Students can Download Tamil Nadu 11th Commerce Model Question Paper 5 English Medium Pdf, Tamil Nadu 11th commerce Model Question Papers helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
TN State Board 11th Commerce Model Question Paper 5 English Medium
Instructions:
- The question paper comprises of four parts.
- You are to attempt all the parts. An internal choice of questions is provided wherever applicable.
- questions of Part I, II. III and IV are to be attempted separately
- Question numbers 1 to 20 in Part I are objective type questions of one -mark each. These are to be answered by choosing the most suitable answer from the given four alternatives and writing the option code and the corresponding answer
- Question numbers 21 to 30 in Part II are two-marks questions. These are to be answered in about one or two sentences.
- Question numbers 31 to 40 in Parr III are three-marks questions, These are to be answered in about three to five short sentences.
- Question numbers 41 to 47 in Part IV are five-marks questions. These are to be answered) in detail. Draw diagrams wherever necessary.
Time: 2\(\frac{1}{2}\) Hours
Maximum Marks: 90
Part – I
Choose the correct answer. Answer all the questions: [20 × 1 = 20]
Question 1.
The Reserve Bank of India commenced its operations from April 1 ………………..
(a) 1936
(b) 1935
(c) 1934
(d)1923
Answer:
(b) 1935
![]()
Question 2.
What kind of tax is the GST?
(a) Direct tax
(b) Indirect tax
(c) Debenture on the type of goods and services
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(b) Indirect tax
Question 3.
Who wrote “Arthasasthra”?
(a) Kautilya
(b) Chanakya
(c) Thiruvalluvar
(d) Elangovadigal
Answer:
(a) Kautilya
Question 4.
Which is not a division of activities based on the ownership?
(a) Private enterprise
(b) Foreign enterprise
(c) Public enterprise
(d) Joint enterprise
Answer:
(b) Foreign enterprise
Question 5.
The board of directors of a company is elected by ………………
(a) creditors
(b) debtors
(c) debenture holders
(d) share holders
Answer:
(d) share holders
![]()
Question 6.
Enterprises operating in several countries but managed from one country is termed as ………………
(a) Government company
(b) Multinational company
(c) Private company
(d) Joint venture
Answer:
(b) Multinational company
Question 7.
The traditional functions of RBI are ………………
(i) Monopoly of note issue
(ii) Monetary authority
(iii) Regulating Banking System
(iv) Banker’s Bank
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (i) and (iii)
(c) (i) and (iv)
(d) (ii) and (iv)
Answer:
(c) (i) and (iv)
Question 8.
Which of the following is not applicable in insurance contract?
(a) Unilateral contract
(b) Conditional contract
(c) Indemnity contract
(d) Inter-personal contract
Answer:
(c) Indemnity contract
Question 9.
The advantages of sole trading are ………………
(i) easy formation
(ii) limited capital
(iii) flexibility
(iv) hasty decision
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (i) and (iii)
(c) (ii) and (iv)
(d) (i) and (iv)
Answer:
(b) (i) and (iii)
![]()
Question 10.
Air consignment note is prepared in ……………. forms.
(a) One
(b) Two
(c) Three
(d) Four
Answer:
(c) Three
Question 11.
Match List – I with List – II and select the correct answer using the codes given below:
List – I
(i) Barter system
(ii) Bank official
(iii) Sole trading
(iv) Joint Hindu family
List – II
(1) Employment
(2) Invention of money
(3) Co-parcener
(4) Non-corporate enterprise
code:
(a) (i) 2, (ii) 1, (iii) 4, (iv) 3
(b) (i) 1, (ii) 2, (iii) 3, (iv) 4
(c) (i) 4, (ii) 2, (iii) 3, (iv) 1
(d) (i) 3, (ii) 2, (iii) 1, (iv) 4
Answer:
(a) (i) 2, (ii) 1, (iii) 4, (iv) 3
Question 12.
