You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 8th Social Science Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 8th Social Science Economics Solutions Term 1 Solutions Chapter 1 Money, Savings and Investments
Samacheer Kalvi 8th Social Science Money, Savings and Investments
I. Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
Which metals were used for metallic money?
(a) Gold
(b) Silver
(c) Bronze
(d) All the above
Answer:
(d) All the above
Question 2.
Who introduced the paper money?
(a) British
(b) Turkish
(c) The Mugual Empire
(d) Mauryas
Answer:
(a) British
Question 3.
The value of money is
(a) Internal value of money
(b) External value of money
(c) Both a & b
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c) Both a & b
Question 4.
Which is the Bank Money?
(a) Cheque
(b) Draft
(c) Credit and Debit cards
(d) All the above
Answer:
(a) Cheque
Question 5.
Pick out the incorrect one:
Investment can be made in different vehicle.
(a) Stock
(b) Bonds
(c) Mutual fund
(d) Pay tax
Answer:
(d) Pay tax
Question 6.
Who is responsible for the collection and publication of monetary and financial information?
(a) Finance commission
(b) Finance Ministry
(c) Reserve Bank of India
(d) Auditor and Comptroller General of India
Answer:
(c) Reserve Bank of India
Fill in the Blanks
- Online Banking is also known as ……………
- ……………. is what money does.
- The term of bank is derived from ……………. word.
- Value of money is meant …………….. of money.
- The Indian banking regulation act of ……………..
Answer:
- Net Banking
- Money
- German
- The purchasing power
- 1949
III. Match the following
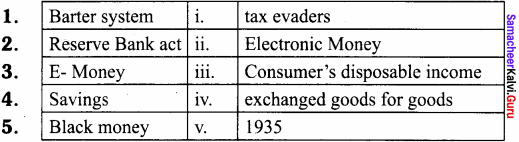
Answer:
- iv
- v
- ii
- iii
- i
IV. Write the one word answer
Question 1.
The word Money is derived from?
Answer:
The word Money is derived from Roman word “Moneta Juno”
Question 2.
Which bank gives to both short term and long term loans?
Answer:
Rural cooperative credit institutions.
V. Choose the correct statement
Question 1.
Barter system had many deficiency like –
I. Lack of double coincidence of wants
II. No difficulties of storing wealth
III. Common measure of value
IV. Indivisibility of commodities
(a) I and II is correct
(b) I and IV is correct
(c) I, III and IV is correct
(d) All are correct
Answer:
(c) I, III and IV is correct
VI. Find out the odd one
Question 1.
Recent forms of money transactions are
(a) Credit card
(b) Barter system
(c) Debit card
(d) Online banking
Answer:
(b) Barter system
Question 2.
Effects of black money on economy is
(a) Dual economy
(b) Undermining equity
(c) No effects on production
(d) Lavish consumption spending
Answer:
(c) No effects on production
VII. Write short answer
Question 1.
What is the Barter System?
Answer:
A barter system is an old method of exchange. Barter system is exchanging goods for goods without the use of money in the primitive stage.
Question 2.
What are the recent forms of money?
Answer:
Plastic Money and E – Money
Question 3.
Short note on E – Banking and E – Money.
Answer:
1. E – Money:
Electronic Money is money which exists in banking computer systems and is available for transactions through electronic system.
2. E – Banking:
Electronic banking, also known as National Electronic Funds Transfer (NEFT), is simply the use of electronic means to transfer funds directly from one account to another rather than by cheque or cash.
Question 4.
What are the essential of Money in your life?
Answer:
Money is used as the source to fulfill basics needs as well as comforts in life. It gets people accommodation, clothes, food and other things which add to luxury in life. It is an important source to live a healthy life too.
Question 5.
What is the Value of Money?
Answer:
Value of money is the purchasing power of money over goods and services in a country.
Question 6.
What is the Commercial Bank and its types of Deposits?
Answer:
A bank that offers services to the General public and companies is a commercial banks. The types of deposits in a commercial bank are
- Time deposits. Example Fixed deposit
- Recurring deposit and Demand deposit Example Current Account and Savings Account.
Question 7.
What is Savings and Investment?
Answer:
- Savings represents that part of the person’s income which is not used for consumption
- Investment refers to the process of investing funds in capital asset, with a view to generate returns
Question 8.
What is meant by Black Money?
Answer:
Black Money is money earned through any illegal activity controlled by country regulations.
Question 9.
What are the effects of black money on economy?
Answer:
- Dual economy
- Tax evasion, thereby loss of revenue to government.
- Undermining equity
- Widening gap between the rich and poor
VIII. Write Brief answer
Question 1.
What are the disadvantages of barter system?
Answer:
- Lack of double coincidence of wants,
- Common measure of value
- Indivisibility of commodities
- Difficulties of storing wealth
Question 2.
Write about the evolution of Money.
Answer:
Money has evolved through different stages according to the time, place and circumstances.
1. Commodity Money:
In the earliest period of human civilization, any commodity that was generally demanded and chosen by common consent was used as money. Example Goods like furs, skins, salt, rice, wheat, utensils, weapons etc. Such exchange of goods for goods was known as ‘Barter Exchange’.
