You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 6th Social Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 6th Social Science History Solutions Term 2 Chapter 2 Great Thinkers And New Faiths
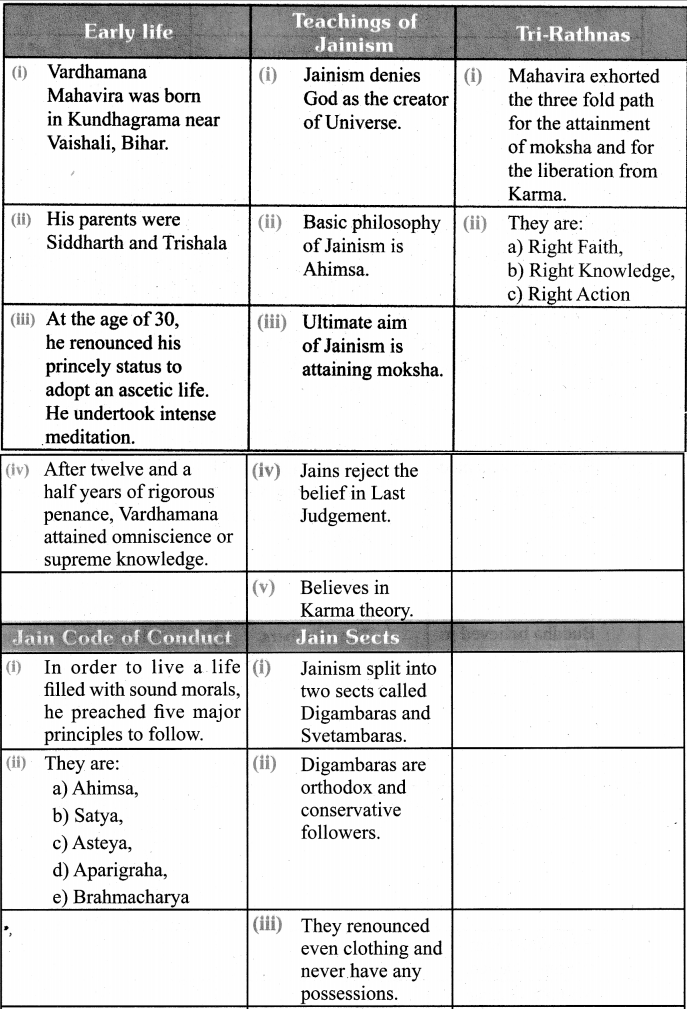
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Social Science Great Thinkers And New Faiths Textual Evaluation
I. Choose the correct answer:
Great Thinkers And New Faiths Questions 1.
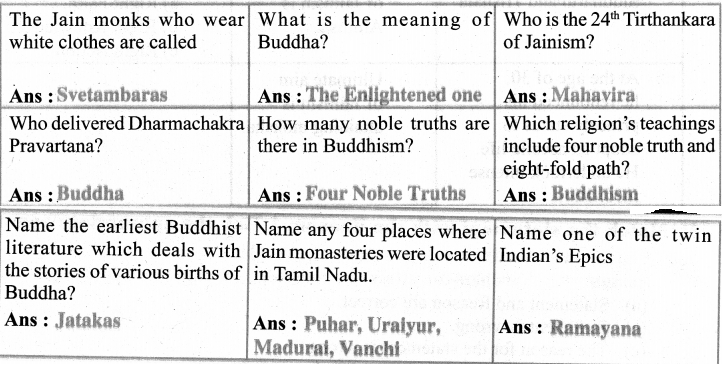
What is the name of the Buddhist scripture?
(a) Angas
(b) Tripitakas
(c) Tirukkural
(d) Naladiyar
Answer:
(b) Tripitakas
Great Thinkers And New Faiths Book Back Answers Questions 2.
Who was the first Tirthankara of Jainism?
(a) Rishabha
(b) Parsava
(c) Vardhamana
(d) Buddha
Answer:
(a) Rishabha
Great Thinkers And New Beliefs Class 6 Questions 3.
How many Tirthankaras were there in Jainism?
(a) 23
(b) 24
(c) 25
(d) 26
Answer:
(b) 24
Great Thinkers And New Beliefs Questions 4.
Where was the third Buddhist Council convened?
(a) Rajagriha
(b) Vaishali
(c) Pataliputra
(d) Kashmir
Answer:
(c) Pataliputra
Samacheer Kalvi Guru 6th Social Science Term 2 Questions 5.
