Students can Download Tamil Nadu 11th Biology Previous Year Question Paper March 2019 English Medium Pdf, Tamil Nadu 11th Biology Model Question Papers helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
TN State Board 11th Biology Previous Year Question Paper March 2019 English Medium
Instructions:
- The question paper comprises of four parts Questions for Botany and Zoology are asked separately.
- You are to attempt all the parts. An internal choice of questions is provided wherever applicable.
- All questions of Part I, II, III, and IV are to be attempted separately.
- Question numbers 1 to 8 in Part I are Multiple Choice Questions of one mark each. These are to be answered by choosing the most suitable answer from the given four alternatives and Writing the option code and the Corresponding answer.
- Question numbers 9 to 4 in Part II are two-marks questions. This also is answered in about one or list sentences.
- Question numbers 15 to 19 in Part III are three-marks questions These are to be answered in about three to five short sentences.
- Question numbers 20 and 21 in Part IV are five-marks questions. These are to be answered in detail Draw diagrams wherever necessary.
Time: 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 70
Bio-Botany [Maximum Marks: 35]
Part – I
Answer all the questions. Choose the correct answer. [8 × 1 = 8]
Choose the most appropriate answer from the given four alternative and write the option code and the corresponding answer.
Question 1.
For every CO2 molecule entering the C3 cycle, the number of ATP and NADPH required is ………………….
(a) 3 ATP + 2 NADPH
(b) 3 ATP + 3 NADPH
(c) 2 ATP + 2 NADPH
(d) 2 ATP + 3 NADPH
Answer:
(a) 3 ATP + 2 NADPH
![]()
Question 2.
If the haploid number of chromosomes for an angiosperm is 14, then the number of chromosome in its endosperm would be………………….
(a) 42
(b) 28
(c) 7
(d) 14
Answer:
(a) 42
Question 3.
Vexillary aestivation is characteristic feature of ……………….family.
(a) Solanaceae
(b) Brassicaceae
(c) Fabaceae
(d) Asteraceae
Answer:
(c) Fabaceae
![]()
Question 4.
Which of the following represents symport?
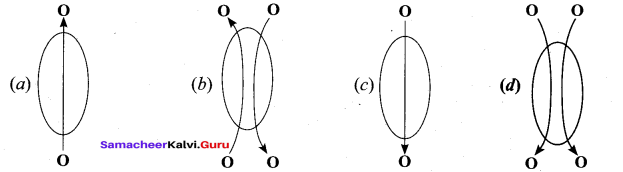
Answer:
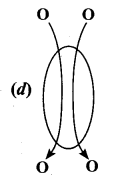
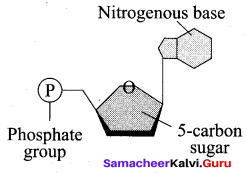
Question 5.
Answer:
The above structure represents a …………………..
(a) Polynucleotide
(b) Amino acid
(c) Nucleoside
(d) Nucleotide
Answer:
(d) Nucleotide
Question 6.
The pairing of Homologous chromosomes on Meiosis is known as …………………..
(a) Disjunction
(b) Synergids
(c) Bivalent
(d) Synapsis
Answer:
(d) Synapsis
![]()
Question 7.
Photosynthetic roots are seen in …………………..
(a) Vanda
(b) Tinospora
(c) Cuscuta
(d) Viscum
Answer:
(b) Tinospora
Question 8.
Match:

(a) (1 )-(iii), (2)-(iv), (3)-(ii), (4)-(i)
(b) (1)-(iii), (2)-(ii), (3)-(i), (4)-(iv)
(c) (1)-(iv), (2)-(ii), (3)-(iii), (4)-(i)
(d) (1)-(i), (2)-(iv), (3)-(iii), (4)-(ii)
Answer:
(a) (1 )-(iii), (2)-(iv), (3)-(ii), (4)-(i)
Part – II
Answer any four of the following questions. [4 × 2 = 8]
Question 9.
(a) What is Plectostele? Give an example.
(b) Mention any one character shared by gymnosperms and angiosperms.
Answer:
(a) Plectostele: Xylem plates alternates with phloem plates, e.g., Lycopodium clavatum.
(b) Gymnosperms :
- Vessels are absent (except Gnetales)
- Phloem lacks companion cells
Angiosperms :
- Vessels are present
- Companion cells are present
Question 10.
List the primary ftmctions of Leaf.
