Students can Download Maths Chapter 3 Geometry Ex 3.2 Questions and Answers, Notes Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 8th Maths Book Solutions Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 8th Maths Solutions Term 2 Chapter 3 Geometry Ex 3.2
Miscellaneous Practice Problems
Question 1.
The sides of a triangle are 1.2 cm, 3.5 cm and 3.7cm. Is this triangle a right triangle? If so, which side is the hypotenuse?
Solution:
The sides of a triangle are a = 1.2 cm; b = 3.5 cm; c = 3.7 cm
By Pythagoras theorem,
c2 = a2 + b2
a2 + b2 = 1.22 + 3
52 – 1.44 +12.25 = 13.69
c2 = 3.72 = 13.69
(1) = (2)
Yes, it is a right angled triangle. The hypotenuse c = 3.7 cm.
![]()
Question 2.
Rithika buys an LED TV which has a 25 inches screen. If its height is 7 inches, how wide is the screen? Her TV cabinet is 20 inches wide. Will the TV fit into the cabinet? Why?
Solution:

Take the sides of a right angled triangle ∆ ABC as
a = 7 inches
b = 25 inches
c = ?
By Pythagoras theorem,
b2 = a2 + c2
25 = 72 + c2
c2 = 252 – 72 = 625 – 49 = 576
∴ c2 = 242
⇒ c = 24 inches
∴ Width of TV cabinet is 20 inches which is lesser than the width of the screen ie.24 inches. The TV will not fit into the cabinet.
Question 3.
Find the length of the support cable required to support the tower with the floor.
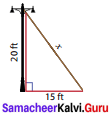
Solution:
From the figure, by Pythagoras theorem,
x2 = 202 + 152 = 400 + 225 = 625
x2 = 252 ⇒ x = 25ft.
∴ The length of the support cable required to support the tower with the floor is 25 ft.
Question 4.
A ramp is constructed in a hospital as shown. Find the length of the ramp.
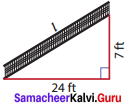
Solution:
Take a = 7 ft ; b = 24 ft.
By Pythagoras theorem,
l2 = c2 + b2
= 72 + 242 = 49 + 576
l = 25ft
![]()
Question 5.
In the figure, find MT and AH
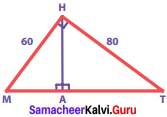
Solution:
By Pythagoras theorem,
MT2 = MH2 + HT2
= 602 + 802 = 3600 + 6400
= 10000 = 1002
∴ MT = 100
By the altitude – on – hypotenuse theorem,
MH2 = MA x MT
602 = MA x 100
MA = \(\frac{3600}{100}\) = 36
∴ In ∆ MAH, by Pythagoras theorem,
AH2 = MH2 – MA2
= 602 – 362 = 3600 – 1296 = 2304 = 482
∴ AH = 48
∴ Ans MT = 100
AH = 48
Challenging Problems
Question 6.
Mayan travelled 28 km due north and then 21 km due east. What is the least distance that he could have travelled from his starting point?
Solution:
From the figure AC is to be found.
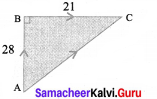
By using Pythagoras theorem,
AC2 = AB2 + BC2
= 282 + 212 = 784 + 441 = 1225 = 352
∴ AC = 35 km
This is the least distance that he could have travelled from his starting point.
Question 7.
If ∆ APK is an isosceles right angled triangle, right angled at K. Prove that AP2 = 2AK2.
Solution:
From the figure, ∆ APK is a right triangle.
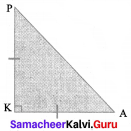
By using Pythagoras theorem,
AP2 = AK2 + PK2
= AK2 + AK2 (since it is an isosceles A)
= 2AK2
Hence it is proved.
![]()
Question 8.
The diagonals of the rhombus is 12 cm and 16 cm. Find its perimeter. (Hint: the diagonals of rhombus bisect each other at right angles).
Solution:
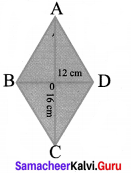
Here AO = CO = 8 cm
BO = DO = 6 cm
(∴ the diagonals of rhombus bisect each other at right angles)
∴ In ∆ AOB,
AB2 = AO2 + OB2 = 82 + 62 = 64 + 36
= 100 = 102
∴ AB = 10
Since it is a rhombus, all the four sides are equal.
AB = BC = CD = DA
∴ Its Perimeter = 10 + 10 + 10 + 10 = 40 cm
Question 9.
In the figure, find AR.
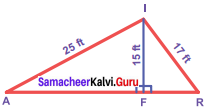
Solution:
∆ AFI, ∆ FRI are right triangles.
By Pythagoras theorem,
AF2 = AT2 – FT2 = 252 – 152
= 625 – 225 = 400 = 202
∴ AF = 20 ft ….(1)
FR2 = RI2 – FI2 = 172 – 152 = 289 – 225 = 64 = 82
FR = 8 ft.
∴ AR = AF + FR = 20 + 8 = 28 ft.
Question 10.
∆ ABC is a right angled triangle in which ∠A = 90° and AM ⊥ BC. Prove that AM = \(\frac{ABxAC}{BC}\). Also if AB = 30 cm and AC = 40 cm, find AM.
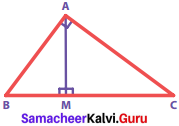
Solution:
Given: ∆ ABC is a right angled triangle.
∠A = 90, AM ⊥ BC
To Prove: AM = \(\frac{ABxAC}{BC}\)
Proof:
In the given figure, Area of the triangle A ABC [taking AB as base and AC as height]
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) x AB x AC ….(1)
And also, Area of the triangle ∆ ABC [taking BC as base and AM as height]
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) x BC x AM ……(2)
Since (1) & (2) are the same, we can equate (2) and (1)
i.e. \(\frac{1}{2}\) x BC x AM = \(\frac{1}{2}\) x AB x AC
AM = \(\frac{ABxAC}{BC}\)
Hence proved. If AB = 30 cm, AC = 40 cm
By Pythagoras theorem, BC2 = AB2 + AC2 = 302 + 402 = 900 + 1600 = 2500 = 502
∴ BC = 50
Using the altitude – on – hypotenuse theorem
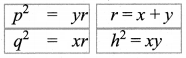
Here AC2 = MC x BC
402 = MC x 50
∴ BM = BC – MC = 50 – 32 = 18 cm
AM2 = BM x MC = 18 x 32 = 576 = 242
∴ AM = 24 cm