Where did Buddha deliver his first sermon?
(a) Lumbini
(b) Saranath
(c) Taxila
(d) Bodh Gaya
(b) Saranath
II. Match the statement with the Reason, Tick the appropriate answer:
6th Standard Social Guide Questions 1.
Statement : A common man could not understand upanishads.
Reason : Upanishads were highly philosophical.
(a) Statement and its Reason are correct.
(b) Statement is wrong.
(c) Statement is true, but the Reason for that is wrong.
(d) Both Statement and Reason are wrong.
Answer:
(a) Statement and its Reason are correct.
6th Social Guide Questions 2.
Statement : The Jatakas are popular tales.
Reason : Frescoes on the ceilings and walls of Ajanta caves depict the Jataka Tales.
(a) Statement and its Reason are correct
(b) Statement is wrong
(c) Statement is true; but the Reason for that is wrong
(d) Both Statement and Reason are wrong
Answer:
(a) Statement and its Reason are correct
6th Standard Social Science Guide Pdf Questions 3.
Find out the correct answer:
Buddha Vlharas are used for
- Education
- Stay of Buddhist monks
- Pilgrims stay
- Prayer hall
(a) 2 is correct
(b) Both 1 and 2
(c) 1, 2, 4 are correct
(d) Neither I nor II
6th Std Social Science Guide Questions 4.
Consider the following statements regarding the causes of the origin of Jainism and Buddhism.
- Sacrificial ceremonies were expensive.
- Superstitious beliefs and practices confused the common man.
Which of the above statement (s) is/are correct?
(a) Only I
(b) Only II
(c) Both I & II
(d) Neither I nor II
Answer:
(c) Both I & II
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Social Guide Term 2 Questions 5.
Which of the following about Jainism is correct?
(a) Jainism denies God as the creator of universe.
(b) Jainism accepts God as the creator of universe.
(c) The basic philosophy of Jainism is idol worship.
(d) Jains accept the belief in Last Judgement.
Answer:
(a) Jainism denies God as tlie creator of universe.
Questions 6.
Circle the odd one:
Parsava, Mahavira, Buddha, Rishaba
Answer:
Buddha
Questions 7.
Find out the wrong pair:
(a) Ahimsa – not to injure
(b) Satya – to speak truth
(c) Asteya – not to steal
(d) Brahmacharya – married status
Answer:
(d) Brahmadiarya – married status
Questions 8.
All the following statements are true of Siddhartha Gautama except:
(a) He is the founder of Hinduism,
(b) He was bom in Nepal.
(c) He attained Nirvana.
(d) He was known as Sakyamuni.
Answer:
(a) He is the founder of Hinduism.
III. Fill in the blanks :
- The doctrine of Mahavira is called_______
- _______is a state of freedom from suffering and rebirth.
- _______was the founder of Buddhism.
- Thiruparthikundram, a village in Kanchipuram was once called_______
- _______were built over the remains of Buddha’s body
Answer:
- Triratnas
- Moksha
- Gauthama Buddha
- Jinn Ranchi
- Sinpas
IV. True or False:
- Buddha believed in Karma.
- Buddha had faith in caste system.
- Gautama Swami compiled the teachings of Mahavira.
- Viharas are temples.
- Emperor Ashoka followed Buddhism.
Answer:
- True
- False
- True
- False
- True
V. Match the following:
- Angas (a) Vardhamana
- Mahavira (b) monks
- Buddha (c) Buddhist shrine
- Chaitya (d) Sakyamuni
- Bhikshus (e) Jain text
Answer:
- (e)
- (a)
- (d)
- (c)
- (b)
VI. Answer in one or two sentences:
Question 1.
What are the Triratnas (three jewels) of Jainism?
Answer:
Triratna (Three Jewels) of Jainism are
- Right Faith
- Right Knowledge
- Right action.
Question 2.
What are the two sects of Buddhism?
Answer:
- Hinayana
- Mahayana
Question 3.
What does Jina mean?
Answer:
Jina means conquering self and the external world.
Question 4.
Write any two common features of Buddhism and Jainism.
Answer:
- Both denied the authority of Vedas
- Both opposed blood sacrifices
Question 5.
Write a note on Buddhist Sangha.
Answer:
- Sangha, meaning ‘association’ for the propagation of Buddha’s faith.
