Students can Download Tamil Nadu 11th Accountancy Previous Year Question Paper June 2019 English Medium Pdf, Tamil Nadu 11th Accountancy Model Question Papers helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
TN State Board 11th Accountancy Previous Year Question Paper June 2019 English Medium
General Instructions:
- The question paper comprises of four parts.
- You are to attempt all the parts. An internal choice of questions is provided wherever applicable.
- All questions of Part I, II, III, and IV are to be attempted separately.
- Question numbers 1 to 20 in Part I are Multiple Choice Questions of one mark each.
These are to be answered by choosing the most suitable answer from the given four alternatives and writing the option code and the corresponding answer. - Question numbers 21 to 30 in Part II are two-mark questions. These are to be answered in about one or two sentences.
- Question numbers 31 to 40 in Part III are three-mark questions. These are to be answered in above three to five short sentences.
- Question numbers 41 to 47 in Part IV are five-mark questions. These are to be answered in detail Draw diagrams wherever necessary.
Time: 2.30 Hours
Maximum Marks: 90
Part – I
Answer all the questions. Choose the correct answer: [20 × 1 = 20]
Question 1.
Financial position of a business is ascertained on the basis of ________.
(a) Journal
(b) Trial balance
(c) Balance Sheet
(d) Ledger
Answer:
(c) Balance Sheet
Question 2.
Who is considered to be the internal user of the financial information?
(a) Creditor
(b) Employee
(c) Customer
(d) Government
Answer:
(b) Employee
Question 3.
“Book-keeping is an art of recording business dealings in a set of books” is said by
(a) R.N.Carter
(b) Menhar
(c) J.R.Batlibai
(d) Kohler
Answer:
(c) J.R.Batlibai
![]()
Question 4.
In India, Accounting Standards are issued by ______.
(a) Reserve Bank of India
(b) Accountant General of India
(c) The Institute of Chartered Accountants of India
(d) The Cost and Management Accountant of India
Answer:
(d) The Cost and Management Accountant of India
Question 5.
Outstanding wages is a ________.
(a) Nominal account
(b) Personal account
(c) Real account
(d) Representative personal account
Answer:
(d) Representative personal account
Question 6.
The process of finding the net amount from the totals of debit and credit columns in a ledger is known as ______.
(a) Casting
(b) Posting
(c) Journalising
(d) Balancing
Answer:
(d) Balancing
Question 7.
The total of the debit column is short by ₹ 500 in the trial balance. This difference will be _____.
(a) Debited to suspense account
(b) Credited to suspense account
(c) Adjusted to any of the debit balance
(d) Adjusted to any of the credit balance
Answer:
(a) Debited to suspense account
Question 8.
Purchase of fixed assets on credit basis is recorded in:
(a) Purchases book
(b) Sales book
(c) Purchases returns book
(d) Journal proper
Answer:
(d) Journal proper
Question 9.
In Triple column cash book, the balance of bank overdraft brought forward will appear in ______.
(a) Cash column credit side
(b) Cash column debit side
(c) Bank column debit side
(d) Bank column credit side
Answer:
(d) Bank column credit side
![]()
Question 10.
A bank reconciliation statement is prepared with the help of ______.
(a) Bank statement
(b) Petty Cash book
(c) Cash book
(d) Bank statement and bank column of the cash book
Answer:
(d) Bank statement and bank column of the cash book
Question 11.
The total of purchases book was undercast. Which of the following accounts should be credited in the rectifying journal entry?
(a) Purchases account
(b) Creditors account
(c) Suspense account
(d) Debtors account
Answer:
(c) Suspense account
Question 12.
The difference in trial balance is taken to _______.
(a) The capital account
(b) The trading account
(c) The suspense account
(d) The profit and loss account
Answer:
(c) The suspense account
Question 13.
Under the written down value method of depreciation, the amount of depreciation is ________.
(a) Decreasing every year
(b) Uniform in all the years
(c) Increasing every year
(d) Fluctuating every year
Answer:
(a) Decreasing every year
Question 14.
Advertisement expenses amounted to ₹ 5 crores to introduce a new product is _______.
(a) Capital expenditure
(b) Revenue expenditure
(c) Deferred revenue expenditure
(d) Capital receipt
Answer:
(b) Revenue expenditure
Question 15.
Short term loan is ________.
(a) Liquid liability
(b) Current liability
(c) Fixed liability
(d) Contingent liability
Answer:
(b) Current liability
Question 16.
Bank overdraft should be shown ________.
(a) In the trading account
(b) On the assets side
(c) Profit and Loss account
(d) On the liabilities side
Answer:
(d) On the liabilities side
Question 17.
Closing stock is valued at _______.
(a) Cost price
(b) Market price
(c) Cost price or market price whichever is higher
(d) Cost price or net realisable value whichever is lower
Answer:
(d) Cost price or net realisable value whichever is lower
Question 18.
Prepaid salary will be shown on _______.
(a) Debit side of trading account
(b) Assets side of Balance sheet
(c) Debit side of profit and loss account
(d) Both (b) and (c)
Answer:
(d) Both (b) and (c)
Question 19.
One of the limitations of computerised accounting system is ________.
(a) System failure
(b) Accuracy
(c) Versatility
(d) Storage
Answer:
(a) System failure
![]()
Question 20.
Accounting software is an example of _______.
(a) Utility software
(b) System software
(c) Application software
(d) Operating software
Answer:
(c) Application software
Part – II
Answer any seven questions in which question No. 30 is compulsory: [7 × 2 = 14]
Question 21.
Complete the accounting equation
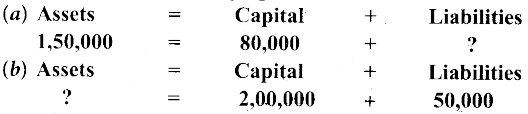
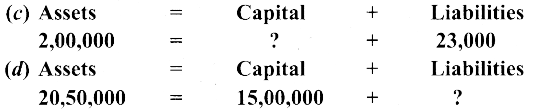
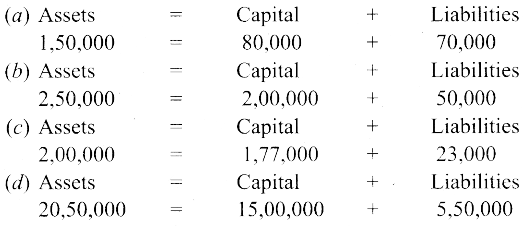
Answer:
Question 22.
