You can Download Samacheer Kalvi 9th Maths Book Solutions Guide Pdf, Tamilnadu State Board help you to revise the complete Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 9th Maths Solutions Chapter 3 Algebra Ex 3.10
9th Maths Exercise 3.10 Solutions Question 1.
Draw the graph for the following
(i) y = 2x
(ii) y = 4x – 1
(iii) y = \(\left(\frac{3}{2}\right)\) x + 3
(iv) 3x + 2y = 14
Solution:
(i) Put x = -1, y = 2 × -1 = -2
When x = 0, y = 2 × 0 = 0
When x = 1, y = 2 × 1 = 2
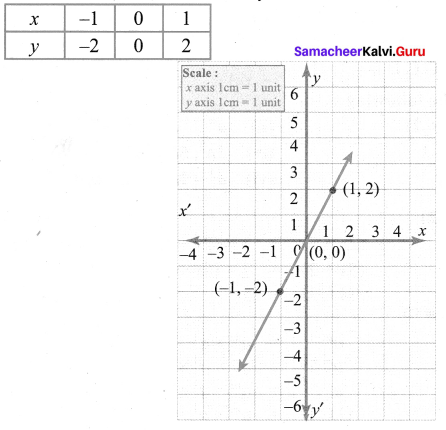
The points (x, y) to be plotted: (-1, -2), (0, 0), (1, 2)
(ii) When x = -1 ⇒ y = 4 (-1) -1
y = – 4 – 1 = – 5
x = 0 ⇒ y = 4 × 0 – 1 = -1
x = 1 ⇒ y = 4 × 1 – 1 = 3
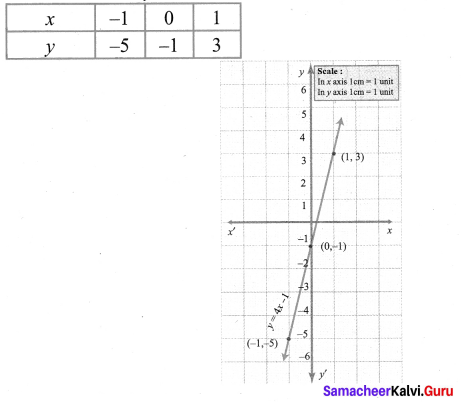
The points (x, y) to be plotted: (-1, -5), (0, -1), (1, 3)
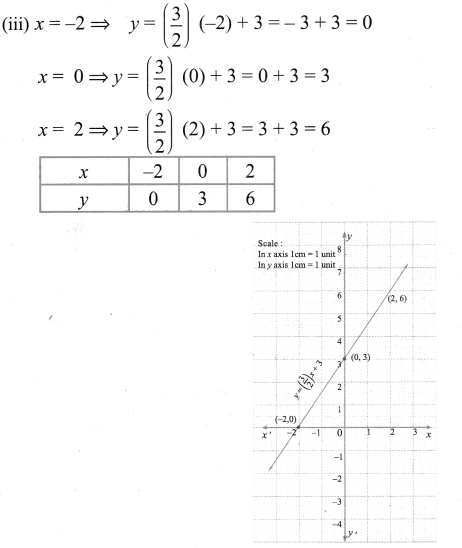
The points to be plotted: (-2, 0), (0, 3), (2, 6)
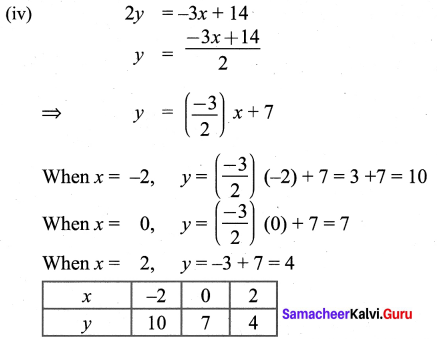
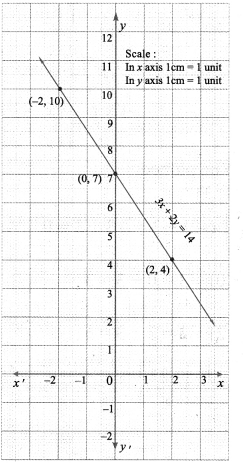
The points to be plotted: (-2, 10), (0, 7), (2, 4)
9th Maths Exercise 3.10 Question 2.
Solve graphically
(i) x + y = 7; x – y = 3
(ii) 3x + 2y = 4; 9x + 6y – 12 =0
(iii) \(\frac{x}{2}+\frac{y}{4}=1 ; \frac{x}{2}+\frac{y}{4}=2\)
(iv) x – y = 0; y + 3 = 0
(v) y = 2x + 1; y + 3x – 6 = 0
(vi) x = -3, y = 3
Solution:
(i) We can find x and y intericepts and thus of the two points on the lines (1), (2)
x + y = 7 ……… (1), x – y = 3 …………. (2)
To draw the graph of (1)
Put x = 0 in (1)
0 + y = 7 ⇒ y = 7
Thus A (0, 7) is a point on the line
Put y = 0 in (1)
x + 0 = 7 ⇒ x = 7
Thus B (7, 0) is another point on the line
Plot A and B. Join them to produce the line (1).
