Students can Download Tamil Nadu 12th Biology Model Question Paper 3 English Medium Pdf, Tamil Nadu 12th Biology Model Question Papers helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
TN State Board 12th Biology Model Question Paper 3 English Medium
General Instructions:
- The question paper comprises of four parts. Questions for Botany and Zoology are asked separately.
- You are to attempt all the parts. An internal choice of questions is provided wherever applicable.
- All questions of Part I, II, III and IV are to be attempted separately.
- Question numbers 1 to 8 in Part I are Multiple Choice Questions of one mark each. These are to be answered by choosing the most suitable answer from the given four alternatives and writing the option code and the corresponding answer.
- Question numbers 9 to 14 in Part II are two-marks questions. These are to be answered in about one or two sentences.
- Question numbers 15 to 19 in Part III are three-marks questions. These are to be answered in about three to five short sentences.
- Question numbers 20 and 21 in Part IV are five-marks questions. These are to be answered in detail. Draw diagrams wherever necessary.
Time: 2.30 Hours
Maximum Marks: 70
Bio-Botany [Maximum Marks: 35]
Part – I
Choose the correct answer. [8 × 1 = 8]
Question 1.
Match the following:
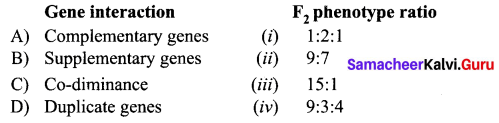
(a) A – (iv), B – (iii), C – (i), D – (ii)
(b) A – (ii), B – (iv), C – (i), D – (iii)
(c) A – (iii), B – (iv), C – (ii), D – (i)
(d) A – (iii), B – (i), C – (iv), D – (i)
Answer:
(b) A – (ii), B – (iv), C – (i), D – (iii)
Question 2.
Changing the codon AGC to AGA represents ___________.
(a) Mis-sense mutation
(b) Non-sense mutation
(c) Frame-shift mutation
(d) Deletion mutation
Answer:
(a) Mis-sense mutation
![]()
Question 3.
Restriction enzymes are ______.
(a) Not always required in genetic engineering
(b) Essential tools in genetic engineering ‘
(c) Nucleases that cleave DNA at specific sites
(d) Both b and c
Answer:
(d) Both b and c
Question 4.
Totipotency refers to _________.
(а) capacity to generate genetically identical plants
(b) capacity to generate a whole plant from any plant cell/explant
(c) capacity to generate hybrid protoplasts
(d) recovery to healthy plants from diseased plants
Answer:
(b) capacity to generate a whole plant from any plant cell/explant
Question 5.
In soil water available for plants is ________.
(a) gravitational water
(b) Chemically bound water
(c) Capillary water
(d) hygroscopic water
Answer:
(c) Capillary water
Question 6.
Which one is in descending order of a food chain?
(a) Producers → Secondary consumers → Primary consumers → Tertiary consumers
(b) Tertiary consumers → Primary consumers → Secondary consumers → Producers
(c) Tertiary consumers → Secondary consumers → Primary consumers → Producers
(d) Tertiary consumers → Producers → Primary consumers → Secondary consumers
Answer:
(c) Tertiary consumers → Secondary consumers → Primary consumers → Producers
Question 7.
Clean Development Mechanism (CDM) is defined is _______.
(a) Copenhagen Acord
(b) Montreal protocol
(c) Paris Agreement
(d) Kyoto protocol
Answer:
(d) Kyoto protocol
![]()
Question 8.
Pick out the odd pair.
(a) Man selection – Morphological characters
(b) Pureline selection – Repeated self pollinartion
(c) Clonal selection – Sexually propagated
(d) Natural selection – Involves nature
Answer:
(a) Man selection – Morphological characters
Part – II
Answer any four of the following questions. [4 × 2 = 8]
Question 9.
Write a short note on pollen kitt.
Answer:
Pollenkitt is contributed by the tapetum and coloured yellow or orange and is chiefly made of carotenoids or flavonoids. It is an oily layer forming a thick viscous coating over pollen surface. It attracts insects and protects damage from UV radiation.
Question 10.
What is back cross?
Answer:
Back cross is a cross of F1 hybrid with any one of the parental genotypes. The back cross is of two types; they are dominant back cross and recessive back cross. It involves the cross between the F1 off spring with either of the two parents.
![]()
Question 11.
Productivity of profundal zone will be low. why?
