Students can Download Tamil Nadu 11th Commerce Previous Year Question Paper June 2019 English Medium Pdf, Tamil Nadu 11th commerce Model Question Papers helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
TN State Board 11th Commerce Previous Year Question Paper June 2019 English Medium
Instructions:
- The question paper comprises of four parts.
- You are to attempt all the parts. An internal choice of questions is provided wherever applicable.
- questions of Part A, B. C and IV are to be attempted separately
- Question numbers 1 to 20 in Part A are objective type questions of one -mark each. These are to be answered by choosing the most suitable answer from the given four alternatives and writing the option code and the corresponding answer
- Question numbers 21 to 30 in Part B are two-marks questions. These are to be answered in about one or two sentences.
- Question numbers 31 to 40 in Parr C are three-marks questions, These are to be answered in about three to five short sentences.
- Question numbers 41 to 47 in Part D are five-marks questions. These are to be answered) in detail. Draw diagrams wherever necessary.
Time: 2\(\frac{1}{2}\) Hours
Maximum Marks: 90
Part – A
Choose the correct answer. Answer all the questions: [20 × 1 = 20]
Question 1.
Hindrance of place is removed by …………
(a) Transport
(b) Warehouse
(c) Salesman
(d) Insurance
Answer:
(a) Transport
Question 2.
Which one of the following is not the characteristics of sole trading?
(a) Ownership by one man
(b) Limited Liability
(c) Enjoying entire profit
(d) Maintenance of secrecy.
Answer:
(b) Limited Liability
![]()
Question 3.
Registration of partnership is …………
(a) Compulsory
(b) Optional
(c) Not necessary
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(b) Optional
Question 4.
Rochdale Society of equitable pioneers was started by …………
(a) Robert Owen
(b) H.C. Calvert
(c) Talmaki
(d) Lambert
Answer:
(a) Robert Owen
Question 5.
Indian Railway is an example of …………
(a) Government Company
(b) Public Corporation
(c) Departmental Undertaking
(d) Board Organisation
Answer:
(c) Departmental Undertaking
Question 6.
NEFT was launched by the RBI in the year …………
(a) 2005
(b) 2013
(c) 2010
(d) 1995
Answer:
(a) 2005
Question 7.
A warehouse holds goods as ………… a center.
(a) Marketing
(b) sorting
(c) distribution
(d) selling
Answer:
(c) distribution
Question 8.
Madras city had tramways till …………
(a) 1932
(b) 1933
(c) 1934
(d) 1935
Answer:
(b) 1933
Question 9.
Which bank has the power to issue bank notes?
(a) Central Bank
(b) Commercial Bank
(c) Co-operative Banks
(d) Foreign Banks
Answer:
(a) Central Bank
Question 10.
The main benefit of logistics is …………
(a) productivity
(b) cost minimisation
(c) profitability
(d) storage
Answer:
(b) cost minimisation
![]()
Question 11.
Social responsible business provides goods at …………
(a) high price
(b) low price
(c) reasonable price
(d) moderate price
Answer:
(c) reasonable price
Question 12.
American Depository Receipts (ADRs) are issued in:
(a) Canada
(b) China
(c) India
(d) The USA
Answer:
(d) The USA
Question 13.
………… is one of the methods of raising business finance through sale or mortgage of book debts.
(a) Factoring
(b) Mortgage
(c) Clean loan
(d) Hire Purchase Finance
Answer:
(a) Factoring
Question 14.
Investment limit of a micro enterprise under manufacturing sector does not exceed lakhs …………
(a) 10
(6) 20
(c) 25
(d) 50
Answer:
(c) 25
Question 15.
The purchase of goods from a foreign country is called …………
(a) Import
(b) Export
(c) Entrepot
(d) Re-export
Answer:
(a) Import
Question 16.
Wholesalers deal in ………… quantity of goods.
(a) small
(b) large
(c) medium
(d) limited
Answer:
(b) large
Question 17.