Prepare Furniture A/c from the following transactions.
| 2017 | ₹ | |
| Jan. 1 | Furniture in hand | 20,000 |
| Jan. 1 | Purchased furniture for cash | 10,000 |
| Jan. 30 | Sold furniture | 4,000 |
Answer:
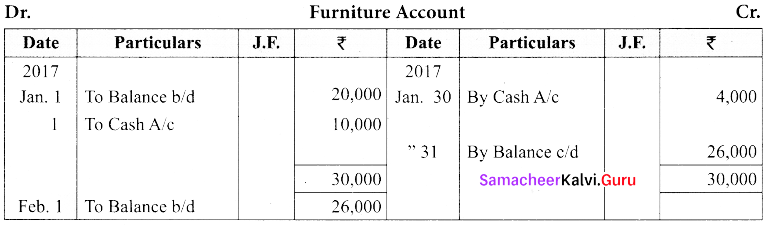
Question 23.
Prepare a trial balance with the following information:
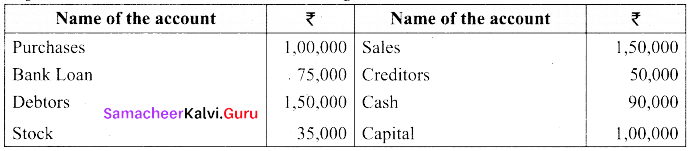
Answer:
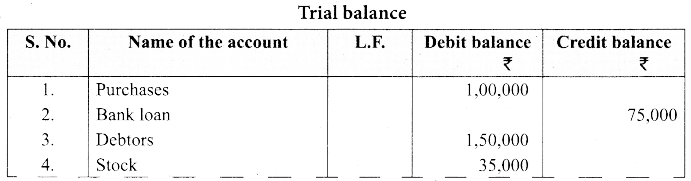

![]()
Question 24.
Enter the following transactions in the Purchases book of M/s. Subhashree Home Appliances.

Answer:
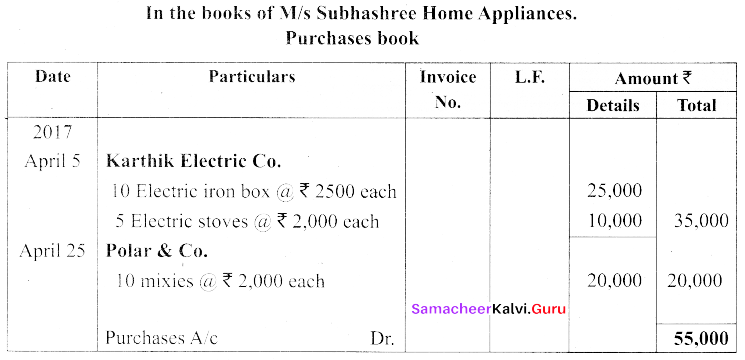
Question 25.
What is bank reconciliation statement?
Answer:
If every entry in the cash book matches with the bank statement, then bank balance will be the same in both the records. But, practically it may not be possible. When the balances do not agree with each other, the need for preparing a statement to explain the causes arises. This statement is called bank reconciliation statement (BRS).
Question 26.
Rectify the following errors discovered before the preparation of trial balance:
(a) Returns inward book was undercast by ₹ 1,000
(b) Returns outward book was overcash by ₹ 2,000
Answer:
(a) Returns inward book should be debited ₹ 1,000
(b) Returns outward book should be debited ₹ 2,000
![]()
Question 27.
What is annuity method of calculating depreciation?
Answer:
To calculate the amount of depreciation, annuity factor is used. Annuity factor can be found out from the annuity table or by using formula.
Amount of depreciation is computed as follows:
Amount of depreciation = Annuity factor × Original cost of the asset.
Question 28.
What is meant by deferred revenue expenditure?
Answer:
An expenditure which is revenue expenditure in nature, the benefits of which is to be derived over a subsequent period or periods is known as deferred revenue expenditure.
Question 29.
Write the components of Computerised Accounting System (CAS)?
Answer:
Components of CAS can be classified into six categories, namely,
- Hardware
- Software
- People
- Procedure
- Data
- Connectivity.
Question 30.
The Trial balance as on 31st December 2018 is given below:
| Particulars | Debit | Credit |
| Loan @ 10% p.a | – | 4,00,000 |
| Interest paid on loan | 30,000 | – |
Pass adjusting entry for interest on loan outstanding ₹ 10,000
Answer:
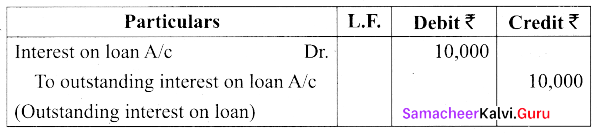
PART – III
Answer any seven questions in which question No. 40 is compulsory: [7 × 3 = 21]
Question 31.
Write the objectives of Accounting.
Answer:
Following are the objectives of accounting:
- To keep a systematic record of financial transactions and events
- To ascertain the profit or loss of the business enterprise
- To ascertain the financial position or status of the enterprise
- To provide information to various stakeholders for their requirements
- To protect the properties of an enterprise and
- To ascertain the solvency and liquidity position of an enterprise
![]()
Question 32.
In a Business concern “Only monetary transactions are recorded in accounting”. Why?
Answer:
This concept implies that only those transactions, which can be expressed in terms of money, are recorded in the accounts. Since, money serves as the medium of exchange transactions expressed in money are recorded and the ruling currency of a country is the measuring unit for accounting.
Transactions which do not involve money will not be recorded in the books of accounts.
For example, working conditions in the work place, strike by employees, efficiency of the management, etc. will not be recorded in the books, as they cannot be expressed in terms of money.
Question 33.
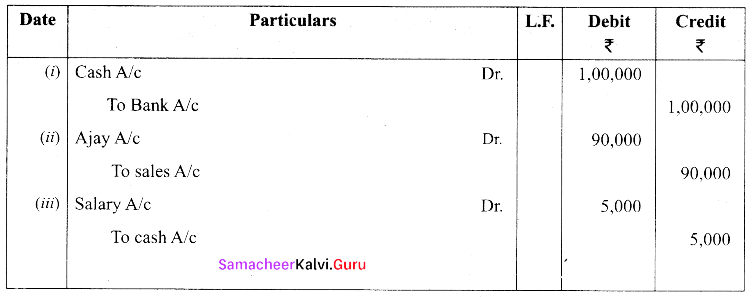
Complete the missing information:
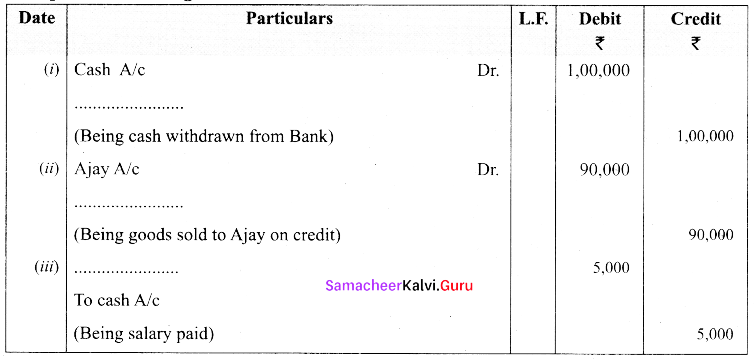
Answer:
Question 34.
