Students can Download Tamil Nadu 12th Biology Model Question Paper 1 English Medium Pdf, Tamil Nadu 12th Biology Model Question Papers helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
TN State Board 12th Biology Model Question Paper 1 English Medium
General Instructions:
- The question paper comprises of four parts. Questions for Botany and Zoology are asked separately.
- You are to attempt all the parts. An internal choice of questions is provided wherever applicable.
- All questions of Part I, II, III and IV are to be attempted separately.
- Question numbers 1 to 8 in Part I are Multiple Choice Questions of one mark each. These are to be answered by choosing the most suitable answer from the given four alternatives and writing the option code and the corresponding answer.
- Question numbers 9 to 14 in Part II are two-marks questions. These are to be answered in about one or two sentences.
- Question numbers 15 to 19 in Part III are three-marks questions. These are to be answered in about three to five short sentences.
- Question numbers 20 and 21 in Part IV are five-marks questions. These are to be answered in detail. Draw diagrams wherever necessary.
Time: 2.30 Hours
Maximum Marks: 70
Bio-Botany [Maximum Marks: 35]
Part – I
Choose the correct answer. [8 × 1 = 8]
Question 1.
Identify plant species which is popularly called as “Terror of Bengal”.
(a) Eichornia Crassipes
(b) Vallisneria spiralis
(c) Pistia stratiotes
(d) Zostera marina
Answer:
(a) Eichornia Crassipes
Question 2.
‘Gametes are never hybrid’ is concluded by __________.
(a) Law of dominance
(b) Law of segregation
(c) Law of lethality
(d) Law of independent assortment
Answer:
(b) Law of segregation
![]()
Question 3.
Match list I with list II
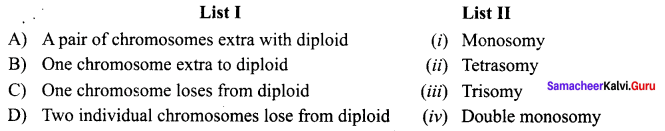
(a) A-i, B-iii, C-ii, D-iv
(b) A-ii, B-iii, C-iv, D-i
(c) A-ii, B-iii, C-i, D-iv
(d) A-iii, B-ii, C-i, D-iv
Answer:
(c) A-ii, B-iii, C-i, D-iv
Question 4.
EcoRI cleaves the DNA at _______.
(a) AGGGTT
(b) GTATATC
(c) GAATTC
(d) TATAGC
Answer:
(c) GAATTC
Question 5.
________ is the climax community of hydrosere.
(a) Reed Swamp stage
(b) Marsh meadow stage
(c) Shrub stage
(d) Forest stage
Answer:
(d) Forest stage
Question 6.
People’s movement for the protection of environment in Sirsi of Karnataka is ________.
(a) Chipko movement
(b) Appiko movement
(c) Amirtha Devi Bishwas movement
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(b) Appiko movement
![]()
Question 7.
Which of the following is incorrectly paired?
(a) Wheat – Himgiri
(b) Rice – Ratna
(c) Milch breed – sahiwal
(d) Pusa komal – Brassica
Answer:
(d) Pusa komal – Brassica
Question 8.
Tectona grandis is coming under the family _______.
(a) Lamiaceae
(b) Fabaceae
(c) Dipterocaipaceae
(d) Ebenaceae
Answer:
(a) Lamiaceae
Part – II
Answer any four of the following questions. [4 x 2 = 8]
Question 9.
Draw and label the structure of a mature embryo sac of angiosperm.
Answer:
Question 10.
What are plasmogenes?
Answer:
Plasmogenes are independent, self-replicating, extra-chromosomal units located in cytoplasmic organelles, chloroplast and mitochondrion.
![]()
Question 11.
Define the terms
(a) Bioventing
(b) Bioaugmentation
Answer:
(a) Bioventing is the process that increases the oxygen or air flow to accelerate the degradation of environmental pollutants.
(b) Bioaugmentation is the addition of selected microbes to speed up degradation process.
Question 12.
Differentiate between Eurythermal animals and Stenothermal animals.
Answer:
Eurythermal: Organisms which can tolerate a wide range of temperature fluctuations. Example: Zostera.
Stenothermal: Organisms which can tolerate only small range of temperature variations. Example: Mango.
Question 13.
What are Blue carbon ecosystems?
Answer:
Sea grasses and mangroves of Estuarine and coastal ecosystems are the most efficient in carbon sequestration. Hence, these ecosystems are called as “ Blue carbon ecosystems”.
![]()
Question 14.
What is silvopasture system? How it helps economy?