The role of government in logistics management is through ………………..
(a) Legislations
(b) Governance
(c) Transport
(d) Distribution
Answer:
(d) Distribution
Question 13.
Which of the following holder is given voting right?
(a) Debentures
(b) Preference shares
(c) Equity shares
(d) Bonds
Answer:
(c) Equity shares
Question 14.
Who is the last middleman in the channel of distribution?
(a) Wholesaler
(b) Producer
(c) Retailer
(d) Customer
Answer:
(c) Retailer
![]()
Question 15.
……………….. warehouses are licensed by the government and are permitted to accept the goods on bond.
(a) Bonded
(b) Cold storage
(c) Public
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(a) Bonded
Question 16.
Which one of the following is correctly matched?
(a) Life insurance – Nearest cause
(b) Causa proxima – Life assurance
(c) Health insurance – Life Insurance
(d) Motor vehicle insurance – Mediciaim policy
Answer:
(d) Motor vehicle insurance – Mediciaim policy
Question 17.
The features of partnership are ………………
(i) contractual relationship
(ii) limited liability
(iii) mutual agency
(iv) common seal
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (i) and (iii)
(c) (ii) and (iv)
(d) (ii) and (iii)
Answer:
(b) (i) and (iii)
Question 18.
Which is not a Regional Rural Bank ?
(a) Pallavan Grama Bank
(b) Valluvar Grama Bank
(c) Pandian Grama Bank
(d) Indian Bank
Answer:
(d) Indian Bank
Question 19.
From the following which one is non-corporate form of business?
(a) Joint stock company
(b) Sole Trading Business
(d) Government Company
(d) Co-operatives
Answer:
(b) Sole Trading Business
![]()
Question 20.
Outsource is carried out for the benefit of ………….
(a) global village
(b) transport
(c) factory
(d) time and money
Answer:
(d) time and money
Part-II
Answer any seven questions in which Question No. 30 is compulsory. [7 x 2 = 14]
Question 21.
Mention any four examples of MNC.
Answer:
- Coca-cola corporation
- Unilever Ltd
- Sony corporation
- IBM
Question 22.
What is meant by Marine Insurance?
Answer:
Marine insurance is a contract of insurance under which the insurer undertakes to indemnify the insured against marine losses. The insured pays the premium for the insurer’s guarantee to make good the losses arising from marine perils. Marine perils may be damage of ship, fire, etc.
Question 23.
Give some examples of sole trading business.
Answer:
Saravana Stores, Hotel Saravana Bhavan, grocery stores, petty shops, etc.
![]()
Question 24.
It is a document involved in export trade. It is issued by the captain of the ship. What does it mean? Write a short note about this.
Answer:
This document is Mate’s Receipt. It is issued by the captain of the ship acknowledging the receipt of goods on board by him to the port of specified destination. This contains details like quantity of goods shipped and number of packages condition for packing, etc.
Question 25.
What is meant by private company?
Answer:
Private limited company is a type of company which is formed with minimum two shareholders and two directors, the minimum requirement with respect to authorised or paid up capital of Rs. 1,00,000 has been omitted by the Companies (Amendment) Act, 2015 w.e.f 29th of May, 2015. Another crucial condition of a private limited company is that it by its articles of association restricts the right to transfer its shares and also prohibits any invitation to the public to subscribe for any securities of the company.
Question 26.
It is a private sector bank. It is also called as non-banking financial companies. What is the name of the bank? Mention any two objectives of the bank.
Answer:
The name of the bank is Small Finance Banks (SFBs). It is a private sector bank. Objectives:
- Mobilising rural savings (accepting deposits).
- Providing credit to farmers and small industries.
Question 27.
Give the meaning of trade.
Answer:
The buying and selling of goods and services consists of trade. Trade is conducted in order to earn profit.
Question 28.
Human activity is divided into:
- economic activity
- non-economic activity.
What is meant by non-economic activity? Mention two examples of this.