- It was formed to propagate Buddha’s faith.
- The members were called Bhikshus (monks).
- They led a life of austerity.
Question 6.
Name the Chinese traveller who visited Kancheepuram in the seventh century AD (CE).
Answer:
Hieun Tsang
Question 7.
Name the female jain monk mentioned in Silapathikaram.
Answer:
Silapathikaram mentions that when Kovalan and Kannagi were on their way to Madurai, Gownthiyadigal a female jain monk blessed the couple and accompanied them.
VII. Answer the following :
Question 1.
Name the eight-fold path of Buddhism.
Answer:
The Eight Fold Path of Buddhism is given below
- Right view
- Right Thought
- Right Speech
- Right Action
- Right Livelihood
- Right Effort
- Right Knowledge
- Right Meditation
Question 2.
What are the five important rules of conduct in Jainism?
Answer:
- Ahimsa – not to injure any living beings
- Satya – to speak truth
- Asteya – not to steal
- Aparigraha – not to own property
- Brahmacharya – Celibacy
Question 3.
Narrate four noble truths of Buddha?
Answer:
Buddha’s Four Noble Truths are given below,
- Life is full of sorrow and misery.
- Desire is the cause of misery.
- Sorrows and sufferings can be removed by giving up one’s desire.
- The desire can be overcome by following the right path (Noble eight-fold path)
Question 4.
Write any three differences between Hinayana and Mahayana sects of Buddhism?
Answer:
Hinayana:
- Did not worship idols or images of Buddha > Practiced austerity
- Used Prakrit language
Mahayana:
- Worshiped images of Buddha
- Observed elaborate rituals
- Used Sanskrit language
Question 5.
Jainism and Buddhism flourished in Sangam period. Give any two evidences for each.
Answer:
(i) In ancient Tamil literature, Jainism is referred to as Samanam. There is a Samanar Hill or Samanar Malai in Keelakuyilkudi village, 15 km away from Madurai. The images of Tirthankaras created by Jain monks are found in the hill. It is a protected monument of Archaeological Survey of India.
(ii) There is a reference to Aravor Palli, place of living for Jain monks, in Manimegalai.
(iii) Buddhism spread to Tamil Nadu much later than Jainism. Manimekalai, one of the epics of the post-Sangam age is a Buddhist literature.
(iv) There is an elaborate description about Kanchipuram in classical epic Manimegalai
VIII. HOTS:
Question 1.
Karma – a person’s action. Name any 10 good actions (deeds).
Answer:
Karma means the sum of a person’s actions in this and previous state of existence, viewed as deciding their fate in future existence.
Some of the good deeds or actions are given below to be followed in our day to day life.
- Always remember and respect Matha, Pitha, Guru and Dhaivam (God).
- Develop the habit of charity.
- Help a friend in need.
- Plant a tree.
- Donate blood.
- Be kind to everyone especially to animals
- Be polite and respect people.
- Conserve energy.
- Be smiling because most smiles are started by another smile.
- Be Positive always.
- Have patience with stressful people.
- Give a compliment.
- Volunteer for charity.
- Be tidy and clean
- Donate books to library.
IX. Student Activity
Question 1.
Read any one story from Jatakas and write a similar story on your own.
THE OX WHO ENVIED THE GOAT
Once upon a time there was an Ox named Big White. He had a younger brother named Little White. These two brothers did all the carting on a large farm.
The farmer had one daughter and she was soon to be married.
The farmer’s wife gave orders that the Goat, in the farm, should be fattened for the wedding feast.
Little White noticed that the Goat was fed on choice food.
He said to his brother, “How is it, Big White, that I and you are given only straw and grass to eat, while we do all the hard work on the farm? That lazy Goat does nothing S but eat the choice food the farmer gives him.”
Said his brother, “My dear Little White, don’t envy him. That little Goat is eating the? food of death! He is being fattened for the wedding feast. Eat your straw and grass and; be content and live long.”
Not long afterwards the fattened Goat was killed and cooked for the wedding feast. Then Big White said, “Did you see what happened to the Goat after all his fine feeding?’ “Yes,” said the little brother, “we can go on eating plain food for years, but the poor little j Goat ate the food of death and now he is dead. His feed was so good while it lasted, but I the Goat did not last long.”
Moral: Be content with what you have and don’t envy others.
Question 2.
Make a tabular column in the following headings.