Goods are imported for purpose of re-export to another country is termed as ……….. Entrepot trade
(a) Import trade
(b) Export trade
(c) Entrepot trade
(d) International trade
Answer:
(c) Entrepot trade
![]()
Question 18.
A contract with or by a minor is a …………
(a) valid contract
(b) void contract
(c) voidable contract
(d) voidable at the option of either party
Answer:
(b) void contract
Question 19.
Period of Assessment year is …………
(a) 1st April to 31st March
(b) 1st March to 28th Dec.
(c) 1st July to 30th June
(d) 1st Jan. to 31st Dec.
Answer:
(a) 1st April to 31st March
Question 20.
GST stands for:
(a) Goods and Supply Tax
(b) Government Sales Tax
(c) Goods and Services Tax
(d) General Sales Tax
Answer:
(c) Goods and Services Tax
Part-B
Answer any seven questions in which Question No. 30 is compulsory. [7 x 2 = 14]
Question 21.
What is meant by Barter?
Answer:
Goods were exchanged for goods prior to invention of money.
Question 22.
Who is a sleeping partner?
Answer:
Such a partner contributes capital and shares in the profits or losses of the firm but does not take part in the management of the business.
Question 23.
Define transport.
Answer:
According to KK Saxena, “the transport system acts with reference to the area it serves in the same way as a candle does in a dark room”.
Question 24.
What do you mean by e-commerce?
Answer:
E-commerce or Electronic commerce is the buying and selling of goods and services through electronic networks like internet.
Question 25.
What is ethics?
Answer:
Ethics is derived from the Greek word ‘ethos’ which means a person’s fundamental orientation towards life. It governs the behaviour, derived from the moral standards which help to determine right or wrong, good or evil.
![]()
Question 26.
What is a Depository Receipt?
Answer:
A depository receipt is a negotiable financial instrument issued by a bank to represent a foreign company’s equity shares or securities. They are issued to attract a greater amount of investment from other countries.
Question 27.
Define Retailer.
Answer:
According to S. Evelyn Thomas “the retailer is the last of the many links in the economic chain whereby the consumer’s wants are satisfied smoothly and efficiently by retailers”.
Question 28.
What is meant by Export trade?
Answer:
When the firm of country sells goods and services to a firm of another country it is called export trade. Export trade indicates selling of goods and services from the home country to a foreign country.
Question 29.
Who can enter into a Contract?
Answer:
The Indian contract Act specifies that every person is competent to contract provided he is of the age of majority according to the Law which he is subject to and who is of sound mind.
Question 30.
Deepak insured his factory for ₹ 5 lakh against fire. Due to fire he suffered a loss of ₹ 2 lakh. How much amount he can recover from the Insurance Company? Why?
Answer:
Factory insured for ₹ 5,00,000
Loss on fire ₹ 2,00,000
Deepak can recover ₹ 2,00,000 because actual loss only can be compensated according to the principle of average clause.
Part-C
Answer any seven questions in which Question No. 40 is compulsory. [7 x 3 = 21]
Question 31.
Write short notes on:
(a) Business
(b) Profession
Answer:
(a) Business refers to any human activity undertaken on a regular basis with the object to earn profit through production, distribution, sale or purchase of goods and services.
(b) Profession are those occupations which involves rendering of personal services of a special and expert nature. A profession is something which is more than a job. It is a career for someone who is competent in their respective areas.
![]()
Question 32.
Write any three features of Hindu Undivided Family?
Answer:
- Governed by Hindu Law:
The business of the Joint Hindu Family is controlled and managed .under the Hindu law. - Membership by Birth:
The membership of the family can be acquired only by birth. As soon as a male child is bom in the family, that child becomes a member. - Liability:
Except the Karta, the liability of all other members is limited to their shares in the business.
Question 33.
What are the objectives involved in Regional Rural Banks?