Answer:
Activities undertaken to satisfy social and psychological needs are called non-economic activities.
Examples – cooking food for family, celebrating festivals, etc.
Question 29.
What do you mean by Articles of Association?
Answer:
Articles of Association is a secondary document which contains the purpose, duties and responsibilities of the members. It has to be filed with the registrar of companies at the time of forming the company. It contains the details of the internal management of the company.
![]()
Question 30.
Who is a franchisee?
Answer:
The individual who acquires the right to operate the business or use the trademark of the seller is known as the franchisee.
Part-III
Answer any seven questions in which Question No. 40 is compulsory. [7 x 3 = 21]
Question 31.
Explain any three objectives of IMF.
Answer:
International Monetary Fund (IMF) is an international organisation, having headquarters in Washington DC.
Objectives:
- Promoting international monetary co-operation.
- Ensuring balanced international trade.
- Ensuring exchange rate stability.
Question 32.
Trade between buyer and seller of different countries is called foreign trade. It is also called international trade. What is the classification of foreign trade?
Answer:
On the basis of sale and purchase of goods and services, international or foreign trade can be divided into three types:
They are –
- Export trade:
Selling of goods from one country to another country. - Import trade:
When a country purchases goods from another country is called import trade. - Entrepot trade:
Goods are imported for the purpose of exporting is called entrepot trade.
Question 33.
What are the various kinds of social responsibilities?
Answer:
- Economic responsibility
- Legal responsibility
- Ethical responsibility
- Discretionary responsibility
Question 34.
For commencing a company, two main documents are needed. They are:
- Memorandum of Association,
- Articles of Association.
Articles of Association is a document which contains the duties and responsibilities of members. What are the contents of Articles of Association? (Any six points)
Answer:
- Amount of shares, capital, value and type of shares.
- Rights of each class of shareholders regarding voting, dividend, return of capital.
- Rules regarding issue of shares and debentures.
- Procedures as well as regulations in respect of making calls on shares.
- Manner of transfer of shares.
- Declaration of dividends.
- Borrowing powers of the company.
- Rules regarding the appointment, remuneration, removal of directors.
- Procedure for conducting proxy, quorum, meetings, etc.
- Procedures concerning keeping of books and audits.
- Seal of the company.
- Procedures regarding the winding up of the company.
Question 35.
Siva takes a policy for the non-recovery of freight.
- What kind of policy is this?
- Also write a brief note about this.
Answer:
- The policy is freight insurance, coming under marine insurance.
- A marine policy is taken to safeguard against non-recovery of freight; it is called as freight insurance. It is useful to the shipping company to collect the freight.
Question 36.
Write any three characteristics of sole trader.
Answer:
- Ownership by one man:
This is owned by single person. The sole trader contributes the required capital. He is not only the owner of the business but also manages the entire affairs. - Freedom of work and Quick Decisions:
Since an individual is himself as a owner, he need not consult anybody else. Hence he can take quick decisions. - Unlimited Liability:
When his business assets are not sufficient to pay off the business debts he has to pay from his personal property.
Question 37.
Write down the functions of IMF.
Answer:
IMF is an international organisation having head quarters at Washington DC.
Functions of IMF:
- It acts as a short term credit institution at the international level. .
- It provides machinery for ordinary adjustments of exchange rates.
- It promotes economic stability and global growth by encouraging countries.
Question 38.
Why is balance of payments prepared?
Answer:
Balance of payments help in framing monetary, fiscal and trade policies of country. Government keenly observes balance of payment position of its important trade partners in making policy decisions. It reveals whether a country produces enough economic output to pay for its growth.
![]()
Question 39.
What is the necessity of entrepot trade?
Answer:
Meaning of Entrepot Trade:
If a country imports goods for the purpose of exporting the same goods to other country, it is known as entrepot trade. Necessity for Entrepot Trade – A country can re-export the goods for the following reasons:
- The country may not have any accessible trade routes connecting the importing country.