Answer:
The producers of the pond ecosystem depends on phytoplankton through photosynthesis. Profundal zone lies below the limnetic zone with no effective light penetration, hence productivity rate is very low.
Question 12.
Explants for tissue culturing has to be surface sterilized. How?
Answer:
The explants are surface sterilized by first exposing the material is running tap water and then treating it in surface sterilizing agents like 0.1 % Mercuric chloride, 70% ethanol under aseptic condition inside the laminar air flow chamber.
Question 13.
Define heterosis, through which way does this condition can be maintained for generation.
Answer:
The superiority of F1 hybrid in performance over its parents is called heterosis or hybrid vigour. Vigour refers to increase in growth, yield, adaptability resistance to disease, pest, etc., Vegetative propogation is the best suited method to maintain hybrid vigour.
Question 14.
Discuss which wood is better for making furniture.
Answer:
Teak wood is the ideal type of wood for making household furnitures because, it is highly durable and shows great resistance against the attack of termites and fungi. Moreover it does not split or crack and is a carpenter friendly wood.
Part – III
Answer any three questions in which question number 19 is compulsory. [3 × 3 = 9]
Question 15.
Give the names of the scientists who rediscovered mendel’s work.
Answer:
- Hugo de Vries of Holland
- Carl Correns of Germany
- Erich von Tschermark of Austria.
![]()
Question 16.
Write the advantages and disadvantages of Bt cotton.
Answer:
The advantages of Bt cotton are:
- Yield of cotton is increased due to effective control of bollworms.
- Reduction in insecticide use in the cultivation of Bt cotton
- Potential reduction in the cost of cultivation.
Bt cotton has some limitations:
- Cost of Bt cotton seed is high.
- Effectiveness upto 120 days after that efficiency is reduced.
- Ineffective against sucking pests like jassids, aphids and whitefly.
- Affects pollinating insects and thus yield.
Question 17.
How cryopreservation works?
Answer:
Cryopreservation, also known as Cryo-conservation, is a process by which protoplasts, cells, tissues, organelles, organs, extracellular matrix, enzymes or any other biological materials are subjected to preservation by cooling to very low temperature of -196°C using liquid nitrogen. At this extreme low temperature any enzymatic or chemical activity of the biological material will be totally stopped and this leads to preservation of material in dormant status. Later these materials can be activated by bringing to room temperature slowly for any experimental work.
Question 18.
What is Co-evolution? Give examples.
Answer:
The interaction between organisms, when continues for generations, involves reciprocal changes in genetic and morphological characters of both organisms. This type of evolution is called Co-evolution. It is a kind of co-adaptation and mutual change among interactive species.
Examples:
- Corolla length and proboscis length of butterflies and moths (Habenaria and Moth).
- Bird’s beak shape and flower shape and size.
![]()
Question 19.
Write a short note on Chipko Movement.
Answer:
Chipko Movement:
The tribal women of Himalayas protested against the exploitation of forests in 1972. Later on it transformed into Chipko Movement by Sundarlal Bahuguna in Mandal village of Chamoli district in 1974. People protested by hugging trees together which were felled by a sports goods company. Main features of Chipko movement were,
- This movement remained non political
- It was a voluntary movement based on Gandhian thought.
- It was concerned with the ecological balance of nature
- Main aim of Chipko movement was to give a slogan of five F’s – Food, Fodder, Fuel, Fibre and Fertilizer, to make the communities self sufficient in all their basic needs.
Part – IV
Answer all the questions. [2 × 5 = 10]
Question 20.
(a) Name the tissue that nourishes the embryo in angiospermic seeds. Explain its types.
Answer:
Structure of ovuIe (Megasporangium)
Endosperm: The primary endosperm nucleus (PEN) divides immediately after fertilization but before the zygote starts to divide, into an endosperm. The primary endosperm nucleus is the result of triple fusion (two polar nuclei and one sperm nucleus) and thus has 3n number of chromosomes. It is a nutritive tissue and regulatory structure that nourishes the developing embryo. Depending upon the mode of development three types of endosperm are recognized in angiosperms. They are nuclear endosperm, cellular endosperm and helobial endosperm.
Nuclear endosperm: Primary Endosperm Nucleus undergoes several mitotic divisions without cell wall formation thus a free nuclear condition exists in the endosperm.
Examples: Coccinia, Capsella and Arachis.
