Students can Download Tamil Nadu 11th Biology Model Question Paper 1 English Medium Pdf, Tamil Nadu 11th Biology Model Question Papers helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
TN State Board 11th Biology Model Question Paper 1 English Medium
Instructions:
- The question paper comprises of four parts Questions for Botany and Zoology are asked separately.
- You are to attempt all the parts. An internal choice of questions is provided wherever applicable.
- All questions of Part I, II, III, and IV are to be attempted separately.
- Question numbers 1 to 8 in Part I are Multiple Choice Questions of one mark each. These are to be answered by choosing the most suitable answer from the given four alternatives and Writing the option code and the Corresponding answer.
- Question numbers 9 to 4 in Part II are two-marks questions. This also is answered in about one or list sentences.
- Question numbers 15 to 19 in Part III are three-marks questions These are to be answered in about three to five short sentences.
- Question numbers 20 and 21 in Part IV are five-marks questions. These are to be answered in detail Draw diagrams wherever necessary.
Time: 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 70
Bio-Botany [Maximum Marks: 35]
Part – I
Answer all the questions. Choose the correct answer. [8 × 1 = 8]
Question 1.
Which of the following pteridophyte is used as a biofertiliser?
(a) Marsilea
(b) Pteridium
(c) Pteris
(d) Azolla
Answer:
(d) Azolla
Question 2.
Which is not a character of root stock?
(a) Nodes
(b) Intemodes
(c) Terminal bud
(d) Root cap
Answer:
(d) Root cap
![]()
Question 3.
Who first proposed the early elementary rule of naming plants?
(a) A.P.de Candolle
(b) Linnaeus
(c) Alphonse de Candolle
(d) Simpson
Answer:
(b) Linnaeus
Question 4.
Which of the following alone is formed in the division of plant cells?
(a) Aster
(b) Centrioles
(c) Spindle
(d) Microtubules
Answer:
(c) Spindle
![]()
Question 5.
A complete turn of the helix comprises
(a) 34 nm
(b) 3.4 nm
(c) 20 nm
(d) 2 nm
Answer:
(b) 3.4 nm
Question 6.
Sun hemp is obtained from
(a) Crotolaria juncea
(b) Corchorus capsularis
(c) Linum ustitaissimum
(d) Cannabis sativa
Answer:
(a) Crotolaria juncea
Question 7.
The color of the light is determined by its
(a) Intensity
(b) Refractive power
(c) Wave length
(d) Reflection
Answer:
(c) Wave length
Question 8.
Which among the following step is common in both aerobic and anaerobic respiration?
(a) Pyruvate oxidation
(b) Glycolysis
(c) ETC
(d) TCA cycle
Answer:
(b) Glycolysis
![]()
Part – II
Answer any four of the following questions. [4 × 2 = 8]
Question 9.
Write the chemical composition of bacterial cell wall.
Answer:
The chemical composition of cell wall is rather complex and is made up of peptidoglycan or mucopeptide (N-acetyl glucosamine, N-acetyl muramic acid and peptide chain of 4 or 5 aminoacids).
Question 10.
Differentiate between vegetative morphology & reproductive morphology.
Answer:
Vegetative morphology :
Vegetative morphology deals with the shoot system and root system.
Reproductive morphology :
Reporductive morphology deals with flowers, inflorescence, fruits and seeds.
Question 11.
What are vernacular names? Give an example.
Answer:
Vernacular names are kjiown as common names, Example: Albizia amara L. is called as Usilai in South Tamil Nadu and Thurinji in North Tamil Nadu.
Question 12.
What is the role of plasmodesmata in a plant cell?
Answer:
Plasmodesmata act as a channel between the protoplasm of adjacent cells through which I many substances pass through.
![]()
Question 13.
Define transport in plants. Mention the tissues involved in transportation.
Answer:
Transport is the process of moving water, minerals and food to all parts of the plant body.
Conducting tissues such as xylem and phloem play an important role in transport.
Question 14.
What is a Lichen?
Answer:
Lichens is a mutual association of Algae and Fungi. Algae prepares food and fungi absorbs water and provides thallus structure.
Part – III
Answer any three questions in which question number 19 is compulsory. [3 x 3 = 9]
Question 15.
List out the importance of Mycorrhiza.
Answer:
- Flelps to derive nutrition in Monotropa, a saprophytic angiosperm.
- Improves the availability of minerals and water to the plants.