- The goods imported may require further processing before exporting. For this, some facilities may not be available in exporting or importing country.
- There may not have any bilateral trade agreement between both the countries.
- Importer and exporter may not share good economic relation with each other.
Question 40.
What is pledge?
Answer:
A customer transfers the possession of an article with the creditor (banker) and receives loan. Till the repayment of loan, the article is under the custody of the borrower. If the debtor fails to refund the loan, creditor (banker) will auction the article pawned and adjust the outstanding loan from the sale proceeds.
Part – IV
Answer all the questions. [7 x 5 = 35]
Question 41(a).
What is IRDAI? Explain the objectives of IRDAI.
Answer:
Insurance Regulatory Development and Authority of India is the statutory and apex body that governs, regulates and supervises the insurance in India. It was constituted in the year 2000 by Parliament of India Act called IRDAI Act, 1999.
Objectives of IRDAI:
- To promote the interest and rights of policy holders.
- To promote and ensure the growth of Insurance industry.
- To ensure speedy settlement of genuine claims and to prevent frauds and malpractices.
- To bring transparency and orderly conduct in financial markets, dealing with insurance.
[OR]
Question 41(b).
Explain the features of factoring.
Answer:
- Maintenance of book-debts:
A factor takes the responsibility of maintaining the accounts of debtors of a business institution. - Credit coverage:
The factor accepts the risk burden of loss of bad debts leaving the seller to concentrate on his core business. - Cash advances:
Around eighty percent of the total amount of accounts receivables is paid as advance cash to the client. - Collection service:
Issuing reminders, receiving part payments, collection of cheques from part of the factoring service. - Advice to clients:
From the past history of debtors, the factor is able to provide advises Jregarding the credit worthiness of customers, perception of customers about the products of the client, etc.
Question 42 (a).
What are the hindrances of business? Explain any five hindrances.
Answer:
There are so many hindrances of business. They are as follows:
(1) Hindrance of Person:
The manufacturers and consumers do not know each other. It is called as hindrance of a person. It is removed by the trade or trader. The trader is connecting the producer and the consumer.
(2) Hindrance of Place:
The manufacturing place is different from the place of consumption. This difficulty is known as hindrance of place. It is removed by the transport.
(3) Hindrance of Time:
Goods are produced in one season but may be demanded throughout the year. Some goods are produced throughout the year, but may be used in certain season. It is known as hindrance of time. It is removed by the warehouse.
(4) Hindrance of risk:
Fire, theft, floods, etc., may bring huge loss to the business. It is known as hindrance of risk. It is overcome by the insurance companies.
(5) Hindrance of knowledge:
The difficulty of not knowing the place and availability of goods is known as hindrance of knowledge. It is removed by advertising and communication.
[OR]
![]()
Question 42 (b).
Every business enterprise has certain objectives which regulate and generate its activities. The objectives may be classified into five types. Explain the objectives of business.
Answer:
(1) Economic Objectives:
Economic objectives of business refer to the objective of earning profit and also other objectives that are necessary to be pursued to achieve the profit objective, which includes creation of customers, regular innovations and best possible use of available resources.
(2) Social Objectives:
Social objective are those objectives of business, which are desired to be achieved for the benefit of the society. Since business operates in a society by utilizing its scarce resources, the society expects something in return for its welfare
(3) Organizational Objectives:
The organizational objectives denote those objectives an organization intends to accomplish during the course of its existence in the economy like expansion and modernization, supply of quality goods to consumers, customers’ satisfaction, etc.
(4) Human Objectives:
Human objectives refer to the objectives aimed at the well-being as well as fulfillment of expectations of employees as also of people who are disabled, handicapped and deprived of proper education and training. The human objectives of business may thus include economic well-being of the employees, social and psychological satisfaction of employees and development of human resources.