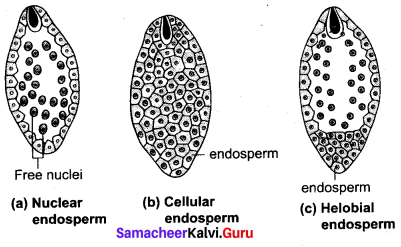
Cellular endosperm:
Primary endosperm nucleus divides into 2 nuclei and it is immediately followed by wall formation. Subsequent divisions also follow cell wall formation.
Examples: Adoxa, Helianthus and Scoparia.
Helobial endosperm: Primary Endosperm Nucleus moves towards base of embryo sac and divides into two nuclei. Cell wall formation takes place leading to the formation of a large micropylar and small chalazal chamber. The nucleus of the micropylar chamber undergoes several free nuclear division whereas that of chalazal chamber may or may not divide. Examples : Hydrilla and Vallisneria.
Ruminate endosperm: The endosperm with irregularity and unevenness in its surface forms ruminate endosperm. Examples : Areca catechu, Passiflora and Myristica.
[OR]
(b) Describe the basic steps involved in recombinant DNA technology.
Answer:
- Isolation of a DNA fragment containing a gene of interest that needs to be cloned. This is called an insert.
- Generation of recombinant DNA (rDNA) molecule by insertion of the DNA fragment into a carrier molecule called a vector that can self-replicate within the host cell.
- Selection of the transformed host cells that is carrying the rDNA and allowing them to multiply thereby multiplying the rDNA molecule.
- The entire process thus generates either a large amount of rDNA or a large amount of protein expressed by the insert.
- Wherever vectors are not involved the desired gene is multiplied by PCR technique. The multiple copies are injected into the host cell protoplast or it is shot into the host cell protoplast by shot gun method.
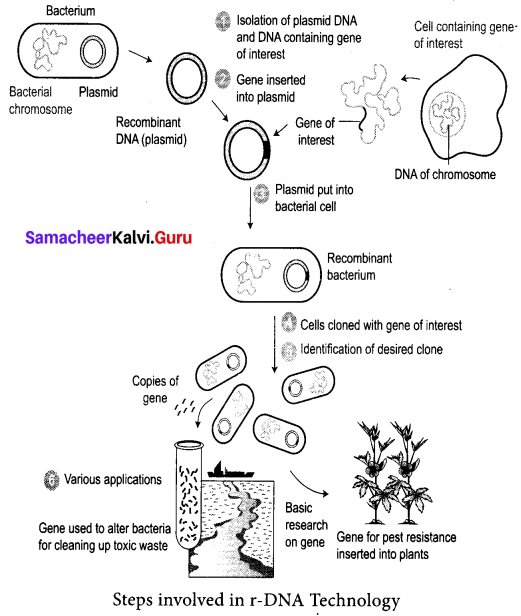
![]()
Question 21.
(a) Derive the protocol for micro propagation of banana.
Answer:
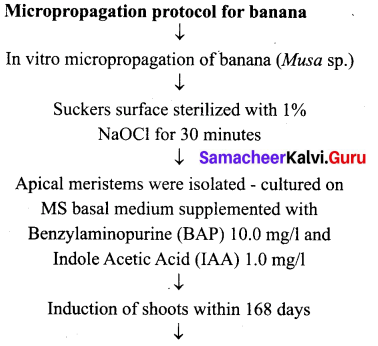
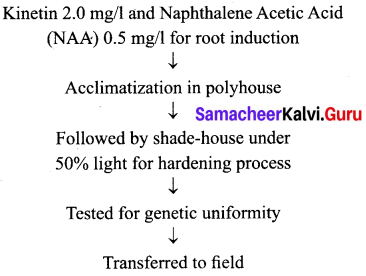
[OR]
(b) Expand NBT and Explain how it is involved in developing new traits in plant breeding.
Answer:
New Breeding Techniques (NBT) are a collection of methods that could increase and accelerate the development of new traits in plant breeding. These techniques often involve genome editing, to modify DNA at specific locations within the plants to produce new traits in crop plants. The various methods of achieving these changes in traits include the following,
- Cutting and modifying the genome during the repair process by tools like CRISPR /Cas.
- Genome editing to introduce changes in few base pairs using a technique called Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis (ODM).
- Transferring a gene from an identical or closely related species (cisgenesis).
- Organising processes that alter gene activity without altering the DNA itself (epigenetic methods).
