement.
Question 1.
The nervous system consists of bones, cartilages and joints.
Answer:
False. The Skeletal system consists of bones, cartilages and joints.
Question 2.
Lower jaw bone is the smallest and strongest bone in the human face.
Answer:
False. Lower jaw bone is the largest and strongest bone in the human face.
Question 3.
The smallest bone in our body is stapes.
Answer:
True.
Question 4.
Intake of oxygen from the air and releasing of carbon-di-oxide from the lungs occur through nostrils is called internal respiration.
Answer:
False. Intake of oxygen from the air and releasing of carbon-di-oxide from the lungs occur through nostrils is called external respiration.
Question 5.
The walls of the heart is made up of cardiac muscle.
Answer:
True.
Questions 6.
Blood is a fluid connective tissue.
Answer:
True.
Question 7.
Kidney is located in the thoracic cavity between the two lungs.
Answer:
False. Heart is located in the thoracic cavity between the two lungs.
Question 8.
A resting person usually has a pulse rate between 72 to 80 beats per minute.
Answer:
True.
Question 9.
Pulmonary artery carries blood from the lungs to the left atrium.
Answer:
False. Pulmonary Vein carries blood from the lungs to the left atrium.
Question 10.
Heart forms an effective barrier against infection by microbes and pathogens.
Answer:
False. Skin forms an effective barrier against infection by microbes and pathogens.
Question 11.
The nitrogenous wastes are removed from the body by the endocrine system.
Answer:
False. The nitrogenous wastes are removed from the body by the excretory system.
![]()
IV. Analogy:
Question 1.
Skull protects : Brain.
Rib cage protects : _______
Answer:
heart and liver.
Questions 2.
The smallest bone of our body : Stapes.
The longest bone of our body : _______
Answer:
Femur.
Question 3.
A newborn baby has bones : More than 300.
An adult has bones : _______
Answer:
206.
Questions 4.
Skeletal muscle : Muscle of arm.
Cardiac muscle: _______
Answer:
Walls of heart.
Question 5.
Heart: Pericardium membrane.
Lungs : _______
Answer:
Pleura membrane.
Question 6.
Carries blood from right ventricle to lungs : Pulmonary artery.
Carries blood from the lungs to left atrium : _______
Answer:
Pulmonary vein.
Question 7.
Carry oxygenated blood : Arteries.
Carry deoxygenated blood : _______
Answer:
Vein.
Question 8.
Neurons : Nervous system.
Nephrons: _______
Answer:
Excretory system.
![]()
V. Match the following :
A

Answer:
- – f
- – d
- – e
- – a
- – c
- – b
B

Answer:
- – c
- – e
- – a
- – b
- – d
C
Answer:
- – c
- – d
- – e
- – b
- – a
![]()
VI. Give short answer
Question 1.
List the major organ system of our body.
Answer:
Human body has eight major organ system. They are:
- Skeletal system
- Digestive system
- Circulatory system
- Endocrine system
- Muscular system
- Respiratory system
- Nervous system
- Excretory system.
Question 2.
Axial skeleton – Explain.
Answer:
Axial skeleton forms the upright axis of the body which includes, skull, vertebral column and Rib cage.
Questions 3.
What are the bones found in the skull?
Answer:
Hyoid bone and the auditory ossicles like Malleus, Incus and Stapes are found in the skull.
Questions 4.
What are the three types of muscles?
Answer:
They are skeletal muscle, smooth muscle and cardiac muscles.
Question 5.
How do muscle work?
Answer:
Muscles pf the body can only pull and they cannot push. Two muscles are required to move a bone at a joint. When one muscle contracts the other muscle relaxes. Thus muscles do work.
Questions 6.
List the parts of digestive system.
Answer:
Parts of digestive systems are Mouth, Buccal cavity, Phanynx, Oesophagus, Stomach, Small intestine, Large intestine, Anus.
Question 7.
List the glands associated for digestion.
Answer:
Salivary glands, Gastric glands, Liver, Pancreas and Intestinal glands are associated glands for digestion.
Questions 8.
List the parts of respiratory system.
Answer:
Respiratory system consists of nostrils, nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi and lungs.
Question 9.
What is internal respiration?
Answer:
Taking in oxygen and giving out CO2 The circulatory system transports O2 and CO2, to and from all parts of body. Hemoglobin in the red blood cells transport O2 and CO2 This is called internal respiration.
![]()
Question 10.
Define – blood.
