Students can Download Science Chapter 5 Reproductive and Modification In Plants Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 7th Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 7th Science Solutions Term 1 Chapter 5 Reproductive and Modification In Plants Questions and Answers
Samacheer Kalvi 7th Science Reproductive and Modification In Plants Textual Evaluation
I. Choose the appropriate answer :
Reproduction and Modification In Plants 7th StandardQuestion 1.
Vegetative propagation by leaves takes place in
(a) Bryophyllum
(b) Fungi
(c) Virus
(d) Bacteria
Answer:
(a) Bryophyllum
Reproduction And Modification In Plants Question 2.
Asexual reproduction in yeast is
(a) Spore formation
(b) Fragmentation
(c) Pollination
(d) Budding
Answer:
(d) Budding
Reproduction And Modification In Plants 7th Standard Book Back Answers Question 3.
Reproductive part of a plant is
(a) Root
(b) Stem
(c) Leaf
(d) Flower
Answer:
(d) Flower
Reproduction And Modification In Plants Class 7 Question 4.
Pollinators are
(a) Wind
(b) Water
(c) Insect
(d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Samacheer Kalvi Guru 7th Science Question 5.
Climbing roots are seen in
(a) Betel
(b) Black pepper
(c) Both of them
(d) None of them
Answer:
(c) Both of them
II. Samacheer Kalvi Guru 7th Science Fill in the blanks :
- The male reproductive part of a flower is __________
- __________ is the basal swollen part of the Gynoecium.
- After fertilization the ovule becomes __________
- Breathing roots are seen in __________ plants.
- Onion and Garlic are example of __________
Answer:
- Androecium
- Ovary
- seed
- mangrove
- Bulb
III. Samacheer Guru 7th Science True (or) False, unrite the correct answer for the false statement.
7th Standard Science Reproduction And Modification In Plants Question 1.
A complete flower has four whorls.
Answer:
True
7th Science Reproduction And Modification In Plants Question 2.
The transfer of pollen to the stigma is known as pollination.
Answer:
True
Samacheer Kalvi Guru Science 7th Question 3.
Conical shaped root is carrot.
Answer:
True
Samacheerkalvi.Guru 7th Science Question 4.
Ginger is an underground root.
Answer:
(False) Correct Statement: Ginger is an underground stem.
Reproduction And Modification In Plants Question 5.
Leaves of Aloe vera are fleshy and store water.
Answer:
True
IV. Match the following :
| 1. | Petal | (a) | Opuntia |
| 2. | Fern | (b) | Chrysanthemum |
| 3. | Phylloclade | (c) | Attracts insect |
| 4. | Hooks | (d) | Spore |
| 5. | Sucker | (e) | Bignonia |
Answer:
- c
- d
- a
- e
- b
V. Reproduction And Modification In Plants Class 7 Very short answers.
Question 1.
Write two types of reproduction in plants.
Answer:
Sexual and Asexual Reproduction.
Question 2.
What are the two important parts of a flower?
Answer:
Androecium and Gynoecium.
Question 3.
Define – pollination.
Answer:
Transfer of pollen grains from the anther to stigma is called pollination.
Question 4.
What are the agents of pollination?
Answer:
Insects, wind, water, animals.
Question 5.
Give example for
(a) Corm
(b) Tuber
Answer:
- Corm-e.g Colocasia
- Tuber – e.g Potato.
Question 6.
What is tendril?
Answer:
- It is an elongated structure produced by the plant to help the plants to climb efficiently.
- e.g In pea, the terminal leaflets are modified into a tendril.
Question 7.
What are thorns?
Answer:
- Thoms are pointed and sharp structures formed in a plant.
- Leaves other parts may be modified into thorns.
- It helps the plant to safeguard itself from animals. Thoms may also help in climbing.
VI. 7th Science Reproduction And Modification In Plants Short answer.
Question 1.
Differentiate bisexual flower from unisexual flower.
Answer:
| S. No. | Bisexual flower | Unisexual flower |
| (a) | It has Androecium and Gynoecium | It has only Androecium or Gynoecium |
| (b) | It can undergo self pollination and cross pollination e.g : Hibiscus | They can be pollinated only by cross pollination eg : papaya. |
Question 2.