(5) National Objectives:
Being an important part of the country, every business must have the objective of fulfilling national goals and aspirations.
![]()
Question 43 (a).
The trade takes place between the traders of one country is known as Internal trade. Whereas the trade takes place between two countries is called as International trade. Distinguish between internal trade and international trade.
Answer:
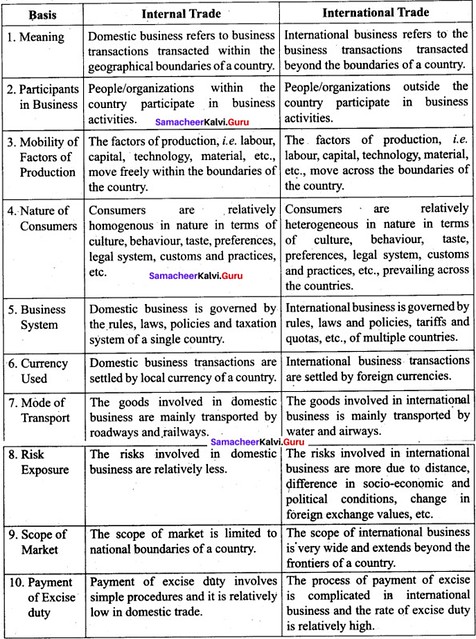
[OR]
Question 43 (b).
Describe the functions of IMF.
Answer:
- It acts as short term.credit institution at the international level.
- It provides machinery for ordinary adjustments of exchange rates.
- It has a reservoir of currencies of the member countries from which a borrower can borrow currencies of other nations.
- It promotes economic stability and global growth by encouraging countries adopt sound economic and financial policies.
- It offers technical assistance and training to help member countries strengthen and implement effective policies. Technical assistance is offered in formulating banking, fiscal, monetary and exchange policies.
- It helps member countries correct their imbalance in balance of payment.
Question 44 (a).
Describe the role of Chamber of Commerce in promotion of internal trade.
Answer:
- Transportation or inter-state movement of goods:
The Chambers facilitate registration of vehicles, surface transport policies, construction of highways and roads in promoting interstate movement of goods. - Harmonisation CGST and SGST structure.
- Marketing of agro products and related issues:
The associations of agriculturists and other federations interact with farming co-operatives to streamline local subsidies and formulate marketing policies for selling agro products. - Weights and measures and prevention of duplication of brands:
They help the Government in formulation and implementation of uniform policies in weights and measures and prevention of duplication of brands. - Promoting sound infrastructure:
They interact with Government to construct roads, ports, electricity, railways, etc. - Labour legislation:
They interact with the Government on regular basis and the issues related to labour laws, retrenchments, compensation, etc., so that the industry can run efficiently, generate employment and achieve maximum productivity.
[OR]
Question 44 (b).
What are the differences between bill of lading and Charter party?
Answer:

![]()
Question 45 (a).
Goods were exchanged for goods prior to invention of money. It is known as barter system. There are certain constraints for the barter system. What are the constraints of the barter system?
Answer:
The constraints of barter system are:
(1) Lack of Double Coincidence of Wants:
Unless two persons who have surplus have the demand for the goods possessed by each other, barter could not materialize. If this “coincidence of wants” does not exist, barter cannot take place.
(2) Non-existence of Common Measure of Value:
Barter system could not determine the value of commodities to be exchanged as they lacked commonly acceptable measures to evaluate each and every commodity.
(3) Lack of Direct Contact between Producer and Consumers:
It was not possible for buyers and sellers to meet face to face in many contexts for exchanging the commodities for commodities.
(4) Lack of surplus stock:
Absence of surplus stock was one of the impediments in barter system. If the buyers and sellers do not have surplus then no barter was possible.
![]()
[OR]
Question 45 (b).
Distinguish between economic and non-economic activity.