Answer:
Primary functions of the leaf:
- Photosynthesis
- Transpiration
- Gaseous exchange
- Protection of buds
- Conduction of water and dissolved solutes
![]()
Question 11.
A series of events leading to the formation of new cell is known as Cell Cycle. Give the diagrammatic view of Cell Cycle.
Answer:
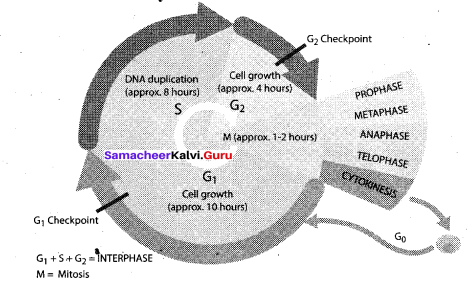
Question 12.
Name the following diagrams.
Answer:
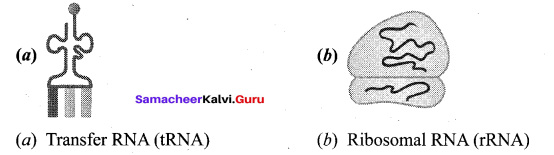
Question 13.
Mention the different types of plasmolysis seen in plant cells.
Answer:
- Incipient plasmolysis
- Evident plasmolysis and
- Final plasmolysis.
![]()
Question 14.
Tabulate any two differences between Cyclic and Non-Cyclic photophosphorylation.
Answer:
Differences between Cyclic Photophosphorylation and Non-Cyclic Photophosphorylation:
Cyclic Photophosphorylation :
- PS I only involved.
- Photolysis of water does not take place.
Non-Cyclic Photophosphorylation :
- PS I and PS II involved.
- Photolysis of water takes place.
![]()
Part – III
Answer any 3 questions. Question No. 19 is compulsory. [3 × 3 = 9]
Question 15.
Explain the different types of placentation with example.
Answer:
- Marginal placentation: It is with the placentae along the margin of a unicarpellate ovary. e.g., Fabaceae.
- Axile placentation: The placentae arises from the column in a compound ovary with septa. e.g., Hibiscus, tomato and lemon.
- Superficial placentation: Ovules arise from the surface of the septa, e.g., Nyrhphaeceae.
- Parietal: It is the placentae on the ovary walls or upon intruding partitions of a unilocular, compound ovary, e.g., Mustard, argemone and cucumber.
- Free-central placentation: It is with the placentae along the column in a compound ovary without septa, e.g., Caryophyllaceae, Dianthus and primrose.
- Basal: It is the placenta at the base of the ovary, e.g, Sunflower (Asteraceae) Marigold.
Question 16.
(a) Draw and label the structure of Mitochondria.
(b) Why Mitochondria is called as ‘the power house of a cell’?
Answer:
(a) Structure of Mitochondrion:
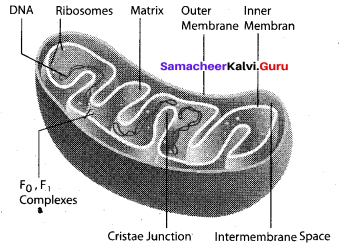
(b) Since huge amount of energy is generated in mitochondria in the form of ATP molecules they are called ‘power house of the cell’.
Question 17.
A transverse section of the trunk of a tree shows concentric rings which are known as growth rings. What are the significances of studying about these rings ?
Answer:
- Age of wood can be calculated
- The quality of timber can be ascertained
- Radio-Carbon dating can be verified
- Past climate and archaeological dating can be made.
- Provides evidence in forensic investigation
![]()
Question 18.
(a) What is the formula for Respiratory Quotient?
(b) Write any two significances of Pentose Phosphate Pathway.
Answer:
(a) Formula for Respiratory Quotient:
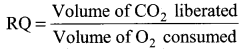
(b) Significances of Pentose Phosphate Pathway:
- HMP shunt is associated with the generation of two important products, NADPH and pentose sugars, which play a vital role in anabolic reactions.
- Coenzyme NADPH generated is used for reductive biosynthesis and counter damaging the effects of oxygen free radicals
Question 19.
(a) The equations given below represent the different stages of Nitrogen Cycle in plants.
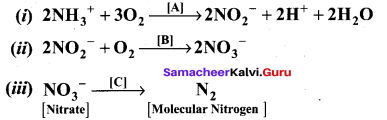
In the above equations [A], [B], [C] indicate the bacteria which is responsible for the reaction. Name them.
(b) Define Denitrification.