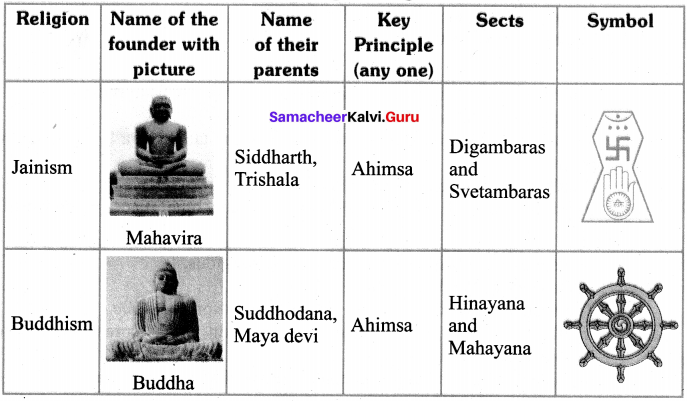
Question 3.
Place the following word In the appropriate column.
Words: Jinn, Mahayana, Ttrthankarai, Stupas Nirvana, Digambara, Tripitakas, Agama
Jainism:
Jina
- Tirthankaras
- Digambara
- Agama
Buddhism:
- Mahayana
- Stupas
- Nirvana
- Tripitakas
Question 4.
Task cards activity:
Make informative cards for the following religions. Hinduism, Christianity, Islam, Buddhism, Jainism
Hinduism:
- It is an Indian Religion or dharma or a way of life.
- It is widely practised in the Indian sub continent.
- Hinduism has been called the oldest religion in the world.
- It is a synthesis of various Indian cultures and traditions with diverse roots and no founder.
- Vedic texts Shrutis and Smritis play a great role in Hinduism.
Christianity:
- Christianity religion is based on the life and teachings of Jesus.
- Jesus is known by Christians as the Christ or Messiah.
- The Christ is the focal point of the Christian Faith.
- It is the world’s largest religion.
- Christians behave that Jesus is the Son of God and the Saviour of Humanity.
- Christianity has played a major role in shaping of western civilization.
- Their holy book is Bible.
Islam:
- Islam teaches that there is only one God, Allah.
- Mohammed is a prophet and the Messenger of God.
- It is the world’s second largest religion.
- Islam teaches that God is merciful, all powerful, unique.
- Its followers are known as Muslims.
- Their holy book is Quran.
Buddhism:
- Buddhism came into existence in 6th Century BC (BCE) in India.
- Gautama Buddha was the founder of Buddhism.
- Tlie teaching of Lord Buddha were simple and taught in a language known to people.
- Buddhist Sanghas propagated his faith.
- It spread to Central Asia, China, Japan and many other places in the world.
Jainism:
- Jainism is one of the world’s oldest living religions.
- Mahavira was the founder of Jainism.
- The basic philosophy of Jainism is Ahimsa or Non- violence.
- Intelligible teachings and perseverance of Jain monks spread the religion in various parts of India.
- In ancient Tamil Literature, Jainism is referred to as Samanam.
Question 5.
Make A Venn diagram to indicate similarities and dissimilarities of Jainism and Buddhism.
Answer:
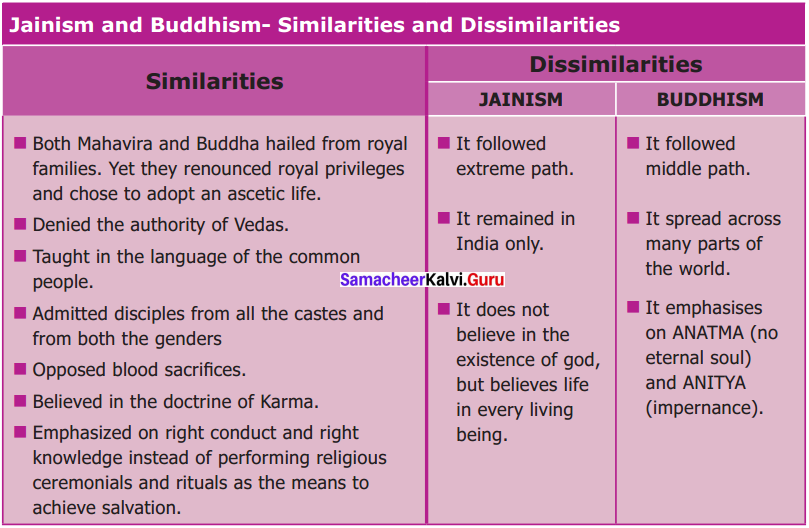
Question 6.