Answer:
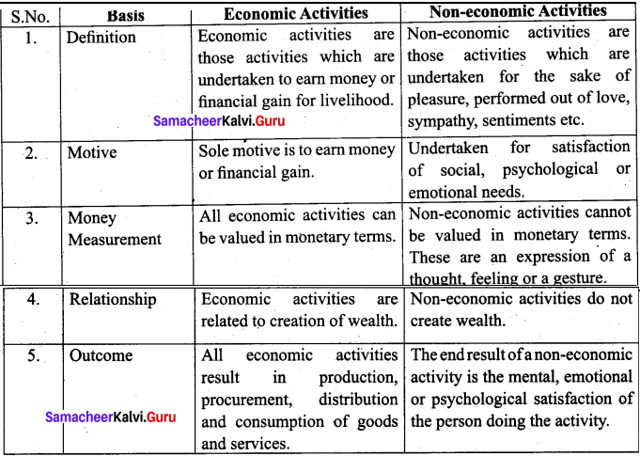
Question 46 (a).
What are the five features of income tax?
Answer:
Features of Income Tax in India:
(1) Levied as Per the Constitution:
Income tax is levied in India by virtue of entry No. 82 of list I (Union List) of Seventh Schedule to the Article 246 of the Constitution of India.
(2) Levied by Central Government:
Income tax is charged by the Central Government on all incomes other than agricultural income. However, the power to charge income tax on agricultural income has been vested wife the State Government as per entry 46 of list II, i.e., State List.
(3) Direct Tax:
Income tax is direct tax. It is because the liability to deposit and ultimate burden are on sane person. The person earning income is liable to pay income tax out of his own pocket am cannot pass on the burden of tax to another person.
(4) Annual Tax:
Income tax is an annual tax because it is the income of a particular year which is chargeable to tax.
(5) Taxon Person:
It is a tax on income earned by a person. The term ‘person’ has been defined under the income tax Act. It includes individual, Hindu Undivided Family, Firm, Company, local authority, Association of person or body of Individual or any other artificial juridical persons. The persons who are covered under Income tax Act are called ‘assessees’
![]()
[OR]
Question 46 (b).
Describe the features of factoring.
Answer:
- Maintenance of book-debts:
A factor takes the responsibility of maintaining the accounts of cebtors of a business institution. - Credit coverage:
The factor accepts the risk burden of loss of bad debts leaving the seller to concentrate on his core business. - Cash advances:
Around eighty percent of the total amount of accounts receivables is paid as advance cash to the client. - Collection service:
Issuing reminders, receiving part payments, collection of cheques from part of the factoring service. - Advice to clients:
From the past history of debtors, the factor is able to provide advices regarding the credit worthiness of customers, perception of customers about tie products of the client, etc.
Question 47 (a).
Compare CGST and SGST
Answer:
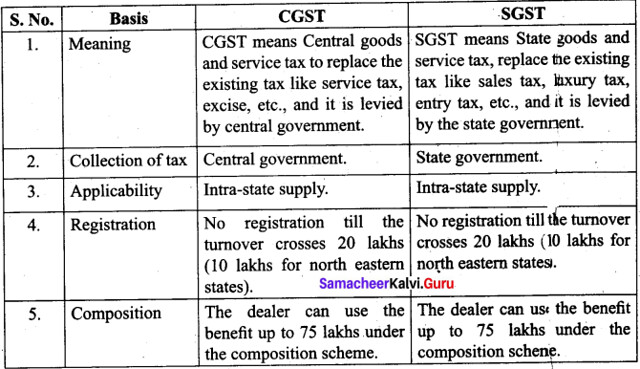
Question 47 (b).
Point out the objectives of WTO.
Answer:
- Improving the standard of living of people in member countries.
- Making optimum utilization of world’s resources for sustainable development of member countries.
- Promoting an integrated more viable and durable trading system in the sphere of international business.
- Expansion of trade in goods and services.
- Ensuring full employment and large steady growth volume of real income and effective demand. .
- Protecting the environment.