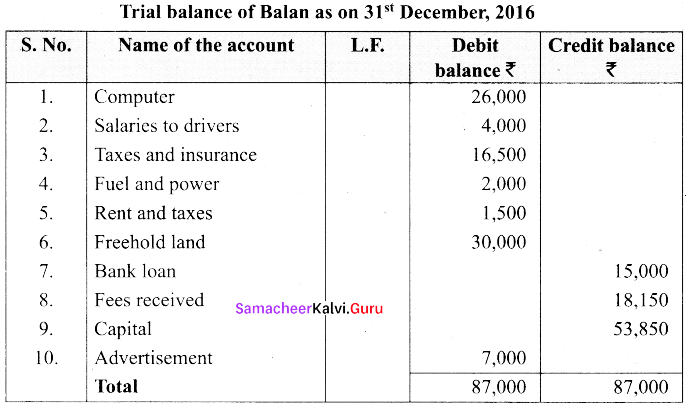
Balan who has a car driving school gives you the following ledger balances. Prepare trial balance as on 31st December, 2016.
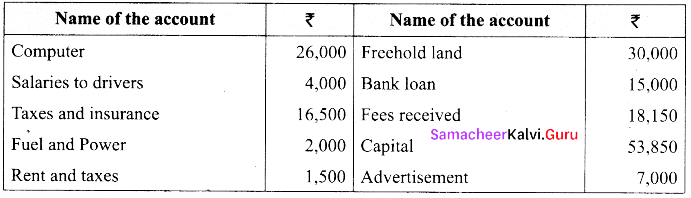
Answer:
![]()
Question 35.
Prepare bank reconciliation statement as on 31st December, 2017 from the following information:
(a) Balance as per bank statement (pass book) is ₹ 25,000
(b) No record has been made in the cash book for a dishonour of a cheque for ₹ 250
(c) Cheques deposited into bank amounting to ₹ 3,500 were not yet collected
(d) Bank charges of ₹ 300 have not been entered in the cash book.
(e) Cheques issued amounting to ₹ 9,000 have not been presented for payment
Answer:

Question 36.
Calculate the amount of depreciation and depreciation rate from the following by using ‘straight line method’.
| ₹ | |
| Purchase price of a machinery | 2,00,000 |
| Transportation cost | 2,000 |
| Installation cost | 18,000 |
| Estimated scrap value | 10,000 |
| Estimated life | 10 years |
Answer:

Note:
Cost of the asset = Purchase price + Transportation cost + Installation cost
= 2,00,000 + 2,000 + 18,000 = ₹ 2,20,000
Question 37.
Write any three differences between capital, revenue and deferred revenue expenditure.
Answer:
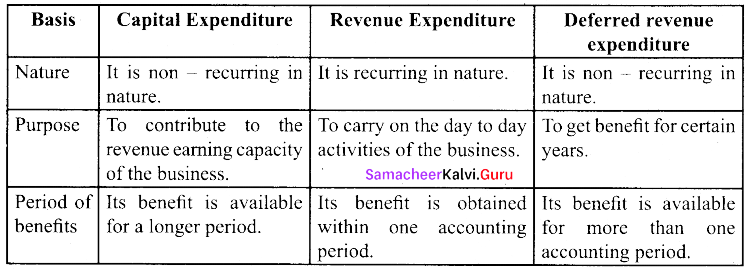
![]()
Question 38.
From the following details for the year ended 31st March, 2018, prepare trading account:
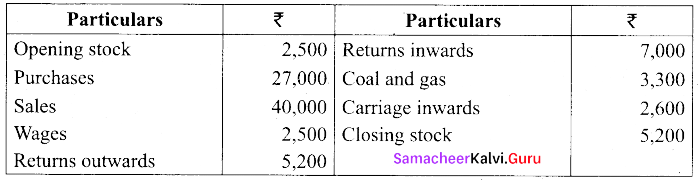
Answer:
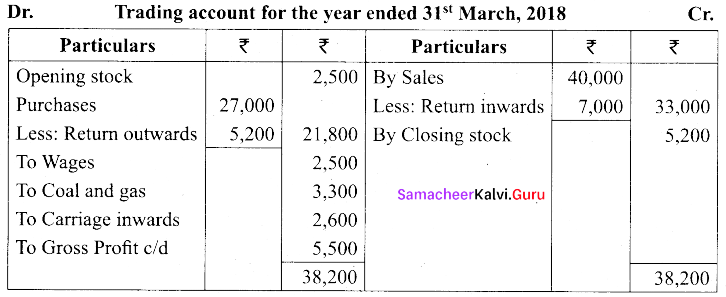
Question 39.
The Trial Balance of Mr.Aravind on 31.3.15 shows capital ₹ 15,00,000. During that year he withdrew ₹ 1,00,000 for his personal use.
Adjustment: Charge interest on drawings at 5%
Pass adjusting entry and transfer entry.