To draw the graph of (2), we can adopt the same procedure.
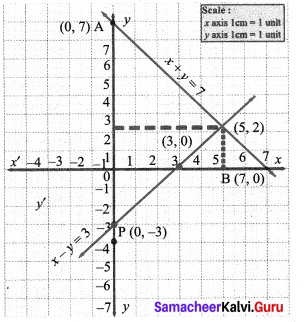
When x = 0,(2) ⇒ x – y = 3
0 – y = 3 ⇒ y = -3
P (0, -3) is a point on the line.
Put y = 0 in (2); x – 0 = 3
x = 3
∴ Q (3, 0) is another point on the line (2)
Plot P, Q
1 The point of intersection (5, 2) of lines (1), (2) is a solution
(ii) 3x + 2y = 4 ……. (1)
9x + 6y= 12 ………. (2)
To draw the graph of (1)
Put x = 0 in (1) ⇒ 3 (0) + 2y = 4
2y = 4
y =2
∴ A (0, 2) is a point on the line (1)
Put y = 0 in (1) ⇒ 3x + 2(0) = 4
3x = 4
x = \(\frac{4}{3}\) = 1.3
∴ B (1.3, 0) is another point on the line (1)
Plot the points A, B. Join them to produce the line (1)
To draw the graph of (2)
Put x = 0 in (2) ⇒ 9 (0) + 6y = 12
6y = 12
y = 2
∴ P (0, 2) is a point on the line (2)
Put y = 0 in (2) ⇒ 9x + 6(0) = 12
9x = 12
x = \(\frac{12}{9}=\frac{4}{3}\)
x = 1.3
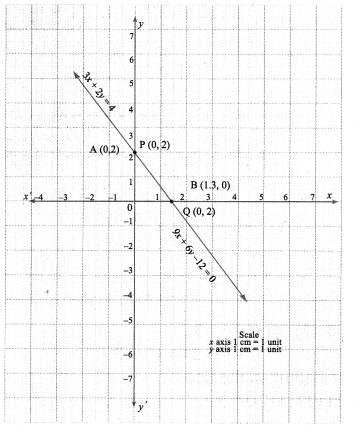
Q (1.3, 0) is another point on the line (2)
Plot P, Q. Join them to produce the line (2).
The point of intersection of the lines (1), (2) is a solution.
[A, B],[P, Q] represent the same line.
∴ All the points on one line are also on the other.
This means we have an infinite number of solutions.
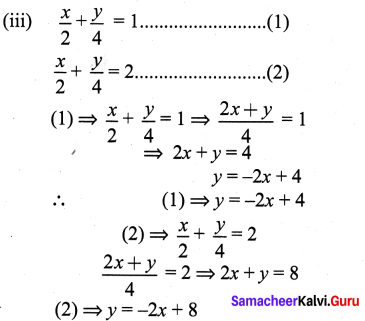
∴ Comparing (1), (2) we can conclude their slopes are equal
∴ The lines are parallel and will not meet at any point and hence no solution exists.
Let us draw the graphs of (1) & (2)
(1) ⇒ 2x + y = 4, Put x = 0 in (1) ⇒ y = 4
∴ A (0, 4) is a point on (1)
Put y = 0 in (1) ⇒ 2x = 4
x = 2
∴ B (2, 0) is another point on (1)
Plot A, B ; Join them to produce the line (1)
(2) ⇒ 2x + y = 8, Put x = 0 in (2)
2(0) + y = 8
y = 8, P (0,8) is a point
Put y = 0 in (2) ⇒ 2x + 0 = 8
2x = 8
x = 4, Q (4, 0) is another point on the line (2)
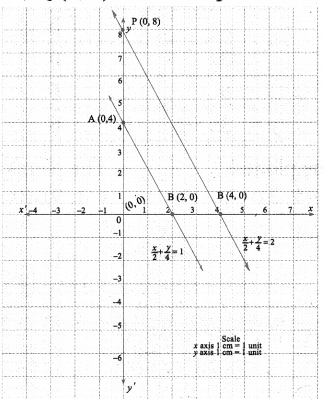
Plot P, Q: Join them to produce the line (2)
(iv) x – y = 0 ………….. (1) ⇒ -y = -x ⇒ y = x
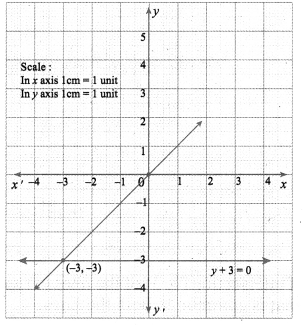
Put x = 0 in (1), 0 – y = 0
-y = 0 ⇒ y = 0
A (0, 0) is a point on the line (1)
Put y = 0 in (1) ⇒ x – 0 = 0 ⇒ x = 0
B (-3, -3) is also the same point as A
(2) ⇒ y + 3 = 0
y = -3
∴ from (1) y = -3 = x