Bio-Zoology [Maximum Marks: 35]
Part – I
Choose the correct answer. [8 × 1 = 8]
Question 1.
Assertion (A): Organisms show three phases in their life cycle.
Reason (R): Juvenile phase is a degenerative phase.
(a) A is correct. R is incorrect
(b) Both A and R are incorrect
(c) R is the correct explantation for A
(d) A is not correct but R is correct.
Answer:
(a) A is correct. R is incorrect
![]()
Question 2.
Find the wrongly matched pair
(a) Bleeding phase – fall in oestrogen and progesterone
(b) Follicular phase – rise in oestrogen
(c) Luteal phase – rise in FSH level
(d) Ovulatory phase – LH surge
Answer:
(c) Luteal phase – rise in FSH level
Question 3.
Identify the correct statements from the following.
(a) chlamydiasis is a viral disease
(b) Gonorrhoea is caused by a spirochaete bacterium, Treponema palladium
(c) The incubation period for syphilis is 2 to 14 days is males and 7 to 21 days in males.
(d) Both syphilis and gonorrhoea are easily cured with antibiotics.
Answer:
(d) Both syphilis and gonorrhoea are easily cured with antibiotics.
Question 4.
Klinefelter’s syndrome is characterized by a karyotype of _______.
(a) XYY
(b) XO
(C) XXX
(d) XXY
Answer:
(d) XXY
Question 5.
The golden age of repetails was _______.
(a) Mesozoic era
(b) Cenozoic era
(c) Paleozoic era
(d) Proterozoic era
Answer:
(a) Mesozoic era
Question 6.
Match list I with list II

(a) A – 2, B – 4, C – 3, D – 1
(b) A – 4, B – 3, C – 2, D – 1
(c) A – 2, B – 3, C – 4, D – 1
(d) A – 3, B – 1, C – 4, D – 2
Answer:
(b) A – 4, B – 3, C – 2, D – 1
![]()
Question 7.
The relation ship between sucker fish and shark is ________.
(a) Competition
(b) Commensalism
(c) Predation
(d) Parasitism
Answer:
(b) Commensalism
Question 8.
Who is called as the forest man of India?
(a) Sunderlal Bahuguna
(b) M.S. Swamination
(c) Dr. V. Kurier
(d) Jadav Payeng
Answer:
(d) Jadav Payeng
Part – II
Answer any four of the following questions. [4 × 2 = 8]
Question 9.
Mention the importance of the position of the testes in humans.
Answer:
The testes are positioned in such a way hanging out from the body in scrotal sac that provides optimal temperature 2°C to 3°C lower than internal body temperature for effective sperm production.
![]()
Question 10.
Type A blood should not be injected to a person having B-blood group. Why?
Answer:
When two different incompatible blood types are mixed, agglutination (clumping together) of erythrocytes (RBC) occurs. The basis of these chemical differences is due to the presence of antigens (surface antigens) on the membrane of RBC and epithelial cells.
Question 11.
Name the anticodons required to recognize the following codons. AAU, CGA, UAU, GCA.
Answer:
UUA, GCU, AUA and CGU.
Question 12.
What is diapedesis?
Tissue damage and infection induce leakage of vascular fluid, containing chemotactic signals like serotonin, histamine and prostaglandins. They influx the phagocytic cells into the affected area. This phenomenon is called diapedesis.
Question 13.
How was Insulin obtained before the advent of rDNA technology? What were the problems encountered?
Answer:
Conventionally, Insulin was isolated and refined from the pancreas of pigs and cows to treat diabetic patients. Though it is effective, due to minor structural changes, the animal insulin caused allergic reactions in few patients.
Question 14.
How many hotspots are there is India? Name them.
Answer:
India encloses 4 biodiversity hotspots. They are
- Himalayan
- Indo-Burma
- Western ghats
- Sundalands
Part – III
Answer any three questions in which question number 19 is compulsory. [3 × 3 = 9]
Question 15.
Define surrogacy.
Answer:
Surrogacy is a method of assisted reproduction or agreement whereby a woman agrees to carry a pregnancy for another person, who will become the newborn child’s parent after birth. Through In Vitro Fertilization (IVF), embryos are created in a lab and are transferred into the surrogate mother’s uterus.
![]()
Question 16.
Differentiate between divergent evolution and convergent evolution with one example for each.