(c) Which enzyme is required for Nitrogen fixation?
Answer:
(a) (i) A – Nitrosomonas
(ii) B – Nitrobacter
(iii) C – Pseudomonas
(b) Denitrification: Nitrates in the soil are converted back into atmospheric nitrogen by a process called denitrification. Bacteria involved in this process are Pseudomonas, Thiobacillus and Bacillus subtilis.
![]()
(c) Enzyme required for Nitrogen fixation: Nitrate Reductase, Nitrite Reductase
![]()
Part – IV
Answer all the questions. [2 × 5 = 10]
Question 20.
(a) (i) A Danish Physician, Christian Gram developed a staining procedure to differentiate bacteria. List the various steps involved in that procedure.
(ii) Distinguish between Deoxy viruses and Ribo viruses with example.
[OR]
(b) Describe the Floral characters of Allium Cepa with a neat floral diagram.
Answer:
(a) (i) Gram staining Techniques :
- Prepare a smear of bacterial culture.
- Stain with crystal violet for 30 seconds
- Rinse in distilled water for 2 seconds
- Grams Iodine for 1 minute
- Rinse in distilled water
- Wash in 95% ethanol or acetone for 10 to 30 seconds
- Rinse in distilled water
- Safranin for 30-60seconds
- Rinse in distilled water and blot
- Observe under microscope
(ii) Deoxy viruses
Viruses having DNA are called deoxyviruses. E.g. Animal viruses except HIV
Ribo viruses :
Viruses having RNA are called riboviruses. E.g. Plant viruses except cauliflower mosaic vims (CMV)
![]()
[OR]
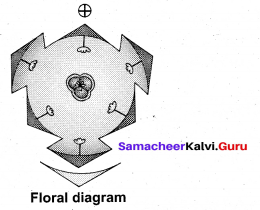
(b) Floral Characters of Allium cepa:
Answer:
- Habit: Perennial herb with bulb.
- Root: Fibrous adventitious root system
- Stem: Underground bulb
- Leaf: A cluster of radical leaves emerges from the underground bulb, cylindrical and fleshy having sheathy leaf bases with parallel venation.
- Inflorescence: Scapigerous i.e. the inflorescence axis (peduncle) arising from the ground bearing a cluster of flowers at its apex. Pedicels are of equal length, arising from the apex of the peduncle which brings all flowers at the same level.
- Flower: Small, white, bracteate, bracteolate, pedicellate, complete, trimerous, actinomorphic and hypogynous. Flowers are protandrous.
- Perianth: Tepals 6, white, arranged in two whorls of three each, syntepalous showing valvate aestivation.
- Androecium: Stamens 6, arranged in two whorls of three each, epitepalous, apostamenous / free and opposite to tepals. Anthers dithecous, basifixed, introse and dehiscing longitudinally.
- Gynoecium: Tricarpellary and syncarpous. Ovary superior, trilocular with two ovules in each locule on axile placentation. Style simple, slender with simple stigma.
- Fruit: A loculicidal capsule.
- Seed: Endospermous .
- Floral Formula:
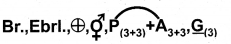
Question 21.
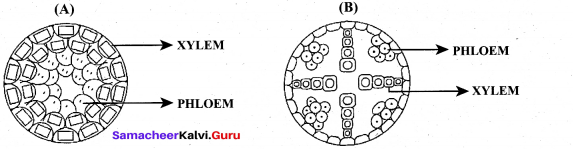
(a) (i) Draw and label the internal structure of Nerium leaf
(ii) Name the following Vascular Bundle.
Answer:
(b) (i) Write any four points regarding Physiological effects of cytokinins.
(ii) Define Vernalisation.
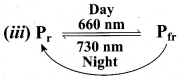
In the above representation, what does Pr and Pfr stand for?