Solve the Puzzle
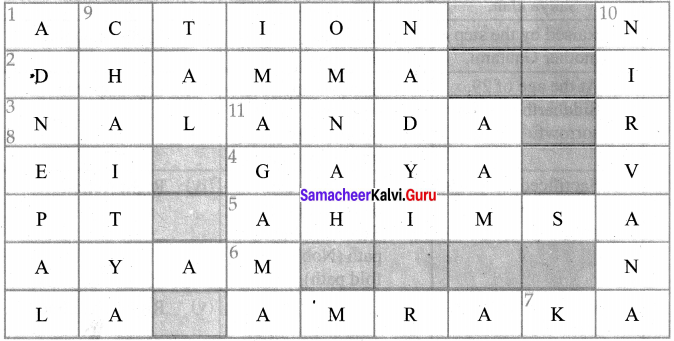
Left to right
1. One of the Tri Rathna: Right
2. Buddha’s teachings are referred as
3. A great centre of education
4. The place where Buddha attained enlightment
5. Not to injure any living being
Answer:
1. ACTION
2. DHAMMA
3. NALANDA
4. GAYA
5. AHIMSA
Right to left
6. Mother of Siddhartha
7. The Quality of man’s life depends on his deed
Answer:
6. MAYA
7. KARMA
Top to bottom
8. Lumbini is in
9. Buddhist prayer hall
10. A state of freedom from, birth
11. jain scripyure compli
Answer:
1. NEPAL
2. CHAITYA
3. NIRVANA
4. AGAMA
X. Life Skills
Question 1.
Create a story board for jaiitism/Buddhistii in a chart.

A Story Board Model I
(a) Buddhism
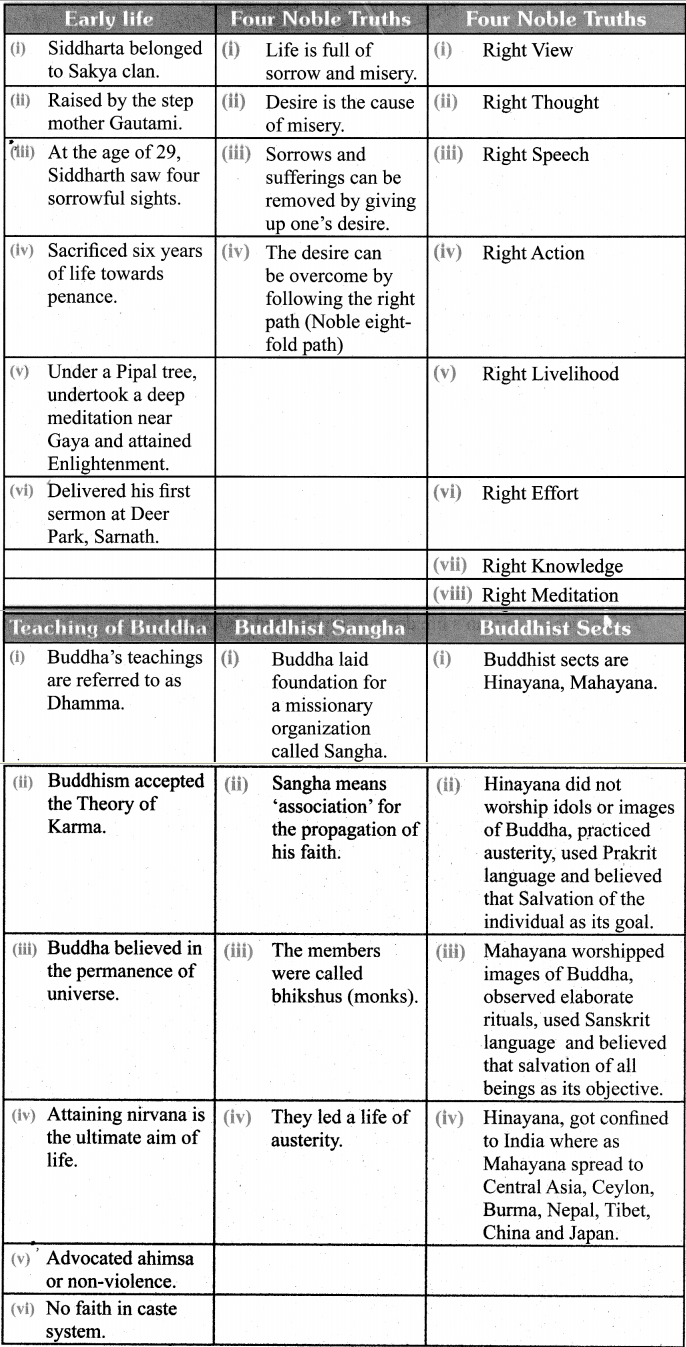
A Story Board – Model II
(b) Jainism
XI. Answer Grid:
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Social Science Great Thinkers And New Faiths Additional Questions
I. Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
Vardhamana was born in
(a) Lumbini
(b) Kundhagrama
(c) Sanchi
(d) Gaya
Answer:
(b) Kundhagrama
Question 2.