2. Metallic Money:
With progress of human civilization, commodity money changed into metallic money. Metals like gold, silver, copper, etc. were used as they could be easily handled. It was the main form of money throughout the major portion of recorded history.
3. Paper Money:
(a) It was found inconvenient as well as dangerous to carry gold and silver coins from place to place. So, invention of paper money marked a very important stage in the development of money.
(b) Paper money is regulated and controlled by Central bank of the country (Reserve Bank of India). At present, a very large part of money consists mainly of currency notes or paper money issued by the central bank.
4. Credit Money or Bank Money:
(a) Emergence of credit money took place almost side by side with that of paper money. Example Cheque.
(b) The cheque (known as credit money or bank money), itself, is not money, but it performs the same as functions of money.
5. Near Money:
The final stage in the evolution of money has been the use of bills of exchange, treasury bills, bonds, debentures, savings certificate etc.
Question 3.
What are the functions of Money? and explain it.
Answer:
Functions of money are classified into Primary or Main function, Secondary function and Contingent function.
Primary or main functions:
The important functions of money performed in very economy are classified under main functions:
1. Medium of exchange or means of payment – Money is used to buy the goods and services.
2. Measure of value – All the values are expressed in terms of money it is easier to determine the rate of exchange between various type of goods and services.
Secondary functions:
The three important of secondary functions are
1. Standard of deferred payment – Money helps the future payments too. A borrower borrowing today places himself under an obligation to pay a specified sum of money on some specified future date.
2. Store of value or store of purchasing power – Savings were discouraged under barter system as some commodities are perishable. The introduction of money has helped to save it for future as it is not perishable.
3. Transfer of value or transfer of purchasing power – Money makes the exchange of goods to distant places as well as abroad possible. It was therefore felt necessary to transfer purchasing power from one place to another.
Contingent functions:
- Basis of credit
- Increase productivity of capital
- Measurement and Distribution of National Income
Question 4.
Explain the types of bank Deposits.
Answer:
1. Student Savings Account:
There are savings accounts some banks offer specifically for young people enrolled in high school or college, and they main feature more flexible terms such as lower minimum balance requirements.
2. Savings Deposits:
Savings deposits are opened by customers to save the part of their current income. The customers can withdraw their money from their accounts when they require it. The bank also gives a small amount of interest to the money in the saving deposits.
3. Current Account Deposit:
Current accounts are generally opened by business firms, traders and public authorities. The current accounts help in frequent banking transactions as they are repayable on demand.
4. Fixed Deposits:
Fixed deposits accounts are meant for investors who want their principle to be safe and yield them fixed yields. The fixed deposits are also called as Term deposit as, normally, they are fixed for specified period.
Question 5.
What are the difference between savings and investment?
Answer:
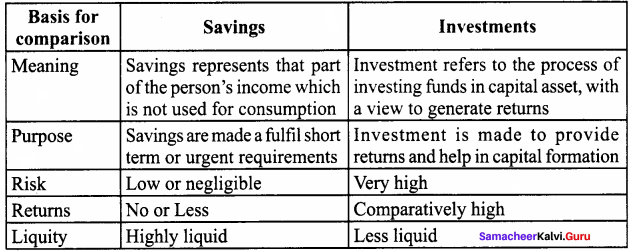
Question 6.
What are the effects of black money on economy?
Answer:|
Effects of Black Money on economy
- Dual economy
- Tax evasion, thereby loss of revenue to government.
- Undermining equity
- Widening gap between the rich and poor
- Lavish consumption spending
- Distortion of production pattern
- Distribution of scarce resource
- Effects on production.
Intext Hots
Question 1.
If there is no invention of money – Imagine.
Answer:
Money is one of the most fundamental inventions of mankind. “Every branch of knowledge has its fundamental discover”. In mechanics, it is the wheel, in science fire, in politics the vote. Similarly in economics, in the whole commercial side of Man’s social existence, money is the essential invention on which all the rest is based.
Intext Activity
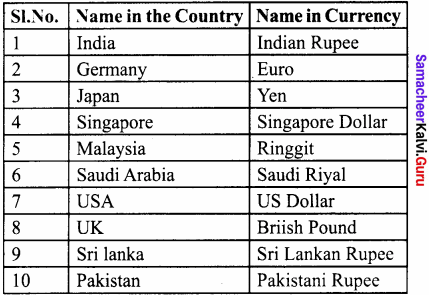
Question 1.
Fill up the following Table:
Answer:
Samacheer Kalvi 8th Social Science Economics Money, Savings and Investments Additional Questions
I. Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
‘Rupya’ in Sanskrit mean ……………. coin.
(a) Gold
(b) Silver
(c) Bronze
(d) Copper
Answer:
(b) silver
Question 2.
……………. doesn’t involve money.
(a) Bartering
(b) Net banking
(c) E – banking
(d) Credit card
Answer:
(a) Bartering
Question 3.