- Provides drought resistance to the plants.
- Protects roots of higher plants from the attack of plant pathogens.
Question 16.
Classify buds based on their origin & function.
Answer:
Based on origin, buds are classified into (a) Terminal or Apical bud and (b) Lateral or Axillary or Axil bud. Based on function, buds are classified into (a) Vegetative bud and (b) Floral or Reproductive bud.
Question 17.
Distinguish between Karyokinesis & Cytokinesis.
Answer:
Karyokinesis
- Involves division of nucleus.
- Nucleus develops a constriction at the center and becomes dumbcllshaped.
- Constriction deepens and divides the nucleus into two.
Cytokinesis :
- Involves division of cytoplasm.
- Plasma membrane develops a constriction along nuclear constriction.
- It deepens centripetally and finally divides the cell into two cells.
Question 18.
Draw & label bicollateral vascular bundle.
Answer:
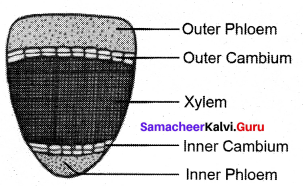
![]()
Question 19.
Point out the significances of photorespiration.
Answer:
Significance of photorespiration
- Glycine and Serine synthesised during this process are precursors of many biomolecules like chlorophyll, proteins, nucleotides.
- It consumes excess NADH + H+ generated.
- Glycolate protects cells from Photo oxidation.
Part – IV
Answer all the questions. [2 × 5 = 10]
Question 20.
Define ptyxis & explain its types.
Answer:
Rolling or folding of individual leaves is called ptyxis. There are seven types of ptyxis as follows:
- Reclinate – When the upper half of the leaf blade is bent upon the lower half as in loquat (Eriobotiya japonica).
- Conduplicate – When the leaf is folded lengthwise along the mid-rib, as in guava, sweet
potato and camel’s foot tree (Bauhinia). - Plicate or Plaited – When the leaf is repeatedly folded longitudinally along ribs in a zig¬zag manner, as in Borassus flabellifer.
- Circinate – When the leaf is rolled from the apex towards the base like the tail of a dog, as in ferns.
- Convolute – When the leaf is rolled from one margin to the other, as in banana, aroids and Indian pennywort. Musa and members of Araceae.
- Involute – When the two margins are rolled on the upper surface of the leaf towards the mid-rib or the centre of the leaf, as in water lily, lotus, Sandwich Island Climber (.Antigonon) and Plumbago.
- Crumpled – When the leaf is irregularly folded as in cabbage.
[OR]
Explain Clitoria ternatea in botanical terms. Draw floral diagram.
Answer:
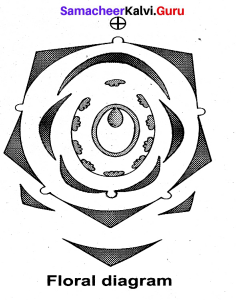
- Habit: Twining climber
- Root: Branched tap root system having nodules.
- Stem: Aerial, weak stem and a twiner.
- Leaf: Imparipinnately compound, alternate, stipulate showing reticulate venation. Leaflets are stipellate.
Petiolate and stipels are pulvinated. - Inflorescence: Solitary and axillary
- Flower: Bracteate, bracteolate, bracteoles usually large, pedicellate, heterochlamydeous, complete, bisexual, pentamerous, zygomorphic and hypogynous.
- Calyx: Sepals 5, synsepalous, green showing valvate aestivation. Odd repel is anterior in position.
- Corolla: Petals 5, white or blue apopetalous, irregular papilionaceous corolla showing, descendingly imbricate aestivation.
- Androecium: Stamens 10, diadelphous (9) + 1 nine stamens fused to form a bundle and the tenth stamen is free. Anthers are dithecous, basifixed, introse and dechising by longitudinal slits.
- Gynoecium: Monocarpellary, uni-locular, with many ovules on marginal placentation, ovary superior, style simple and incurved with feathery stigma.
- Fruit: Legume
- Seed: Non-endospermous, reniform.
- Floral Formula:
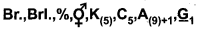
![]()
Question 21.
Explain about Cohesion – Tension Theory.