What is cross pollination?
Answer:
- Pollen grains are transferred from the anther of one flower to the stigma of another flower of the same kind or different plant.
- Plants need to produce pollen grains in larger quantities to increase the chance of pollination.
- Cross pollination does introduce variations in characteristics of new plants.
- Cross pollination is brought about by agencies like wind, water, animals and Insects of plums, apples.
Question 3.
Write notes on phyllode.
Answer:
In Acacia auriculiformis, petioles expand to form leaf like structure. They carry out the function of leaf (Photosynthesis).
VII. Answer in Details.
Question 1.
Write a brief account on pollination.
Answer:
Transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma is called pollination. There are two types of Pollination.
(a) Self Pollination
(b) Cross Pollination
(a) Self pollination
- Pollen grains are transferred from the anther to the stigma of the same flower or to another flower of the same plant.
- Plants do not need to produce pollen grains in a large quantity for self pollination.
- It does not produce changes in the characteristics of new plants
(b) Cross Pollination
- Pollen grains are transferee! for the anther of one flower to the stigma of anoter flower of the same kind or different plant.
- Plants need to produce pollen grains in larger quantities to increase the chance of pollination.
- Cross pollination does introduce variations in characteristics of new plants, e.g (apples, plums)
- Agents like wind, water, insects and animals are helpful for pollination and are known as pollinators.
- Wind pollinated plants produce pollen which are light. Insect pollinated flowers are brightly coloured and produce lot of pollen which sticks to the body of insects and are caused to other plants.
- Pollination that occurs in nature is called Natural pollination.
- Pollination between desired plants can be brought about by artificial methods.
Question 2.
Explain the underground stems.
Answer:
There are some stems that grow under the ground to store food. These underground stems swell and become thick.
There are four types of underground stems:
- Rhizome.
- Corm
- Tuber
- Bulb
(i) Rhizome : It is an underground thick stem with nodes and intemodes with scale , leaves at the node. It grows horizontally and has an irregular shape. Rhizome have buds. It gives rise to new stem and leaves. E.g. Ginger and Turmeric.
(ii) Corm: This underground stem is round in shape and flat at the top and bottom. It
is a condensed form of rhizome and bears one or more buds in the axils of scale leaves. Daughter plants arise from their buds. E.g. Colocasia.
(iii) Tuber: It is an enlarged, spherical underground stem that stores food. It has many dormant buds on its surface known as “Eyes”. If we plant a part of tuber with the bud, it grows into a new plant. E.g. Potato.
(iv) Bulb: It is condensed stem which is disc like and stores food in the fleshy leaves. The bulb has two types of leaves.
- Fleshy Leaves
- Scaly Leaves
The upper part of the stem has a terminal bud and it is covered by many scaly leaves, the inner fleshy leaves store food as seen in Garlic and Onion
VIII. Higher Order Questions :
Question 1.
Ginger is considered to be a stem, not a root. Why?
Answer:
Ginger has the following characteristics of a stem.
- It has scale leaves
- It has nodes and Intemodes
- It has axillary buds and a terminal bud.
Therefore Ginger is considered to be a stem but is is a modified underground stem which stores food.
Question 2.
What will happen if pollen grain of rose gets deposited on stigma of lily flower? Will pollen germination takes place? Why?
Answer:
No pollen of rose will get wasted and will not germinate on the stigma of lily flower. This is because pollen of a flower is compatible (match) only with stigma of a flower of the same species.
IX. Assertion and Reasoning types of Question :
Question 1.
Assertion : Pollination and fertilization in flowers, produces fruits and seeds. Reasoning :After fertilization the ovary becomes fruit and ovule becomes seed.
(a) Assertion is correct, Reasoning is incorrect
(b) Assertion is incorrect, Reasoning is correct
(c) Assertion is correct, Reasoning is correct
(d) Assertion is incorrect, Reasoning is incorrect
Answer:
(c) Assertion is correct, Reasoning is correct.
Question 2.
Assertion : The example of conical root is carrot.