Answer:
| Divergent Evolution | Convergent Evolution |
| Divergent evolution is a result of homology. eg: The wings of bird and the forelimbs of human both are homologous structures modified according to functions. In birds, it is used for flight and in humans used for writing and other purposes. |
Convergent evolution is a result of analogy. eg: Root modification in sweet potato, and stem modification in potato are analogous structures both performing same function i.e., storage. |
Question 17.
Under which conditions does a bacterium develops resistance against antibiotics?
Answer:
Antibiotic resistance occurs when bacteria develop the ability to defeat the drug designed to kill or inhibit their growth. It is one of the most acute threat to public health. Antibiotic resistance is accelerated by the misuse and over use of antibiotics, as well as poor infection prevention control.
Antibiotics should be used only when prescribed by a certified health professional. When the bacteria become resistant, antibiotics cannot fight against them and the bacteria multiply. Narrow spectrum antibiotics are preferred over broad spectrum antibiotics. They effectively and accurately target specific pathogenic organisms and are less likely to cause resistance.
Question 18.
Expand (i) CFC (ii)AQI (w) PAN
Answer:
(i) CFC – Chloro fluro carbon
(ii) AQI – Air Quality Index
(iii) PAN – Peroxyacetyl nitrate .
![]()
Question 19.
Mention the number of primers required in each cycle of PCR. Write the role of primers arid DNA polymerase in PCR. Name the source organism of DNA polymerase used in PCR.
Answer:
- For each cycle of PCR two primers are required.
- Primers are the small fragments of single stranded DNA or RNA which serves as template for initiating DNA polymerization.
- DNA polymerase is an enzyme that synthesize DNA molecules by pairing the Deoxyribo Nucleotides leading to formation of new strands.
- DNA polymerase used in PCR is Taq polymerase which is isolated from a thermophilic bacteria called Thermus aquatics. Taq polymerase will remain active ever at very high temperature (80°C) and hence used in PCR amplification technique.
Part – IV
Answer all the questions. [2 × 5 = 10]
Question 20.
(a) Menstruation – a cyclic event occurring in every normal woman throughout her fertile period. Name the various phases of the menstruation and explain it.
Answer:
Menstrual cycle: The menstrual or ovarian cycle occurs approximately once in every 28/29 days during the reproductive life of the female from menarche (puberty) to menopause except during pregnancy. The cycle of events starting from one menstrual period till the next one is called the menstrual cycle during which cyclic changes occurs in the endometrium every month. Cyclic menstruation is an indicator of normal reproductive phase.
Menstrual cycle comprises of the following phases:
- Menstrual phase
- Follicular or proliferative phase
- Ovulatory phase
- Luteal or secretory phase
1. Menstrual phase: The cycle starts with the menstrual phase when menstrual flow occurs and lasts for 3-5 days. Menstrual flow is due to the breakdown of endometrial lining of the uterus, and its blood vessels due to decline in the level of progesterone and oestrogen. Menstruation occurs only if the released ovum is not fertilized. Absence of menstruation may be an indicator of pregnancy. However it could also be due to stress, hormonal disorder and anaemia.
2. Follicular or proliferative phase: The follicular phase extends from the 5th day of the cycle until the time of ovulation. During this phase, the primary follicle in the ovary grows to become a fully mature Graafian follicle and simultaneously, the endometrium regenerates through proliferation. These changes in the ovary and the uterus are induced by the secretion of gonadotropins like FSH and LH, which increase gradually during the follicular phase. It stimulates follicular development and secretion of oestrogen by the follicle cells.
3. Ovulatory phase: Both LH and FSH attain peak level in the middle of the cycle (about the 14th day). Maximum secretion of LH during the mid cycle called LH surge induces the rupture of the Graafian follicle and the release of the ovum (secondary oocyte) from the ovary wall into the peritoneal cavity. This process is called as ovulation.
4. Luteal or secretory phase: During luteal phase, the remaining part of the Graafian follicle is transformed into a transitory endocrine gland called corpus luteum. The corpus luteum secretes large amount of progesterone which is essential for the maintenance of the endometrium. If fertilization takes place, it paves way for the implantation of the fertilized ovum. The uterine wall secretes nutritious fluid in the uterus for the foetus. So, this phase is also called as secretory phase. During pregnancy all events of menstrual cycle stop and there is no menstruation.
In the absence of fertilization, the corpus luteum degenerates completely and leaves a scar tissue called corpus albicans. It also initiates the disintegration of the endometrium leading to menstruation, marking the next cycle.