Answer:
Their objective is to develop rural economy and play supplementary role to cooperative societies. They mobilise deposits from the mral public and provide finance to rural artisans, small entrepreneurs and farmers and try to avoid their dependency on money lenders. As on 31.3.2016, there were 56 RRBs in India with 14,494 branches. They are regulated and supervised by NABARD.
Question 34.
What are the types of franchising?
Answer:
- Product / trade name franchising: In this type, the franchisee exclusively deals with a manufacture’s product, e.g., Kidzee, French Loaf outlets.
- Business format franchising: When a franchisor awards rights covering all business aspects as a complete business package to the franchisee it is called as business format franchising. e.g., McDonald’s, Pizza Hut.
Question 35.
Why you do think Social Responsibility of business is needed? (Any three reason)
Answer:
- Self-Interest:
A business unit can sustain in the market for a longer period only by assuming some social obligations. Normally businessmen recognise that they can succeed better by fulfilling the demands and aspirations of society. - Creation of Society:
Business is a creation of society and uses the resources of society. Therefore, it should fulfil its obligations to society. - Social Power:
Businessmen collectively determine for the nation such important matters as level of employment, rate of economic progress and distribution of income among various groups.
Question 36.
Explain any three features of Self Help Group.
Answer:
- The motto of every group members should be “saving first – credit latter”.
- Self Help Group is homogeneous in terms of economic status.
- The ideal size of a Self Help Group ranges between 10 and 20 members.
![]()
Question 37.
What are the contents of Indents?
Answer:
Contents of an Indent:
(a) Quantity of goods sent
(b) Design of goods
(c) Price
(d) Nature of packing shipment
(e) Mode of shipment
(f) Period of delivery
(g) Mode of payment
Question 38.
What do you mean by Agreement?
Answer:
An “agreement” means ‘a promise or a set of promises’ forming consideration for each other. A promise arises when a proposal is accepted. By implication, an agreement is an accepted proposal. In other words, an agreement consists of an ‘offer’ and its ‘acceptance’.
Agreement = offer / Proposal + Acceptance
Question 39.
Write any three differences between Direct tax and Indirect tax.
Answer:
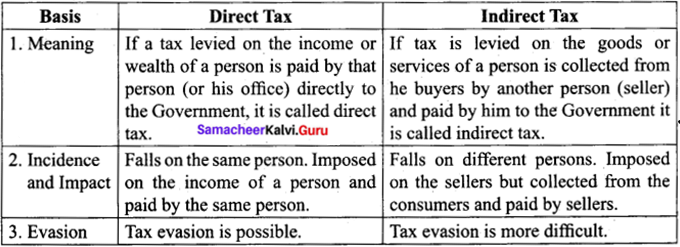
Question 40.
Name the partner who has not completed 18 years of age. Can he be admitted into partnership? Why?
Answer:
The partner who has not completed the age of 18 is known as minor partner. He can be admitted into the partnership for. the benefit of the firm. But a minor has no contractual capacity. The consent of all partners is a ‘must’ for such admission.
Part – D
Answer all the questions. [7 x 5 = 35]
Question 41(a).
Distinguish between economic and non-economic activity. (Any five)
Answer:
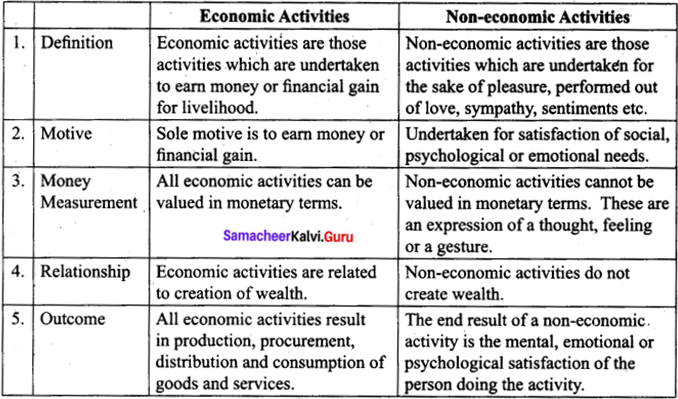
[OR]
Question 41 (b).