Answer:
Interest on drawings = ₹ 1,00,000 × 5/100 = ₹ 5000. The adjusting entry is:
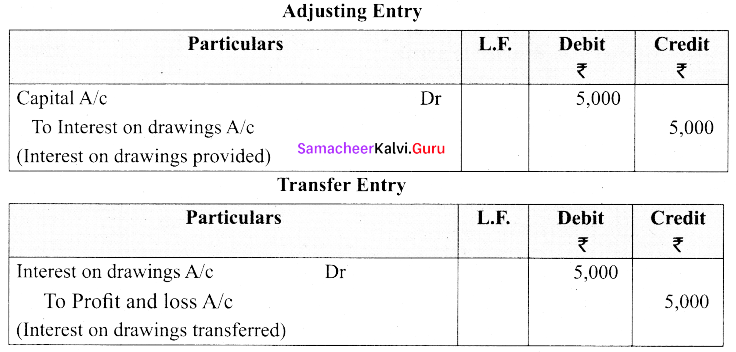
![]()
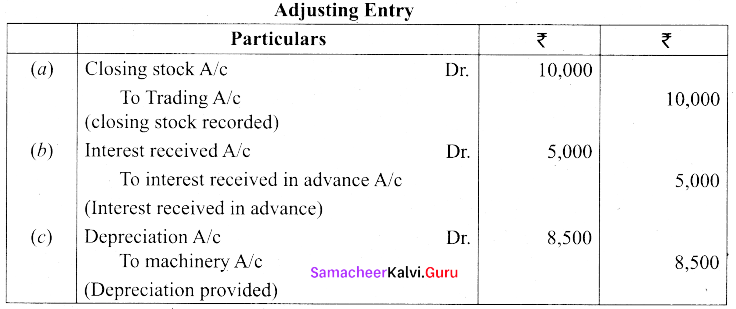
Question 40.
Pass Adjusting Entries for the following adjustments in the books of Mr.MuraIi.
(a) Closing stock – ₹ 10,000
(b) Interest received in advance – ₹ 5,000
(c) Depreciation on Machinery – ₹ 8,500
Answer:
Part – IV
Answer all the questions: [7 × 5 = 35]
Question 41.
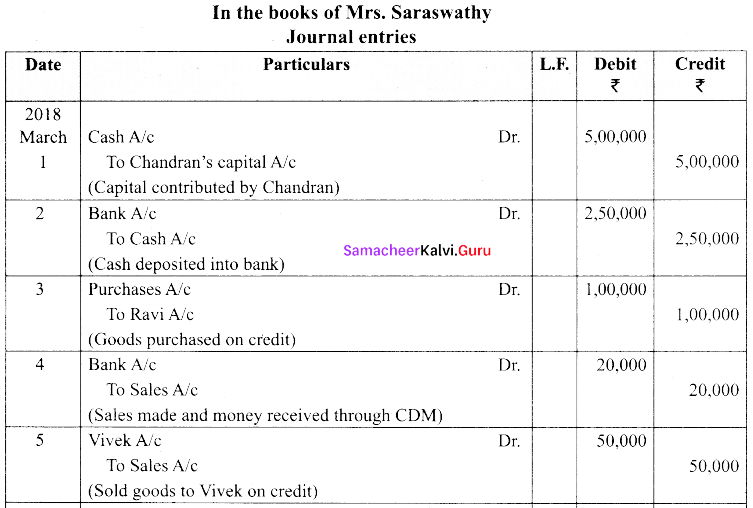
(a) Mrs. Saraswathy is a sole trader dealing in sports items. From the following transactions, pass journal entries for the month of March, 2017.
|
March |
₹ |
|
| 1 | Commenced business with cash | 5,00,000 |
| 2 | Cash deposited into bank | 2,50,000 |
| 3 | Purchased goods from Ravi | 1,00,000 |
| 4 | Sales made to Kumar, who deposited the money through CDM | 20,000 |
| 5 | Sold goods to Vivek, on credit | 50,000 |
| 6 | Cash purchases | 30,000 |
| 7 | Dividend directly received by bank | 3,000 |
| 8 | Salaries paid through ECS | 6,000 |
| 9 | Money withdrawn from ATM | 9,000 |
| 10 | Cricket balls donated to a trust | 2,500 |
Answer:

[OR]
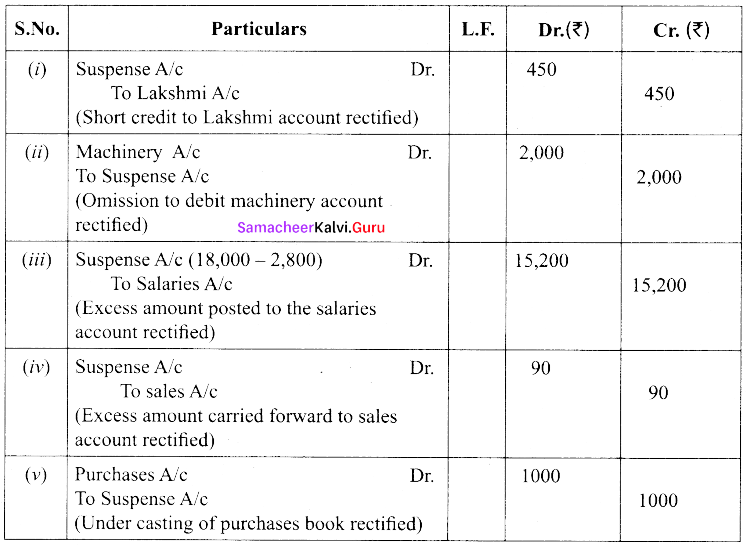
(b) The following errors were located after the preparation of the trial balance. Assume that their exists a suspense account. Rectify them.
(i) Bought goods from Lakshmi on credit for ₹ 500. Credited to her account as ₹ 50.
(ii) Purchased machinery for cash ₹ 2,000 was posted to machinery account.
(iii) Salaries ₹ 2,800 were posted as ₹ 18,000
(iv) The total of sales book ₹ 890 was carried forward as ₹ 980
(v) The total of purchase book was undercast by ₹ 1,000
Answer:
![]()
Question 42.