Answer:
The production of woody plants combined with pasture is referred to silvopasture system. The trees and shrubs may be used primarily to produce fodder for livestock or they may be grown for timber, fuel wood and fruit or to improve the soil.
Part – III
Answer any three questions in which question number 19 is compulsory. [3 × 3 = 9]
Question 15.
Given an account an king of spices and its uses.
Answer:
King of Spices:
Pepper is one of the most important Indian spices referred to as the “King of Spices” and also termed as “Black Gold of India”. Kerala, Karnataka and Tamil Nadu are the top producers in India. The characteristic pungency of the pepper is due to the presence of alkaloid Pipeline. There are two types of pepper available in the market namely black and white pepper.
Uses:
It is used for flavouring in the preparation of sauces, soups, curry powder and pickles. It is used in medicine as an aromatic stimulant for enhancing salivary and gastric secretions and also as a stomachic. Pepper also enhances the bio-absorption of medicines.
Question 16.
Distinguish between primary production and secondary production.
Answer:
| Primary Production | Secondary Production |
| When the introduced variety is well adapted to the new environment without any alternation to the original genotype. | When the introduced variety is subjected to selection to isolate a superior variety and hybridized with a local variety to transfer one or a few characters to them. |
![]()
Question 17.
What is co-evolution? Explain with example.
Answer:
The interaction between organisms, when continues for generations, involves reciprocal changes in genetic and morphological characters of both organisms. This type of evolution is called Co-evolution. It is a kind of co-adaptation and mutual change among interactive species.
Examples:
- Corolla length and proboscis length of butterflies and moths (Habenaria and Moth).
- Bird’s beak shape and flower shape and size.
Question 18.
What do you mean by Germplasm conservation? Describe it.
Answer:
Germplasm conservation refers to the conservation of living genetic resources like pollen, seeds or tissue of plant material maintained for the purpose of selective plant breeding, preservation in live condition and used for many research works.
Germplasm conservation resources is a part of collection of seeds and pollen that are stored in seed or pollen banks, so as to maintain their viability and fertility for any later use such as hybridization and crop improvement. Germplasm conservation may also involve a gene bank, DNA bank of elite breeding lines of plant resources for the maintenance of biological diversity and also for food security.
![]()
Question 19.
Point out the reasons for Mendels’ success in his breeding experiment.
Answer:
- He applied mathematics and statistical methods to biology and laws of probability to his breeding experiments.
- He followed scientific methods and kept accurate and detailed records that include quantitative data of the outcome of his crosses.
- His experiments were carefully planned and he used large samples.
- The pairs of contrasting characters which were controlled by factor (genes) were present on separate chromosomes.
- The parents selected by Mendel were pure breed lines and the purity was tested by self crossing the progeny for many generations.
Part – IV
Answer all the questions. [2 × 5 = 10]
Question 20.
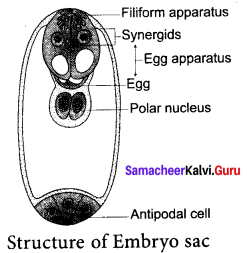
(a) Explain how Nicotiana exhibit self-compatibility in detail.
Answer:
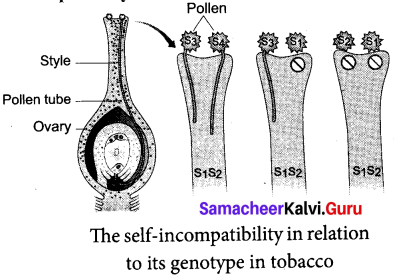
Self-sterility means that the pollen from a plant is unable to germinate on its own stigma and will not be able to bring about fertilization in the ovules of the same plant. East (1925) observed multiple alleles in Nicotiana which are responsible for self-incompatibility or self-sterility. The gene for self-incompatibility can be designated as S, which has allelic series S1, S2, S3, S4 and S5
The cross-fertilizing tobacco plants were not always homozygous as S1S1 or S2S2, but all plants were heterozygous as S1S2, S3S4 and S5S6. When crosses were made between different S1S2 plants, the pollen tube did not develop normally. But effective pollen tube development was observed when crossing was made with other than S1S2 for example S3S4.
When crosses were made between seed parents with S1S2 and pollen parents with S2S3, two kinds of pollen tubes were distinguished. Pollen grains carrying S3 were not effective, but the pollen grains carrying S3 were capable of fertilization. Thus, from the cross S1, S2 X S3, S4, all the pollens were effective and four kinds of progency resulted: S1S3, S1S4, S2S3 and S2S4.
[OR]
(b) Point out the applications of plant tissue culture.