Answer:
(a) (i) Internal structure of Nerium leaf:
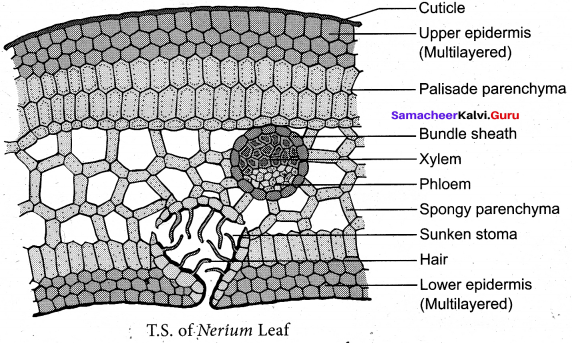
(ii) Vascular Bundle :
(A) Concentric Amphivasal vascular bundle
(B) Radial arrangement
![]()
[OR]
(b) (i) Physiological effects of cytokinins:
- Cytokinin promotes cell division in the presence of auxin (IAA)
- Cytokinin can break the dormancy of certain light-sensitive seeds like tobacco and induces seed germination
- Cytokinin promotes the growth of lateral bud in the presence of apical bud
- Cytokinin (i) increases rate of protein synthesis (ii) induces the formation of inter-fascicular cambium (iii) overcomes apical dominance (iv) induces formation of new leaves, chloroplast and lateral shoots.
(ii) Vernalisation: Many species of biennials and perennials are induced to flower by low temperature exposure (0°C to 5°C). This process is called vernalization. The term vernalization was first used by T.D. Lysenko (1938).
(iii) Pr – Phytochrome red (660 nm)
Pfr– Phytochrome far red(730 nm)
Bio-Zoology[Maximum Marks: 35]
Part – I
Answer all the questions. [8 × 1 = 8]
Choose the most appropriate answer from the given four alternative and write the option code and the corresponding answer.
Question 1.
Vital Capacity is ………………………………
(a) RV + ERV
(b) TV + IRV + ERV
(c) TV + IRV
(d) TV + ERV
Answer:
(b) TV + IRV + ERV
Question 2.
When a cockroach tries to enter into the ear of a sleeping person, which one of the following process will start ?
(a) Stimulation of negative feedback mechanism
(b) Neuromuscular fatigue
(c) Unconditioned reflex
(d) Conditioned reflex
Answer:
(c) Unconditioned reflex
![]()
Question 3.
Which one of the following is correct pair ?
(a) Exotic breed – Cyprinus Carpio
(b) Apiculture – Reeling
(c) Sericulture – Propolis
(d) Milch breed – Malvi
Answer:
(a) Exotic breed – Cyprinus Carpio
Question 4.
If Henle ’s Loop were absent from mammalian nephron, which one of the following is to be expected ?
(a) The urine will be more concentrated
(b) The urine will be more diluted
(c) There will be no urine formation
(d) There will be hardly any change in the quality and quantity of urine formed
Answer:
(b) The urine will be more diluted
Question 5.
The cytoplasm of the muscle fibre is called …………………….
(a) Myofibril
(b) Sarcoplasm
(c) Sarcomere
(d) Sarcolemma
Answer:
(b) Sarcoplasm
Question 6.
Three domain classification was proposed by
(a) Cavalier Smith
(b) R.H. Whittaker
(c) Carolus Linnaeus
(d) Carl Woese
Answer:
(d) Carl Woese
![]()
Question 7.
Which of the statements regarding lac insect is True ?
(i) Microscopic resinous crawling scale insect.
(ii) Inserts its proboscis into plant tissue, suck juices and grows.
(iii) Secretes lac from the hind end of the body.
(iv) The male lac insect is responsible for large scale production of lac.
(a) (ii), (i) and (iv) are correct
(b) (i), (iii) and (iv) are correct
(c) (i), (ii) and (iii) are correct
(d) (ii), (iii) and (iv) are correct
Answer:
(c) (i), (ii) and (iii) are correct
Question 8.
Which of the following is not present in the same rank ?
(a) Diptera
(b) Insecta
(c) Primata
(d) Orthoptera
Answer:
(c) Primata
![]()
Part – II
Answer any four of the following questions. [4 × 2 = 8]
Question 9.
Classify the animals based on the body cavity.
Answer:
The cavity between the body wall and the gut wall is called coelom. In some animals, the body cavity is not fully lined by the mesodermal epithelium. The mesoderm is formed as scattered pouches between the ectoderm and endoderm. Such a body cavity is called a pseudocoel. The animals which have pseudocoel e.g. round worms.
If the coelom develops within the mesoderm and is lined by mesodermal epithelium it is called eucoelom. The animals which have true coelom are called eucoelomates. If the body cavity is formed by splitting of mesoderm, the animals are called schizocoelomates. e.g., Annelids, arthropods and molluscs. If the body cavity is formed from the mesodermal pouches of archenteron, the animals are called enterocoelomate animals, e.g., echinoderms, hemichordates and chordates.
Question 10.
Name the layers found in Human Blood Vessels.
Answer:
- The blood vessels in humans are composed of three layers, tunica intima, tunica media and tunica externa.