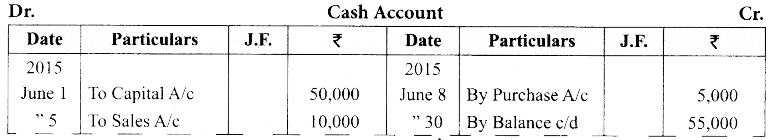
(a) Show the direct ledger postings for the following transactions:
| 2015 | ₹ | |
| June 1 | Subash commenced business with cash | 50,000 |
| June 5 | Sold goods for cash | 10,000 |
| June 8 | Goods purchased for cash | 5,000 |
| June 20 | Goods purchased from Shankar on credit | 6,000 |
Answer:

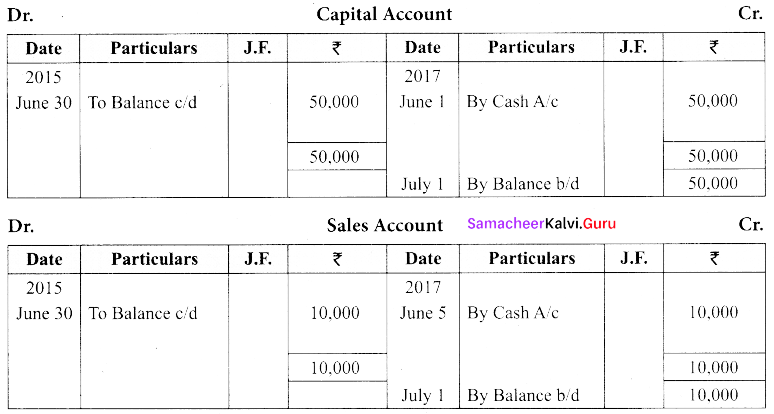
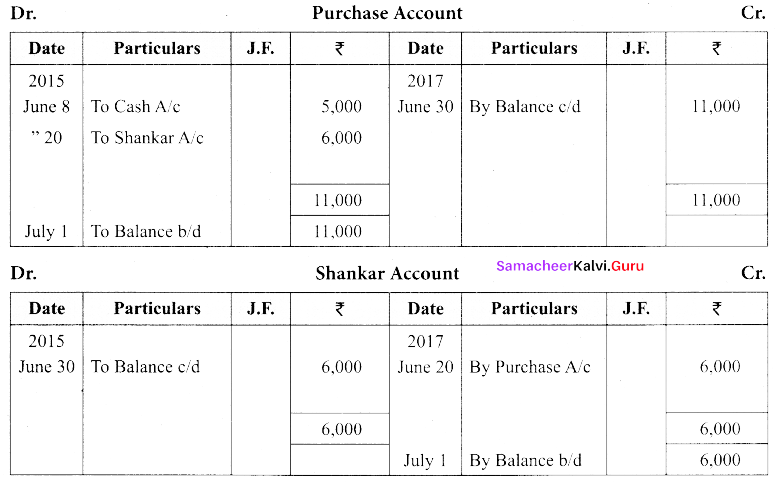
[OR]
(b) Enter the following transactions in three column cash book of Mr. Raja.

Answer:
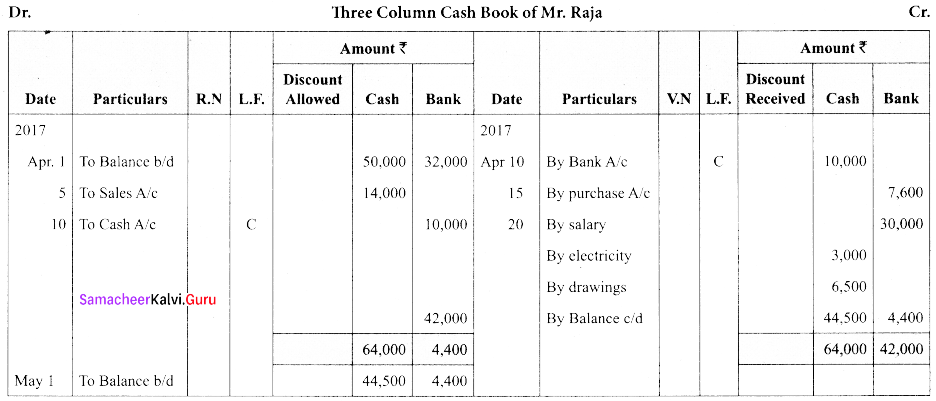
Question 43.
(a) Prepare accounting equation for the following transactions.
| (i) Mrs. Rani started business with cash | ₹ 50,000 |
| (ii) Opened bank account with a deposit of | ₹ 10,000 |
| (iii) Bought goods from Ravi on credit for | ₹ 12,000 |
| (iv) Sold goods (costing 10,000) for | ₹ 15,000 |
| (v) Salaries paid for | ₹ 5,000 |
Answer:
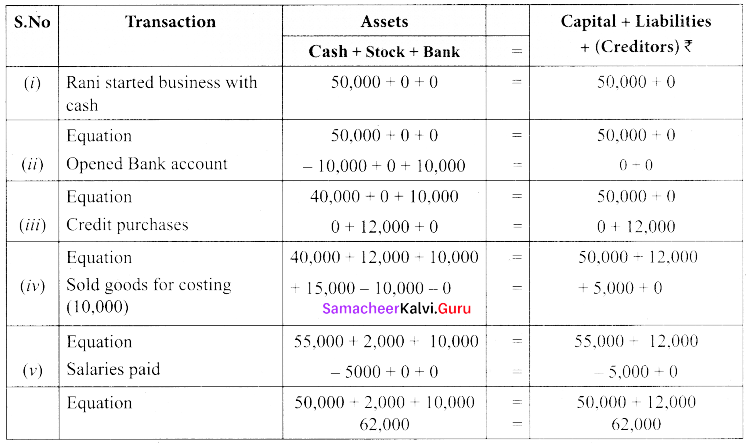
(b) From the following information, prepare the necessary subsidiary books for Nalanda Book stores.

Answer:
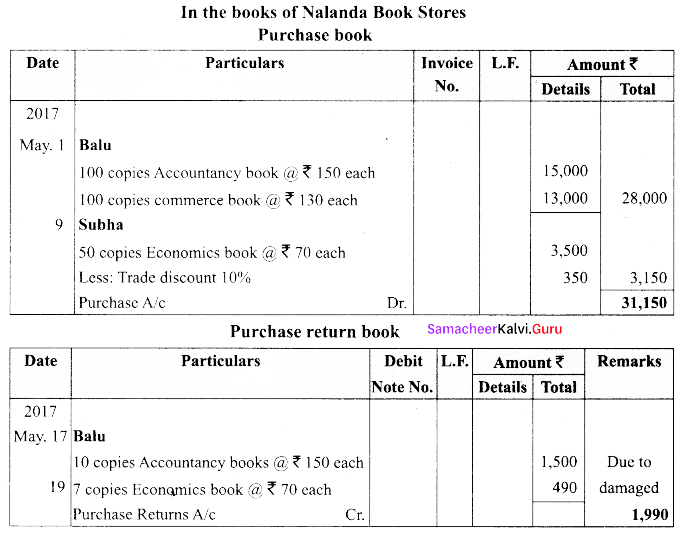
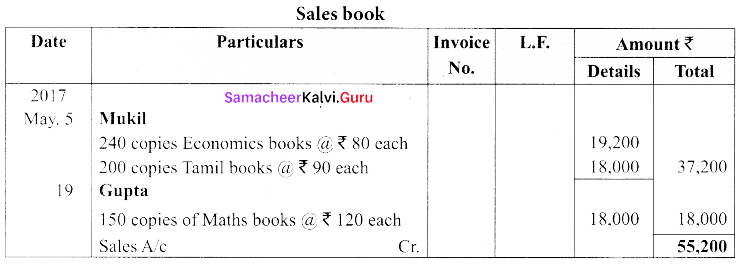
![]()
Question 44.