Answer:
Cohesion-tension theory was originally proposed by Dixon and Jolly (1894) and again put forward by Dixon (1914, 1924). This theory is based on the following features:
i. Strong cohesive force or tensile strength of water: Water molecules have the strong mutual force of attraction called cohesive force due to which they cannot be easily separated from one another. Further, the attraction between a water molecule and the wall of the xylem element is called adhesion. These cohesive and adhesive force works together to form an unbroken continuous water column in the xylem. The magnitude of the cohesive force is much high (350 atm) and is more than enough to ascent sap in the tallest trees.
ii. Continuity of the water column in the plant: An important factor which can break the water column is the introduction of air bubbles in the xylem. Gas bubbles expanding and displacing water within the xylem element is called cavitation or embolism. However, the overall continuity of the water column remains undisturbed since water diffuses into the adjacent xylem elements for continuing ascent of sap.
iii. Transpiration pull or Tension in the unbroken water column: The unbroken water column from leaf to root is just like a rope. If the rope is pulled from the top, the entire rope will move upward. In plants, such a pull is generated by the process of transpiration which is known as transpiration pull. Water vapour evaporates from mesophyll cells to the intercellular spaces near stomata as a result of active transpiration.
The water vapours are then transpired through the stomatal pores. Loss of water from mesophyll cells causes a decrease in water potential. So, water moves as a pull from cell to cell along the water potential gradient. This tension, generated at the top (leaf) of the unbroken water column, is transmitted downwards from petiole, stem and finally reaches the roots. The cohesion theory is the most accepted among the plant physiologists today.
[OR]
Demonstrate alcoholic fermentation using Kuhne’s apparatus.
Answer:
Demonstration of alcoholic fermentation:
Take a Kuhne’s fermentation tube which consists of an upright glass tube with side bulb. Pour 10% sugar solution mixed with baker’s yeast into the fermentation tube the side tube is filled plug the mouth with lid. After some time, the glucose solution will be fermented. The solution will give out an alcoholic smell and level of solution in glass column will fall due to the accumulation of CO2 gas.
It is due to the presence of zymase enzyme in yeast which converts the glucose solution into alcohol and CO2. Now introduce a pellet of KOH into the tube, the KOH will absorb CO2 and the level of solution will rise in upnght tube.
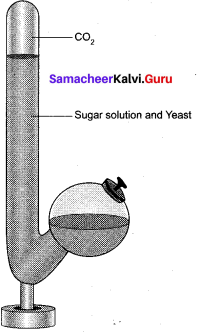
![]()
Bio-Zoology[Maximum Marks: 35]
Part – I
Answer all the questions. Choose the correct answer. [Answers are in bold] [8 × 1 = 8]
Question 1.
Two words comprising the binomial nomenclature are
(a) Family & genus
(b) Order & Family
(c) Genus & species
(d) Species & Variety
Answer:
(c) Genus & species
Question 2.
Which of the following animals has a true coelom?
(a) Ascaris
(b) Pheretima
(c) Sycon
(d) Taenia Solium
Answer:
(b) Pheretima
![]()
Question 3.

Answer:
(a) 1 – (ii), 2 – (i), 3 – (iv), 4 – (iii)
Question 4.
ERV stands for ………..
(a) Expiratory Reserve Volume
(b) Exchange Reserve Volume
(c) Exchange Residual Volume
(d) Expiratory Residual Volume
Answer:
(a) Expiratory Reserve Volume
Question 5.
Which of the following is an correct statement?
(a) There are about 5 to 6-5 millions of RBC mnr3 of blood in a healthy man.
(b) Approximately 7000 to 8000 per cubic mm of WBC’s are seen in the blood of an average healthy individuals. ‘
(c) Lymphocytes constitute 38% of WBC’s
(d) Blood normally contains 1,50,000-3,50,000 platelets mm-3 of blood.
Answer:
(d) Blood normally contains 1,50,000-3,50,000 platelets mm-3 of blood.
Question 6.
Which of the following is an incorrect statement?
(a) Sarcomere is the functional unit of cardiac muscles.
(b) Myoglobin is a red-coloured respiratory pigment of the muscle fibre.
(c) The study of muscle is called myology.
(d) Skeletal muscle is attacked to the bone by a bundle of collagen fibres known as tendon.
Answer:
(a) Sarcomere is the functional unit of cardiac muscles.
![]()
Question 7.
Which is right combination of names of ear ossicles?
(a) Malleus, incus and cochlus
(b) Malleus, incus and stapes
(c) Magnus, incus and stapes
(d) Malleus, incus and cochlea
Answer:
(b) Malleus, incus and stapes
Question 8.