- The inner layer, tunica intima or tunica interna supports the vascular endothelium, the middle layer.
- Tunica media is composed of smooth muscles and an extra cellular matrix which contains a protein, elastin.
- The outer layer, tunica externa or tunica adventitia is composed of collagen fibres.
Question 11.
We are not consuming urea. But in our body urea is produced. Why?
Answer:
If too much of protein is consumed, the body cannot store the excess amino acids formed from the digestion of proteins. The liver breaks down the excess amino acids and produces urea.
![]()
Question 12.
List the disorders of muscular system.
Answer:
Myasthenia gravis, tetany, muscle fatigue, atrophy, muscle pull and muscular dystrophy are the disorders of muscular system.
Question 13.
Do you know your lower limb segments ? Write the 3 segments of lower limb.
Answer:
- Hinge joint which is the knee joint
- Gliding joint is between the tarsals
- Ball and socket joint which is between femur and hip bone
- Saddle joint is between the tarsal and metatarsal
Question 14.
Name the three zones which are present in Adrenal gland.
Answer:
- Zona glomerulosa : The outer thin layer constitutes about 15% of adrenal cortex, and secretes mineralocorticoids.
- Zona fasciculata: The middle widest layer constitutes about 75% of adrenal cortex and secretes glucocorticoids such as cortisol, corticosterone and trace amounts of adrenal androgen and oestrogen.
- Zona reticularis: The inner zone of adrenal cortex constitute about 10% of adrenal cortex and secretes the adrenal androgen, trace amount of oestrogen and glucocorticoids.
Part – III
Answer any three questions in which question number 19 is compulsory. [3 × 3 = 9]
Question 15.
Compare the anatomical features between Phylum Annelida and Arthropoda.
Answer:
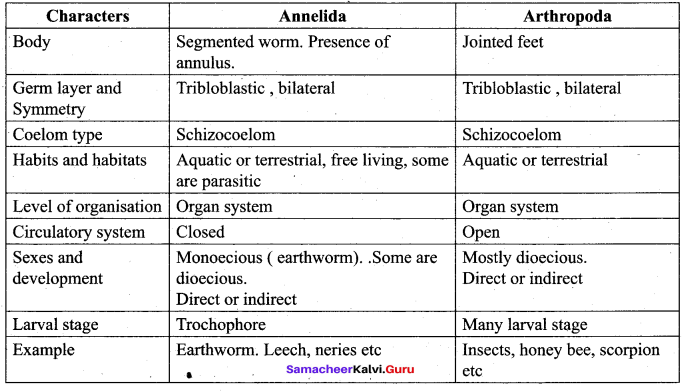
Question 16.
Why do we call cockroach a vector ?
Answer:
Cockroaches carry with them harmful germs of various bacterial diseases like cholera, diarrhoea, tuberculosis, and typhoid and hence are known as “Vectors”.
Question 17.
Why, villi present in the intestine, are not present in the stomach?
Answer:
In small intestine digestion gets completed and the absorption of digested food materials like glucose, amino acids, fatty acids and glycerol takes place. The food materials are to be retained in the intestine by increasing the surface area. Hence villi are present in the intestine. Stomach is the temporary storing organ of food. In the stomach, HCl pepsin, renin and lipase are secreted. These are concerned with digestion. Hence villi are not present in the stomach.
![]()
Question 18.
Enumerate the benefits of Poultry Farming.
Answer:
Benefits of Poultry farming are:
- It does not require high capital for construction and maintenance of the poultry farming.
- It does not require a big space.
- It ensures high return of investment within a very short period of time.
- It provides fresh and nutritious food and has a huge global demand.
- It provides employment opportunities for the people.
Question 19.
Pituitary gland is commonly called “master gland” of the body. Why?
Answer:
Pituitary gland is commonly called the master gland” of the body because it regulates the activity of other endocrine glands such as adrenal gland, thyroid gland, testis and ovary.
Part – IV
Answer all the questions. [2 × 5 = 10]
Question 20.
Write the kingdom, phylum and class for Pigeon. Write the characteristics of birds that are suitable for flying.
Answer:
- Kigdom : Animalia
- Phylum: chordata
- Class : Aves
- The forelimbs are modified into wings,
- The hind limbs are adapted for walking, running, and swimming and perching.
- The endoskeleton is fully ossified (bony) and the long bones are hollow with air cavities.
- The pectoral muscles of flight (pectoralis major and pectoralis minor) are well developed.