Reasoning : It is an adventitious root modification.
(a) Assertion is incorrect, Reasoning is correct.
(b) Assertion is incorrect, Reasoning is incorrect
(c) Assertion is correct, Reasoning is correct
(d) Assertion is correct, Reasoning is incorrect
Answer:
(a) Assertion is incorrect, Reasoning is correct.
X. Picture Based question.
Question 1.
Observe the picture and draw the labels.
Parts of a Flower
Label the parts below :
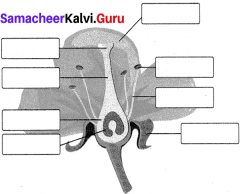
Answer:
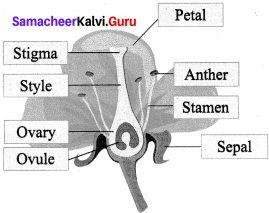
- Stigma
- Pistil
- Filament
- Ovule
- Sepal
- Stamen
Question 2.
Identify the four plants shown in the following Name the different modification in each of them.
| Name | Modification | |
| 1. | Garlic | |
| 2. | Turnip | |
| 3. | Rose plant |
Answer:
| Name | Modification | |
| 1. | Garlic | Underground stem modification |
| 2. | Turnip | Top Root modified for storage (Top shaped) |
| 3. | Rose plant | Stem used for vegetative propagation / Asexual Reproduction by cutting |
| 4. | Maize | Stilt Roots (Adventitious roots produced from the node for mechanical support). |
Samacheer Kalvi 7th Science Reproductive and Modification In Plants Intext Activities
Activity 1
Using the information from the above complete the following table:
| SI.No. | Name of the flower | Complete / incomplete | Unisexual / bisexual | If unisexual male or female |
| 1. | Hibiscus | Complete | Bisexual | Both male & female present is same flower |
| 2 | Pumpkin | Incomplete | Unisexual | Male in separate single flower & female in separate single flower |
| 3. | Rose | Complete | Bisexual | Both male & female present is same flower |
| 4. | Coconut | Incomplete | Unisexual | Male in separate single flower & female in separate single flower |
| 5. | Jasmine | Complete | Bisexual | Both male & female present is same flower |
Samacheer Kalvi 7th Science Reproductive And Modification Additional Questions
I. Choose the appropriate answer.
Question 1.
___________ do not produce spores.
(a) Algae
(b) Fungi
(c) Datura
(d) Ferns
Answer:
(c) Datura
Question 2.
___________ have the smallest seeds in the plant kingdom.
(a) Coconut
(b) Orchids
(c) Onion
(d) Pumpkin
Answer:
(b) Orchids
Question 3.
Breathing Roots are seen in ___________
(a) Tarpa
(b) Avicennia
(c) Eicchomia
(d) pisum
Answer:
(b) Avicennia
Question 4.
___________ is a parasite.
(a) Cuscuta
(b) Hibiscus
(c) yeast
(d) Spirogyra
Answer:
(a) Cuscuta
Question 5.
In ___________ sepal is seen on the fruit after fertilization
(a) Brinjal
(b) Pumpkin
(c) Onion
(d) Garlic
Answer:
(a) Brinjal
II. Fill in the Blanks.
- The tissue seen in epiphytic roots is called _________
- Cactus is a example for _________
- Ginger and _________ are examples of Rhizome.
- In Gloriosa _________ is modified into a tendil leaf tip.
- Spirogyra reproduces by _________
Answer:
- Velamen
- Phylloclade
- Turmeric
- leaf tip
- fragmentation
III. True or False – if false give the correct statement.
Question 1.
In cactus stem is modified into spines.
Answer:
(False) In cactus, leaf is modified into spines
Question 2.
Ovules fall off after fertilization.
Answer:
(False) Style and stigma fall off after fertilization.
Question 3.
In Nepenthes, leaf is modified into a flask shaped structure.
Answer:
True
Question 4.
Tuber is an enlarged underground root.
Answer:
(False) Tuber is an enlarged underground stem.
Question 5.
Scaly leaves are seen in onion.