Enumerate any five disadvantages of International trade.
Answer:
1. Economic Dependence:
International trade is more likely to make the country too much dependent on imports from foreign countries. The former may not take any efforts to produce goods and services indigenously to substitute.imported goods and thus becoming self sufficient.
2. Inhibition of Growth of Home Industries:
International business may discourage the growth of indigenous industry. Unrestricted imports and severe competition from foreign companies may ruin the home industries altogether.
3. Import of Harmful Goods:
International business may lead to import of luxurious goods, spurious goods, dangerous goods, etc. It may harm the well-being of people.
4. Shortage of Essential Goods in Home Country:
The export of essential commodities out of the greed of earning more foreign exchange may result in absolute shortage of these goods at home country and people may have to buy these commodities at exorbitant price in the local market.
5. Misuse of Natural Resources:
Excessive export of scarce natural resources to variotis countries across the world may lead to faster depletion of the resources in the exporting countries.
![]()
Question 42 (a).
Explain the characteristics of sole trading business.
Answer:
- Ownership by one man:
This is owned by single person. The sole trader contributes the required capital. He is not only the owner of the business but also manages the entire affairs. - Freedom of work and Quick Decisions:
Since an individual is himself as a owner, he need not consult anybody else. Hence he can take quick decisions. - Unlimited Liability:
When his business assets are not sufficient to pay off the business debts he has to pay from his personal property. - Enjoying Entire Profit:
He strives tirelessly for the improvement and expansion of his business and enjoys all the benefits of his hard work. - Absence of Government Regulation:
A sole proprietor concern is free from Government regulations. No legal formalities are to be observed in its formation, management or in its closure. - No Separate Entity:
The sole trading concern comes to an end with death, disability, insanity and insolvency of the individual. - Maintenance of Secrecy:
Since he / she manages all the affairs of the business, the secrecy can be maintained easily.
[OR]
Question 42 (b).
Mention any five functions of wholesaler.
Answer:
Following are the functions of wholesalers:
- Collection of Goods:
Wholesaler collects the goods from manufacturers or producers in bulk. - Storage of Goods:
Wholesaler collects and stores them safely in warehouses, till they are sold out. - Distribution:
Wholesaler sells goods to different retailers. Thus he performs the function of distribution. - Financing:
Wholesalers provide financial support to producers and manufacturers by providing money in advance to them. - Risk Taking:
Wholesaler buys finished goods from the producer and keeps them in the warehouses till the time they are sold and assumes.the risk arising from price, spoilage of goods, and changes in demand.
![]()
Question 43(a).
Explain the principles of insurance.
Answer:
1. Utmost Good Faith:
According to this principle, both insurer and insured should enter into contract in good faith. Insured should provide all the information that impacts the subject matter. Insurer should provide all the details regarding insurance contract.
2. Insurable Interest:
The insured must have an insurable interest in the subject matter of insurance. Insurable interest means some pecuniary interest in the subject matter of the insurance contract.
3. Indemnity:
Indemnity means security or compensation against loss or damages. In insurance, the insured would be compensated with the amount equivalent to the actual loss and not the amount exceeding the loss. This principle ensures that the insured does not make any profit out of the insurance. This principle of indemnity is applicable to property insurance alone.
4. Causa Proxima:
The word ‘Causa proxima’ means ‘nearest cause’. According to this principle, when the loss is the result of two or more cause, the proximate cause, i.e. the direct. The direct, the most dominant and most effective cause of loss should be taken into consideration. The insurance company is not liable for the remote cause.
5. Contribution:
The same subject matter may be insured with more than one insurer then it is known as ‘Double Insurance’. In such a case, the insurance claim to be paid to the insured must be shared on contributed by all insurers in proportion to the sum assured by each one of them.
6. Subrogation:
Subrogation means ‘stepping the shoes on others’. According to this principle, once the claim of the insured has been settled, the ownership right of the subject matter of insurance passes on to the insurer.