Siddhartha saw four sorrowful sights at the age of ………………
(a) 19
(b) 29
(c) 39
(d) 49
Answer:
(b) 29
Question 3.
Vardhamiana means
(a) Healthy
(b) Wealthy
(c) Happy
(d) Prosperous
Answer:
(d) Prosperous
Question 4.
The language used in Mahayana is …………….
(a) Sanskrit
(b) Prakrit
(c) Brahmi
(d) Aramic
Answer:
(a) Sanskrit
Question 5.
Samanam refers to
(a) Hindusim
(b) Buddhism
(c) Jainism
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(c) Jainism
Question 6.
Sakya Muni refers to
(a) Buddha
(b) Mahavira
(c) Sages
(d) Thirthankara
Answer:
(a) Buddha
Question 7.
Buddha was opposed to
(a) rituals
(b) sacrifices
(c) caste system
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) AH of the above
Question 8.
Sangha means
(a) Prayer Hall
(b) Monument
(c) Monastries
(d) Association
Answer:
(d) Association
Question 9.
Mahayana sect used to spread the principles of Buddhism
(a) Sanskrit
(b) Tamil
(c) Prakrit
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(a) Sanskrit
Question 10.
Buddhism received royal patronage from
(a) Ashoka
(b) Kanishka
(c) Harsha
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Question 11.
The classical epic gives an elaborate description about Kanehipuram,
(a) Kundalakesi
(b) Valaiyapathi
(c) Manimekalai
(d) Jeevaka Chinthamani
Answer:
(c) Manimekalai
II. Match the statements with the Reason. Tick the appropriate answer:
Question 1.
Statement : Vardhamana was known as kevala,
Reason : Vardhamana attained omniscience or supreme knowledge
(a) Statement and Reason are correct.
(b) Statement is wrong.
(c) The reason for the statement is wrong.
(d) Both Statement and Reason are reduce space wrong.
Answer:
(a) Statement and Reason are correct
Question 2.
Statement : Teachings of Lord Buddha were single and reached people.
Reason : Buddha taught in a language which people used for communication.
(a) Statement is wrong.
(b) Statement is true.
(c) Statement and Reason are correct. –
(d) Both Statement and Reason are wrong.
Answer:
(c) Statement and Reason are correct
Question 3.
Find out the correct answer:
Hinayana Sect of Buddhism followed
- Elaborate Rituals
- Prakrit language
- Worship of the images of the Buddha
- Salvation of the individual.
(a) 1 is correct
(b) 2 and 4 are correct
(c) 3 is correct
(d) 1 and 3 are correct
Answer:
(b) 2 and 4 are correct
Question 4.
Consider the following statements regarding the causes for the spread of Buddhism.
- Buddha’s emphasis was on observance of Dhamma.
- Buddhist Sanghas played an important role in spreading the messages of Buddha
Which of the above statement(s) is/are correct?
(a) Only I
(b) Only II
(c) Both I and II
(d) Neither I nor II
Answer:
(c) Both I and II
Question 5.
Which of the following about Buddhism is correct?
(a) The fourth Buddhist council was held at Rajagriha.
(b) Buddhism spread to Tamil Nadu much later than Jainism.
(c) Hieun Tsang visited Madurai in the seventh century AD.
(d) Buddhism followed extreme path.
Answer:
(b) Buddhism spread to Tamil Nadu much later than Jainism, j
Question 6.