Answer:
True
IV. Match the following :
Question 1.
| Vanda | (a) | Climber |
| Pea | (b) | epiphyte |
| Eicchomia | (c) | offset |
| wild strawberry | (d) | Runner stolon |
Answer:
- b
- a
- c
- d
Question 2.
| Pollen | (a) | anther |
| Ovule | (b) | protection |
| stamen | (c) | Powdery |
| Sepal | (d) | Seed |
Answer:
- c
- d
- a
- b
V. Assertion and Reason types of Question.
(a) Assertion is correct, Reason is incorrect
(b) Assertion is incorrect, Reason is correct
(c) Assertion is correct, Reason is correct
(d) Assertion is incorrect, Reason is incorrect
Assertion : In potato shoot arises from eyes.
Reason : Eyes represent the buds.
(c) Assertion is correct, Reasoning is correct.
Assertion : In Banyan prop roots grow horizontally from the tree.
Reason : They give additional support to the tree.
(b) Assertion is incorrect, Reasoning is correct.
Assertion : Corm is a condensed form of Bulb.
Reason : It has dry and fleshy scale leaves.
(d) Assertion is incorrect, Reasoning is incorrect.
VI. Find the odd one out.
Question 1.
Pollen, anther, ovule, filament Ovule
Reason : It is a part of Gynoecium whereas others are parts of Androecium.
Question 2.
Corm, Bulb, Rhizome, sucker
Answer:
Sucker
Reason : It is a sub aerial stem modification whereas others are underground stem modification.
Question 3.
Haustoria, Velamen, Prop Roots, Phylloda.
Answer:
Phylloda
Reason : It is a leaf modification whereas others are root modifications.
VII. Complete the table
Question 1.
| Underground stem | _____(1)_____ | Ginger |
| _____(2)_____ | Runner | _____(3)_____ |
| Leaf modification | _____(4)_____ | Acacia |
| Root modification | sucking Roots | _____(5)_____ |
Answer:
- Rhizome
- Sub aerial stem
- Centella
- phylloda
- Cuscuta.
Question 2.
| Caly x | _____(1)_____ | _____(2)_____ |
| _____(3)_____ | petal | attract insects |
| Androecium | _____(4)_____ | Male reproductive part |
| _____(5)_____ | _____(6)_____ | Female reproductive part. |
Answer:
- sepal
- protection
- corolla
- stamen
- Gynoecium
- Ovary, style, stigma.
VIII.Very short answers:
Question 1.
Name the whorls of a flower
Answer:
Calyx, corolla, Androecium and Gynoecium.
Question 2.
What is an inflorescence?
Answer:
A group of flowers is called an inflorescence, e.g sunflower.
Question 3.
What is fertilization.
Answer:
Male gamete fuses with the female gamete to form zygote. This process is known as fertilization.
Question 4.
Name the sub aerial modifications of stem.
Answer:
Runner, stolum, sucker, offset.
Question 5.
Name the underground stem modifications.
Answer:
Rhizome, Corm, Tuber, Bulb.
Question 6.
What are sucking Roots?
Answer:
- Sucking roots (or) Haustoria are found in parasite plants.
- These roots penetrate the tissues of host plant and suck nutrients from then, e.g cuscuta.
Question 7.
Differentiate Phyllode and Phylloclade.
Answer:
| Phyllode | Phylloclade |
| Petioles are modified to form leaf like structure, e.g. Acacia. | stem is modified to form leaf like structure, e.g. Cactus. |
Question 8.
What are breathing Roots or Pneumatophores?
Answer:
- Mangrove plants roots which are seen above the ground for the purpose of gaseous exchange.
- These roots are erect, peg like structures with numerous pores through which air circulates.
- These roots are called breathing roots, or pneumatophores. e.g Avicennia.
IX. Short answers.
Question 1.
List the post fertilization changes in a flower.
Answer:
- Calyx sometimes persist with fruit
- Petals wither / fall off
- Androecium fall off
- Pistil remain and develops into a fruit
- Style and stigma fall off
- Ovary enlarges to store food materials and develops into a fruit.
- Ovules present inside the ovary develops into seeds.
Question 2.