- The skin is dry and devoid of glands except the oil gland or preen gland at the base of the tail.
- The exoskeleton consists of epidermal feathers, scales, claws on legs and the homy covering on the beak.
- Respiration is by compact, elastic, spongy lungs that are continuous with air sacs to supplement respiration.
- The heart is four chambered. Aves are homeothermic.
- Urinary bladder is absent.
![]()
[OR]
In our heart, all the four chambers are completely partitioned. It results in non-mixing of oxygenated blood with deoxygenated blood. Explain the double circulation related to it.
Answer:
- Circulation of the blood was first described by William Harvey in 1628. There are two types of blood circulation in vertebrates, single circulation and double circulation.
- The blood circulates twice through the heart first on the right side then on the left side to complete one cardiac cycle.
- The complete double blood circulation is more prominent in mammals because of the complete partition of all the chambers (Auricles and ventricles) in the heart.
- In systemic circulation, the oxygenated blood entering the aorta from the left ventricle is carried by a network of arteries, arterioles and capillaries to the tissues. The deoxygenated blood from the tissue.
- This increases the diffusion distance and reduces the efficiency of the gas exchange.
- In contrast high pressure is required to force blood through the long systemic circuits.
- Hence the arteries close to the heart have increased pressure than the arteries away from the heart.
- Completely separated circuits (pulmonary and systemic) allow these two different demands
to be met with. ‘
Question 21.
Differentiate between sympathetic and parasympathetic Neural system.
Answer:
Sympathetic Neural system (SNS)
- SNS originates in the thoracic and lumbar region of the spinal cord.
- Sympathetic ganglia are linked up to form a chain.
- Preganglionic fibres are short and the postganglionic fibres are long.
- Noradrenaline is produced at the terminal ends of the postganglionic fibres at the effector organs. Hence the system is adrenergic.
- Active during stressful conditions preparing the body to face them.
- The overall effect is excitatory and stimulating.
- It is considered as the flight or fight system.
Parasympathetic Neural system (PNS) :
- PNS originates in the cranial region of the brain and the sacral region of the spinal cord.
- Its ganglia remain isolated.
- Preganglionic fibres are long and the postganglionic fibres are short.
- Acetylcholine is produced at the terminal ends of the postganglionic fibres at the effector organs. Hence the system is cholinergic.
- Active during relaxing times restoring normal activity after a stress.
- The overall effect is inhibitory.
- It is considered as ‘The Rest and Digest System’ or ‘The Feed and Breed System’.
![]()
[OR]
Discuss the various techniques adopted in cattle breeding.
Answer:
There are two methods of animal breeding, namely inbreeding and outbreeding
1. Inbreeding: Breeding between animals of the same breed for 4-6 generations is called inbreeding. Inbreeding increases homozygosity and exposes the harmful recessive genes. Continuous inbreeding reduces fertility and even productivity, resulting in “inbreeding depression”. This c^n be avoided by breeding selected animals of the breeding population and they should be mated with superior animals of the same breed but unrelated to the
breeding population. It helps to restore fertility and yield.
2. Outbreeding: The breeding between unrelated animals is called outbreeding. Individuals produced do not have common ancestors for 4-6 generations. Outbreeding helps to produce new and favourable traits, to produce hybrids with superior qualities and helps to create new breeds. New and favourable genes can be introduced into a population through outbreeding.
Out crossing: It is the breeding between unrelated animals of the same breed but having no common ancestry. The offspring of such a cross is called outcross. This method is suitable for breeding animals below average in productivity.
Cross breeding: Breeding between a superior male of one breed with a superior female of another breed. The cross bred progeny has superior traitsfhybrid vigour or heterosis.)
Interspecific hybridization: In this method of breeding mating is between male and female of two different species. The progeny obtained from such crosses are different from their parents, and may possess the desirable traits of the parents. Have you heard about Mule? It was produced by the process of interspecific hybridization between a male donkey and a female horse.
3. Artificial insemination: Artificial insemination is a technique in which the semen collected from the male is injected to the reproductive tract of the selected female. Artificial insemination is economical measure where fewer bulls are required and maximum use can be made of the best sire.
4. Multiple ovulation embryo transfer technology (MOET) : It is another method of propagation of animals with desirable traits. This method is applied when the success rate of crossing is low even after artificial insemination. In this method Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) is administered to cows for inducing follicular maturation and super ovulation. Instead of one egg per cycle, 6-8 eggs can be produced by this technology.