Answer:
Plant tissue culture techniques have several applications such as:
- Improved hybrids production through somatic hybridization.
- Somatic embryoids can be encapsulated into synthetic seeds (synseeds). These encapsulated seeds or synthetic seeds help in conservation of plant biodiversity.
- Production of disease resistant plants through meristem and shoot tip culture.
- Production of stress resistant plants like herbicide tolerant, heat tolerant plants.
- Micro-propagation technique to obtain large numbers of plantlets of both crop and tree species useful in forestry within a short span of time and all through the year.
- Production of secondary metabolites from cell culture utilized in pharmaceutical, cosmetic and food industries.
![]()
Question 21.
(a) Describe the various stages of decomposition process.
Answer:
(1) Fragmentation: The breaking down of detritus into smaller particles by detritivores like bacteria, fungi and earth worm is known as fragmentation. These detritivores secrete certain substances to enhance the fragmentation process and increase the surface area of detritus particles.
(2) Catabolism: The decomposers produce some extracellular enzymes in their surroundings to break down complex organic and inorganic compounds in to simpler ones. This is called catabolism.
(3) Leaching or Eluviation: The movement of decomposed, water soluble organic and inorganic compounds from the surface to the lower layer of soil or the carrying away of the same by water is called leaching or eluviation.
(4) Humification: It is a process by which simplified detritus is changed into dark coloured amorphous substance called humus. It is highly resistant to microbial action, therefore decomposition is very slow. It is the reservoir of nutrients.
(5) Mineralisation: Some microbes are involved in the release of inorganic nutrients from the humus of the soil, such process is called mineralisation.
[OR]
(b) Explain the steps involved in hybridization.
Answer:
Steps involved in hybridization are as follows:
- Selection of Parents: Male and female plants of the desired characters are selected. It should be tested for their homozygosity.
- Emasculation: It is a process of removal of anthers to prevent self pollination before anthesis (period of opening of a flower).
- Bagging: The stigma of the flower is protected against any undesirable pollen grains, by covering it with a bag.
- Crossing: Transfer of pollen grains from selected male flower to the stigma of the female emasculated flower.
- Harvesting seeds and raising plants: The pollination leads to fertilization and finally seed formation takes place. The seeds are grown into new generation which are called hybrid.
Bio-Zoology [Maximum Marks: 35]
Part – I
Choose the correct answer. [8 × 1 = 8]
Question 1.
Assertion (A): In bee society, all the members are diploid, except drones.
Reason (R): Drones are produced by parthenogenesis.
(a) A and R are true, R is the correct explanation for A
(b) A and R are true, R is not the correct explanation for A
(c) A is true, R is false
(d) Both A and R are false
Answer:
(a) A and R are true, R is the correct explanation for A
![]()
Question 2.
Colotrum is rich in ______.
(a) IgE
(b) IgA
(c) IgD
(d) IgM
Answer:
(b) IgA
Question 3.
Match column I with column II

(a) A-iv, B-ii, C-i, D-iii
(b) A-iv, B-i, C-ii, D-iii
(c) A-iv, B-i, C-ii, D-iii
(d) A-i, B-iv, C-iii, D-ii
Answer:
(b) A-iv, B-i, C-ii, D-iii
Question 4.
Which of the following is the correct sequence of event with reference to central dogma?
(a) Transcription, Translation, Replication
(b) Transcription, Replication, Translation
(c) Duplication, Transcription, Translation
(d) Replication, Transcription, Translation
Answer:
(d) Replication, Transcription, Translation
Question 5.
Spread of cancerous cells to distant sites is termed as ______.
(a) Metastasis
(b) Oncogenes
(c) Proto-oncogenes
(d) Malignant neoplasm
Answer:
(a) Metastasis
Question 6.
How many amino acids are arranged in the two chains of Insulin?
(a) Chain A has 12 and Chain B has 13 amino acids
(b) Chain A has 21 and Chain B has 30 amino acids
(c) Chain A has 20 and chain B has 30 amino acids
(d) Chain A has 12 and chain B has 20 amino acids
Answer:
(b) Chain A has 21 and Chain B has 30 amino acids
![]()
Question 7.
Who introduced the term biodiversity?
(a) Edward Wilson
(b) Walter Rosen
(c) Norman Myers
(a) Alice Norman
Answer:
(b) Walter Rosen
Question 8.
What is the name of the action plan for sustainable development framed in Rio conference in 1992?
(a) Action 21
(b) Agenda 21
(c) Declaration 21
(d) Protocol 21
Answer:
(b) Agenda 21
Part – II
Answer any four of the following questions. [4 × 2 = 8]
Question 9.