(a) Ram and Co. purchased on 1st April 2014, a plant and machinery for ₹ 6,50,000 and spend ₹ 50,000 on its installation. After having used it for three years, it was sold for ₹ 4,00,000. Depreciation is to be provided every year at the rate of 15% per annum on the fixed instalment method. Accounts are closed on 31st March every year. Prepare plant and machinery account and depreciation account for three years.
Answer:
Workings:
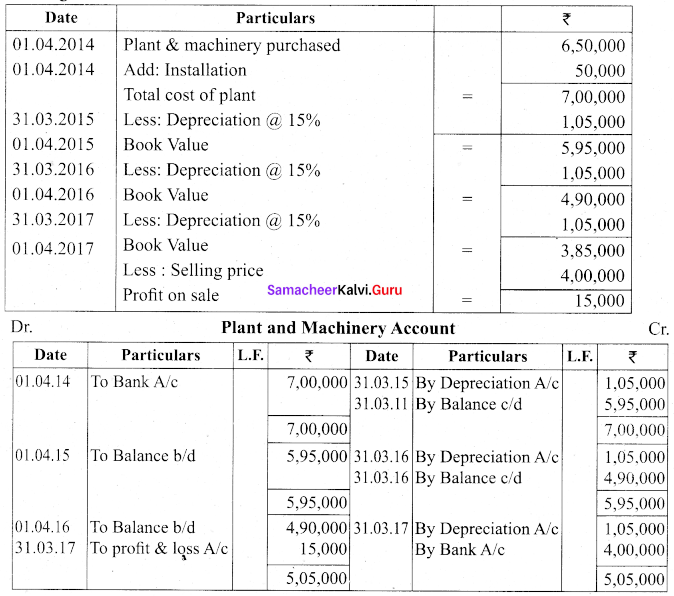
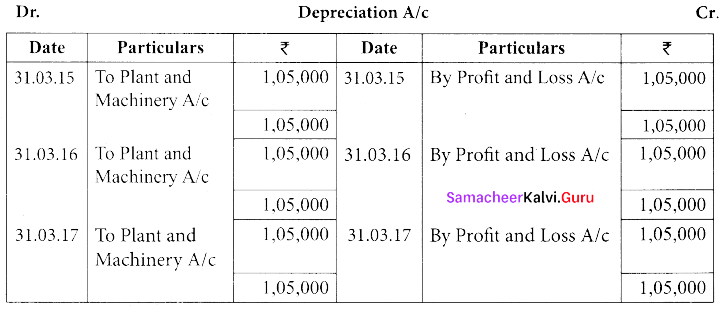
[OR]
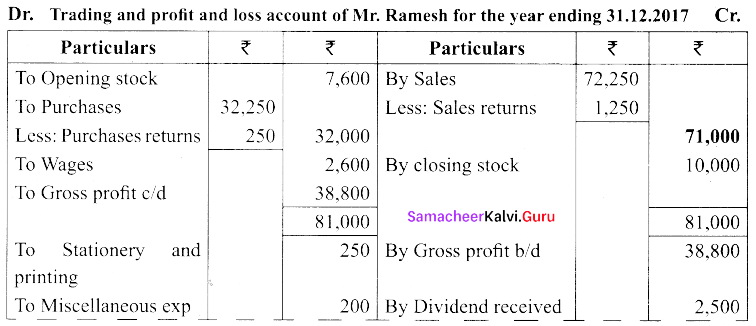
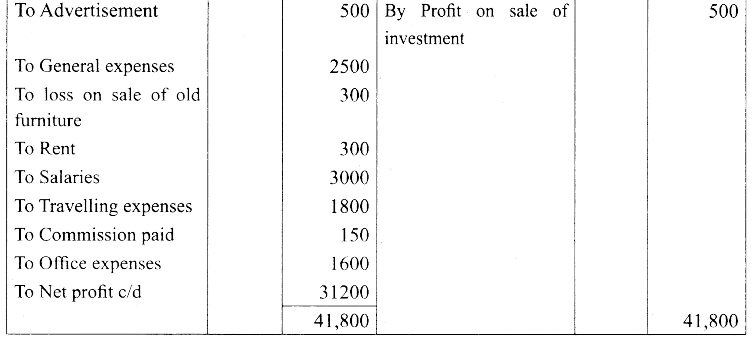
(b) From the following balances obtained from the books of Mr. Ramesh, prepare trading and profit and loss account.
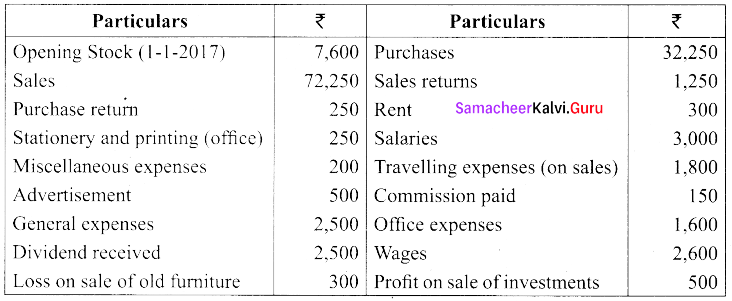
Closing stock on December 31.12.17 was ₹ 10,000/-
Answer:
![]()
Question 45.