7. Mitigation:
In case of a mishap, the insured must take off all possible steps to reduce or mitigate the loss or damage to the subject matter of insurance.
[OR]
Question 43 (b).
Difference between Contract and Agreement.
Answer:
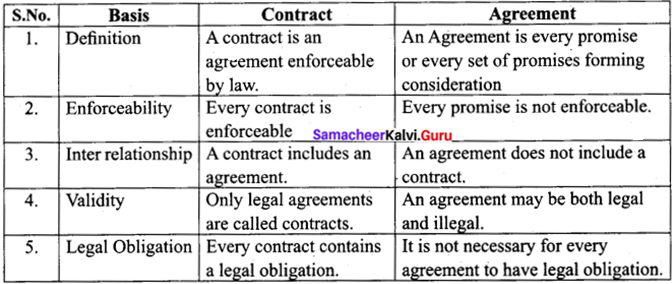
Question 44(a).
Explain the different key elements of business ethics.
Answer:
1. Top Management Commitment:
Top management has a very important role to guide the entire organization towards ethical behaviour. The top level personnel in any organisation should work openly and strongly committed towards ethical conducts and guide people working at’ middle and low level to follow ethical behaviour.
2. Establishment of Compliance Mechanism:
To make sure that actual decisions match with a firm’s ethical standards, suitable mechanism should be established.
3. Publication of a “Code”:
Generally organisations formulate their own ethical codes for the conduct of the enterprise; it should followed by the employees of the organisation. The organisation principles are defined in the written document called code.
4. Involving Employees at All Levels:
It is the employees at different levels who implement ethics policies to make ethical business a reality. Therefore, their involvement in ethics programmes becomes a must.
5. Measuring Results: .
The organisations from time to time keep a check on ethical practise followed. Although it is difficult to accurately measure the end results of ethics programmes, the firms can certainly audit to monitor compliance with ethical standards.
[OR]
Question 44(b).
Write any five advantages of Co-operative Society.
Answer:
1. Voluntary organisation:
The membership of a co-operative society is open to all. Any person with common interest can become a member. The membership fee is kept low so that everyone would be able to join and benefit from co-operative societies.
2. Easy formation:
Co-operatives can be formed much easily when compared to a company. Any 10 members who have attained majority can join together for forming a co-operative society by observing simple legal formalities.
3. Democracy :
A co-operative society is run on the principle of ‘ one man one vote ‘. It implies that all members have equal rights in managing the affairs of the enterprises.
4. Equal distribution of surplus:
The surplus generated by the co-operative societies is distributed in an equitable manner among members. Therefore all the members of the co-operative society are benefited.
5. Limited liability:
The liability of the members in a co-operative society is limited to the extent of their capital contribution. They cannot be personally held liable for the debts of the society.
![]()
Question 45 (a).
Answer any five salient features of Government Company.
Answer
1. Registration Under the Companies Act:
A Government company is formed through registration under the Companies Act, 1956; and is subject to the provisions of this Act, like any other company. However, the Central Government may direct that any of the provisions of the Companies Act shall not apply to a Government company or shall apply with certain modifications.
2. Executive Decision of Government:
A Government company is created by an executive decision of the Government, without seeking the approval of the Parliament or the State Legislature.
3. Separate Legal Entity:
A Government company is a legal entity separate from the Government. It can acquire property; can make contracts and can file suits, in its own name.
4. Whole or Majority Capital Provided by Government:
The whole or majority (at least 51 %) of the capital of a Government company is provided by the Government; but the revenues of the company are not deposited into the treasury.
5. Majority of Government Directors:
Being in possession of a majority of share capital, the Government has authority to appoint majority of directors, on the Board of Directors of a government company.
[OR]
Question 45 (b).
Describe the benefits of outsourcing.
Answer:
1. Focusing on Core Activities:
Companies can focus on their core competence, a few areas where the company has distinct capability. The rest of the activities (non-core) can be outsource to outside agencies.