∴ B (-3, -3) is the solution
(v) y = 2x + 1 …………… (1)
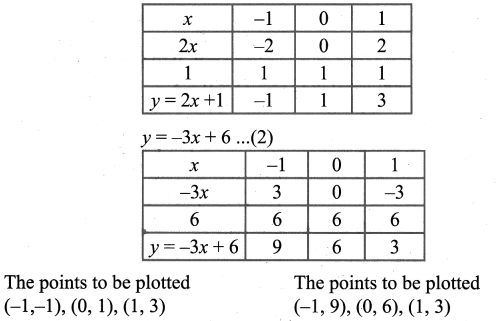
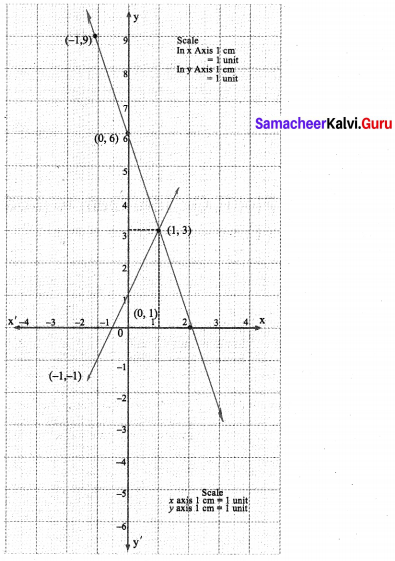
The points of intersection (1, 3) of the lines (1) and (2) is a solution. The solution is the point that is common to both the lines.
∴ The solution is as x = 1, y = 3.
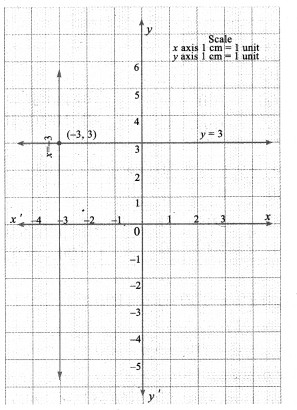
(vi) The point of intersection (-3, 3) is a solution.
x + y = 7 ……… (1), x – y = 3 …………. (2)
To draw the graph of (1)
Put x= 0 in (1)
0 + y = 7 ⇒ y =7
Thus A (0, 7) is a point on the line
Put y = 0 in (1)
x + 0 = 7 ⇒ x =7
Thus B (7, 0) is another point on the line
Plot A and B. Join them to produce the line (1).
To draw the graph of (2), we can adopt the same procedure.
When x = 0, …….. (2) ⇒ x – y = 3
0 – y = 3 ⇒ y = -3
P (0, -3) is a point on the line.
Put y = 0 in (2) ; x – 0 = 3
x = 3
∴ Q (3, 0) is another point on the line (2) Plot P, Q
9th Standard Graph Question 3.
Two cars are 100 miles apart. If they drive towards each other they will meet in 1 hour. If they drive in the same direction they will meet in 2 hours. Find their speed by using graphical method.
Solution:
Let x, y be the speed of the two cars. If the two cars travel towards each other they will meet in 1 hr. The distance between them d = 100; \(\frac{d}{s}\) = t
i.e., \(\frac{100}{x+y}\) = 1 ⇒ x + y = 100 ………. (1)
If the two cars travel in the same direction they will meet in 2 hrs.
x + y = \(\frac{100}{2}\) ⇒ x – y = 50 ………….. (2)
x + y = 10 ………….. (1)
Put x = 0 in (1), then 0 + y = 100 ⇒ y =100
A (0, 100) is a point on (1)
Put y = 0 in (1), then x + 0 = 100 ⇒ x =100
B (100, 0) is another point on (1)
Plot A & B. Join them to produce the line (1)
Similarly by x – y = 50
Put x = 0 in (2), then 0 – y = 50 ⇒ y = -50
P (0, -50) is a point on (2)
Put y = 0 in (2), then x – 0 = 50 ⇒ x = 50
Q (50, 0) is another point on (2)
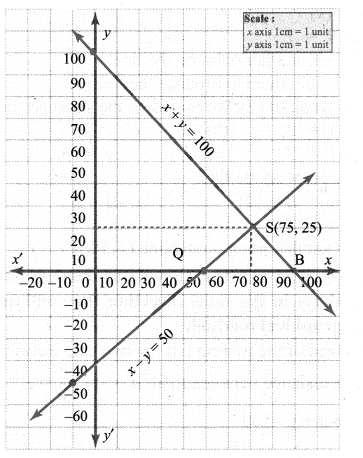
Plot P & Q. Join them to produce the line (2)
The point of intersection (75, 25) of the two lines (1) & (2) is the solution.
∴ The solution i.e., the speed of the two cars x and y is given by x = 75 km and y = 25 km