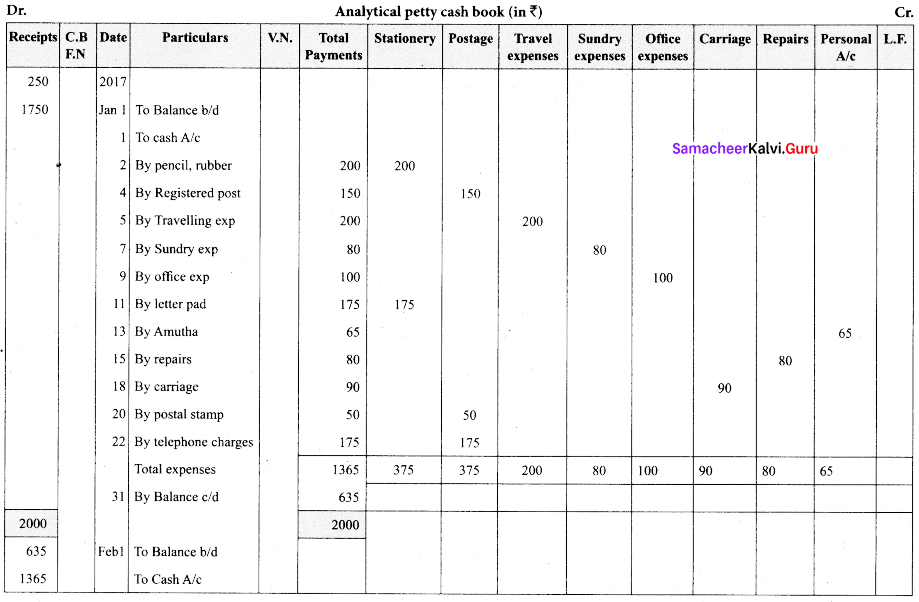
(a) Enter the following transactions in Rahim’s petty cash book with analytical columns under imprest system:
| 2017 | ₹ | |
| Jan. 1 | Balance on hand | 250 |
| Jan. 1 | Cash received from chief cashier | 1,750 |
| Jan. 2 | Purchased pencil, rubber and paper | 200 |
| Jan. 4 | Sent documents to Head office by Registered post | 150 |
| Jan. 5 | Travelling expenses paid to salesman | 200 |
| Jan. 17 | Paid for sundry expenses | 80 |
| Jan. 19 | Paid for office expenses | 100 |
| Jan. 11 | Paid for letter pad | 175 |
| Jan. 13 | Paid to Amutha on account | 65 |
| Jan. 15 | Paid for repairs to furniture | 80 |
| Jan. 18 | Carriage paid | 90 |
| Jan. 20 | Brought postal stamps | 50 |
| Jan. 22 | Paid for telephone charges | 175 |
Answer:
[OR]
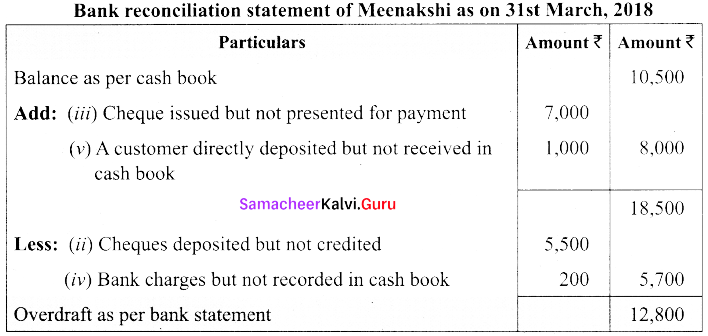
(b) From the following particulars of Meenakshi Traders, prepare a bank reconciliation statement as on 31st March 2018.
(i) Debit balance as per cash book ₹ 10,500.
(ii) Cheque deposited into bank amounting to ₹ 5,500 credited by bank, but entered twice in the Cash book.
(iiii) Cheques issued and presented for payment amounting to ₹ 7,000 omitted in the cash book.
(iv) Cheque book charges debited by the bank ₹ 200 not recorded in the cash book.
(v) Cash of ₹ 1,000 deposited by a customer of the business in cash deposit machine not recorded in the cash book.
Answer:
![]()
Question 46.
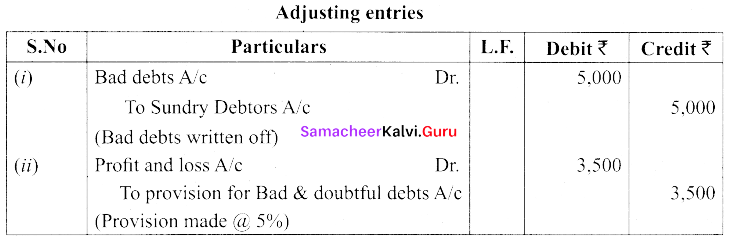
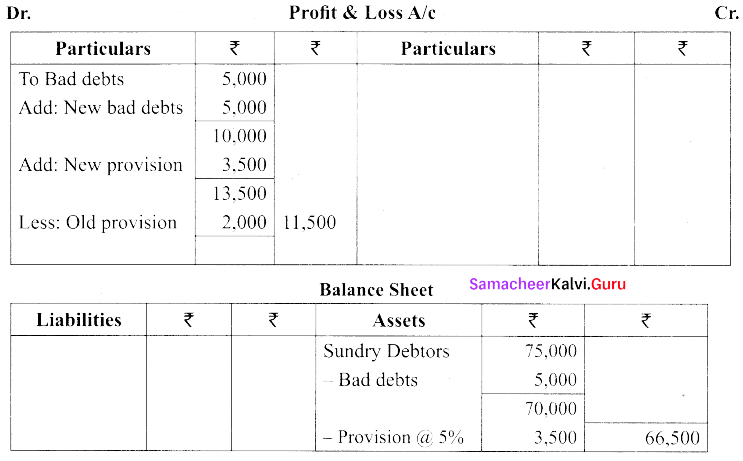
(a) The following are the extracts from the trial balance:
| Particulars | Dr. (₹) | Cr.(₹) |
| Sundry Debtors Bad debts
Provision for doubtful debts |
75,000
5,000 |
2,000 |
Additional Information:
(i) Additional bad debts ₹ 5,000
(ii) Provision for bad and doubtful debts @ 5% on sundry debtors.
You are required to pass necessary adjusting entries and show how these items will appear in profit and loss account and balance sheet.