Circle the odd one:
(a) Chaitya
(b) Stupas
(c) Agama Siddharta
(d) Viharas
Answer:
(e) Agama Siddharta
Question 7.
(a) Angans – Jain Texts
(b) Satya – Truth
(c) Digambaras – Progressive
(d) Dharmapala – Great Scholar
Answer:
(c) Digambaras – Progressive
Question 8.
All the following statements are true of the teachings of Buddha except
(a) Buddhism denied the theory of Karma.
(b) Buddha’s teachings are referred to as Dhammas.
(c) Buddha believed in the laws of universe.
(d) Buddha advocated Ahimsa.
Answer:
(a) Buddhism denied the theory of Karma.
III. Fill in the blanks:
- Historian Will Durant referred to 6th century BC as _______
- Vardhamana was bom in Kundhagrama near _______ Bihar
- The word Jain derives from the Sanskrit word _______
- Basic Philosophy of Jainism is _______
- Literature from the cycle of birth and death is known as _______
- A chief desciple of Mahavira was _______
- Digambaras are the _______ followers of Jainism.
- In ancient Tamil literature, Jainism is referred to as _______
- Silappathikaram mentions about a female Jain Monk called _______
- Siddharta was raised by his step mother _______
- At the age of _______ Siddhartha left the palace and became a hermit.
- Dharma Chakra Pravartana means _______
- The members of the Sangha were called _______
- Buddhist monasteries became great centres of _______
- Buddhism crossed the frontiers of _______
Answers:
- Shower of stars
- Vaishali
- Jina
- Ahimsa
- Moksha
- Gautama swami
- Orthodox
- Samanam
- Gownthiyadigal
- Gautami
- 29
- Turning of the Wheel of Law
- Bhikshus / Monks
- Education
- Indian sub-continent
IV. State True or False:
- ‘Shower of Stars’, the remark was given by Will Durant.
- Gender discrimination contributed to the New awakening.
- Mahavir did not like meditation.
- The real founder of Jainism was Rishaba.
- Pandavar Padukkai is the bed of Jain Saints.
- Buddha sat under a Neem Tree for Meditation.
- Desire causes misery.
- The wheel of life represents the Jain view of the world.
- Buddhism spread to Central Asia, Ceylon and Burma.
- Nalanda was a Chaitya.
- Buddhism and Jainism Denied the authority of Vedas.
- The second Buddhist council was held at Vaishali.
Answer:
- True
- True
- False
- False
- True
- False
- True
- False
- True
- False
- True
- True
V. Match the following:
- Rishaba (a) Not to own property
- Tri Rathna (b) Karuvur
- Aparigraha (c) Samath
- Vanchi (d) Thirthankara
- Deer Park (e) Three Jewels [Ans
Answer:
- (d)
- (e)
- (a)
- (b)
- (c)
VI. Answer In one or two sentences :
Question 1.
Why Is Vardhamana called Kevala?
Answer:
- After twelve and a half years of rigorous penance, Vardhamana attained omniscience or supreme knowledge.
- Hence Vardhamana Mahavira known as Kevala.
Question 2.
What is “Dharma Chakra Pravartana”?
Answer:
- Buddha delivered his first sermon at Deer Park in Sarnath.
- This was called “Dharma Chakra Pravartana”.
Question 3.
Mention the causes for the spread of Jainism in India.
Answer:
Use of people’s language, Intelligible teachings, Support from rulers and traders and Perseverance of Jain monks all these were the main causes for the spread of Jainism in India.
Question 4.
Name the Royal patronage who helped the spread of Buddhism.
Answer:
- Ashoka
- Kanishka
- Harsha
Question 5.
Why was Buddha known as Sakya Muni?
Answer:
- Siddhartha was a Kshatriya prince.
- He belonged to the ruling Sakya clan.
- Hence Buddha was known as Sakya Muni.
Question 6.
What are Fresco Paintings?
Answer:
- Frescoes are paintings of the Ajanta caves in Aurangabad, Maharashtra.
- They depict the Jataka Tales.
Question 7.
Explain the term middle path.
Answer:
Middle path refers to neither indulging in extreme attachment to worldly pleasure nor committing severe penance.
VII. Answer the following :
Question 1.
Mention the causes for the spread of Buddhism.
Answer:
- Simplicity of the teachings of Buddha in local language appealed to people.
- Buddhism rejected elaborate religious customs whereas the practice of orthodox Vedic religion insisted on expensive rituals and sacrifices.