This breed is chiefly found in West Bengal.
(a) Brahma
(b) Aseet
(c) Leghorn
(d) Chittagorg
Answer:
(d) Chittagorg
Part – II
Answer any four of the following questions. [4 × 2 = 8]
Question 9.
Name the sensory organs of arthopods?
Answer:
Antennae, Simple and Compound eyes, statocysts.
Question 10.
Distinguish between living and non living things
Answer:
Living things :
- Living things exhibit life processes such as nutrition, respiration, excretion, metabolism. growth, movement.
- These are b lotie component of ecosystem.
Non-living things
- Non living things do not exhibit life processes.
- These are abiotic component of ecosystem.
Question 11.
Define tissues.
Answer:
Group of cells that are similar in structure and perform a common or related functions are called tissues.
Question 12.
Draw the diagram of Rana hexadactlya – Brain dorsal view.
Answer:
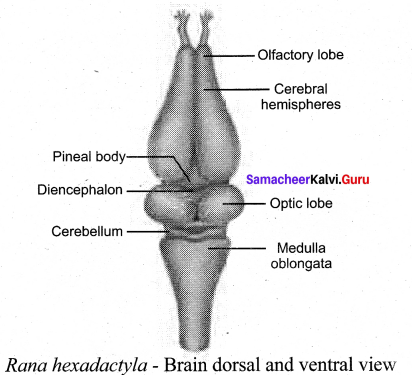
Question 13.
Name the proteins which regulates the contraction of muscles.
Answer:
Actin, myosin, tropomyosin and troponin.
![]()
Question 14.
List any three common uses of shellac.
Answer:
- Shellac with denatural alcohol is used to remove dust on the walls.
- Coating of metals with shellac prevents rusting.
- Shellac coating on citrus fruits increases their shelf life.
Part – III
Answer any three questions in which question number 19 is compulsory. [3 × 3 = 9]
Question 15.
What are flame cells and their functions?
Answer:
Flame cells are the specialized excretory cells in flatworms. They help in excretion and osmoregulation. Flame cells or solanocytes are the excretory cells.
Question 16.
How does cockroach survive without a head?
Answer:
A cockroach can live for a week without its head. Due to their open circulatory system, and the fact that they breathe through little holes on each of their body segments, since they are not dependent on the mouth or head to breathe. The cockroach dies later due to starvation.
Question 17.
Distinguish between Oviparous and Viviparous animals.
Answer:
Oviparous animals :
- The egg laying animals are known as Oviparous animals.
- They make contain yolk for embryonic development, eg. Birds
Viviparous animals :
- The animals which give birth to young ones are called Viviparous animals.
- The developing embryo derives nutrients from the parent, eg. Man
Question 18.
Explain limbic systems.
Answer:
Limbic system: The inner part of the cerebral hemisphere constitutes the limbic system. The main components of limbic system are olfactory bulbs, cingulate gyrus, mammillary body, . amygdala, hippocampus and hypothalamus. The limbic system is called ‘emotional brain’ because it plays a primary role in the regulation of pleasure, pain, anger, fear, sexual feeling and affection. The hippocampus and amygdala also play a role in memory. Brain stem is the part of the brain between the spinal cord and the diencephalon. It consists of mid brain, pons varolii and medulla oblongata.
Question 19.
Draw the diagram and label the parts of lobes of cerebral hemisphere.
Answer:
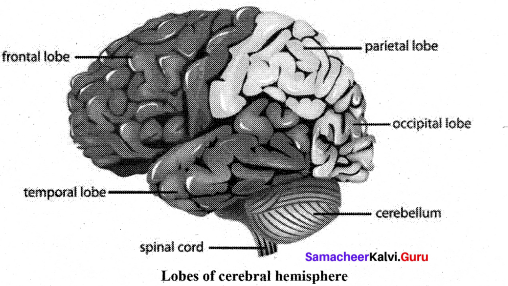
![]()
Part – IV
Answer all the questions. [2 x 5 = 10]
Question 20.
Write the general characteristics of phylum Echinodermata.
Answer:
All Echinoderms are marine animals. The adults are radially symmetrical but the larvae are bilaterally symmetrical. These animals have a mesodermal endoskeleton of calcareous ossicles and hence the name Echinodermata (spiny skin). They are exclusively marine with organ system level of organisation. The most distinctive feature of echinoderms is the presence of the water vascular system or ambulacral system with tube feet or podia, which helps in locomotion, capture and transport of food and respiration.