2. To Fill up Economic Development:
Outsourcing stimulates entrepreneurship, encourages employment opportunities, expands exports, enables tremendous growth of the economy.
3. Encourages Employment Opportunities:
Companies that are outsourcing their non core activities provide chances for other small business units to take up the activities. This paves way for more job opportunities and new employment avenues.
4. Reduction in Investment:
Companies through outsourcing avails the services of outsiders which in turn reduces the investment requirements. The amount so available can be utilized productively and this increases the profits.
5. Quest for Excellence:
Outsourcing enables the firms to pursue excellence in two ways namely excelling themselves in the activities they do and excel outsiders by extending their capabilities through contracting out.
Question 46(a).
Explain any five different kinds of warehouses.
Answer:
Different kinds of warehouses on the basis of ownership:
- Private Warehouses:
Private warehouses are built and owned by private business enterprises in order to store the products produced by them. - Government Warehouses:
They are created and operated by the Government to implement the programmes of the Government. - Public Warehouse:
It is open for public at large. Most of the business organisations, especially small and medium scale units cannot afford to have their own warehouses. - Co-operative Warehouses:
There are warehouses owned and managed by the marketing co-operative societies or agricultural co-operative societies. They are setup to provide warehousing facilities to their members. - Bonded Warehouses:
Bonded warehouses are those warehouses, which are licensed by the government to accept storage of imported goods which are not cleared due to non-payment of customs duty by the importer.
[OR]
Question 46 (b).
Distinguish between GDR and ADR.
Answer:
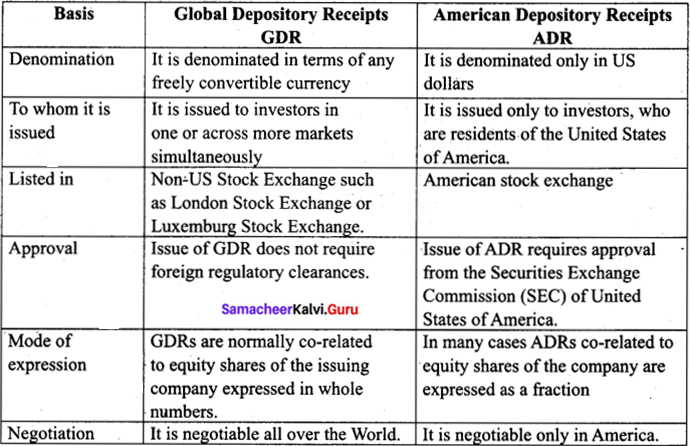
![]()
Question 47 (a).
A number of identical retail shops with similar appearance normally deal in standardised and branded products. Name the shop and explain its features.
Answer:
The name of the shop is Chain Stores or Multiple Shops. A number of same type of retail shops with similar appearance, selling branded products is known as multiple shops.
Features:
- Location:
These shops are located in fairly populous localities. - Nature of product:
These shops deal in a particular line of products only. Also they specialise in the same product. - Centralised management:
The goods’ are purchased by the head office and despatched’ to all the shops. - Fixed price:
The price of the goods are fixed and goods are sold on cash basis. - Role of Sales personnel:
The sales persons play an active role in helping the consumers to complete their shopping.
[OR]
Question 47 (b).
Who are the intermediaries involved in Import trade? Explain about them.
Answer:
Intermediaries in Import Trade:
1. Indent Houses / Import Agent:
This intermediary is specialized in a particular trade. He charges fees for his service. Importer has to enter into contract with indent house to avail himself of his service.
Services rendered by Indent Houses/Import Agent:
- Helping the importer to get orders from foreign countries.
- Providing information about the availability of goods and arranging the letter of credit facilities to importer.
- Maintaining regular contact with the exporter to obtain sample.
2. Clearing Agent- Clearing Agent is specialised in clearing the goods from the port of discharge destination and transport it over to the importer. They fulfill the various custom formalities on behalf of the importer and get the goods cleared from the port. They charge commission for their service.