- Buddha’s emphasis was on the observance of Dhamma.
- Buddhist Sanghas played an important role in spreading the messages of Buddha.
- Royal patronage under Ashoka, Kanishka and Harsha also helped the causes of Buddhism.
- Viharas or the Buddhist monasteries became great centres of education. One such centre was Nalanda, where Hiuen Tsang, the Chinese pilgrim, studied for many years.
Question 2.
Explain the similarities of Buddhism and Jainism,
Answer:
- Both Mahavira and Buddha hailed from royal families. Yet they renounced royal privileges and chose to adopt an ascetic life.
- Denied the authority of Vedas.
- Taught in the language of the common people.
- Admitted disciples from all the castes and from both the genders.
- Opposed blood sacrifices.
- Believed in the doctrine of Karma.
- Emphasized on right conduct and right knowledge instead of performing religious ceremonials and rituals as the means to achieve salvation.
Question 3.
Write about the influence of Buddhism in Tamil Nadu.
- Buddhism spread to Tamil Nadu much later than Jainism.
- Manimekalai, one of the epics of the post-Sangam age is a Buddhist literature.
- There is an elaborate description about Kanchipuram in classical epic Manimegalai.
- Kanchipuram was a famous Buddhist Centre, from where Dinnaga, the famous Buddhist logician, and Dharmapala, a great scholar of Nalanda University hailed.
- Hieun Tsang who,visited Kanchipuram in the seventh century A.D. (CE). noticed the presence of 100 feet stupa built by Ashoka there.
Question 4.
Write a note on
a) Confucianism
b) Zoroastrianism
(a) Confucianism
- Confucianism originated in China.
- It is also known as Ruism.
- The Chinese philosopher Confucius contributed his teachings.
- He emphasised on the importance of the family and social harmony, rather than on spiritual values.
- The core of Confucianism is humanistic.
(b) Zoroastrianism
- Zoroastrianism is one of the world’s oldest religions that remain active.
- It originated in Percia (Iran)
- The Iranian speaking prophet Zoroaster exalts a deity of wisdom, Ahura Mazda as its Supreme Being.
- Zend Avesta is the most important text of this religion.
- Zoroastrians usually pray in the presence of some form of fire.
VIII. HOTS:
Question 3.
Thiruparathi Kundram, Sithanavasal and Chithara Malai are closely connected with Jainism – how?
Answer:
(a) Tbiruparthi Kundram
- It is located in the suburbs of Kanchipuram.
- The Jain Temple here in the standing example for the existence of Jainism in Kanchipuram in ancient period.
- Built in 9th Century by Pallavas, there are two Jain temples named as Trilokyanatha temple and Chandra Prabha temple.
- The suburb where these twin temples are located is called Jain Kanchi.
- Tourists can see beautiful paintings on the ceilings of the temple.
- The main deity Mahavira was made up of bright pink stone.
- Temple was built out of yellow stone.
- It has inscriptions belonging to the 9th Century.
- Currently the temple is under the control of Tamil Nadu Archaeological department.
(b) SittanaVasal
- It Sittanavasal is a small hamlet in Pudukottai district of Tamil Nadu.
- It is known for the Sittanavasal cave, a 2nd century Jain cave complex.
- From the 7th to 9th Century AD the village flourished as a Jain Centre.
- The Sittanavasal cave is also known as Arivar Kovil.
- It is a Jain monastery of the 7th Century, small in size.
- It is noted for its fresco paintings.
- The painting themes depict a beautiful lotus pond and figures, lilies, fish, geese, buffaloes and elephants.
- The cave temples has the sculpture of Jain Thirthankaras.
- Ezhadippattam or Jaina beds is a natural cave, marked by a horizontal floor space. It is laid out with well-polished rock
- beds that were used by Jaina ascetics.
(c) The Chitharal Malai
- The Chitharal Jain monuments is also known as Chitharal Malai kovil.
- It is literally on the hill.
- It is also known as Bhagawathi temple.
- Chitharal is situated on the Thiruchanathar Malai near Chitharal Village, Kanyakumari district.
- Chitharal hills are locally known as Chokkanthoongi Hills.
- There are two monuments found here.
- They were likely built by Digambara Jains in the Ninth Century, when the region was under the influence of Jainism.
- Jain influences in this region was due to the king Mahendra Varma.