Write a note an roots modified for mechanical support.
Answer:
Many Plants require additional support. Such plants develop roots on their aerial parts to provide mechanical support. These roots grow downward and act as supportive organs. There are three types of modified roots for support.
- Prop roots : Roots are modified to provide mechanical support as seen in Banyan tree. These roots grow vertically from horizontal branches of a tree.
- Stilt roots : In sugarcane, and maize adventitious roots arise from the nodes in cluster at the base of the stem. These roots are called stilt roots which gives additional support.
- Climbing roots : In betel and black pepper, nodes or intermodes bear roots which help in climbing.
Question 3.
How do Epiphytic roots differ from Sucking roots?
Answer:
| Epiphytic roots | Sucking roots |
| Vanda is an epiphytic plant, which grows on trees. The velamen tissue present in the epiphytic root, absorbs moisture, to perform photosynthesis. | Cuscuta a parasite plant, climb the trees and other vegetation and use the haustorial roots Sucking roots to penetrate the tissue of the host plant and suck nutrients from them. They are usually found in parasitic plants that depend on the host plants for nutrients. |
Question 4.
Write a note on phylloclade.
Answer:
- Plants growing in deserts try to store water. If the surface area is large, more water is lost by evaporation.
- In plants like cactus, the stem is thick and becomes flat like leaves to do photosynthesis.
- The leaves are reduced to small spines with less surface area. This kind of modification is called phylloclade. e.g. cactus.
Question 5.
What are traps or Insectivorous plants?
Answer:
- These plants grow in nitrogen deficient places. In Nepenthes, the leaves are modified into a flask like structure, which is used to attract insects and other tiny animals.
- The inner wall of the leaf secretes digestive enzymes that help to digest the insects and extract the nitrogen needed for the plant. E.g: Nepenthes.
Question 6.
Differentiate self pollination and cross pollination.
Answer:
| S.no | Self pollination | Cross pollination |
| 1. | Pollen grains are transferred from the anther to the stigma of the same flower or to another flower of the same plant. | Pollen grains are transferred from the anther of one flower to the stigma of another flower of the same kind or different plant. |
| 2. | Plants do not need to produce pollen grains in a large quantity for self pollination | Plants need to produce pollen grains in larger quantities to increase the chance of pollination. |
| 3. | It does not produce changes in the characteristics of new plants. | Cross pollination does introduce variations in characteristics of new plants. |
Question 7.
Identify the plant and the modification seen in it
.
Answer:
Chrysanthemum
Modification : Sucker (sub aerial stem modification).
X. Answer in detail
Question 1.
Write a note an sub aerial modifications of the stem.
Answer:
Sub- aerial Modifications : Stem of some plants remains sub- aerial which grow horizontally on the surface of the soil for the purpose of reproduction. There are four types.
- Runner: The stem grows laterally on the surface of the soil, breaks up to produce roots where it touches the ground to give rise to new plants. Eg: Centelk (Vallarai).
- Stolon: Stolon is a slender branch of the stem that grows upwards to some distance and then bends towards the ground. Upon touching the ground, it gives rise to a new plant. Eg. Wild strawberry.
- Sucker Sucker is a short and weak lateral branch that grows diagonally upwards and directly gives rise to a new shoot. Eg. Chrysanthemum.
- Offset: An offset is a short and thick branch that arises from the axial part of a leaf. It has thick intemodes. It produces a tuft of leaves and cluster of small roots below. Eg: Eichhornia.
Question 2.
Draw a diagram to show the life cycle of a plant.
Answer:
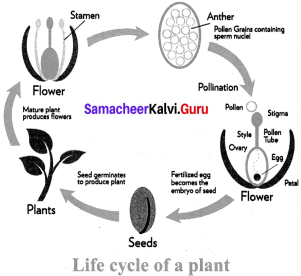
XI. Higher Order Questions : (HOTS)
Question 1.
Parasitic plants lack leaves.
Answer:
Parasites are plants which live on other living plants and derive nutrients from them. They are non-green and do not photosynthesize. They have sucking roots to absorb the nutrients directly from the host tissue. Thus they lack leaves.