How is polyspermy avoided in humans?
Answer:
Once fertilization is accomplished, cortical granules from the cytoplasm of the ovum form a barrier called the fertilization membrane around the ovum preventing further penetration of other sperms. Thus polyspermy is prevented.
Question 10.
What are holandric genes?
Answer:
The genes present in the differential region of Y chromosome are called Y- linked or holandric genes. The Y linked genes have no corresponding allele in X chromosome.
![]()
Question 11.
What are connecting links? Give example.
Answer:
The organisms which possess the characters of two different groups (transitional stage) are called connecting links. Example Peripatus (connecting link between Annelida and Arthropoda) Archaeopteryx (connecting link between Reptiles and Aves).
Question 12.
Saccharomyces cerevisiae is called as brewer’s yeast. Justify.
Answer:
Saccharomyces cerevisiae commonly called brewer’s yeast is used for fermenting malted cereals and fruit juices to produce various alcoholic beverages. Wine and beer are produced without distillation, whereas whisky, brandy and rum are obtained by fermentation and distillation.
Question 13.
Give the diagnostic characters of a Biome.
Answer:
- Location, Geographical position (Latitude and Longitude)
- Climate and physiochemical environment
- Predominant plant and animal life
- Boundaries between biomes are not always sharply defined. Transition or transient zones are seen.
Question 14.
What would Earth be like without the greenhouse effect?
Answer:
Greenhouse effect is vital for the sustenance of life. Greenhouse gases like CO2, water vapour etc absorb some of the reflected sun’s radiation and radiate back it to the Earth surface, thus maintaining the Earth’s warm condition. Without this effect, life on Earth would be difficult or rather impossible for existence or become hostile to most living organisms.
Part – III
Answer any three questions in which question number 19 is compulsory. [3 × 3 = 9]
Question 15.
Write a short note on phases of life cycle.
Answer:
- Juvenile phase – Period of growth between birth of an individual and reproductive maturity.
- Reproductive phase – Period of growth when an organism attain reproductive maturity and produces new offsprings.
- Senescent plane – Period of growth when the structure and functioning of body starts degenerating.
![]()
Question 16.
What is MTP? Add a note on it.
Answer:
Medical Termination of Pregnancy (MTP): Medical method of abortion is a voluntary or intentional termination of pregnancy in a non-surgical or non-invasive way. Early medical termination is extremely safe upto 12 weeks (the first trimester) of pregnancy and generally has no impact on a women’s fertility. Abortion during the second trimester is more risky as the foetus becomes intimately associated with the maternal tissue.
Question 17.
Genetic code is ‘universal’. Give reason.
Answer:
The genetic code is universal. It means that all known living systems use nucleic acids and the same three base codons (triplet codon) direct the synthesis of protein from amino acids. For example, the mRNA (UUU) codon codes for phenylalanine in all cells of all organisms. Some exceptions are reported in prokaryotic, mitochondrial and chloroplast genomes. However similarities are more common than differences.
Question 18.
Autoimmunity is a misdirected immune response. Justify.
Answer:
Autoimmune diseases : Autoimmunity is due to an abnormal immune response in which the immune system fails to properly distinguish between self and non-self and attacks its own body. Our body produces antibodies (auto antibodies) and cytotoxic T cells that destroy our own tissues. If a disease-state results, it is referred to as auto-immune disease. Thus, autoimmunity is a misdirected immune response.
Question 19.
PCR is a useful tool for early diagnosis of an Infectious disease. Elaborate.
Answer:
The specificity and sensitivity of PCR is useful for the diagnosis of inherited disorders (genetic diseases), viral diseases, bacterial diseases, etc., The diagnosis and treatment of a particular disease often requires identifying a particular pathogen. Traditional methods of identification involve culturing these organisms from clinical specimens and performing metabolic and other tests to identify them.
The concept behind PCR based diagnosis of infectious diseases is simple – if the pathogen is present in a clinical specimen its DNA will be present. Its DNA has unique sequences that can be detected by PCR, often using the clinical specimen (for example, blood, stool, spinal fluid, or sputum) in the PCR mixture.
Part – IV
Answer all the questions. [2 × 5 = 10]
Question 20.
(a) Give an detailed account on various natural methods of contraception.
Answer:
Natural method is used to prevent meeting of sperm with ovum, i.e., Rhythm method (safe period), coitus interruptus, continuous abstinence and lactational amenorrhoea.
1. Periodic abstinence/rhythm method: Ovulation occurs at about the 14th day of the menstrual cycle. Ovum survives for about two days and sperm remains alive for about 72 hours in the female reproductive tract. Coitus is to be avoided during this time.