The digestive system is complete with mouth on ventral side and anus on the dorsal side. Excretory organs are absent. The nervous system and sensory organs are poorly developed. The circulatory system is open type without heart and blood vessels. Sexes are separate. Reproduction is sexual and fertilization is external, pevelopment is indirect with free swimming bilaterally symmetrical larval forms. Some echinoderms exhibit autotomy with remarkable powers of regeneration.
Examples: Asterias (Starfish or sea star), Echinus (Sea-urchin), Antedon (Sea-lily), Cucumaria (Sea-cucumber), Ophiura (Brittle star)
[OR]
Explain the respiratory system of Rana hexadactyla.
Answer:
Frog respires on land and in the water by two different methods. In water, skin acts as aquatic respiratory organ (cutaneous respiration). Dissolved oxygen in the water gets, exchanged through the skin by diffusion. On land, the buccal cavity, skin and lungs act as the respiratory organs. In buccal respiration on land, the mouth remains permanently closed while the nostrils remain open. The floor of the buccal cavity is alternately raised and lowered, so air is drawn into and expelled out of the buccal cavity repeatedly through the open nostrils. Respiration • by lungs is called pulmonary respiration. The lungs are a pair of elongated, pink coloured saclike structures present in the upper part of the trunk region (thorax). Air enters through the nostrils into the buccal cavity and then to the lungs. During aestivation and hibernation gaseous exchange takes place through skin.
Question 21.
What are the steps of insertion of nucleus into Oyster?
Answer:
In this method, a piece of mantle of living oyster is cut off and inserted together with a suitable nucleus inside the living tissue of another oyster. Following steps are taken for the insertion of nucleus.
a. Fitness of oyster for operation
The selected oysters for the insertion of nucleus should be healthy and strong enough to overcome the stress during operation
b. Preparation of graft tissues
The piece of tissue which is inserted inside the mantle is called as ‘GRAFT’ tissue. The outer edges of these graft squares must be known because nacre secreting cells are found only on the outer surface of the mantle so it is essential to keep the outer surface in contact with the inserted nucleus.
c. Preparation of nucleus
Any small particle may function as nucleus to initiate the pearl formation but it is reported that calcareous nucleus is the best because the deposition of nacre was found to be more on calcarious nucleus.
d. Insertion of nucleus
For the insertion of nucleus, oysters are fixed in a desk clamp in the position of right valve facing upward. Mantle folds are smoothly touched to expose the foot and the main body mass, followed by an incision into the epithelium of the foot and a slender channel into the main mass one graft tissue which functions as a bed for the nucleus.
e. Post operation care :
Nucleated oysters are placed into cages and suspended into sea water and attached with floating rafts to a depth of 2 to 3 metres for about 6 to 7 days to recover from the shocks due to operation. This period of 6 to 7 days is known as ‘Recovery period’. About 3000 to 3600 nucleated oysters are kept in different cages suspended in sea water at 2 to 3 meters depth for 3 to 6 years and undisturbed except at the time of clearing and inspection.
![]()
[OR]
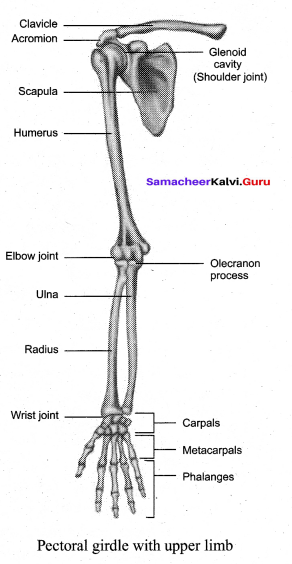
Write a note on Pectoral girdle.
Answer:
The upper limbs are attached to the pectoral girdles. These are very light and allow the upper limbs a degree of mobility not seen anywhere else in the body. The girdle is formed of two halves. Each half of the pectoral girdle consists of a clavicle or collar bone and a scapula. The scapula is a large, thin, triangular bone situated in the dorsal surface of the ribcage between the second and seventh ribs. It has a slightly elevated ridge called the spine which projects as a flat, expanded process called the acromion.
The clavicle articulates with this process. Below the acromion is a depression called the glenoid cavity which articulates with the head of the humerus to form the shoulder joint. Each clavicle is a long slender bone with two curvatures which lies horizontally and connects axial skeleton with appendicular skeleton.