The ……………… came up with the Punch Marked Coins minting of silver, gold copper or lead.
(a) Mughals
(b) Kushans
(c) Mauryas
(d) Greeks
Answer:
(c) Mauryas
Question 4.
The …………… Empire from 1526 AD consolidated the monetary system for the entire empire.
(a) Greeks
(b) Turks
(c) Mauryas
(d) Mughals
Answer:
(d) Mughals
Question 5.
The receipts of ………….. were a substitute for money and became paper money.
(a) Bankers
(b) Gold smiths
(c) Carpenters
(d) Zamindars
Answer:
(b) Gold smiths
Question 6.
The symbol of Rupee was approved by the Government of India on ……………..
(a) 15 July 2010
(b) 15 June 2010
(c) 10 July 2011
(d) 12 July 2011
Answer:
(a) 15 July 2010
II. Fill in the blanks
- …………… of Lydia innovated mental coin the 8th Century BC.
- …………… kings introduced the Greek custom of engraving portraits on the coins.
- …………… Sultans of Delhi replaced the royal designs of Indian king with Islamic Calligraph.
- In the 12th Century AD, the currency made up of gold, silver and copper was known as ……………. and lower valued coin as ……………
- Silver coin of 178gms issued by Sher Shah Suri was called ……………….
- ……………. the Mughal Emperor gave permission to the Britishes to coin Mughal money at the Bombay mint.
- The relation between the value of money and price level is an ……………. one.
- The Indian Rupee symbol was designed by ……………. of Villupuram district.
- …………….. has the legal power to discharge debts.
- The Government of India announced demonitization on ……………..
Answer:
- Kind Midas
- Indo – Greek Kushan
- Turkish
- Tanka, Jittal
- Rupiya
- Farrukhsiyar
- Inverse
- Udayakumar
- Money
- 8 November 2016
III. Match the following
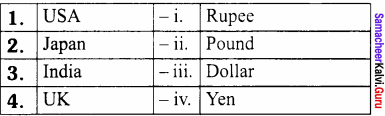
Answer:
- iii
- iv
- i
- ii
IV. Choose the correct statement
Question 1.
(i) In November 2016, Government of India announced demonetization of all 100 rupee bank notes
(ii) Demonetization is a step against Black money.
(iii) Prevention of corruption Act was passed in 1988.
(iv) Benami transactions prohibition act 1988 was amended in 2011.
(a) i and ii are correct
(b) ii and iii are correct
(c) iii and iv are correct
(d) i, ii and iii are correct.
Answer:
(b) ii and iii are correct
V. Find the odd one
Question 1.
Investment can be made in
(a) Stock
(b) Bonds
(c) Insurance
(d) Credit card
Answer:
(d) Credit card
VI. Give Short Answers
Question 1.
What is Robertson’s definition of money?
Answer:
Robertson is defined as, “Money is anything which is widely accepted in payment for goods or in discharge of other business obligations”.
Question 2.
Name the stages through which money has evolved.
Answer:
Commodity Money, Metallic Money, Paper Money, Credit Money, Near Money and recent forms of Money.
Question 3.
How were the British coins termed?
Answer:
The British gold coins were termed as Carolina, the silver coins as Angelina, the copper coins as cupperoon and the tin coins as tinny.
Question 4.
What is plastic money?
Answer:
The latest type of money is plastic money in the form of Credit cards and Debit cards. They aim for cashless transactions.
Question 5.
Write a short note on Online banking.
Answer:
- Online Banking, also known as internet banking is an electronic payment system.
- It enables customers of a bank or other financial institutions to conduct a range of financial transactions through website.
Question 6.
Mention the types of value of money and describe them.
Answer:
The value of money is of two types
- Internal value of money
- External value of money
The Internal value of money refers to the purchasing power of money over domestic goods and services. The External value of money refers to the purchasing power of money over foreign goods and services.
Question 7.
Answer:
Define Inflation and Deflation.
- Inflation refers to the prices are rising, the value of money will fall.
- Deflation refers to the prices are falling, the value of money will rise.
Question 8.
State some ways in which investments are made.
Answer:
Investment can be made in different investment vehicles like,
- Stock
- Bonds
- Mutual funds
- Commodity futures
- Insurance
- Annuities
- Deposit account or any other securities or assets
Question 9.
What is the root cause for the increasing rate of black money in a country?
Answer:
The root cause for the increasing rate of black money in the country is the lack of strict punishments for the offenders.
Question 10.
Brief the recent steps of the Government of India against black money.
Answer:
- Under pressure from India and other countries, Switzerland has made key changes in its local laws governing assist foreign allegedly stashed in Swiss Banks.
- Special Investigation Team appointed by government on the directions of Supreme Court on black money.
- Demonetization
VII. Answer the following
Question 1.
What are the benefits of saving?
Answer:
Benefits of Savings
- You will be financially independent sooner.
- You would not have to worry any unforeseen expenses.
- In future, you will have financial backup in place if you lose your job.
- You will be prepared if your circumstances change.
- You will be more comfortable in retirement.
- Save today for better tomorrow.