Answer:
Blood is a fluid connective tissue of red colour containing plasma and blood cells. There are three types of blood cells namely, Red blood corpuscles (RBCs), White Blood corpuscles (WBCs) and Blood Platelets. RBCs are produced in the bone marrow.
Question 11.
What is pulse rate?
Answer:
The number of beats per minute is called pulse rate.
Question 12.
Name the three regions of brain.
Answer:
The three regions of brain are fore brain, mid brain and hind brain.
Question 13.
List the endocrine glands found in our body.
Answer:
Pituitary gland, Pineal gland, Thyroid gland, Thymus gland, Pancreas, Adrenal gland, Gonads are found in our endocrine system.
![]()
VIII. Answer in detail:
Question 1.
(a) How do muscles work.
(b) How circulatory system is important for human life?
Answer:
(a) Muscles work.
- Muscles of the body can only pull and they can not push.
- Two muscles are required to move a bone at a joint.
- When one muscle contracts, the other muscle relaxes.
- For example to move the lower arm up and down biceps and triceps muscles are required.
- When we raise our lower hand the biceps in front become short by contraction and the triceps at the back stretch to pull up the arm.
- When we lower our arm the triceps at the back contract and biceps stretch to pull the arm down.
(b) Circulatory system – importance :
- It is one of the important system consisting of heart, blood vessels and blood.
- It transports respiratory gases, nutrients, hormones and waste materials within the body.
- If protects the body from harmful pathogens.
- Regulates the body temperature.
- The heart pumps blood continuously throughout our lifetime.
Question 2.
Describe construction of eye with neat diagram.
Answer:
Eyes help us to see things around us i.e., their colour, shape, size whether they are near or far, moving or at rest. The eyelids and eyelashes keep the eyes safe. The eye has three main parts namely cornea, iris and pupil.
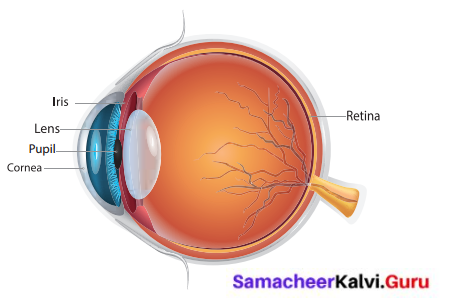
Question 3.
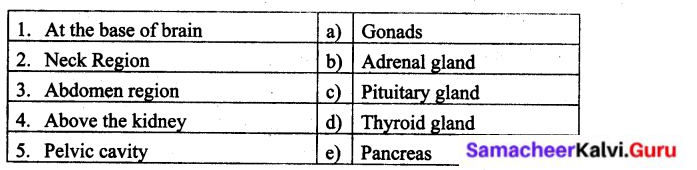
Tabulate the names of glands of endocrine system and their locations.
Answer:
Glands:
- Pituitary gland
- Pineal Gland
- Thyroid Gland
- Thymus Gland
- Pancreas (Islets of Langerhans)
- Adrenal Gland
- Gonads
Location:
- At the base of brain
- At the base of brain
- Neck
- Chest
- Abdomen
- Above the kidney
- Pelvic cavity
![]()
Question 4.
Draw and lable the parts of kidney.
Answer:
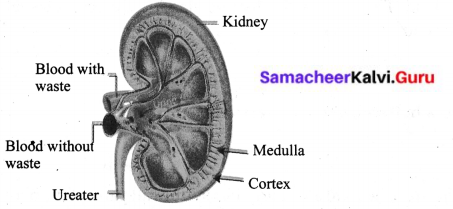
Question 5.
List the parts of excretory system and write their functions.
Answer:
- Renal artery : Brings blood containing oxygen and urea from the aorta to the kidneys.
- Renal vein : Brings filtered blood from the kidneys to the inferior vena cave.
- kidneys : Regulate the chemical composition Of fluids in the body.
- Ureter : Carries urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder.
- Urinary bladder : An expandable, muscular sac that retains urine until it is discharged from the body.
- Urethra : The tube through which urine is discharged from the body, it is surrounded by muscles that allow us to control urination.
Question 6.
Give any five endocrine glands and their location.
Answer:
| (Glands) | (Location) |
| Pituitary gland | At the base of brain |
| Pineal Gland | At the base of brain |
| Thyroid Gland | Neck |
| Thymus Gland | Chest |
| Pancreas (Islets of Langerhans) | Abdomen |
| Adrenal Gland | Above the kidney |
| Gonads | Pelvic cavity |