Answer:
[OR]
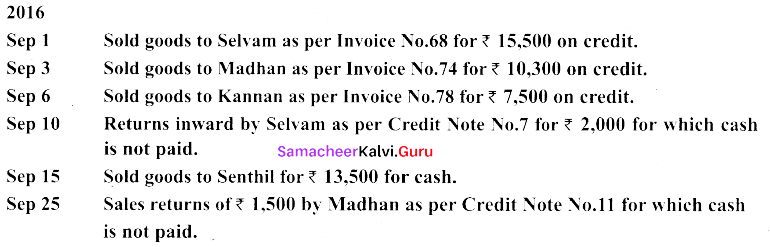
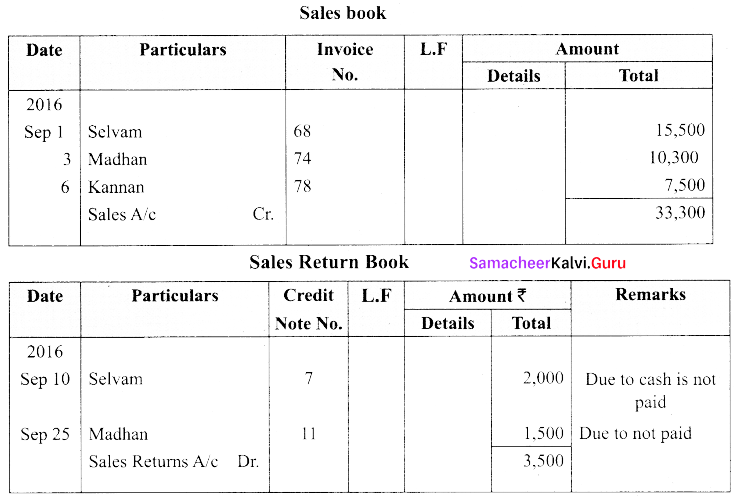
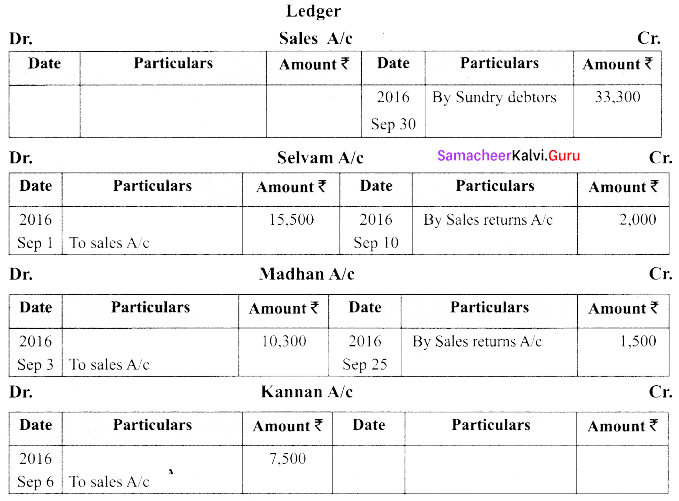
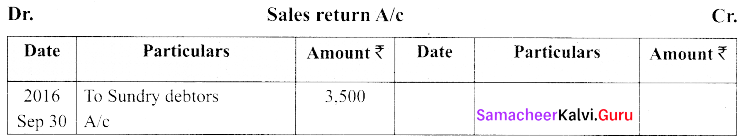
(b) Record the following transactions in the sales book and sales returns book of M/s. Roobini and Co., and post them to ledger.
Answer:
![]()
Question 47.
(a) Consider the following balances, extracted from the books of Jain as on 31st December 2016. Prepare the final accounts.
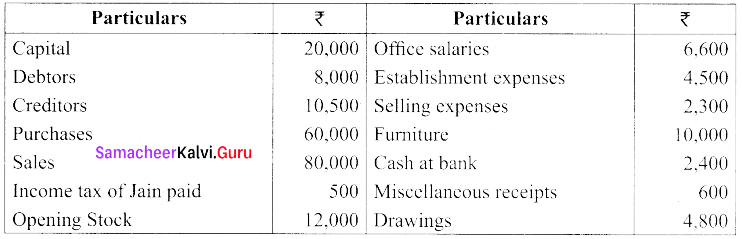
Adjustments:
(i) Salaries outstanding for December, 2016 amounted to ₹ 600
(ii) Provide depreciation on furniture @ 10% p.a
(iii) Provide Interest on capital for the year @ 5 % p.a
(iv) Stock on 31st December, 2016 ₹ 14,000
Answer:
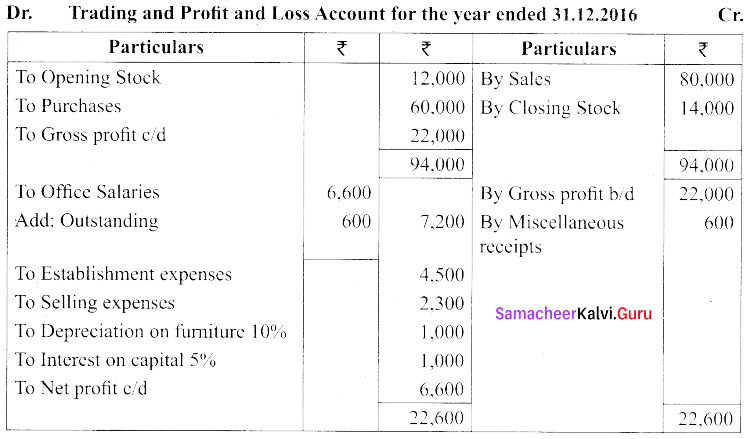
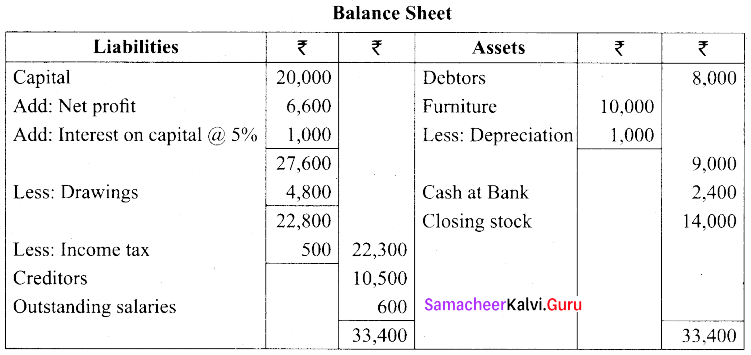
[OR]
(b) Write the advantages of Computerised Accounting System.
Answer:
Advantages of Computerised Accounting System:
The main advantages of computerised accounting system are as follows:
Faster processing: Computers require far less time than human beings in performing a particular task. Therefore, accounting data are processed faster using a computerised accounting system.
Accurate information: There is less space for error because only one account entry is needed for each transaction unlike repeated posting of the same accounting data in manual system.
Reliability: Computer systems are immune to boredom, tiredness or fatigue. Therefore, these can perform repetitive functions effectively and are highly reliable.
Easy availability of information: The data are easily available and Can be communicated to different users at the same time.
Up-to-date information: Account balances will always be up to date since the records are automatically updated as and when accounting data are entered or stored.
Efficiency: The computer based accounting system ensures better use of time and resources.
Storage and retrieval: Computer based systems require a fractional amount of physical space as compared to the books of accounts in the form of journals, ledgers and accounting registers.
Works as a motivator to employees: Employees using computer systems feel more valued as they are trained and specialised for the job.
Automated document production: Accounting reports like trial balance and financial statements are generated automatically and are easily accessible just by a click of the mouse.
MIS Reports: It is easier to monitor and control the business using the real time management reports generated by the computerised information systems.