[OR]
(b) Deoxy Ribo Nucleic Acid the life thread which acts as a genetic material for majority of living organism. Enlist the properties of DNA that makes it an ideal genetic material.
Answer:
(1) Self Replication: It should be able to replicate. According to the rule of base pairing and complementarity, both nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) have the ability to direct duplications. Proteins fail to fulfill this criteria.
(2) Stability: It should be stable structurally and chemically. The genetic material should be stable enough not to change with different stages of life cycle, age or with change in physiology of the organism. Stability as one of property of genetic material was clearly evident in Griffith’s transforming principle. Heat which killed the bacteria did not destroy some of the properties of genetic material. In DNA the two strands being complementary, if separated (denatured) by heating can come together (renaturation) when appropriate condition is provided.
Further 2’ OH group present at every nucleotide in RNA is a reactive group that makes RNA liable and easily degradable. RNA is also known to be catalytic and reactive. Hence, DNA is chemically more stable and chemically less reactive when compared to RNA. Presence of thymine instead of uracil in DNA confers additional stability to DNA.
(3) Information storage: It should be able to express itself in the form of ‘Mendelian characters’. RNA can directly code for protein synthesis and can easily express the characters. DNA, however depends on RNA for synthesis of proteins. Both DNA and RNA can act as a genetic material, but DNA being more stable stores the genetic information and RNA transfers the genetic information.
(4) Variation through mutation: It should be able to mutate. Both DNA and RNA are able to mutate. RNA being unstable, mutates at a faster rate. Thus viruses having RNA genome with shorter life span can mutate and evolve faster. The above discussion indicates that both RNA and DNA can function as a genetic material. DNA is more stable, and is preferred for storage of genetic information.
![]()
Question 21.
(a) Explain the structure of Immunoglobulin molecule with a suitable diagram.
Answer:
An antibody molecule is Y shaped structure that comprises of four polypeptide chains, two identical light chains (L) of molecular weight 25,000 Da (approximately 214 amino acids) and two identical heavy chains (H) of molecular weight 50,000 Da (approximately 450 amino acids). The polypeptide chains are linked together by di-sulphide (S-S) bonds. One light chain is attached to each heavy chain and two heavy chains are attached to each other to form a Y shaped structure. Hence, an antibody is represented by H2 L2. The heavy chains have a flexible hinge region at their approximate middles.
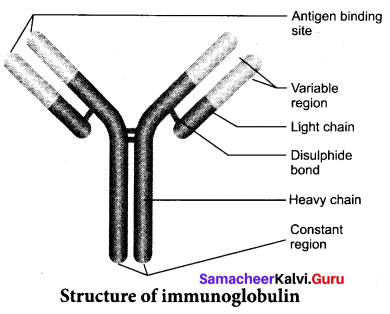
Each chain (L and H) has two terminals. They are C – terminal (Carboxyl) and amino or N-terminal. Each chain (L and H) has two regions. They have variable (V) region at one end and a much larger constant (C) region at the other end.
Antibodies responding to different antigens have very different (V) regions but their (C) regions are the same in all antibodies. In each arm of the monomer antibody, the (V) regions of the heavy and light chains combines to form an antigen – binding site shaped to ‘fit’ a specific antigenic determinant.
Consequently each antibody monomer has two such antigen – binding regions. The (C) regions that forms the stem of the antibody monomer determine the antibody class and serve common functions in all antibodies.
[OR]
(b) List out the uses of Transgenesis.
Answer:
(1) Transgenesis is a powerful tool to study gene expression and developmental processes in
higher organisms.
(2) Transgenesis helps in the improvement of genetic characters in animals. Transgenic animals serve as good models for understanding human diseases which help in the investigation of new treatments for diseases. Transgenic models exist for many human diseases such as cancer, Alzheimer’s, cystic fibrosis, rheumatoid arthritis and sickle cell anemia.
(3) Transgenic animals are used to produce proteins which are important for medical and pharmaceutical applications.
(4) Transgenic mice are used for testing the safety of vaccines.
(5) Transgenic animals are used for testing toxicity in animals that carry genes which make them sensitive to toxic substances than non-transgenic animals exposed to toxic substances and their effects are studied.
(6) Transgenesis is important for improving the quality and quantity of milk, meat, eggs and wool production in addition to testing drug resistance.