2. Continuous abstinence is the simplest and most reliable way to avoid pregnancy is not to have coitus for a defined period that facilitates conception.
3. Coitus interruptus is the oldest family planning method. The male partner withdraws his penis before ejaculation, thereby preventing deposition of semen into the vagina.
4. Lactational amenorrhoea : Menstrual cycles resume as early as 6 to 8 weeks, from parturition. However, the reappearance of normal ovarian cycles may be delayed for six months during breast-feeding. This delay in ovarian cycles is called lactational amenorrhoea. It serves as a natural, but an unreliable form of birth control. Suckling by the baby during breast-feeding stimulates the pituitary to secrete increased prolactin hormone in order to increase milk production.
This high prolactin concentration in the mother’s blood may prevent menstrual cycle by suppressing the release of GnRH (Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone) from hypothalamus and gonadotropin secretion from the pituitary.
[OR]
(b) Explain the three major categories in which fossilization occur.
Answer:
(1) Actual remains is the most common method of fossilization. When marine animals die, their hard parts such as bones and shells, etc. are covered with sediments and are protected from further deterioration. They get preserved as such as they are preserved in vast ocean; the salinity in them prevents decay.
The sediments become hardened to form definite layers or strata. For example, Woolly Mammoth that lived 22 thousand years ago were preserved in the frozen coast of Siberia as such. Several human beings and animals living in the ancient city of Pompeii were preserved intact by volcanic ash which gushed out from Mount Vesuvius.
(2) Petrifaction – When animals die the original portion of their body may be replaced . molecule for molecule by minerals and the original substance being lost through disintegration. This method of fossilization is called petrifaction. The principle minerals involved in this type fossilization are iron pyrites, silica, calcium carbonate and bicarbonates of calcium and magnesium.
(3) Natural moulds and casts – Even after disintegration, the body of an animal might leave indelible impression on the soft mud which later becomes hardened into stones. Such impressions are called moulds. The cavities of the moulds may get filled up by hard minerals and get fossilized, which are called casts. Hardened faecal matter termed as coprolites occur as tiny pellets. Analysis of the coprolites enables us to understand the nature of diet, the prehistoric animals thrived.
![]()
Question 21.
(a) Explain in detail about stem cell therapy.
Answer:
Stem cells are undifferentiated cells found in most of the multi cellular animals. These cells maintain their undifferentiated state even after undergoing numerous mitotic divisions.
Stem cell research has the potential to revolutionize the future of medicine with the ability to regenerate damaged and diseased organs. Stem cells are capable of self renewal and exhibit ‘cellular potency’. Stem cells can differentiate into all types of cells that are derived from any of the three germ layers ectoderm, endoderm and mesoderm.
In mammals there are two main types of stem cells – embryonic stem cells (ES cells) and adult stem cells. ES cells are pluripotent and can produce the three primary germ layers ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm. Embryonic stem cells are multipotent stem cells that can differentiate into a number of types of cells. ES cells are isolated from the epiblast tissue of the inner cell mass of a blastocyst. When stimulated ES can develop into more than 200 cells types of the adult body. ES cells are immortal i.e. they can proliferate in a sterile culture medium and maintain their undifferentiated state.
Adult stem cells are found in various tissues of children as well as adults. An adult stem cell or somatic stem cell can divide and create another cell similar to it. Most of the adult stem cells are multipotent and can act as a repair system of the body, replenishing adult tissues.The red bone marrow is a rich source of adult stem cells.
The most important and potential application of human stem cells is the generation of cells and tissues that could be used for cell based therapies. Human stem cells could be used to test new drugs.
[OR]
(b) Explain in detail about various types of extinctions.
Answer:
There are three types of Extinctions
(1) Natural extinction: It is a slow process of replacement of existing species with better adapted species due to changes in environmental conditions, evolutionary changes, predators and diseases. A small population can get extinct sooner than the large population due to inbreeding depression (less adaptivity and variation)
(2) Mass extinction: The Earth has experienced quite a few mass extinctions due to environmental catastrophes. A mass extinction occurred about 225 million years ago during the Permian, where 90% of shallow water marine invertebrates disappeared.
(3) Anthropogenic extinctions: These are abetted by human activities like hunting, habitat destruction, over exploitation, urbanization and industrialization. Some examples of extinctions are Dodo of Mauritius and Steller’s sea cow of Russia. Amphibians seem to be at higher risk of extinction because of habitat destruction. The most serious aspect of the loss of biodiversity is the extinction of species. The unique information contained in its genetic material (DNA) and the niche it possesses are lost forever.